6 Ways To Look After Your Back
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Back To Back
When people think about looking after their back, often thought does not go much further than sitting with good posture, and perhaps even standing with good posture. And those things are important, but:
1) People’s efforts to have good posture often result in overcorrecting creating an anterior pelvic tilt that causes lower back problems.
Quick tip: if you’re sticking your butt out, you’re doing it wrong (no matter how great your butt is). Instead, to find the correct posture, go up on your tip-toes for a moment, then imagine a plumb-line down the center of your body, thus perpendicular to the floor, going all the way down to the ground. Now, slowly return your heels to the ground, but as you do so, keep your spine aligned to the plumb-line, so you’re not moving backwards as you drop, just directly down. This will land you in perfect posture.
Unless you have scoliosis. In which case, it’ll get you as close to good posture as is likely attainable from any quick tip.
2) There’s a lot more to looking after our back than just good posture!
Here are 5 other important things to do:
Be strong
Do strength-training for your back. How to do that is beyond the scope of today’s feature, but there are many good guides and also personal trainers that can be found.
Start off easy and work up, but do start. The stronger your back is, the less likely a momentary lapse in concentration is to throw out your back because you picked something up with imperfect form.
See also: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Stretch intentionally
Many back injuries occur as a result of stretching and/or twisting awkwardly, so if you ensure your basic mobility and range of motion is good, the less likely it is that unthinkingly twisting around 270° to see where that wasp was going will slip a disk.
The more you stretch intentionally (carefully, please), the more you will be able to stretch unintentionally without injury.
See also: Building & Maintaining Mobility
Stand when you can, walk when you can
We humans have outrun our evolution in a lot of ways, and/but one thing our bodies are definitely not well-adapted for is sitting. Unless we are sitting in a low squat the way you might often see an orang-utan sitting, sitting is not a good way of being for us. Even sitting seiza-style or cross-legged is passable for a short while, not for too long.
So, while there sure are times we need to sit (especially if you’re driving!) minimizing those times is ideal. There are a lot of activities that are traditionally done sitting, where there’s no need for it to be so. For example, your writer here sits for the day’s main meal, but takes any smaller meal standing (and when guests visit for a coffee or such, I’ll offer them the couch while I myself prop up the fireplace). Standing desks are also great if you spend a lot of time at the computer for any reason.
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less & Move More
Rest when you need to
You can’t stand all the time! But know this: if you want to rest your legs, lying down is a lot better for your back (and internal organs) than sitting.
Taking a 5 minute break lying on your couch, or bed, or floor, is a perfectly good option and only social convention says otherwise.
If you want a compromise option, though? A recliner chair, in the reclined position, is a better for your back than being scrunched up in the Economy Class Flight position.
PS: About that bed situation…
What Mattress Is Best, By Science?
Kill pain before it kills you
Painkillers aren’t great for the health per se, but pain (or rather, our bodily responses to such) can be worse. Half the time, when it comes to musculoskeletal problems, things get a lot worse a lot more quickly because of how we overcompensate due to the pain. So, take your pain seriously, and remember, the right amount of pain is zero.
If you’re thinking “but pain relief option xyz isn’t good for me”, we strongly recommend checking out:
The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
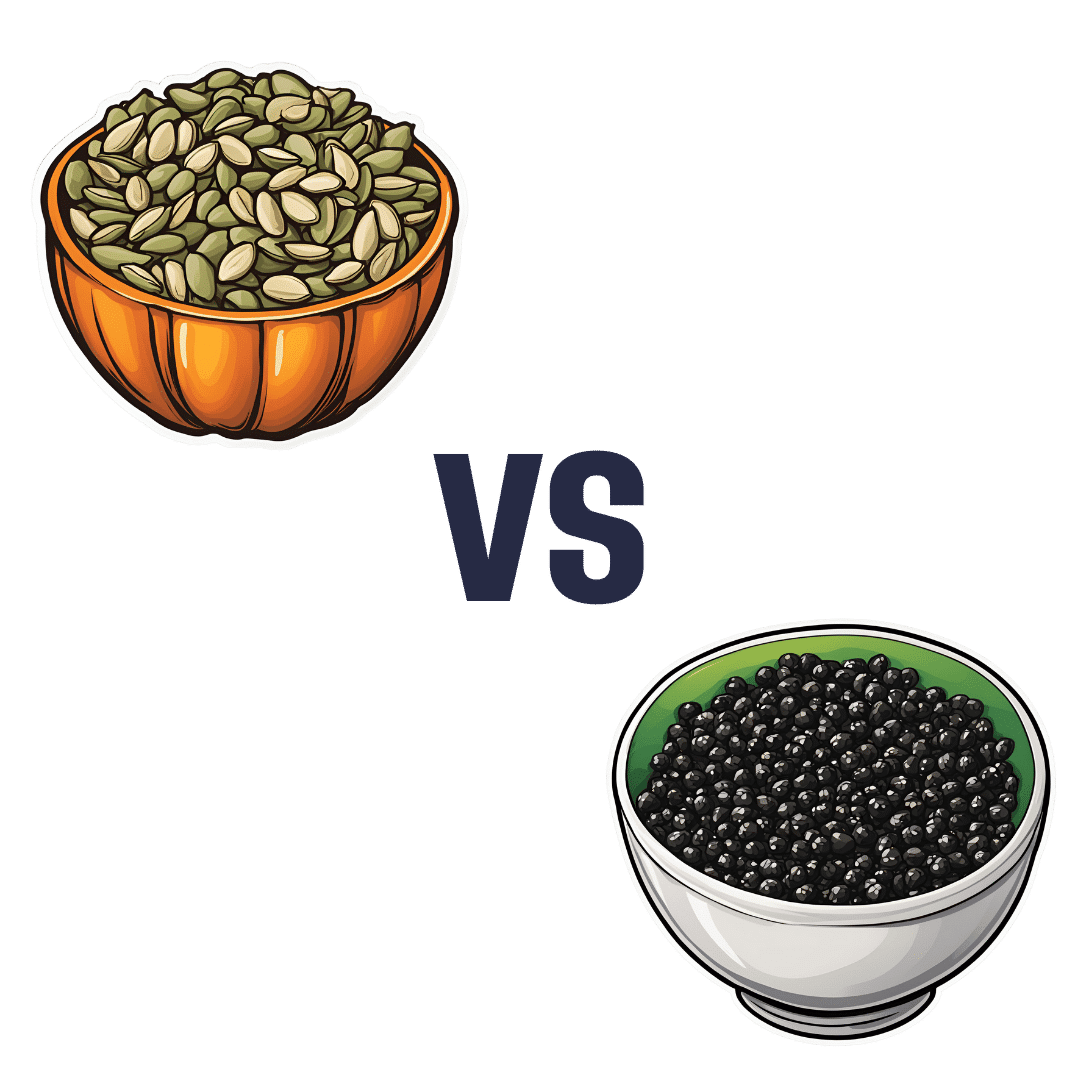
Pumpkin Seeds vs Watermelon Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pumpkin seeds to watermelon seeds, we picked the watermelon.
Why?
Starting with the macros: pumpkin seeds have a lot more carbs, while watermelon seeds have a lot more protein, despite pumpkin seeds being famous for such. They’re about equal on fiber. In terms of fats, watermelon seeds are higher in fats, and yes, these are healthy fats, mostly polyunsaturated.
When it comes to vitamins, pumpkin seeds are marginally higher in vitamins A and C, while watermelon seeds are a lot higher in vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and B9. An easy win for watermelon seeds here.
In the category of minerals, despite being famous for zinc, pumpkin seeds are higher only in potassium, while watermelon seeds are higher in iron, magnesium, manganese, and phosphorus; the two seeds are equal on calcium, copper, and zinc. Another win for watermelon seeds.
In short, enjoy both, but watermelon has more to offer. Of course, if buying just the seeds and not the whole fruit, it’s generally easier to find pumpkin seeds than watermelon seeds, so do bear in mind that pumpkin seeds’ second place isn’t that bad here—it’s just a case of a very nutritious food looking bad by standing next to an even better one.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Seed Saving Secrets – by Alice Mirren
Take care!
Share This Post
-
7 Steps to Get Off Sugar and Carbohydrates – by Susan Neal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We will not keep the steps a mystery; abbreviated, they are:
- decide to really do this thing
- get knowledge and support
- clean out that pantry/fridge/etc and put those things behind you
- buy in healthy foods while starving your candida
- plan for an official start date, so that everything is ready
- change the way you eat (prep methods, timings, etc)
- keep on finding small ways to improve, without turning back
Particularly important amongst those are starving the candida (the fungus in your gut that is responsible for a lot of carb cravings, especially sugar and alcohol—which latter can be broken down easily into sugar), and changing the “how” of eating as well as the “what”; those are both things that are often overlooked in a lot of guides, but this one delivers well.
Walking the reader by the hand through things like that is probably the book’s greatest strength.
In the category of subjective criticism, the author does go off-piste a little at the end, to take a moment while she has our attention to talk about other things.
For example, you may not need “Appendix 7: How to Become A Christian and Disciple of Jesus Christ”.
Of course if that calls to you, then by all means, follow your heart, but it certainly isn’t a necessary step of quitting sugar. Nevertheless, the diversion doesn’t detract from the good dietary change advice that she has just spent a book delivering.
Bottom line: there’s no deep science here, but there’s a lot of very good, very practical advice, that’s consistent with good science.
Click here to check out 7 Steps to Get Off Sugar, and watch your health improve!
Share This Post
-
What causes the itch in mozzie bites? And why do some people get such a bad reaction?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you one of these people who loathes spending time outdoors at dusk as the weather warms and mosquitoes start biting?
Female mosquitoes need blood to develop their eggs. Even though they take a tiny amount of our blood, they can leave us with itchy red lumps that can last days. And sometimes something worse.
So why does our body react and itch after being bitten by a mosquito? And why are some people more affected than others?
Arthur Poulin/Unsplash What happens when a mosquito bites?
Mosquitoes are attracted to warm blooded animals, including us. They’re attracted to the carbon dioxide we exhale, our body temperatures and, most importantly, the smell of our skin.
The chemical cocktail of odours from bacteria and sweat on our skin sends out a signal to hungry mosquitoes.
Some people’s skin smells more appealing to mosquitoes, and they’re more likely to be bitten than others.
Once the mosquito has made its way to your skin, things get a little gross.
The mosquito pierces your skin with their “proboscis”, their feeding mouth part. But the proboscis isn’t a single, straight, needle-like tube. There are multiple tubes, some designed for sucking and some for spitting.
Once their mouth parts have been inserted into your skin, the mosquito will inject some saliva. This contains a mix of chemicals that gets the blood flowing better.
There has even been a suggestion that future medicines could be inspired by the anti-blood clotting properties of mosquito saliva.
A common pest mosquito around the world, Culex quinquefasciatus. Cameron Webb (NSW Health Pathology), CC BY It’s not the stabbing of our skin by the mosquito’s mouth parts that hurts, it’s the mozzie spit our bodies don’t like.
Are some people allergic to mosquito spit?
Once a mosquito has injected their saliva into our skin, a variety of reactions can follow. For the lucky few, nothing much happens at all.
For most people, and irrespective of the type of mosquito biting, there is some kind of reaction. Typically there is redness and swelling of the skin that appears within a few hours, but often more quickly, after just a few minutes.
Occasionally, the reaction can cause pain or discomfort. Then comes the itchiness.
Some people do suffer severe reactions to mosquito bites. It’s a condition often referred to as “skeeter syndrome” and is an allergic reaction caused by the protein in the mosquito’s saliva. This can cause large areas of swelling, blistering and fever.
The chemistry of mosquito spit hasn’t really been well studied. But it has been shown that, for those who do suffer allergic reactions to their bites, the reactions may differ depending on the type of mosquito biting.
We all probably get more tolerant of mosquito bites as we get older. Young children are certainly more likely to suffer more following mosquito bites. But as we get older, the reactions are less severe and may pass quickly without too much notice.
How best to treat the bites?
Research into treating bites has yet to provide a single easy solution.
There are many myths and home remedies about what works. But there is little scientific evidence supporting their use.
The best way to treat mosquito bites is by applying a cold pack to reduce swelling and to keep the skin clean to avoid any secondary infections. Antiseptic creams and lotions may also help.
There is some evidence that heat may alleviate some of the discomfort.
It’s particularly tough to keep young children from scratching at the bite and breaking the skin. This can form a nasty scab that may end up being worse than the bite itself.
Applying an anti-itch cream may help. If the reactions are severe, antihistamine medications may be required.
To save the scratching, stop the bites
Of course, it’s better not to be bitten by mosquitoes in the first place. Topical insect repellents are a safe, effective and affordable way to reduce mosquito bites.
Covering up with loose fitted long sleeved shirts, long pants and covered shoes also provides a physical barrier.
Mosquito coils and other devices can also assist, but should not be entirely relied on to stop bites.
There’s another important reason to avoid mosquito bites: millions of people around the world suffer from mosquito-borne diseases. More than half a million people die from malaria each year.
In Australia, Ross River virus infects more than 5,000 people every year. And in recent years, there have been cases of serious illnesses caused by Japanese encephalitis and Murray Valley encephalitis viruses.
Cameron Webb, Clinical Associate Professor and Principal Hospital Scientist, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How We Age: The Science of Longevity – by Dr. Coleen Murphy
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author is not a glossy “name brand” and has nothing to sell (besides her book). This shows, because it’s clearly not a book that was rushed out as a marketing ploy. Indeed, she begins with the words:
❝This book took me several years to write and is largely based on information I gathered while teaching my class, “Molecular Mechanisms of Longevity: The Genetics, Genomics, and Cell Biology of Aging,” at Princeton University.❞
~ Dr. Coleen Murphy
Thus, as you may imagine, it’s a thorough book, thoughtful, with conscientious attention to detail. As a reader, you are essentially getting the knowledge of a Princeton genomics class.
She covers what’s going on in our genes, in our cells, and in our bodies, when we age; why some animals don’t, and what things affect that. She talks biomarkers of aging and the industry gold standard “Health-Related Quality of Life” metrics. We learn about insulin signalling and FOXO targets; the role of caloric restriction or intermittent fasting, topics such as molecular homeostasis in the regulation of longevity (hello senolytics and chaperone-mediated autophagy), the microbiome and epigenetics, as well as mitochondrial management, cell replacement (including induced pluripotent stem cells), and even DNA repair. And yes, a lot about cognitive aging and how to slow it too.
The style is academic and/but perfectly readable; she explains everything as we go. We’ll note, though, that it’s not dry academic—her personality comes through throughout, in a good way that makes it a pleasant read as well as an informative one.
Bottom line: if you’d like a much deeper understanding of the mechanics of aging than we have room to get into in our articles at 10almonds, this book is a highly recommendable perfect opportunity.
Click here to check out How We Age, and learn about the science of longevity!
PS: we’ve reviewed a few books about the science of aging/longevity recently, and they’ve each been good, but if you’re going to get only one, we recommend this one, as in this reviewer’s opinion, it’s the best 😎
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sun-dried Tomatoes vs Black Olives – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sun-dried tomatoes to black olives, we picked the sun-dried tomatoes.
Why?
These common snack-salad items may seem similar in consistency, but their macros are very different: the tomatoes, being dried, have proportionally a lot more protein, carbs, and fiber. The olives, meanwhile, have more fat (and/but yes, a very healthy blend of fats). Note that these comments are true for the things themselves; be aware that sun-dried tomatoes are often sold in vegetable oil, which would obviously change the macros considerably and be much less healthy. So, for the sake of statistics, we’re assuming you got sun-dried tomatoes that aren’t soaked in oil. All in all, we’re calling this category a win for the tomatoes, but those fats from the olives are very good too.
In terms of vitamins, the sun-dried tomatoes being dried again means that the loss of water weight means the vitamin content is proportionally much higher; the tomatoes are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and K, while olives are higher only in vitamin E (but in their defence, olives have 165x more vitamin E than sun-dried tomatoes). Still, a win for sun-dried tomatoes here.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a similar story for the same reason; the loss of water weight in the sun-dried tomatoes makes them much more nutritionally dense; they are higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while the olives are higher only in sodium. Note, we’re looking at black olives today; green olives would be even higher in sodium than black ones, as they are “cured” for longer.
Lastly, in terms of polyphenols, they both have a lot of great things to bring, but sun-dried tomatoes are pretty much the richest natural source of lycopene, which itself a very powerful polyphenol even my general polyphenol standards, so we’d call this one a win for the sun-dried tomatoes too.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Complex PTSD – by Pete Walker
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about Complex PTSD, but there’s a lot more to be said than we can fit into an article or two.
Pete Walker, a licensed marriage and family therapist, does an excellent job and pulls no punches, starting from the book’s dedication and carrying the hard-hitting seriousness all the way through to the Appendices.
To this end, it absolutely may not be an easy book to read at times (emotionally speaking), especially if you have C-PTSD. On the other hand, you may also find it a very validating 300-odd pages of “Yes, he is telling my life story in words, now this makes sense!”
That said, it’s mostly not an anecdotes-based book and nor is it just a feelsy ride; it’s also a textbook and a how-to manual. It’s a textbook of how and why things come about the way they do, and a manual of how to effectively manage C-PTSD, and find peace. There’s no silver bullet here, but there is a very comprehensive guide, and chapters full of tools to use (and no, not the same CBT things you’ve probably read a hundred times, this is C-PTSD-specific stuff).
Bottom line: this is the C-PTSD book; if you buy only one book on the topic, make it this one.
Click here to check out Complex PTSD: From Surviving To Thriving, and indeed thrive!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: