No-Exercise Exercise!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you love to go to the gym?
If so, today’s article might not be for you so much. Or maybe it will, because let’s face it, exercise is fun!
At least… It can be, and should be 😎
So without further ado, here’s a slew of no-exercise exercise ideas; we’re willing to bet that somewhere in the list there’s at least some you haven’t tried before, and probably some you haven’t done in a while but might enjoy making a reprise!
Walking
No surprises here: walking is great. Hopefully you have some green spaces near you, but if you don’t, [almost] any walking is better than no walking. So unless there’s some sort of environmental disaster going on outside, lace up and get stepping.
If you struggle to “walk for walking’s sake” give yourself a little mission. Walk to the shop to buy one item. Walk to the park and find a flower to photograph. Walk to the library and take out a book. Whatever works for you!
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Take the stairs
This one doesn’t need many words, just: make it a habit.
Treat the elevators as though they aren’t there!
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Dance
Dance is amazing! Any kind of dance, whatever suits your tastes. This writer loves salsa and tango, but no matter whether for you it’s zouk or zumba, breakdancing or line dancing, whatever gets you moving is going to be great for you.
If you don’t know how, online tutorials abound, and best of all is to attend local classes if you can, because they’re always a fun social experience too.
Make music
Not something often thought of as an exercise, but it is! Most instruments require that we be standing or siting with good posture, focusing intently on our movements, and often as not, breathing very mindfully too. And yes, it’s great for the brain as well!
Check out: This Is Your Brain on Music: The Science of a Human Obsession – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
Take a stand
If you spend a lot of time at a desk, please consider investing in a standing desk; they can be truly life-changing. Not only is it so much better for your back, hips, neck, and internal organs, but also it burns hundreds more calories than sitting, due to the no-exercise exercise that is keeping your body constantly stabilized while on your feet.
(or, if you’re like this writer: on your foot. I do have two feet, I just spend an inordinate amount of time at my desk standing on one leg at a time; I’m a bit of a flamingo like that)
See also: Deskbound: Standing Up to a Sitting World – by Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
Sit, but…
Sit in a sitting squat! Sometimes called a Slav squat, or an Asian squat, or a resting squat, or various other names:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Alternatively, sitting in seiza (the traditional Japanese sitting position) is also excellent, but watch out! While it’s great once your body is accustomed to it, if you haven’t previously sat this way much, you may cut off your own circulation, hurt your knees, and (temporarily) lose feeling in your feet. So if you don’t already sit in seiza often, gradually work up the time period you spend sitting in seiza, so that your vasculature can adapt and improve, which honestly, is a very good thing for your legs and feet to have.
Breathe
Perhaps the absolute most “no-exercise exercise” there is. And yes, of course you are (hopefully) breathing all the time, but how you are breathing matters a lot:
The Inside Job Of Fixing Our Breathing: Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More)
Clean
This doesn’t have to mean scrubbing floors like a sailor—even merely giving your house the Marie Kondo treatment counts, because while you’re distracted with all the objects, you’re going to be going back and forth, getting up and down, etc, clocking up lots of exercise that you barely even notice!
PS, check out: The Life-Changing Manga Of Tidying Up – by Marie Kondo
Garden
As with the above, it’s lots of activity that doesn’t necessarily feel like it (assuming you’re doing more pruning and weeding etc, and less digging ditches etc), and as a bonus, there are a stack of mental health benefits to being in a green natural environment and interacting with soil:
Read more: The Antidepressant In Your Garden
Climb
Depending on where you live, this might mean an indoor climbing wall, but give it a go! They have color-coded climbs from beginner to advanced, so don’t worry about being out of your depth.
And the best thing is, the beginner climbs will be as much a workout to a beginner as the advanced climbs will be to an advanced climber, because at the end of the day, you’re still clinging on for dear life, no matter whether it’s a sizeable handhold not far from the ground, or the impression of a fingernail crack in an overhang 100ft in the air.
Video games (but…)
Less in the category of Stardew Valley, and more in the category of Wii Fit.
So, dust off that old controller (or treat yourself to one if you didn’t have one already), and get doing a hundred sports and other physical activities in the comfort of your living room, with a surprisingly addictive gaming system!
Sex!
You probably don’t need instructions here, and if you do, well honestly, we’re running out of space today. But the answer to “does xyz count?” is “did it get your heart racing?” because if so, it counts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Starch Solution – by Dr. John McDougall & Mary McDougall
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Carb-strong or carb-wrong? We’ve written about this ourselves before, and it comes down to clarifying questions of what and how and why. Even within the general field of carbs, even within the smaller field of starch, not all foods are equal. A slice of white bread and a baked potato are both starchy, but the latter also contains fiber, vitamins, minerals, and suchlike.
The authors make the case for a whole-foods plant-based diet in which one need not shy away from starchy foods in general; one simply must enjoy them discriminately—whole grains, and root vegetables that have not been processed to Hell and back, for examples.
The style is “old-school pop-sci” but with modern science; claims are quite well-sourced throughout, with nine pages of bibliography at the end. Right after the ninety-nine pages of recipes!
Bottom line: if you’re a carb-enjoyer, all is definitely not lost healthwise, and in fact on the contrary, this can be the foundation of a very healthy and nutrient-rich diet.
Click here to check out The Starch Solution, and enjoy the foods you love, healthily!
Share This Post
-
Can you ‘boost’ your immune system?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As flu season and a likely winter COVID-19 wave approach, you may encounter both proven and unproven methods claiming to “boost” your immune system. Before you reach for supplements, learn more about how the immune system works, how vaccines give us the best protection against many illnesses, and how some lifestyle factors can help your immune system function properly.
What is the immune system?
The immune system is the body’s first line of defense against invaders like viruses, bacteria, or fungi. You develop immunity—or protection from infection—when your immune system has learned how to recognize an invader and attack it before it makes you sick.
How can you boost your immune system?
You can teach your immune system how to fight back against dangerous invaders by staying up to date on vaccines. This season’s updated flu and COVID-19 vaccines target newer variants and are recommended for everyone 6 months and older.
Vaccines reduce your risk of getting sick and spreading illness to others. Even if you get infected with a disease after you’ve been vaccinated against it, the vaccine will still increase protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
People who have compromised immune systems due to certain health conditions or because they need to take immunosuppressant medications may need additional vaccine doses.
Find out which vaccines you and your children need by using the CDC’s Adult Vaccine Assessment Tool and Child and Adolescent Vaccine Assessment Tool. Talk to your health care provider about the best vaccines for your family.
Find pharmacies offering updated flu and COVID-19 vaccines by visiting Vaccines.gov.
Can supplements boost your immune system?
Many vitamin, mineral, and herbal supplements that are marketed as “immune boosting” have little to no effect on your immune system. Research is split on whether some of these supplements—like vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc—are capable of helping your body fight infections.
Plus, the Food and Drug Administration typically does not review supplements until after they have reached store shelves, and companies can sell supplements without notifying the FDA. This means that supplements may not be accurately labeled.
Eating a diverse diet rich in fruits and vegetables is the best way for most people to absorb nutrients that support optimal immune system function. People with certain health conditions and deficiencies may need specific supplements prescribed by a health care provider. For example, people with anemia may need iron supplements in order to maintain appropriate iron levels.
Before you begin taking a new supplement, talk to your health care provider, as some supplements may interact with medications you are taking or worsen certain health conditions.
Can lifestyle factors strengthen your immune system?
Based on current evidence, there is no direct link between lifestyle changes and enhanced immunity to infections. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through the following practices can help ensure that your immune system functions as it should:
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Exercise regularly.
- Don’t smoke.
- Limit or eliminate alcohol consumption.
- Get seven or more hours of sleep per night.
- Reduce stress.
Taking steps to avoid contact with germs also reduces your risk of getting sick. Safer sex barriers like condoms protect against HIV, while wearing a high-quality, well-fitting mask—especially in high-risk environments—protects against COVID-19. Both of these illnesses can reduce your production of white blood cells, which protect against infection.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Coffee, From A Blood Sugar Management Perspective
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our favorite French biochemist (Jessie Inchauspé) is back, and this time, she’s tackling a topic near and dear to this writer’s heart: coffee ☕💕
What to consider
Depending on how you like your coffee, some or all of these may apply to you:
- Is coffee healthy? Coffee is generally healthy, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes by improving fat burning in the liver and protecting beta cells in the pancreas.
- Does it spike blood sugars? Usually not so long as it’s black and unsweetened. Black coffee can cause small glucose spikes in some people due to stress-induced glucose release, but only if it contains caffeine.
- When is it best to drink it? Drinking coffee after breakfast, especially after a poor night’s sleep, can actually reduce glucose and insulin spikes.
- What about milk? All milks cause some glucose and insulin spikes. While oat milk is generally healthy, for blood sugar purposes unsweetened nut milks or even whole cow’s milk (but not skimmed; it needs the fat) are better options as they cause smaller spikes.
- What about sweetening? Adding sugar to coffee, especially on an empty stomach, obviously leads to large glucose spikes. Alternative sweeteners like stevia or sweet cinnamon are fine substitutes.
For more details on all of those things, plus why Kenyan coffee specifically may be the best for blood sugars, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Art of Being Unflappable (Tricks For Daily Life)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Art of Being Unflappable
From Stoicism to CBT, thinkers through the ages have sought the unflappable life.
Today, in true 10almonds fashion, we’re going to distil it down to some concentrated essentials that we can all apply in our daily lives:
Most Common/Impactful Cognitive Distortions To Catch (And Thus Avoid)
These are like the rhetorical fallacies with which you might be familiar (ad hominem, no true Scotsman, begging the question, tu quoque, straw man, etc), but are about what goes on between your own ears, pertaining to your own life.
If we learn about them and how to recognize them, however, we can catch them before they sabotage us, and remain “unflappable” in situations that could otherwise turn disastrous.
Let’s take a look at a few:
Catastrophizing / Crystal Ball
- Distortion: not just blowing something out of proportion, but taking an idea and running with it to its worst possible conclusion. For example, we cook one meal that’s a “miss” and conclude we are a terrible cook, and in fact for this reason a terrible housewife/mother/friend/etc, and for this reason everyone will probably abandon us and would be right to do so
- Reality: by tomorrow, you’ll probably be the only one who even remembers it happened
Mind Reading
- Distortion: attributing motivations that may or may not be there, and making assumptions about other people’s thoughts/feelings. An example is the joke about two partners’ diary entries; one is long and full of feelings about how the other is surely dissatisfied in their marriage, has been acting “off” with them all day, is closed and distant, probably wants to divorce, may be having an affair and is wondering which way to jump, and/or is just wondering how to break the news—the other partner’s diary entry is short, and reads “motorcycle won’t start; can’t figure out why”
- Reality: sometimes, asking open questions is better than guessing, and much better than assuming!
All-or-Nothing Thinking / Disqualifying the Positive / Magnifying the Negative
- Distortion: having a negative bias that not only finds a cloud in every silver lining, but stretches it out so that it’s all that we can see. In a relationship, this might mean that one argument makes us feel like our relationship is nothing but strife. In life in general, it may lead us to feel like we are “naturally unlucky”.
- Reality: those negative things wouldn’t even register as negative to us if there weren’t a commensurate positive we’ve experienced to hold them in contrast against. So, find and remember that positive too.
For brevity, we put a spotlight on (and in some cases, clumped together) the ones we think have the most bang-for-buck to know about, but there are many more.
So for the curious, here’s some further reading:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Seniors: Improve Blood Flow & Circulation In Your Legs
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Doug Weiss, a physiotherapist (and thus: a doctor of physical therapy), has advice on how and why to increase blood flow and circulation in your legs, keeping yourself healthier for longer and avoiding a lot of potential unpleasantries.
The exercises
The exercises here are not complex; they are as follows, and he suggests 3 sets of 10 reps of each, daily:
- Sitting ankle pumps: sitting on a chair or the edge of a bed, lift the toes up, then heels up, squeezing the muscles.
- Sitting knee extensions: sitting as before, kick one leg up until knee is straight, then switch legs.
- Heel raises: standing this time, with a sturdy support such as a countertop, raise on toes as high as possible, then lower heels back to the ground
- Pillow squats: placing pillows on a chair, cross hands on chest, and simply stand up and sit down—similar to the “getting up off the floor without using your hands” exercise, but an easier version.
For visuals on these, and more details including the specific benefits of each, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
4 Tips To Stand Without Using Hands ← this time it’s the full movement, from the floor, and this is a really important movement to be able to do, as it’s a big indicator of healthy longevity
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Terminal lucidity: why do loved ones with dementia sometimes ‘come back’ before death?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dementia is often described as “the long goodbye”. Although the person is still alive, dementia slowly and irreversibly chips away at their memories and the qualities that make someone “them”.
Dementia eventually takes away the person’s ability to communicate, eat and drink on their own, understand where they are, and recognise family members.
Since as early as the 19th century, stories from loved ones, caregivers and health-care workers have described some people with dementia suddenly becoming lucid. They have described the person engaging in meaningful conversation, sharing memories that were assumed to have been lost, making jokes, and even requesting meals.
It is estimated 43% of people who experience this brief lucidity die within 24 hours, and 84% within a week.
Why does this happen?
Terminal lucidity or paradoxical lucidity?
In 2009, researchers Michael Nahm and Bruce Greyson coined the term “terminal lucidity”, since these lucid episodes often occurred shortly before death.
But not all lucid episodes indicate death is imminent. One study found many people with advanced dementia will show brief glimmers of their old selves more than six months before death.
Lucidity has also been reported in other conditions that affect the brain or thinking skills, such as meningitis, schizophrenia, and in people with brain tumours or who have sustained a brain injury.
Moments of lucidity that do not necessarily indicate death are sometimes called paradoxical lucidity. It is considered paradoxical as it defies the expected course of neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia.
But it’s important to note these episodes of lucidity are temporary and sadly do not represent a reversal of neurodegenerative disease.
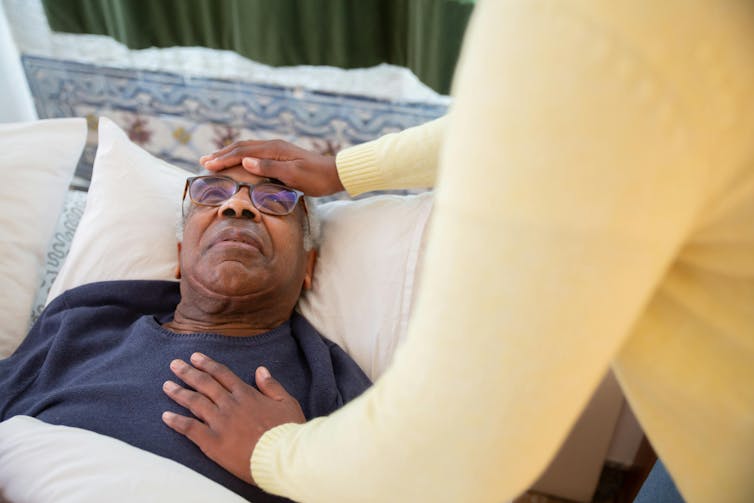
Sadly, these episodes of lucidity are only temporary. Pexels/Kampus Production Why does terminal lucidity happen?
Scientists have struggled to explain why terminal lucidity happens. Some episodes of lucidity have been reported to occur in the presence of loved ones. Others have reported that music can sometimes improve lucidity. But many episodes of lucidity do not have a distinct trigger.
A research team from New York University speculated that changes in brain activity before death may cause terminal lucidity. But this doesn’t fully explain why people suddenly recover abilities that were assumed to be lost.
Paradoxical and terminal lucidity are also very difficult to study. Not everyone with advanced dementia will experience episodes of lucidity before death. Lucid episodes are also unpredictable and typically occur without a particular trigger.
And as terminal lucidity can be a joyous time for those who witness the episode, it would be unethical for scientists to use that time to conduct their research. At the time of death, it’s also difficult for scientists to interview caregivers about any lucid moments that may have occurred.
Explanations for terminal lucidity extend beyond science. These moments of mental clarity may be a way for the dying person to say final goodbyes, gain closure before death, and reconnect with family and friends. Some believe episodes of terminal lucidity are representative of the person connecting with an afterlife.
Why is it important to know about terminal lucidity?
People can have a variety of reactions to seeing terminal lucidity in a person with advanced dementia. While some will experience it as being peaceful and bittersweet, others may find it deeply confusing and upsetting. There may also be an urge to modify care plans and request lifesaving measures for the dying person.
Being aware of terminal lucidity can help loved ones understand it is part of the dying process, acknowledge the person with dementia will not recover, and allow them to make the most of the time they have with the lucid person.
For those who witness it, terminal lucidity can be a final, precious opportunity to reconnect with the person that existed before dementia took hold and the “long goodbye” began.
Yen Ying Lim, Associate Professor, Turner Institute for Brain and Mental Health, Monash University and Diny Thomson, PhD (Clinical Neuropsychology) Candidate and Provisional Psychologist, Monash University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: