Jasmine McDonald’s Ballet Stretching Routine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Why Jasmine’s Video is Useful
Jasmine McDonald is not only a professional ballerina, but is also a certified personal trainer, so when it comes to keeping her body strong and flexible, she’s a wealth of knowledge. Her video (below) is a great example of this.
In case you’re interested in learning more, she currently (privately) tutors over 30 people on a day-to-day basis. You can contact her here!
Other Stretches?
If you think that Jasmine’s stretches may be out of your league, we recommend checking out our other articles on stretching, including:
- 11 Minutes to Pain-Free Hips
- How to Permanently Loosen a Tight Psoas
- Stretching Scientifically
- Stretching & Mobility
- Stretching to Stay Young
Otherwise, let loose on these dancer stretches and exercises:
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Almond Butter vs Cashew Butter – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almond butter to cashew butter, we picked the almond.
Why?
They’re both good! But, our inherent pro-almond bias notwithstanding, the almond butter does have a slightly better spread of nutrients.
In terms of macros, almond butter has more protein while cashew butter has more carbs, and of their fats, they’re broadly healthy in both cases, but almond butter does have less saturated fat.
In the category of vitamins, both are good sources of vitamin E, but almond butter has about 4x more. The rest of the vitamins they both contain aren’t too dissimilar, aside from some different weightings of various different B-vitamins, that pretty much balance out across the two nut butters. The only noteworthy point in cashew butter’s favor here is that it is a good source of vitamin K, which almond butter doesn’t have.
When it comes to minerals, both are good sources of lots of minerals, but most significantly, almond butter has a lot more calcium and quite a bit more potassium. In contrast, cashew butter has more selenium.
In short, they’re both great, but almond butter has more relative points in its favor than cashew butter.
Here are the two we depicted today, by the way, in case you’d like to try them:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Fast Burn – by Dr. Ian K. Smith
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Intermittent fasting seems simple enough: how complicated can “stop eating for a bit” be? Well, there are nuances and tweaks and hacks and “if you do this bit wrong it will sabotage your benefits” things to know about, too.
Dr. Smith takes us through the basic essentials first, and covers each of the main kinds of intermittent fasting, for example:
- Time-restricted eating; 12:12, 16:8, etc, with those being hours fasting vs hours eating
- Caloric restriction models; for example 5:2, where one eats “normally” for 5 days a week, and on two non-consecutive days, eats only 500 calories
- Day off models and more; for example, “no eating on Sundays” that can, depending on your schedule, be anything from a 24-hour fast to 36 hours or more.
…and, most notably, what they each do metabolically.
Then, the real meat of the book is his program. Taking into account the benefits of each form of fasting, he weaves together a 9-week program to first ease us gently into intermittent fasting, and then enjoy the maximum benefits with minimum self-sabotage.
Which is the biggest stumbling-block for many trying intermittent fasting for the first time, so it’s a huge help that he takes care of this here.
He also includes meal plans and recipes; readers can use those or not; the fasting plan stands on its own two feet without them too.
Bottom line: if you’ve been thinking of trying intermittent fasting but have been put off by all the kinds or have had trouble sticking to it, this book may be just what you need.
Click here to check out Fast Burn on Amazon and see what you can achieve!
Share This Post
-
Will there soon be a cure for HIV?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, is a chronic health condition that can be fatal without treatment. People with HIV can live healthy lives by taking antiretroviral therapy (ART), but this medication must be taken daily in order to work, and treatment can be costly. Fortunately, researchers believe a cure is possible.
In July, a seventh person was reportedly cured of HIV following a 2015 stem cell transplant for acute myeloid leukemia. The patient stopped taking ART in 2018 and has remained in remission from HIV.
Read on to learn more about HIV, the promise of stem cell transplants, and what other potential cures are on the horizon.
What is HIV?
HIV infects and destroys the immune system’s cells, making people more susceptible to infections. If left untreated, HIV will severely impair the immune system and progress to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). People living with untreated AIDS typically die within three years.
People with HIV can take ART to help their immune systems recover and to reduce their viral load to an undetectable level, which slows the progression of the disease and prevents them passing the virus to others.
How can stem cell transplants cure HIV?
Several people have been cured of HIV after receiving stem cell transplants to treat leukemia or lymphoma. Stem cells are produced by the spongy tissue located in the center of some bones, and they can turn into new blood cells.
A mutation on the CCR5 gene prevents HIV from infecting new cells and creates resistance to the virus, which is why some HIV-positive people have received stem cells from donors carrying this mutation. (One person was reportedly cured of HIV after receiving stem cells without the CCR5 mutation, but further research is needed to understand how this occurred.)
Despite this promising news, experts warn that stem cell transplants can be fatal, so it’s unlikely this treatment will be available to treat people with HIV unless a stem cell transplant is needed to treat cancer. People with HIV are at an increased risk for blood cancers, such as Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which stem cell transplants can treat.
Additionally, finding compatible donors with the CCR5 mutation who share genetic heritage with patients of color can be challenging, as donors with the mutation are typically white.
What are other potential cures for HIV?
In some rare cases, people who started ART shortly after infection and later stopped treatment have maintained undetectable levels of HIV in their bodies. There have also been some people whose bodies have been able to maintain low viral loads without any ART at all.
Researchers are studying these cases in their search for a cure.
Other treatment options researchers are exploring include:
- Gene therapy: In addition to stem cell transplants, gene therapy for HIV involves removing genes from HIV particles in patients’ bodies to prevent the virus from infecting other cells.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment is typically used in cancer patients to teach their immune systems how to fight off cancer. Research has shown that giving some HIV patients antibodies that target the virus helps them reach undetectable levels of HIV without ART.
- mRNA technology: mRNA, a type of genetic material that helps produce proteins, has been used in vaccines to teach cells how to fight off viruses. Researchers are seeking a way to send mRNA to immune system cells that contain HIV.
When will there be a cure for HIV?
The United Nations and several countries have pledged to end HIV and AIDS by 2030, and a 2023 UNAIDS report affirmed that reaching this goal is possible. However, strategies to meet this goal include HIV prevention and improving access to existing treatment alongside the search for a cure, so we still don’t know when a cure might be available.
How can I find out if I have HIV?
You can get tested for HIV from your primary care provider or at your local health center. You can also purchase an at-home HIV test from a drugstore or online. If your at-home test result is positive, follow up with your health care provider to confirm the diagnosis and get treatment.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Green Roasting Tin – by Rukmini Iyer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: “do I really need a book to tell me to put some vegetables in a roasting tin and roast them?” and maybe not, but the book offers a lot more than that.
Indeed, the author notes “this book was slightly in danger of becoming the gratin and tart book, because I love both”, but don’t worry, most of the recipes are—as you might expect—very healthy.
As for formatting: the 75 recipes are divided first into vegan or vegetarian, and then into quick/medium/slow, in terms of how long they take.
However, even the “slow” recipes don’t actually take more effort, just, more time in the oven.
One of the greatest strengths of this book is that not only does it offer a wide selection of wholesome mains, but also, if you’re putting on a big spread, these can easily double up as high-class low-effort sides.
Bottom line: if you’d like to eat more vegetables in 2024 but want to make it delicious and with little effort, put this book on your Christmas list!
Click here to check out The Green Roasting Tin, and level-up yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why do some people’s hair and nails grow quicker than mine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Throughout recorded history, our hair and nails played an important role in signifying who we are and our social status. You could say, they separate the caveman from businessman.
It was no surprise then that many of us found a new level of appreciation for our hairdressers and nail artists during the COVID lockdowns. Even Taylor Swift reported she cut her own hair during lockdown.
So, what would happen if all this hair and nail grooming got too much for us and we decided to give it all up. Would our hair and nails just keep on growing?
The answer is yes. The hair on our head grows, on average, 1 centimeter per month, while our fingernails grow an average of just over 3 millimetres.
When left unchecked, our hair and nails can grow to impressive lengths. Aliia Nasyrova, known as the Ukrainian Rapunzel, holds the world record for the longest locks on a living woman, which measure an impressive 257.33 cm.
When it comes to record-breaking fingernails, Diana Armstrong from the United States holds that record at 1,306.58 cm.
Most of us, however, get regular haircuts and trim our nails – some with greater frequency than others. So why do some people’s hair and nails grow more quickly?
Jari Lobo/Pexels Remind me, what are they made out of?
Hair and nails are made mostly from keratin. Both grow from matrix cells below the skin and grow through different patterns of cell division.
Nails grow steadily from the matrix cells, which sit under the skin at the base of the nail. These cells divide, pushing the older cells forward. As they grow, the new cells slide along the nail bed – the flat area under the fingernail which looks pink because of its rich blood supply.
Nails, like hair, are made mostly of keratin. Scott Gruber/Unsplash A hair also starts growing from the matrix cells, eventually forming the visible part of the hair – the shaft. The hair shaft grows from a root that sits under the skin and is wrapped in a sac known as the hair follicle.
This sac has a nerve supply (which is why it hurts to pull out a hair), oil-producing glands that lubricate the hair and a tiny muscle that makes your hair stand up when it’s cold.
At the follicle’s base is the hair bulb, which contains the all-important hair papilla that supplies blood to the follicle.
Matrix cells near the papilla divide to produce new hair cells, which then harden and form the hair shaft. As the new hair cells are made, the hair is pushed up above the skin and the hair grows.
But the papilla also plays an integral part in regulating hair growth cycles, as it sends signals to the stem cells to move to the base of the follicle and form a hair matrix. Matrix cells then get signals to divide and start a new growth phase.
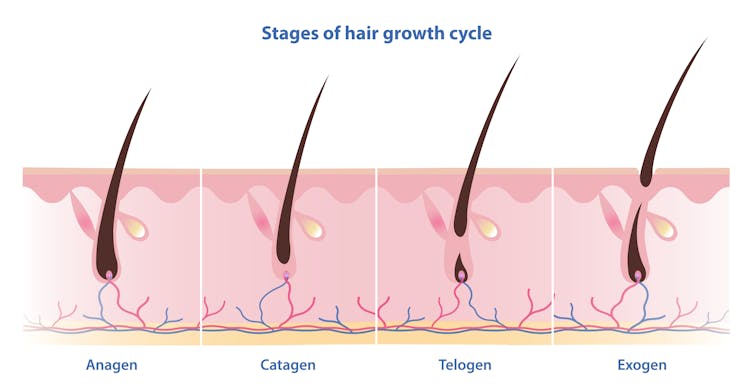
Unlike nails, our hair grows in cycles
Scientists have identified four phases of hair growth, the:
- anagen or growth phase, which lasts between two and eight years
- catagen or transition phase, when growth slows down, lasting around two weeks
- telogen or resting phase, when there is no growth at all. This usually lasts two to three months
- exogen or shedding phase, when the hair falls out and is replaced by the new hair growing from the same follicle. This starts the process all over again.
Hair follicles enter these phases at different times so we’re not left bald. Mosterpiece/Shutterstock Each follicle goes through this cycle 10–30 times in its lifespan.
If all of our hair follicles grew at the same rate and entered the same phases simultaneously, there would be times when we would all be bald. That doesn’t usually happen: at any given time, only one in ten hairs is in the resting phase.
While we lose about 100–150 hairs daily, the average person has 100,000 hairs on their head, so we barely notice this natural shedding.
So what affects the speed of growth?
Genetics is the most significant factor. While hair growth rates vary between individuals, they tend to be consistent among family members.
Nails are also influenced by genetics, as siblings, especially identical twins, tend to have similar nail growth rates.
Genetics have the biggest impact on growth speed. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels But there are also other influences.
Age makes a difference to hair and nail growth, even in healthy people. Younger people generally have faster growth rates because of the slowing metabolism and cell division that comes with ageing.
Hormonal changes can have an impact. Pregnancy often accelerates hair and nail growth rates, while menopause and high levels of the stress hormone cortisol can slow growth rates.
Nutrition also changes hair and nail strength and growth rate. While hair and nails are made mostly of keratin, they also contain water, fats and various minerals. As hair and nails keep growing, these minerals need to be replaced.
That’s why a balanced diet that includes sufficient nutrients to support your hair and nails is essential for maintaining their health.
Nutrition can impact hair and nail growth. Cottonbro Studio/Pexels Nutrient deficiencies may contribute to hair loss and nail breakage by disrupting their growth cycle or weakening their structure. Iron and zinc deficiencies, for example, have both been linked to hair loss and brittle nails.
This may explain why thick hair and strong, well-groomed nails have long been associated with perception of good health and high status.
However, not all perceptions are true.
No, hair and nails don’t grow after death
A persistent myth that may relate to the legends of vampires is that hair and nails continue to grow after we die.
In reality, they only appear to do so. As the body dehydrates after death, the skin shrinks, making hair and nails seem longer.
Morticians are well aware of this phenomenon and some inject tissue filler into the deceased’s fingertips to minimise this effect.
So, it seems that living or dead, there is no escape from the never-ending task of caring for our hair and nails.
Michelle Moscova, Adjunct Associate Professor, Anatomy, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Spectrum of Hope – by Dr. Gayatri Devi
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve written before about Dr. Devi’s work (See: “Alzheimer’s: The Bad News And The Good“) but she has plenty more to say than we could fit in an article.
The book is written for patients, family/carers, and clinicians—without getting deep into the science, which it is assumed clinicians will know. the general style of the book is pop-science, and it’s more about addressing the misconceptions around Alzheimer’s, rather than focusing on neurological features such as beta amyloid plaques and tau proteins and the like.
Dr. Devi explains a lot about the experience of Alzheimer’s—what to expect, or rather, what to know about in advance. Because, as she explains, there are a lot of different manifestations of Alzheimer’s that are all lumped under the same umbrella.
This means that a person could have negligible memory but perfect language and reasoning skills, or the other way around, or some other combination of symptoms showing up or not.
Which means that any plan for managing one’s Alzheimer’s needs to be adaptable and personalized, which is something Dr. Devi talks us through, too.
Bottom line: if you are a loved one has Alzheimer’s, or you just like to be prepared, this is a great book to prepare anybody for just that.
Click here to check out The Spectrum of Hope, and hold onto that hope!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: