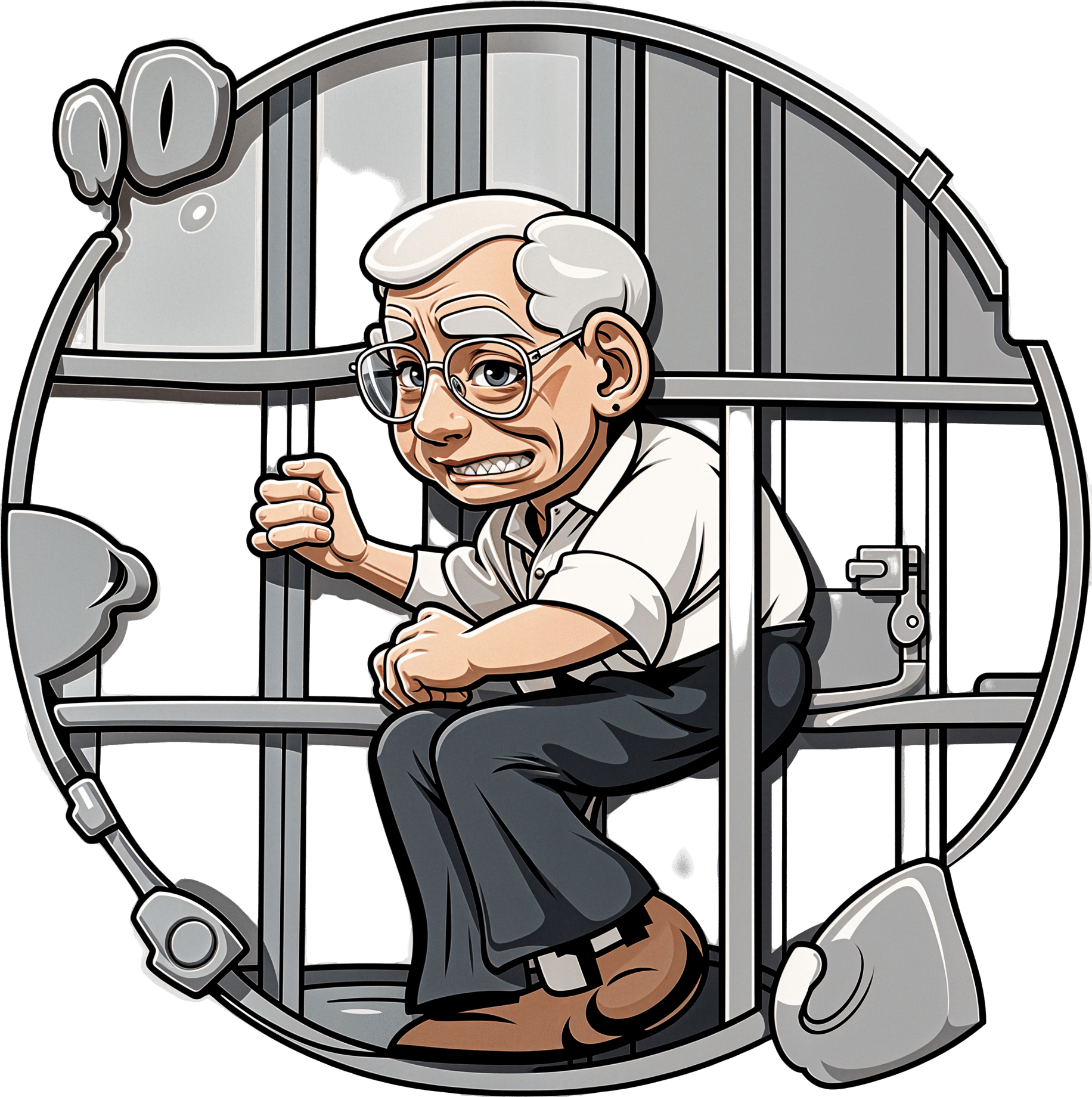
Older Americans Say They Feel Trapped in Medicare Advantage Plans
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In 2016, Richard Timmins went to a free informational seminar to learn more about Medicare coverage.
“I listened to the insurance agent and, basically, he really promoted Medicare Advantage,” Timmins said. The agent described less expensive and broader coverage offered by the plans, which are funded largely by the government but administered by private insurance companies.
For Timmins, who is now 76, it made economic sense then to sign up. And his decision was great, for a while.
Then, three years ago, he noticed a lesion on his right earlobe.
“I have a family history of melanoma. And so, I was kind of tuned in to that and thinking about that,” Timmins said of the growth, which doctors later diagnosed as malignant melanoma. “It started to grow and started to become rather painful.”
Timmins, though, discovered that his enrollment in a Premera Blue Cross Medicare Advantage plan would mean a limited network of doctors and the potential need for preapproval, or prior authorization, from the insurer before getting care. The experience, he said, made getting care more difficult, and now he wants to switch back to traditional, government-administered Medicare.
But he can’t. And he’s not alone.
“I have very little control over my actual medical care,” he said, adding that he now advises friends not to sign up for the private plans. “I think that people are not understanding what Medicare Advantage is all about.”
Enrollment in Medicare Advantage plans has grown substantially in the past few decades, enticing more than half of all eligible people, primarily those 65 or older, with low premium costs and perks like dental and vision insurance. And as the private plans’ share of the Medicare patient pie has ballooned to 30.8 million people, so too have concerns about the insurers’ aggressive sales tactics and misleading coverage claims.
Enrollees, like Timmins, who sign on when they are healthy can find themselves trapped as they grow older and sicker.
“It’s one of those things that people might like them on the front end because of their low to zero premiums and if they are getting a couple of these extra benefits — the vision, dental, that kind of thing,” said Christine Huberty, a lead benefit specialist supervising attorney for the Greater Wisconsin Agency on Aging Resources.
“But it’s when they actually need to use it for these bigger issues,” Huberty said, “that’s when people realize, ‘Oh no, this isn’t going to help me at all.’”
Medicare pays private insurers a fixed amount per Medicare Advantage enrollee and in many cases also pays out bonuses, which the insurers can use to provide supplemental benefits. Huberty said those extra benefits work as an incentive to “get people to join the plan” but that the plans then “restrict the access to so many services and coverage for the bigger stuff.”
David Meyers, assistant professor of health services, policy, and practice at the Brown University School of Public Health, analyzed a decade of Medicare Advantage enrollment and found that about 50% of beneficiaries — rural and urban — left their contract by the end of five years. Most of those enrollees switched to another Medicare Advantage plan rather than traditional Medicare.
In the study, Meyers and his co-authors muse that switching plans could be a positive sign of a free marketplace but that it could also signal “unmeasured discontent” with Medicare Advantage.
“The problem is that once you get into Medicare Advantage, if you have a couple of chronic conditions and you want to leave Medicare Advantage, even if Medicare Advantage isn’t meeting your needs, you might not have any ability to switch back to traditional Medicare,” Meyers said.
Traditional Medicare can be too expensive for beneficiaries switching back from Medicare Advantage, he said. In traditional Medicare, enrollees pay a monthly premium and, after reaching a deductible, in most cases are expected to pay 20% of the cost of each nonhospital service or item they use. And there is no limit on how much an enrollee may have to pay as part of that 20% coinsurance if they end up using a lot of care, Meyers said.
To limit what they spend out-of-pocket, traditional Medicare enrollees typically sign up for supplemental insurance, such as employer coverage or a private Medigap policy. If they are low-income, Medicaid may provide that supplemental coverage.
But, Meyers said, there’s a catch: While beneficiaries who enrolled first in traditional Medicare are guaranteed to qualify for a Medigap policy without pricing based on their medical history, Medigap insurers can deny coverage to beneficiaries transferring from Medicare Advantage plans or base their prices on medical underwriting.
Only four states — Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, and New York — prohibit insurers from denying a Medigap policy if the enrollee has preexisting conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
Paul Ginsburg is a former commissioner on the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, also known as MedPAC. It’s a legislative branch agency that advises Congress on the Medicare program. He said the inability of enrollees to easily switch between Medicare Advantage and traditional Medicare during open enrollment periods is “a real concern in our system; it shouldn’t be that way.”
The federal government offers specific enrollment periods every year for switching plans. During Medicare’s open enrollment period, from Oct. 15 to Dec. 7, enrollees can switch out of their private plans to traditional, government-administered Medicare.
Medicare Advantage enrollees can also switch plans or transfer to traditional Medicare during another open enrollment period, from Jan. 1 to March 31.
“There are a lot of people that say, ‘Hey, I’d love to come back, but I can’t get Medigap anymore, or I’ll have to just pay a lot more,’” said Ginsburg, who is now a professor of health policy at the University of Southern California.
Timmins is one of those people. The retired veterinarian lives in a rural community on Whidbey Island just north of Seattle. It’s a rugged, idyllic landscape and a popular place for second homes, hiking, and the arts. But it’s also a bit remote.
While it’s typically harder to find doctors in rural areas, Timmins said he believes his Premera Blue Cross plan made it more challenging to get care for a variety of reasons, including the difficulty of finding and getting in to see specialists.
Nearly half of Medicare Advantage plan directories contained inaccurate information on what providers were available, according to the most recent federal review. Beginning in 2024, new or expanding Medicare Advantage plans must demonstrate compliance with federal network expectations or their applications could be denied.
Amanda Lansford, a Premera Blue Cross spokesperson, declined to comment on Timmins’ case. She said the plan meets federal network adequacy requirements as well as travel time and distance standards “to ensure members are not experiencing undue burdens when seeking care.”
Traditional Medicare allows beneficiaries to go to nearly any doctor or hospital in the U.S., and in most cases enrollees do not need approval to get services.
Timmins, who recently finished immunotherapy, said he doesn’t think he would be approved for a Medigap policy, “because of my health issue.” And if he were to get into one, Timmins said, it would likely be too expensive.
For now, Timmins said, he is staying with his Medicare Advantage plan.
“I’m getting older. More stuff is going to happen.”
There is also a chance, Timmins said, that his cancer could resurface: “I’m very aware of my mortality.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Genius Foods – by Max Lugavere
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There is a lot of seemingly conflicting (or sometimes: actually conflicting!) information out there with regard to nutrition and various aspects of health. Why, for example, are we told:
- Be sure to get plenty of good healthy fats from nuts and seeds, for metabolic health and brain health too!
- But these terrible nut and seed oils lead to heart disease and dementia! Avoid them at all costs!
Max Lugavere demystifies this and more.
His science-led approach is primarily focused on avoiding dementia, and/but is at least not bad when it comes to other areas of health too.
He takes us on a tour of different parts of our nutrition, including:
- Perhaps the clearest explanation of “healthy” vs “unhealthy” fats this reviewer has read
- Managing carbs (simple and complex) for healthy glucose management—essential for good brain health
- What foods to improve or reduce—a lot you might guess, but this is a comprehensive guide to brain health so it’d be remiss to skip it
- The role that intermittent fasting can play as a bonus extra
While the main thrust of the book is about avoiding cognitive impairment in the long-term (including later-life dementia), he makes good, evidence-based arguments for how this same dietary plan improves cognitive function in the short-term, too.
Speaking of that dietary plan: he does give a step-by-step guide in a “make this change first, then this, then this” fashion, and offers some sample recipes too. This is by no means a recipe book though—most of the book is taking us through the science, not the kitchen.
Bottom line: this is the book for getting unconfused with regard to diet and brain health, making a lot of good science easy to understand. Which we love!
Click here to check out “Genius Foods” on Amazon today, give your brain a boost!
Share This Post
-
The Dental Diet – by Dr. Steven Lin
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As it turns out, there’s a lot more to healthy teeth than skipping the sugar and getting some calcium.
The author’s journey started with the realization that most of his work as a dentist should be unnecessary, and not just in the “you should have been flossing” sense. Rather, he came to the same conclusions as his fellow dentist Weston Price before him, and this time (unlike Price) he stuck to his own field, dentistry—meaning that the conclusions he kept were the more valid ones.
Another thing he does better than Price is that he contextualizes the information—we don’t need, for example, to be eating seal fat as a main component of our diet, but we do need to be getting sufficient amounts of certain fat-soluble vitamins. And most people aren’t. Same with what’s good or bad for our oral microbiome, and by extension, our saliva, and by extension, our teeth and gums.
There’s a lot of nutritional information in here; macros and micronutrients alike, but the book goes further than that, to also recommend minimally-processed food that requires more chewing, for example. Not just for its nutritional content, but because that helps our teeth move to (and then stay) where they are ideally supposed to be. No amount of perfectly-blended nutritional supplement drink will align your maxilla for you, say. But chomping on raw carrots? Different story.
Dr. Lin offers a 40-day meal plan, but aware that if you’re vegetarian or vegan you’re probably going to have to rethink it yourself using the information he gives, because his meal plan includes animal products.
Bottom line: if you’d like to eat for better oral health (nutritionally, physically, and for your oral microbiome), this book has all the information you’ll need.
Share This Post
-
How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Overcoming Loneliness & Isolation
One of the biggest mental health threats that faces many of us as we get older is growing isolation, and the loneliness that can come with it. Family and friends thin out over the years, and getting out and about isn’t always as easy as it used to be for everyone.
Nor is youth a guaranteed protection against this—in today’s world of urban sprawl and nothing-is-walkable cities, in which access to social spaces such as cafés and the like means paying the rising costs with money that young people often don’t have… And that’s without getting started on how much the pandemic impacted an entire generation’s social environments (or lack thereof).
Why is this a problem?
Humans are, by evolution, social creatures. As individuals we may have something of a spectrum from introvert to extrovert, but as a species, we thrive in community. And we suffer, when we don’t have that.
What can we do about it?
We can start by recognizing our needs, such as they are, and identifying to what extent they are being met (or not).
- Some of us may be very comfortable with a lot of alone time—but need someone to talk to sometimes.
- Some of us may need near-constant company to feel at our best—and that’s fine too! We just need to plan accordingly.
In the former case, it’s important to remember that needing someone to talk to is not being a burden to them. Not only will our company probably enrich them too, but also, we are evolved to care for one another, and that itself can bring fulfilment to them as much as to you. But what if you don’t a friend to talk to?
- You might be surprised at who would be glad of you reaching out. Have a think through whom you know, and give it a go. This can be scary, because what if they reject us, or worse, they don’t reject us but silently resent us instead? Again, they probably won’t. Human connection requires taking risks and being vulnerable sometimes.
- If that’s not an option, there are services that can fill your need. For some, therapy might serve a dual purpose in this regard. For others, you might want to check out the list of (mostly free) resources at the bottom of this article
In the second case (that we need near-constant company to feel at our best) we probably need to look more at our overall lifestyle, and find ways to be part of a community. That can include:
- Living in a close-knit community (places with a lot of retirees in one place often have this; or younger folk might look at communal living/working spaces, for example)
- Getting involved in local groups (you can check out NextDoor.com or MeetUp.com for this)
- Volunteering for a charity (not only are acts of service generally fulfilling in and of themselves, but also, you will probably be working with other people of a charitable nature, and such people tend to make for good company!)
Need a little help?
There are many, many organizations that will love to help you (or anyone else) overcome loneliness and isolation.
Rather than list them all here and make this email very long by describing how each of them works, here’s a great compilation of resources:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Is Cutting Calories The Key To Healthy Long Life?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Caloric Restriction with Optimal Nutrition
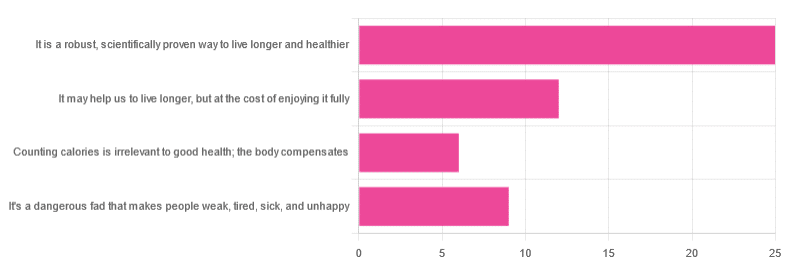
Yesterday, we asked you “What is your opinion of caloric restriction as a health practice?” and got the above-depicted, below-described spread of responses:
- 48% said “It is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier”
- 23% said “It may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully”
- 17% said “It’s a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy”
- 12% said “Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates”
So… What does the science say?
A note on terms, first
“Caloric restriction” (henceforth: CR), as a term, sees scientific use to mean anything from a 25% reduction to a 50% reduction, compared to metabolic base rate.
This can also be expressed the other way around, “dropping to 60% of the metabolic base rate” (i.e., a 40% reduction).
Here we don’t have the space to go into much depth, so our policy will be: if research papers consider it CR, then so will we.
A quick spoiler, first
The above statements about CR are all to at least some degree True in one way or another.
However, there are very important distinctions, so let’s press on…
CR is a robust, scientifically proven way to live longer and healthier: True or False?
True! This has been well-studied and well-documented. There’s more science for this than we could possibly list here, but here’s a good starting point:
❝Calorie restriction (CR), a nutritional intervention of reduced energy intake but with adequate nutrition, has been shown to extend healthspan and lifespan in rodent and primate models.
Accumulating data from observational and randomized clinical trials indicate that CR in humans results in some of the same metabolic and molecular adaptations that have been shown to improve health and retard the accumulation of molecular damage in animal models of longevity.
In particular, moderate CR in humans ameliorates multiple metabolic and hormonal factors that are implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, the leading causes of morbidity, disability and mortality❞
Source: Ageing Research Reviews | Calorie restriction in humans: an update
See also: Caloric restriction in humans reveals immunometabolic regulators of health span
We could devote a whole article (or a whole book, really) to this, but the super-short version is that it lowers the metabolic “tax” on the body and allows the body to function better for longer.
CR may help us to live longer, but at the cost of enjoying it fully: True or False?
True or False, contingently, depending on what’s important to you. And that depends on psychology as much as physiology, but it’s worth noting that there is often a selection bias in the research papers; people ill-suited to CR drop out of the studies and are not counted in the final data.
Also, relevant for a lot of our readers, most (human-based) studies recruit people over 18 and under 60. So while it is reasonable to assume the same benefits will be carried over that age, there is not nearly as much data for it.
Studies into CR and Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) have been promising, and/but have caveats:
❝In non-obese adults, CR had some positive effects and no negative effects on HRQoL.❞
❝We do not know what degree of CR is needed to achieve improvements in HRQoL, but we do know it requires an extraordinary amount of support.
Therefore, the incentive to offer this intervention to a low-risk, normal or overweight individual is lacking and likely not sustainable in practice.❞
CR a dangerous fad that makes people weak, tired, sick, and unhealthy: True or False?
True if it is undertaken improperly, and/or without sufficient support. Many people will try CR and forget that the idea is to reduce metabolic load while still getting good nutrition, and focus solely on the calorie-counting.
So for example, if a person “saves” their calories for the day to have a night out in a bar where they drink their calories as alcohol, then this is going to be abysmal for their health.
That’s an extreme example, but lesser versions are seen a lot. If you save your calories for a pizza instead of a night of alcoholic drinks, then it’s not quite so woeful, but for example the nutrition-to-calorie ratio of pizza is typically not great. Multiply that by doing it as often as not, and yes, someone’s health is going to be in ruins quite soon.
Counting calories is irrelevant to good health; the body compensates: True or False?
True if by “good health” you mean weight loss—which is rarely, if ever, what we mean by “good health” here at 10almonds (unless we clarify such), but it’s a very common association and indeed, for some people it’s a health goal. You cannot sustainably and healthily lose weight by CR alone, especially if you’re not getting optimal nutrition.
Your body will notice that you are starving, and try to save you by storing as much fat as it can, amongst other measures that will similarly backfire (cortisol running high, energy running low, etc).
For short term weight loss though, yes, it’ll work. At a cost. That we don’t recommend.
❝By itself, decreasing calorie intake will have a limited short-term influence.❞
Source: Reducing Calorie Intake May Not Help You Lose Body Weight
See also…
❝Caloric restriction is a commonly recommended weight-loss method, yet it may result in short-term weight loss and subsequent weight regain, known as “weight cycling”, which has recently been shown to be associated with both poor sleep and worse cardiovascular health❞
Source: Dieting Behavior Characterized by Caloric Restriction
In summary…
Caloric restriction is a well-studied area of health science. We know:
- Practised well, it can extend not only lifespan, but also healthspan
- Practised well, it can improve mood, energy, sexual function, and the other things people fear losing
- Practised badly, it can be ruinous to the health—it is critical to practise caloric restriction with optimal nutrition.
- Practised badly, it can lead to unhealthy weight loss and weight regain
One final note…
If you’ve tried CR and hated it, and you practised it well (e.g., with optimal nutrition), then we recommend just not doing it.
You could also try intermittent fasting instead, for similar potential benefits. If that doesn’t work out either, then don’t do that either!
Sometimes, we’re just weird. It can often be because of a genetic or epigenetic quirk. There are usually workarounds, and/but not everything that’s right for most people will be right for all of us.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Aging Minds: Normal vs Abnormal Cognitive Decline
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Having a “senior moment” and having dementia are things that are quite distinct from one another; while we may very reasonably intend to fight every part of it, it’s good to know what’s “normal” as well as what is starting to look like progress into something more severe:
Know the differences
Cognitive abilities naturally decline with age, often beginning around 30 (yes, really—the first changes are mostly metabolic though, so this is far from set in stone). Commonly-noticed changes include:
- slower thinking
- difficulty multitasking
- reduced attention
- weaker memory.
Over time, these changes have what is believed to be a two-way association (as in, each causes/worsens the other) with changes in brain structure, especially reduced hippocampal and frontal lobe volume.
- Gradual cognitive changes are normal with age, whereas dementia involves a pathological decline affecting memory, problem-solving, and behavior.
- Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) involves noticeable cognitive decline without disrupting daily life, while dementia affects everyday tasks like cooking or driving.
- Dementia causes significant impairments, including motor challenges like falls or tremors, and dementia-induced cognitive decline symptoms include forgetfulness, getting lost, personality changes, and planning difficulties, often worsening with stress or illness.
To best avoid these, consider: regular exercise, a nutritious diet, good quality sleep, social interaction, and mentally stimulating activities.
Also, often forgotten (in terms of its relevance at least): managing cardiovascular health is very important too. We’ve said it before, and we’ll say it again: what’s good for your heart is good for your brain (since the former feeds the latter with oxygen and nutrients, and also takes away detritus that will otherwise build up in the brain).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Is It Dementia? Spot The Signs (Because None Of Us Are Immune) ← we go into more specific detail here
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Antihistamines’ Generation Gap
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are You Ready For Allergy Season?
For those of us in the Northern Hemisphere, fall will be upon us soon, and we have a few weeks to be ready for it. A common seasonal ailment is of course seasonal allergies—it’s not serious for most of us, but it can be very annoying, and can disrupt a lot of our normal activities.
Suddenly, a thing that notionally does us no real harm, is making driving dangerous, cooking take three times as long, sex laughable if not off-the-table (so to speak), and the lightest tasks exhausting.
So, what to do about it?
Antihistamines: first generation
Ye olde antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine are probably not what to do about it.
They are small molecules that cross the blood-brain barrier and affect histamine receptors in the central nervous system. This will generally get the job done, but there’s a fair bit of neurological friendly-fire going on, and while they will produce drowsiness, the sleep will usually be of poor quality. They also tax the liver rather.
If you are using them and not experiencing unwanted side effects, then don’t let us stop you, but do be aware of the risks.
See also: Long-term use of diphenhydramine ← this is the active ingredient in Benadryl in the US and Canada, but safety regulations in many other countries mean that Benadryl has different, safer active ingredients elsewhere.
Antihistamines: later generations
We’re going to aggregate 2nd gen, 3rd gen, and 4th gen antihistamines here, because otherwise we’ll be writing a history article and we don’t have room for that. But suffice it to say, later generations of antihistamines do not come with the same problems.
Instead of going in all-guns-blazing to the CNS like first-gens, they are more specific in their receptor-targetting, resulting in negligible collateral damage:
Special shout-out to cetirizine and loratadine, which are the drugs behind half the brand names you’ll see on pharmacy shelves around most of the world these days (including many in the US and Canada).
Note that these two are very often discussed in the same sentence, sit next to each other on the shelf, and often have identical price and near-identical packaging. Their effectiveness (usually: moderate) and side effects (usually: low) are similar and comparable, but they are genuinely different drugs that just happen to do more or less the same thing.
This is relevant because if one of them isn’t working for you (and/or is creating an unwanted side effect), you might want to try the other one.
Another honorable mention goes to fexofenadine, for which pretty much all the same as the above goes, though it gets talked about less (and when it does get mentioned, it’s usually by its most popular brand name, Allegra).
Finally, one that’s a little different and also deserving of a special mention is azelastine. It was recently (ish, 2021) moved from being prescription-only to being non-prescription (OTC), and it’s a nasal spray.
It can cause drowsiness, but it’s considered safe and effective for most people. Its main benefit is not really the difference in drug, so much as the difference in the route of administration (nasal rather than oral). Because the drug is in liquid spray form, it can be absorbed through the mucus lining of the nose and get straight to work on blocking the symptoms—in contrast, oral antihistamines usually have to go into your stomach and take their chances there (we say “usually”, because there are some sublingual antihistamines that dissolve under the tongue, but they are less common.)
Better than antihistamines?
Writer’s note: at this point, I was given to wonder: “wait, what was I squirting up my nose last time anyway?”—because, dear readers, at the time I got it I just bought one of every different drug on the shelf, desperate to find something that worked. What worked for me, like magic, when nothing else had, was beclometasone dipropionate, which a) smelled delightfully of flowers, which might just be the brand I got, b) needs replacing now because I got it in March 2023 and it expired July 2024, and c) is not an antihistamine at all.
But, that brings us to the final chapter for today: systemic corticosteroids
They’re not ok for everyone (check with your doctor if unsure), and definitely should not be taken if immunocompromised and/or currently suffering from an infection (including colds, flu, COVID, etc) unless your doctor tells you otherwise (and even then, honestly, double-check).
But! They can work like magic when other things don’t. Unlike antihistamines, which only block the symptoms, systemic corticosteroids tackle the underlying inflammation, which can stop the whole thing in its tracks.
Here’s how they measure up against antihistamines:
❝The results of this systematic review, together with data on safety and cost effectiveness, support the use of intranasal corticosteroids over oral antihistamines as first line treatment for allergic rhinitis.❞
~ Dr. Robert Puy et al.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: