No, your aches and pains don’t get worse in the cold. So why do we think they do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s cold and wet outside. As you get out of bed, you can feel it in your bones. Your right knee is flaring up again. That’ll make it harder for you to walk the dog or go to the gym. You think it must be because of the weather.
It’s a common idea, but a myth.
When we looked at the evidence, we found no direct link between most common aches and pains and the weather. In the first study of its kind, we found no direct link between the temperature or humidity with most joint or muscle aches and pains.
So why are so many of us convinced the weather’s to blame? Here’s what we think is really going on.

Weather can be linked to your health
The weather is often associated with the risk of new and ongoing health conditions. For example, cold temperatures may worsen asthma symptoms. Hot temperatures increase the risk of heart problems, such as arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat), cardiac arrest and coronary heart disease.
Many people are also convinced the weather is linked to their aches and pains. For example, two in every three people with knee, hip or hand osteoarthritis say cold temperatures trigger their symptoms.
Musculoskeletal conditions affect more than seven million Australians. So we set out to find out whether weather is really the culprit behind winter flare-ups.
What we did
Very few studies have been specifically and appropriately designed to look for any direct link between weather changes and joint or muscle pain. And ours is the first to evaluate data from these particular studies.
We looked at data from more than 15,000 people from around the world. Together, these people reported more than 28,000 episodes of pain, mostly back pain, knee or hip osteoarthritis. People with rheumatoid arthritis and gout were also included.
We then compared the frequency of those pain reports between different types of weather: hot or cold, humid or dry, rainy, windy, as well as some combinations (for example, hot and humid versus cold and dry).

What we found
We found changes in air temperature, humidity, air pressure and rainfall do not increase the risk of knee, hip or lower back pain symptoms and are not associated with people seeking care for a new episode of arthritis.
The results of this study suggest we do not experience joint or muscle pain flare-ups as a result of changes in the weather, and a cold day will not increase our risk of having knee or back pain.
In order words, there is no direct link between the weather and back, knee or hip pain, nor will it give you arthritis.
It is important to note, though, that very cold air temperatures (under 10°C) were rarely studied so we cannot make conclusions about worsening symptoms in more extreme changes in the weather.
The only exception to our findings was for gout, an inflammatory type of arthritis that can come and go. Here, pain increased in warmer, dry conditions.
Gout has a very different underlying biological mechanism to back pain or knee and hip osteoarthritis, which may explain our results. The combination of warm and dry weather may lead to increased dehydration and consequently increased concentration of uric acid in the blood, and deposition of uric acid crystals in the joint in people with gout, resulting in a flare-up.
Why do people blame the weather?
The weather can influence other factors and behaviours that consequently shape how we perceive and manage pain.
For example, some people may change their physical activity routine during winter, choosing the couch over the gym. And we know prolonged sitting, for instance, is directly linked to worse back pain. Others may change their sleep routine or sleep less well when it is either too cold or too warm. Once again, a bad night’s sleep can trigger your back and knee pain.
Likewise, changes in mood, often experienced in cold weather, trigger increases in both back and knee pain.
So these changes in behaviour over winter may contribute to more aches and pains, and not the weather itself.
Believing our pain will feel worse in winter (even if this is not the case) may also make us feel worse in winter. This is known as the nocebo effect.

What to do about winter aches and pains?
It’s best to focus on risk factors for pain you can control and modify, rather than ones you can’t (such as the weather).
You can:
- become more physically active. This winter, and throughout the year, aim to walk more, or talk to your health-care provider about gentle exercises you can safely do at home, with a physiotherapist, personal trainer or at the pool
- lose weight if obese or overweight, as this is linked to lower levels of joint pain and better physical function
- keep your body warm in winter if you feel some muscle tension in uncomfortably cold conditions. Also ensure your bedroom is nice and warm as we tend to sleep less well in cold rooms
- maintain a healthy diet and avoid smoking or drinking high levels of alcohol. These are among key lifestyle recommendations to better manage many types of arthritis and musculoskeletal conditions. For people with back pain, for example, a healthy lifestyle is linked with higher levels of physical function.
Manuela Ferreira, Professor of Musculoskeletal Health, Head of Musculoskeletal Program, George Institute for Global Health and Leticia Deveza, Rheumatologist and Research Fellow, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It
We’ve talked before about how waist circumference is a much more useful indicator of metabolic health than BMI.
So, let’s say you’ve a bit more around the middle than you’d like, but it stubbornly stays there. What’s going on underneath what you can see, why is it going on, and how can you get it to change?
What is visceral fat?
First, let’s talk about subcutaneous fat. That’s the fat directly under your skin. Women usually have more than men, and that’s perfectly healthy (up to a point); it’s supposed to be that way. We (women) will tend to accumulate this mostly in places such as our breasts, hips, and butt, and work outwards from there. Men will tend to put it on more to the belly and face.
Side-note: if you’re undergoing (untreated) menopause, the changes in your hormone levels will tend to result in more subcutaneous fat to the belly and face too. That’s normal, and/but normal is not always good, and treatment options are great (with hormone replacement therapy, HRT, topping the list).
Visceral fat (also called visceral adipose tissue), on the other hand, is the fat of the viscera—the internal organs of the abdomen.
So, this is fat that goes under your abdominal muscles—you can’t squeeze this (directly).
So what can we do?
Famously “you can’t do spot reduction” (lose fat from a particular part of your body by focusing exercises on that area), but that’s about subcutaneous fat. There are things you can do that will reduce your visceral fat in particular.
Some of these advices you may think “that’s just good advice for losing fat in general” and it is, yes. But these are things that have the biggest impact on visceral fat.
Cut alcohol use
This is the biggie. By numerous mechanisms, some of which we’ve talked about before, alcohol causes weight gain in general yes, but especially for visceral fat.
Get better sleep
You might think that hitting the gym is most important, but this one ranks higher. Yes, you can trim visceral fat without leaving your bed (and even without getting athletic in bed, for that matter). Not convinced?
- Here’s a study of 101 people looking at sleep quality and abdominal adiposity
- Oh, and here’s a meta-analysis with 56,000 people (finding the same thing), in case that one study didn’t convince you.
So, the verdict is clear: you snooze, you lose (visceral fat)!
Tweak your diet
You don’t have to do a complete overhaul (unless you want to), but a few changes can make a big difference, especially:
- Getting more fiber (this is the biggie when it comes to diet)
- Eating less sugar (not really a surprise, but relevant to mention)
- Eat whole foods (skip the highly processed stuff)
If you’d like to learn more and enjoy videos, here’s an informative one to get you going!
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically! Share This Post
-
Cupping: How It Works (And How It Doesn’t)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Good Health By The Cup?
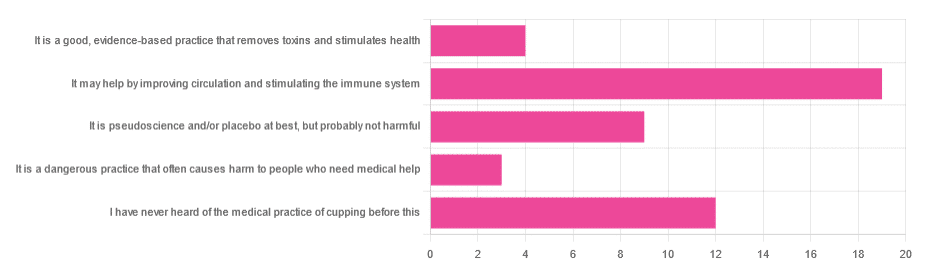
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of cupping (the medical practice), and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 40% said “It may help by improving circulation and stimulating the immune system”
- About 26% said “I have never heard of the medical practice of cupping before this”
- About 19% said “It is pseudoscience and/or placebo at best, but probably not harmful
- About 9% said “It is a good, evidence-based practice that removes toxins and stimulates health”
- About 6% said “It is a dangerous practice that often causes harm to people who need medical help”
So what does the science say?
First, a quick note for those unfamiliar with cupping: it is the practice of placing a warmed cup on the skin (open side of the cup against the skin). As the warm air inside cools, it reduces the interior air pressure, which means the cup is now (quite literally) a suction cup. This pulls the skin up into the cup a little. The end result is visually, and physiologically, the same process as what happens if someone places the nozzle of a vacuum cleaner against their skin. For that matter, there are alternative versions that simply use a pump-based suction system, instead of heated cups—but the heated cups are most traditional and seem to be most popular. See also:
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health | Cupping
It is a dangerous practice that often causes harm to people who need medical help: True or False?
False, for any practical purposes.
- Directly, it can (and usually does) cause minor superficial harm, much like many medical treatments, wherein the benefits are considered to outweigh the harm, justifying the treatment. In the case of cupping, the minor harm is usually a little bruising, but there are other risks; see the link we gave just above.
- Indirectly, it could cause harm by emboldening a person to neglect a more impactful treatment for their ailment.
But, there’s nothing for cupping akin to the “the most common cause of death is when someone gets a vertebral artery fatally severed” of chiropractic, for example.
It is a good, evidence-based practice that removes toxins and stimulates health: True or False?
True and False in different parts. This one’s on us; we included four claims in one short line. But let’s look at them individually:
- Is it good? Well, those who like it, like it. It legitimately has some mild health benefits, and its potential for harm is quite small. We’d call this a modest good, but good nonetheless.
- Is it evidence-based? Somewhat, albeit weakly; there are some papers supporting its modest health claims, although the research is mostly only published in journals of alternative medicine, and any we found were in journals that have been described by scientists as pseudoscientific.
- Does it remove toxins? Not directly, at least. There is also a version that involves making a small hole in the skin before applying the cup, the better to draw out the toxins (called “wet cupping”). This might seem a little medieval, but this is because it is from early medieval times (wet cupping’s first recorded use being in the early 7th century). However, the body’s response to being poked, pierced, sucked, etc is to produce antibodies, and they will do their best to remove toxins. So, indirectly, there’s an argument.
- Does it stimulate health? Yes! We’ll come to that shortly. But first…
It is pseudoscience and/or placebo at best, but probably not harmful: True or False?
True in that its traditionally-proposed mechanism of action is a pseudoscience and placebo almost certainly plays a strong part, and also in that it’s generally not harmful.
On it being a pseudoscience: we’ve talked about this before, but it bears repeating; just because something’s proposed mechanism of action is pseudoscience, doesn’t necessarily mean it doesn’t work by some other mechanism of action. If you tell a small child that “eating the rainbow” will improve their health, and they believe this is some sort of magical rainbow power imbuing them with health, then the mechanism of action that they believe in is a pseudoscience, but eating a variety of colorful fruit and vegetables will still be healthy.
In the case of cupping, its proposed mechanism of action has to do withbalancing qi, yin and yang, etc (for which scientific evidence does not exist), in combination with acupuncture lore (for which some limited weak scientific evidence exists). On balancing qi, yin and yang etc, this is a lot like Europe’s historically popular humorism, which was based on the idea of balancing the four humors (blood, yellow bile, black bile, phlegm). Needless to say, humorism was not only a pseudoscience, but also eventually actively disproved with the advent of germ theory and modern medicine. Cupping therapy is not more scientifically based than humorism.
On the placebo side of things, there probably is a little more to it than that; much like with acupuncture, a lot of it may be a combination of placebo and using counter-irritation, a nerve-tricking method to use pain to reduce pain (much like pressing with one’s nail next to an insect bite).
Here’s one of the few studies we found that’s in what looks, at a glance, to be a reputable journal:
Cupping therapy and chronic back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis
It may help by improving circulation and stimulating the immune system: True or False?
True! It will improve local circulation by forcing blood into the area, and stimulate the immune system by giving it a perceived threat to fight.
Again, this can be achieved by many other means; acupuncture (or just “dry needling”, which is similar but without the traditional lore), a cold shower, and/or exercise (and for that matter, sex—which combines exercise, physiological arousal, and usually also foreign bodies to respond to) are all options that can improve circulation and stimulate the immune system.
You can read more about using some of these sorts of tricks for improving health in very well-evidenced, robustly scientific ways here:
The Stress Prescription (Against Aging!)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Could ADHD drugs reduce the risk of early death? Unpacking the findings from a new Swedish study
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can have a considerable impact on the day-to-day functioning and overall wellbeing of people affected. It causes a variety of symptoms including difficulty focusing, impulsivity and hyperactivity.
For many, a diagnosis of ADHD, whether in childhood or adulthood, is life changing. It means finally having an explanation for these challenges, and opens up the opportunity for treatment, including medication.
Although ADHD medications can cause side effects, they generally improve symptoms for people with the disorder, and thereby can significantly boost quality of life.
Now a new study has found being treated for ADHD with medication reduces the risk of early death for people with the disorder. But what can we make of these findings?
A large study from Sweden
The study, published this week in JAMA (the prestigious journal of the American Medical Association), was a large cohort study of 148,578 people diagnosed with ADHD in Sweden. It included both adults and children.
In a cohort study, a group of people who share a common characteristic (in this case a diagnosis of ADHD) are followed over time to see how many develop a particular health outcome of interest (in this case the outcome was death).
For this study the researchers calculated the mortality rate over a two-year follow up period for those whose ADHD was treated with medication (a group of around 84,000 people) alongside those whose ADHD was not treated with medication (around 64,000 people). The team then determined if there were any differences between the two groups.
What did the results show?
The study found people who were diagnosed and treated for ADHD had a 19% reduced risk of death from any cause over the two years they were tracked, compared with those who were diagnosed but not treated.
In understanding this result, it’s important – and interesting – to look at the causes of death. The authors separately analysed deaths due to natural causes (physical medical conditions) and deaths due to unnatural causes (for example, unintentional injuries, suicide, or accidental poisonings).
The key result is that while no significant difference was seen between the two groups when examining natural causes of death, the authors found a significant difference for deaths due to unnatural causes.
So what’s going on?
Previous studies have suggested ADHD is associated with an increased risk of premature death from unnatural causes, such as injury and poisoning.
On a related note, earlier studies have also suggested taking ADHD medicines may reduce premature deaths. So while this is not the first study to suggest this association, the authors note previous studies addressing this link have generated mixed results and have had significant limitations.
In this new study, the authors suggest the reduction in deaths from unnatural causes could be because taking medication alleviates some of the ADHD symptoms responsible for poor outcomes – for example, improving impulse control and decision-making. They note this could reduce fatal accidents.
The authors cite a number of studies that support this hypothesis, including research showing ADHD medications may prevent the onset of mood, anxiety and substance use disorders, and lower the risk of accidents and criminality. All this could reasonably be expected to lower the rate of unnatural deaths.
Strengths and limitations
Scandinavian countries have well-maintained national registries that collect information on various aspects of citizens’ lives, including their health. This allows researchers to conduct excellent population-based studies.
Along with its robust study design and high-quality data, another strength of this study is its size. The large number of participants – almost 150,000 – gives us confidence the findings were not due to chance.
The fact this study examined both children and adults is another strength. Previous research relating to ADHD has often focused primarily on children.
One of the important limitations of this study acknowledged by the authors is that it was observational. Observational studies are where the researchers observe and analyse naturally occurring phenomena without intervening in the lives of the study participants (unlike randomised controlled trials).
The limitation in all observational research is the issue of confounding. This means we cannot be completely sure the differences between the two groups observed were not either partially or entirely due to some other factor apart from taking medication.
Specifically, it’s possible lifestyle factors or other ADHD treatments such as psychological counselling or social support may have influenced the mortality rates in the groups studied.
Another possible limitation is the relatively short follow-up period. What the results would show if participants were followed up for longer is an interesting question, and could be addressed in future research.
What are the implications?
Despite some limitations, this study adds to the evidence that diagnosis and treatment for ADHD can make a profound difference to people’s lives. As well as alleviating symptoms of the disorder, this study supports the idea ADHD medication reduces the risk of premature death.
Ultimately, this highlights the importance of diagnosing ADHD early so the appropriate treatment can be given. It also contributes to the body of evidence indicating the need to improve access to mental health care and support more broadly.
Hassan Vally, Associate Professor, Epidemiology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Feel Better In 5 – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve featured Dr. Rangan Chatterjee before, and here’s a great book of his.
The premise is a realistic twist on a classic, the classic being “such-and-such, in just 5 minutes per day!”
In this case, Dr. Chatterjee offers many lifestyle interventions that each take just 5 minutes, with the idea that you implement 3 of them per day (your choice which and when), and thus gradually build up healthy habits. Of course, once things take as habits, you’ll start adding in more, and before you know it, half your lifestyle has changed for the better.
Which, you may be thinking “my lifestyle’s not that bad”, but if you improve the health outcomes of, say, 20 areas of your life by just a few percent each, you know much better health that adds up to? We’ll give you a clue: it doesn’t add up, it compounds, because each improves the other too, for no part of the body works entirely in isolation.
And Dr. Chatterjee does tackle the body systematically, by the way; interventions for the gut, heart, brain, and so on.
As for what these interventions look like; it is very varied. One might be a physical exercise; another, a mental exercise; another, a “make this health 5-minute thing in the kitchen”, etc, etc.
Bottom line: this is the most supremely easy of easy-ins to healthier living, whatever your starting point—because even if you’re doing half of these interventions, chances are you aren’t doing the other half, and the idea is to pick and choose how and when you adopt them in any case, just picking three 5-minute interventions each day with no restrictions. In short, a lot of value to had here when it comes to real changes to one’s serious measurable health.
Click here to check out Feel Better In 5, and indeed feel better in 5!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wildfires ignite infection risks, by weakening the body’s immune defences and spreading bugs in smoke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Over the past several days, the world has watched on in shock as wildfires have devastated large parts of Los Angeles.
Beyond the obvious destruction – to landscapes, homes, businesses and more – fires at this scale have far-reaching effects on communities. A number of these concern human health.
We know fire can harm directly, causing injuries and death. Tragically, the death toll in LA is now at least 24.
But wildfires, or bushfires, can also have indirect consequences for human health. In particular, they can promote the incidence and spread of a range of infections.
Effects on the immune system
Most people appreciate that fires can cause burns and smoke inhalation, both of which can be life-threatening in their own right.
What’s perhaps less well known is that both burns and smoke inhalation can cause acute and chronic changes in the immune system. This can leave those affected vulnerable to infections at the time of the injury, and for years to come.
Burns induce profound changes in the immune system. Some parts go into overdrive, becoming too reactive and leading to hyper-inflammation. In the immediate aftermath of serious burns, this can contribute to sepsis and organ failure.
Other parts of the immune system appear to be suppressed. Our ability to recognise and fight off bugs can be compromised after sustaining burns. Research shows people who have experienced serious burns have an increased risk of influenza, pneumonia and other types of respiratory infections for at least the first five years after injury compared to people who haven’t experienced burns.
Wildfire smoke is a complex mixture containing particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, ozone, toxic gases, and microbes. When people inhale smoke during wildfires, each of these elements can play a role in increasing inflammation in the airways, which can lead to increased susceptibility to respiratory infections and asthma.
Research published after Australia’s Black Summer of 2019–20 found a higher risk of COVID infections in areas of New South Wales where bushfires had occurred weeks earlier.
We need more research to understand the magnitude of these increased risks, how long they persist after exposure, and the mechanisms. But these effects are thought to be due to sustained changes to the immune response.
Microbes travel in smoky air
Another opportunity for infection arises from the fire-induced movement of microbes from niches they usually occupy in soils and plants in natural areas, into densely populated urban areas.
Recent evidence from forest fires in Utah shows microbes, such as bacteria and fungal spores, can be transported in smoke. These microbes are associated with particles from the source, such as burned vegetation and soil.
There are thousands of different species of microbes in smoke, many of which are not common in background, non-smoky air.
Only a small number of studies on this have been published so far, but researchers have shown the majority of microbes in smoke are still alive and remain alive in smoke long enough to colonise the places where they eventually land.
How far specific microbes can be transported remains an open question, but fungi associated with smoke particles have been detected hundreds of miles downwind from wildfires, even weeks after the fire.
So does this cause human infections?
A subset of these airborne microbes are known to cause infections in humans.
Scientists are probing records of human fungal infections in relation to wildfire smoke exposure. In particular, they’re looking at soil-borne infectious agents such as the fungi Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii which thrive in dry soils that can be picked up in dust and smoke plumes.
These fungi cause valley fever, a lung infection with symptoms that can resemble the flu, across arid western parts of the United States.
A study of wildland firefighters in California showed high rates of valley fever infections, which spurred occupational health warnings including recommended use of respirators when in endemic regions.
A California-based study of the wider population showed a 20% increase in hospital admissions for valley fever following any amount of exposure to wildfire smoke.
However, another found only limited evidence of excess cases after smoke exposure in wildfire-adjacent populations in California’s San Joaquin Valley.
These contrasting results show more research is needed to evaluate the infectious potential of wildfire smoke from this and other fungal and bacterial causes.
Staying safe
Much remains to be learned about the links between wildfires and infections, and the multiple pathways by which wildfires can increase the risk of certain infections.
There’s also a risk people gathering together after a disaster like this, such as in potentially overcrowded shelters, can increase the transmission of infections. We’ve seen this happen after previous natural disasters.
Despite the gaps in our knowledge, public health responses to wildfires should encompass infection prevention (such as through the provision of effective masks) and surveillance to enable early detection and effective management of any outbreaks.
Christine Carson, Senior Research Fellow, School of Medicine, The University of Western Australia and Leda Kobziar, Professor of Wildland Fire Science, University of Idaho
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Build Strong Feet: Exercises To Strengthen Your Foot & Ankle
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot depends on the health of our feet, especially when it comes to their strength and stability. But they often get quite neglected, when it comes to maintenance. Here’s how to help your feet keep the rest of your body in good condition:
On a good footing
The foot-specific exercises recommended here include:
- Active toe flexion/extension: curl and extend your toes
- Active toe adduction/abduction: use a towel for feedback this time as you spread your toes
- “Short foot” exercise: create an arch by bringing the base of your big toe towards your heel
- Resisted big toe flexion: use resistance bands; flex your big toe while controlling the others.
- Standing big toe flexion (isometric): press your big toe against an inclined surface as forcefully as you can
- Foot bridge exercise: hold your position with the front part of your feet on an elevated surface, to strengthen the arch.
- Heel raises: which can be progressed from basic to more advanced variations, increasing difficulty
- Ankle movements: dorsiflexion, inversion, etc, to increase mobility
It’s important to also look after your general lower body strength and stability, including (for example) single-leg deadlifts, step-downs, and lunges
Balance and proprioceptive exercises are good too, such as a static or dynamic one-leg balances, progressing to doing them with your eyes closed and/or on unstable surfaces (be careful, of course, and progress to this only when confident).
For more on all of these, an explanation of the anatomy, some other exercises too, and visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Steps For Keeping Your Feet A Healthy Foundation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: