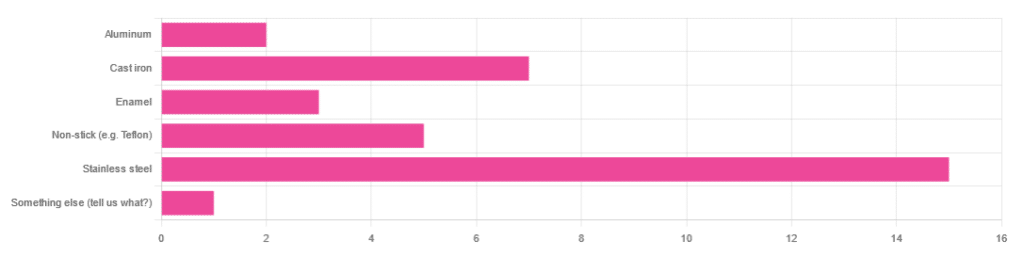Nudge – by Richard Thaler & Cass Sunstein
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How often in life do we make a suboptimal decision that ends up plaguing us for a long time afterwards? Sometimes, a single good or bad decision can even directly change the rest of our life.
So, it really is important that we try to optimize the decisions we do make.
Professors Richard Thaler and Cass Sunstein look at all kinds of decision-making in this book. Their goal, as per the subtitle, is “improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness”.
For the most part, the book concentrates on “nudges”. Small factors that influence our decisions one way or another.
Most importantly: that some of them are very good reasons to be nudged; others, very bad ones. And they often look similar.
Where this book excels is in highlighting the many ways we make decisions without even thinking about it… or we think about it, but only down a prescribed, foreseen track, to an externally expected conclusion (for example, an insurance company offering three packages, but two of them exist only to direct you to the “correct” choice).
A weakness of the book is that in some aspects it’s a little inconsistent. The authors describe their economic philosophy as “libertarian paternalism”, and as libertarians they’re against mandates, except when as paternalists they’re for them. But, if we take away their labels, this boils down to “some mandates can be good and some can be bad”, which would not be so inconsistent after all.
Bottom line: if you’d like to better understand your own decision-making processes through the eyes of policy-setting economists (especially Sunstein, who worked for the White House Office of Information & Regulatory Affairs) whose job it is to make sure you make the “right” decisions, then this is a very enlightening book.
Click here to check out Nudge and improve your decision-making clarity!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are plant-based burgers really bad for your heart? Here’s what’s behind the scary headlines
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re hearing a lot about ultra-processed foods and the health effects of eating too many. And we know plant-based foods are popular for health or other reasons.
So it’s not surprising new research out this week including the health effects of ultra-processed, plant-based foods is going to attract global attention.
And the headlines can be scary if that research and the publicity surrounding it suggests eating these foods increases your risk of heart disease, stroke or dying early.
Here’s how some media outlets interpreted the research. The Daily Mail ran with:
Vegan fake meats are linked to increase in heart deaths, study suggests: Experts say plant-based diets can boost health – but NOT if they are ultra-processed
The New York Post’s headline was:
Vegan fake meats linked to heart disease, early death: study
But when we look at the study itself, it seems the media coverage has focused on a tiny aspect of the research, and is misleading.
So does eating supermarket plant-based burgers and other plant-based, ultra-processed foods really put you at greater risk of heart disease, stroke and premature death?
Here’s what prompted the research and what the study actually found.
Nina Firsova/Shutterstock Remind me, what are ultra-processed foods?
Ultra-processed foods undergo processing and reformulation with additives to enhance flavour, shelf-life and appeal. These include everything from packet macaroni cheese and pork sausages, to supermarket pastries and plant-based mince.
There is now strong and extensive evidence showing ultra-processed foods are linked with an increased risk of many physical and mental chronic health conditions.
Although researchers question which foods should be counted as ultra-processed, or if all of them are linked to poorer health, the consensus is that, generally, we should be eating less of them.
We also know plant-based diets are popular. These are linked with a reduced risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and stroke, cancer and diabetes. And supermarkets are stocking more plant-based, ultra-processed food options.
How about the new study?
The study looked for any health differences between eating plant-based, ultra-processed foods compared to eating non-plant based, ultra-processed foods. The researchers focused on the risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease and stroke) and deaths from it.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods in this study included mass-produced packaged bread, pastries, buns, cakes, biscuits, cereals and meat alternatives (fake meats). Ultra-processed foods that were not plant-based included milk-based drinks and desserts, sausages, nuggets and other reconstituted meat products.
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank. This is a large biomedical database that contains de-identified genetic, lifestyle (diet and exercise) and health information and biological samples from half a million UK participants. This databank allows researchers to determine links between this data and a wide range of diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
They used data from nearly 127,000 people who provided details of their diet between 2009 and 2012. The researchers linked this to their hospital records and death records. On average, the researchers followed each participant’s diet and health for nine years.
Plant-based, ultra-processed foods included in this study included packaged supermarket bread. doublelee/Shutterstock What did the study find?
With every 10% increase of total energy from plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods there was an associated 5% increased risk of cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or stroke) and a 12% higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
But for every 10% increase in plant-sourced, non-ultra-processed foods consumed there was an associated 7% lower risk of cardiovascular disease and a 13% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
The researchers found no evidence for an association between all plant-sourced foods (whether or not they were ultra-processed) and either an increased or decreased risk of cardiovascular disease or dying from it.
This was an observational study, where people recalled their diet using questionnaires. When coupled with other data, this can only tell us if someone’s diet is associated with a particular risk of a health outcome. So we cannot say that, in this case, the ultra-processed foods caused the heart disease and deaths from it.
Why has media coverage focused on fake meats?
Much of the media coverage has focused on the apparent health risks associated with eating fake meats, such as sausages, burgers, nuggets and even steaks.
These are considered ultra-processed foods. They are made by deconstructing whole plant foods such as pea, soy, wheat protein, nuts and mushrooms, and extracting the protein. They are then reformulated with additives to make the products look, taste and feel like traditional red and white meats.
However this was only one type of plant-based, ultra-processed food analysed in this study. This only accounted for an average 0.2% of the dietary energy intake of all the participants.
Compare this to bread, pastries, buns, cakes and biscuits, which are other types of plant-based, ultra-processed foods. These accounted for 20.7% of total energy intake in the study.
This image was at the top of the media release. Screenshot/Imperial It’s hard to say why the media focused on fake meat. But there is one clue in the media release issued to promote the research.
Although the media release did not mention the words “fake meat”, an image of plant-based burgers, sausages and meat balls or rissoles featured prominently.
The introduction of the study itself also mentions plant-sourced, ultra-processed foods, such as sausages, nuggets and burgers.
So it’s no wonder people can be confused.
Does this mean fake meats are fine?
Not necessarily. This study analysed the total intake of plant-based, ultra-processed foods, which included fake meats, albeit a very small proportion of people’s diets.
From this study alone we cannot tell if there would be a different outcome if someone ate large amounts of fake meats.
In fact, a recent review of fake meats found there was not enough evidence to determine their impact on health.
We also need more recent data to reflect current eating patterns of fake meats. This study used dietary data collected from 2009 to 2012, and fake meats have become more popular since.
What if I really like fake meat?
We have known for a while that ultra-processed foods can harm our health. This study tells us that regardless if an ultra-processed food is plant-based or not, it may still be harmful.
We know fake meat can contain large amounts of saturated fats (from coconut or palm oil), salt and sugar.
So like other ultra-processed foods, they should be eaten infrequently. The Australian Dietary Guidelines currently recommends people should only consume foods like this sometimes and in small amounts.
Are some fake meats healthier than others?
Check the labels and nutrition information panels. Look for those lowest in fat and salt. Burgers and sausages that are a “pressed cake” of minced ingredients such as nuts, beans and vegetables will be preferable to reformulated products that look identical to meat.
You can also eat whole plant-based protein foods such as legumes. These include beans, lentils, chickpeas and soy beans. As well as being high in protein and fibre, they also provide essential nutrients such as iron and zinc. Using spices and mushrooms alongside these in your recipes can replicate some of the umami taste associated with meat.
Evangeline Mantzioris, Program Director of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Accredited Practising Dietitian, University of South Australia
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Mythbusting Cookware Materials
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you what kind of cookware you mostly use, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 45% said stainless steel
- About 21% said cast iron
- About 15% said non-stick (e.g. Teflon)
- About 9% said enamel
- About 6% said aluminum
- And 1 person selected “something else”, but then commented to the contrary, writing “I use all of the above”
So, what does the science say about these options?
Stainless steel cookware is safe: True or False?
True! Assuming good quality and normal use, anyway. There really isn’t a lot to say about this, because it’s very unexciting. So long as it is what it is labelled as: there’s nothing coating it, nothing comes out of it unless you go to extremes*, and it’s easy to clean.
*If you cook for long durations at very high temperatures, it can leach nickel and chromium into food. What this means in practical terms: if you are using stainless steel to do deep-frying, then maybe stop that, and also consider going easy on deep-frying in general anyway, because obviously deep-frying is unhealthy for other reasons.
Per normal use, however: pretty much the only way (good quality) stainless steel cookware will harm you is if you touch it while it’s hot, or if it falls off a shelf onto your head.
That said, do watch out for cheap stainless steel cookware that can contain a lot of impurities, including heavy metals. Since you probably don’t have a mass spectrometer and/or chemistry lab at home to check for those impurities, your best guard here is simply to buy from a reputable brand with credible certifications.
Ceramic cookware is safe: True or False?
True… Most of the time! Ceramic pans usually have metal parts and a ceramic cooking surface coated with a very thin layer of silicon. Those metal parts will be as safe as the metals used, so if that’s stainless steel, you’re just as safe as the above. As for the silicon, it is famously inert and body-safe (which is why it’s used in body implants).
However: ceramic cookware that doesn’t have an obvious metal part and is marketed as being pure ceramic, will generally be sealed with some kind of glaze that can leach heavy metals contaminants into the food; here’s an example:
Lead toxicity from glazed ceramic cookware
Copper cookware is safe: True or False?
False! This is one we forgot to mention in the poll, as one doesn’t see a lot of it nowadays. The copper from copper pans can leach into food. Now, of course copper is an important mineral that we must get from our diet, but the amount of copper that that can leach into food from copper pans is far too much, and can induce copper toxicity.
In addition, copper cookware has been found to be, on average, highly contaminated with lead:
Non-stick cookware contaminates the food with microplastics: True or False?
True! If we were to discuss all the common non-stick contaminants here, this email would no longer fit (there’s a size limit before it gets clipped by most email services).
Suffice it to say: the non-stick coating, polytetrafluoroethylene, is itself a PFAS, that is to say, part of the category of chemicals considered environmental pollutants, and associated with a long list of health issues in humans (wherein the level of PFAS in our bloodstream is associated with higher incidence of many illnesses):
You may have noticed, of course, that the “non-stick” coating doesn’t stick very well to the pan, either, and will tend to come off over time, even if used carefully.
Also, any kind of wet cooking (e.g. saucepans, skillets, rice cooker inserts) will leach PFAS into the food. In contrast, a non-stick baking tray lined with baking paper (thus: a barrier between the tray and your food) is really not such an issue.
We wrote about PFAS before, so if you’d like a more readable pop-science article than the scientific paper above, then check out:
PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
Aluminum cookware contaminates the food with aluminum: True or False?
True! But not usually in sufficient quantities to induce aluminum toxicity, unless you are aluminum pans Georg who eats half a gram of aluminum per day, who is a statistical outlier and should not be counted.
That’s a silly example, but an actual number; the dose required for aluminum toxicity in blood is 100mg/L, and you have about 5 liters of blood.
Unless you are on kidney dialysis (because 95% of aluminum is excreted by the kidneys, and kidney dialysis solution can itself contain aluminum), you will excrete aluminum a lot faster than you can possibly absorb it from cookware. On the other hand, you can get too much of it from it being a permitted additive in foods and medications, for example if you are taking antacids they often have a lot of aluminum oxide in them—but that is outside the scope of today’s article.
However, aluminum may not be the real problem in aluminum pans:
❝In addition, aluminum (3.2 ± 0.25 to 4.64 ± 0.20 g/kg) and copper cookware (2.90 ± 0.12 g/kg) were highly contaminated with lead.
The time and pH-dependent study revealed that leaching of metals (Al, Pb, Ni, Cr, Cd, Cu, and Fe, etc.) into food was predominantly from anodized and non-anodized aluminum cookware.
More metal leaching was observed from new aluminum cookware compared to old. Acidic food was found to cause more metals to leach during cooking.❞
~ the same paper we cited when talking about copper
Cast iron cookware contaminates the food with iron: True or False?
True, but unlike with the other metals discussed, this is purely a positive, and indeed, it’s even recommended as a good way to fortify one’s diet with iron:
The only notable counterpoint we could find for this is if you have hemochromatosis, a disorder in which the body is too good at absorbing iron and holding onto it.
Thinking of getting some new cookware?
Here are some example products of high-quality safe materials on Amazon, but of course feel free to shop around:
Stainless Steel | Ceramic* | Cast Iron
*it says “non-stick” in the description, but don’t worry, it’s ceramic, not Teflon etc, and is safe
Bonus: rice cooker with stainless steel inner pot
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Diet Compass – by Bas Kast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Facts about nutrition and health can be hard to memorize. There’s just so much! And often there are so many studies, and while the science is not usually contradictory, pop-science headlines sure can be. What to believe?
Bas Kast brings us a very comprehensive and easily digestible solution.
A science journalist himself, he has gone through the studies so that you don’t have to, and—citing them along the way—draws out the salient points and conclusions.
But, he’s not just handing out directions (though he does that too); he’s arranged and formatted the information in a very readable and logical fashion. Chapter by chapter, we learn the foundations of important principles for “this is better than that” choices in diet.
Most importantly, he lays out for us his “12 simple rules for healthy eating“, and they are indeed as simple as they are well-grounded in good science.
Bottom line: if you want “one easy-reading book” to just tell you how to make decisions about your diet, simply follow those rules and enjoy the benefits… Then this book is exactly that.
Click here to check out The Diet Compass and get your diet on the right track!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
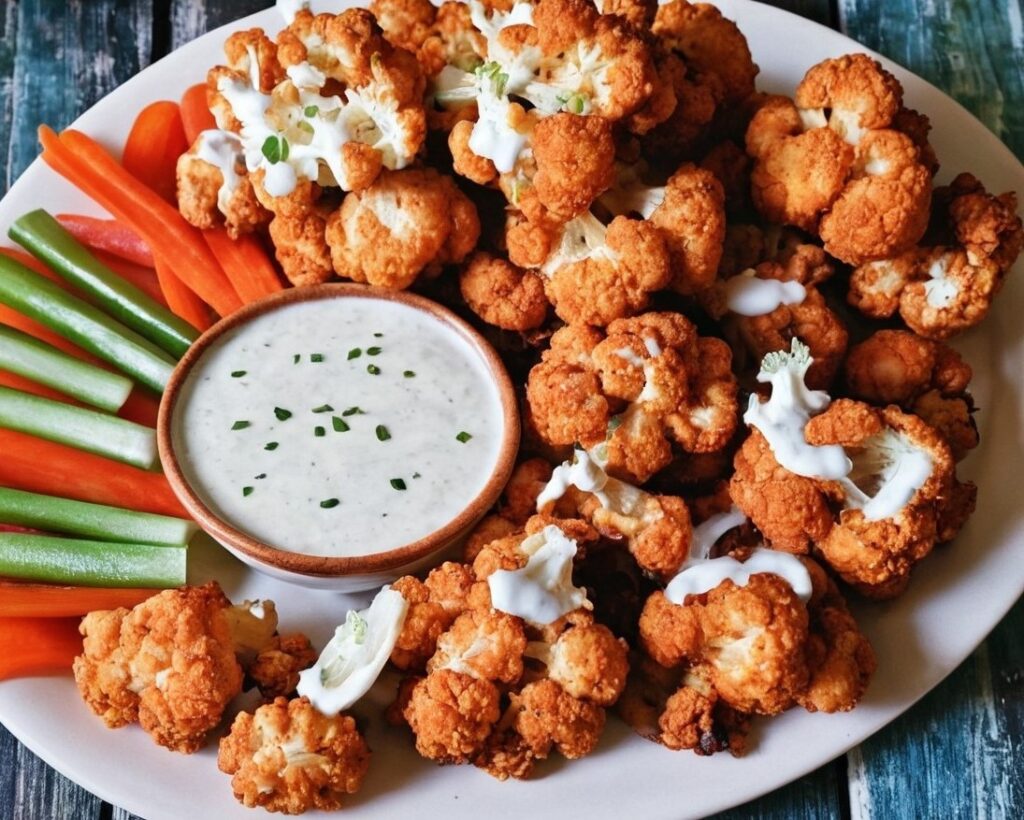
Buffed-Up Buffalo Cauliflower
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a tasty snack that also more protein than you’d think, because of the garbanzo bean flour. It also has plenty of health-giving spices, as well as blood-sugar-balancing vinegar, no added sugar, and very little salt.
You will need
- 1 medium head of cauliflower, cut into florets
- ½ cup garbanzo bean flour
- ½ cup water
- ⅓ cup hot sauce (we recommend a low-sugar kind; Nando’s hot sauce is good for this if available where you are, as it has no added sugar and its main ingredient by volume is vinegar, which is good for balancing blood sugars)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for the pan
- 2 tsp garlic powder
- 2 tsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, freshly ground
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low sodium salt
For the ranch sauce:
- ½ cup raw sunflower seeds
- ⅓ cup water
- ⅓ cup milk (plant milk being healthiest if you choose one that’s unsweetened)
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tsp onion powder
- 1 tsp dried thyme
- 1 tsp dried oregano
- 1 tsp dried dill
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉/200℃.
2) Blend the ranch sauce ingredients until smooth, and set aside.
3) Mix the buffalo cauliflower ingredients except for the cauliflower, in a big bowl.
4) Add the cauliflower to the big bowl, mixing well to coat evenly.
5) Bake the buffalo cauliflower florets on a baking tray lined with baking paper, for about 25 minutes, turning gently if it seems they are at risk of cooking unevenly.
6) Serve hot, with the sunflower ranch on the side!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
When the Body Says No – by Dr. Gabor Maté
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know that chronic stress is bad for us because of what it does to our cortisol levels, so what is the rest of this book about?
Dr. Gabor Maté is a medical doctor, heavily specialized in the impact of psychological trauma on long term physical health.
Here, he examies—as the subtitle promises—the connection between stress and disease. As it turns out, it’s not that simple.
We learn not just about the impact that stress has on our immune system (including increasing the risk of autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis), the cardiovascular system, and various other critical systems fo the body… But also:
- how environmental factors and destructive coping styles contribute to the onset of disease, and
- how traumatic events can warp people’s physical perception of pain
- how certain illnesses are associated with particular personality types.
This latter is not “astrology for doctors”, by the way. It has more to do with what coping strategies people are likely to employ, and thus what diseases become more likely to take hold.
The book has practical advice too, and it’s not just “reduce your stress”. Ideally, of course, indeed reduce your stress. But that’s a) obvious b) not always possible. Rather, Dr. Maté explains which coping strategies result in the least prevalence of disease.
In terms of writing style, the book is very much easy-reading, but be warned that (ironically) this isn’t exactly a feel-good book. There are lot of tragic stories in it. But, even those are very much well-worth reading.
Bottom line: if you (and/or a loved one) are suffering from stress, this book will give you the knowledge and understanding to minimize the harm that it will otherwise do.
Click here to check out When The Body Says No, and take good care of yourself; you’re important!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
When Age Is A Flexible Number
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Aging, Counterclockwise!
In the late 1970s, Dr. Ellen Langer hypothesized that physical markers of aging could be affected by psychosomatic means.
Note: psychosomatic does not mean “it’s all in your head”.
Psychosomatic means “your body does what your brain tells it to do, for better or for worse”
She set about testing that, in what has been referred to since as…
The Counterclockwise Study
A small (n=16) sample of men in their late 70s and early 80s were recruited in what they were told was a study about reminiscing.
Back in the 1970s, it was still standard practice in the field of psychology to outright lie to participants (who in those days were called “subjects”), so this slight obfuscation was a much smaller ethical aberration than in some famous studies of the same era and earlier (cough cough Zimbardo cough Milgram cough).
Anyway, the participants were treated to a week in a 1950s-themed retreat, specifically 1959, a date twenty years prior to the experiment’s date in 1979. The environment was decorated and furnished authentically to the date, down to the food and the available magazines and TV/radio shows; period-typical clothing was also provided, and so forth.
- The control group were told to spend the time reminiscing about 1959
- The experimental group were told to pretend (and maintain the pretense, for the duration) that it really was 1959
The results? On many measures of aging, the experimental group participants became quantifiably younger:
❝The experimental group showed greater improvement in joint flexibility, finger length (their arthritis diminished and they were able to straighten their fingers more), and manual dexterity.
On intelligence tests, 63 percent of the experimental group improved their scores, compared with only 44 percent of the control group. There were also improvements in height, weight, gait, and posture.
Finally, we asked people unaware of the study’s purpose to compare photos taken of the participants at the end of the week with those submitted at the beginning of the study. These objective observers judged that all of the experimental participants looked noticeably younger at the end of the study.❞
Remember, this was after one week.
Her famous study was completed in 1979, and/but not published until eleven years later in 1990, with the innocuous title:
Higher stages of human development: Perspectives on adult growth
You can read about it much more accessibly, and in much more detail, in her book:
Counterclockwise: A Proven Way to Think Yourself Younger and Healthier – by Dr. Ellen Langer
We haven’t reviewed that particular book yet, so here’s Linda Graham’s review, that noted:
❝Langer cites other research that has made similar findings.
In one study, for instance, 650 people were surveyed about their attitudes on aging. Twenty years later, those with a positive attitude with regard to aging had lived seven years longer on average than those with a negative attitude to aging.
(By comparison, researchers estimate that we extend our lives by four years if we lower our blood pressure and reduce our cholesterol.)
In another study, participants read a list of negative words about aging; within 15 minutes, they were walking more slowly than they had before.❞
Read the review in full:
Aging in Reverse: A Review of Counterclockwise
The Counterclockwise study has been repeated since, and/but we are still waiting for the latest (exciting, much larger sample, 90 participants this time) study to be published. The research proposal describes the method in great detail, and you can read that with one click over on PubMed:
It was approved, and has now been completed (as of 2020), but the results have not been published yet; you can see the timeline of how that’s progressing over on ClinicalTrials.gov:
Clinical Trials | Ageing as a Mindset: A Counterclockwise Experiment to Rejuvenate Older Adults
Hopefully it’ll take less time than the eleven years it took for the original study, but in the meantime, there seems to be nothing to lose in doing a little “Citizen Science” for ourselves.
Maybe a week in a 20 years-ago themed resort (writer’s note: wow, that would only be 2004; that doesn’t feel right; it should surely be at least the 90s!) isn’t a viable option for you, but we’re willing to bet it’s possible to “microdose” on this method. Given that the original study lasted only a week, even just a themed date-night on a regular recurring basis seems like a great option to explore (if you’re not partnered then well, indulge yourself how best you see fit, in accord with the same premise; a date-night can be with yourself too!).
Just remember the most important take-away though:
Don’t accidentally put yourself in your own control group!
In other words, it’s critically important that for the duration of the exercise, you act and even think as though it is the appropriate date.
If you instead spend your time thinking “wow, I miss the [decade that does it for you]”, you will dodge the benefits, and potentially even make yourself feel (and thus, potentially, if the inverse hypothesis holds true, become) older.
This latter is not just our hypothesis by the way, there is an established potential for nocebo effect.
For example, the following study looked at how instructions given in clinical tests can be worded in a way that make people feel differently about their age, and impact the results of the mental and/or physical tests then administered:
❝Our results seem to suggest how manipulations by instructions appeared to be more largely used and capable of producing more clear performance variations on cognitive, memory, and physical tasks.
Age-related stereotypes showed potentially stronger effects when they are negative, implicit, and temporally closer to the test of performance. ❞
(and yes, that’s the same Dr. Francesco Pagnini whose name you saw atop the other study we cited above, with the 90 participants recreating the Counterclockwise study)
Want to know more about [the hard science of] psychosomatic health?
Check out Dr. Langer’s other book, which we reviewed recently:
The Mindful Body: Thinking Our Way to Chronic Health – by Dr. Ellen Langer
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: