Is thirst a good predictor of dehydration?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Water is essential for daily functioning and health, and we can only survive a few days without it. Yet we constantly lose water through sweat, urination and even evaporation when we breathe.
This is why we have evolved a way to regulate and maintain water in our bodies. Like other animals, our survival relies on a strong biological drive that tells us to find and drink water to balance fluid loss.
This is thirst – a sensation of dryness in the mouth signalling we need to have a drink. This basic physiological mechanism is controlled mainly by part of the brain’s “control centre”, called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus receives signals from various regions of the body and in return, releases hormones that act as a messenger to signal the thirst sensation.

What is dehydration?
Staying hydrated (having enough water in our bodies) is important for several reasons, including:
- regulating body temperature through sweat and respiration
- lubricating joints and eyes
- preventing infections
- digesting and absorbing nutrients
- flushing out waste (via the kidneys)
- preventing constipation
- brain function (including memory and concentration)
- mood and energy levels
- physical performance and recovery from exercise
- skin health.
Dehydration occurs when our body doesn’t have enough water. Even slight drops in fluid levels have noticeable consequences, such as headaches, feeling dizzy, lethargy and struggling to concentrate.
Chronic dehydration can pose more serious health risks, including urinary tract infections, constipation and kidney stones.
What does the evidence say?
Despite thirst being one of the most basic biological drivers for good hydration, science suggests our feelings of thirst and subsequent fluid intake don’t always correlate with hydration levels.
For example, a recent study explored the impact of thirst on fluid intake and hydration status. Participants attended a lab in the morning and then later in the afternoon to provide markers of hydration status (such as urine, blood samples and body weight). The relationship between levels of thirst in the morning and afternoon hydration status was negligible.
Further, thirst may be driven by environmental factors, such as access to water. For example, one study looked at whether ample access to water in a lab influenced how much people drank and how hydrated they were. The link between how thirsty they felt and how hydrated they were was weak, suggesting the availability of water influenced their fluid intake more than thirst.
Exercise can also change our thirst mechanism, though studies are limited at this stage.

Interestingly, research shows women experience thirst more strongly than men, regardless of hydration status. To understand gender differences in thirst, researchers infused men and women with fluids and then measured their thirst and how hydrated they were. They found women generally reported thirst at a lower level of fluid loss. Women have also been found to respond more to feeling thirsty by drinking more water.
Other ways to tell if you need to drink some water
While acknowledging some people will need to drink more or less, for many people, eight cups (or two litres) a day is a good amount of water to aim for.
But beyond thirst, there are many other ways to tell whether you might need to drink more water.
1. urine colour: pale yellow urine typically indicates good hydration, while darker, concentrated urine suggests dehydration
2. frequency of going to the toilet: urinating regularly (around four to six times a day) indicates good hydration. Infrequent urination can signal dehydration
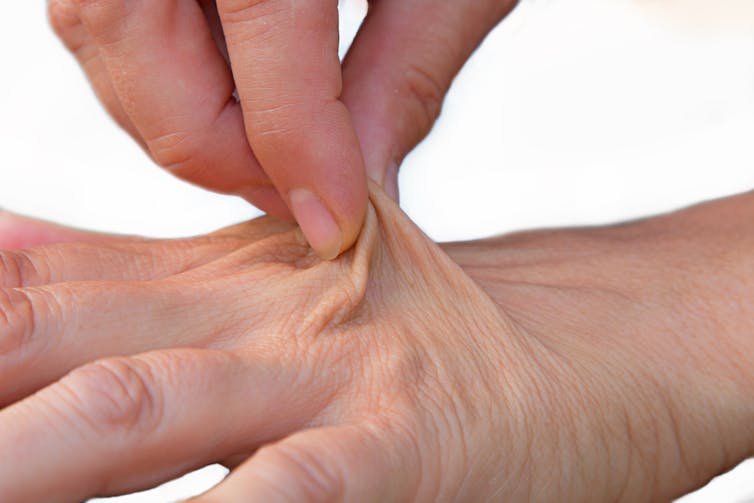
3. skin turgor test: gently pinching the skin (for example, on the back of the hand) and observing how quickly the skin returns to its normal position can help assess hydration. Slow return may indicate dehydration
4. mouth and lips: a dry mouth or cracked lips can be early signs of dehydration
5. headaches and fatigue: frequent headaches, dizziness, or unexplained fatigue can be signs of inadequate hydration
6. sweating: in physically active people, monitoring how much they sweat during activity can help estimate fluid loss and hydration needs. Higher levels of sweat may predispose a person to dehydration if they are unable to replace the fluid lost through water intake
These indicators, used together, provide a more comprehensive picture of hydration without solely depending on the sensation of thirst.
Of course, if you do feel thirsty, it’s still a good idea to drink some water.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Kiara Too, PhD candidate, School of Human Movement and Nutrition Sciences, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Super Gut – by Dr. William Davis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may be wondering: what sets this book apart from the other gut health books we’ve reviewed? For this one, mostly it’s depth.
This is the most scientifically dense book we’ve reviewed on gut health, so if you’re put off by that, this might not be one for you. However, you don’t need prior knowledge, as he does explain things as he goes. The advice in this book is not just the usual “gut health 101” stuff, either!
A particular strength of this book is that it looks at a wide variety of gut- and gut-related disorders, and ways certain readers may need to do different things than others, to address those problems on the path to good gut health.
The style, for all its hard science content, is quite sensationalist, and that may take some getting used to for non-Americans. However, it doesn’t affect the content!
Bottom line: if you just want simple basic advice, then probably best to skip this one. However, if you are sincerely serious about gut health (or just like reading this sort of thing because learning is satisfying), then this book is packed with relevant and detailed information.
Click here to check out Super Gut, and get to know and improve yours!
Share This Post
-
Why You’re Tired & How To Fix It
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Sadia Badiei. A dietician by academic and professional background, she’s nowadays hung up her lab coat for a chef’s jacket, and is best known for her “Pick Up Limes” brand. Today, we’ll be taking her advice on managing energy levels with what’s on our plates!
Quick note: our usual medical/legal disclaimer applies, and this article cannot diagnose you from afar, and thus neither can it make any certain prescription; this is for educational purposes, and aimed at being applicable to most of our readers.
There are many possible things that can cause chronic fatigue, and not all of them can be fixed by diet. Your doctor will have access to tests and such that we, being a humble health science publication, do not.
You may recognize her; we’ve featured her videos occasionally, mostly recently:
Pick Up A Zest For Life: 10 Lessons For A Healthy Mind & Body
But, what does she want us to know about living life with more energy?
It starts with balance
Badiei makes the case that we should strive for a nutritionally-balanced diet; that may not come as much of a revelation, but what does that look like for a vegan (Badiei advocates for plant-based eating)?
She recommends that our diet consist of:
- About 50% fruits and vegetables
- About 25% grains and starches
- About 25% proteins
- Modest amounts of fats
- A little of well-chosen dairy substitutions
- Finally, a few judicious supplements to top it off
That does add up to more than 100%, but 1) we did say “About n%” and 2) this is not a bad thing to note, actually, since Badiei advocates (as we do) for focussing more on what we add into our diet, rather than what we take out.
Breaking it down a little further, she recommends making sure to get “the foundational seven”, which is a little like “Dr. Greger’s Daily Dozen”, but in this case it’s counted on a per-food-type basis.
Thus, she recommends:
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Assorted other non-starchy vegetables (your choice what kind)
- Fruit, of any kinds (unlike Dr. Greger separating berries)
- Grains and starches (so for example, potatoes are lumped in with rice here, botanically very different, but often fulfil a similar culinary role)
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes
- Fortified dairy alternatives
For full details including how much of each, and “what counts”, etc, see:
Pick Up Limes | The Nourish Method
Time your carbs
Slow-release carbohydrates, those with the most fiber, are best most of the time, giving us more sustained fuel, keeping us energized for longer after meals—even if we would rather sleep:
She cites: Fiber and Saturated Fat Are Associated with Sleep Arousals and Slow Wave Sleep
Quick-release carbohydrates, those with what’s generally considered a less favorable carb:fiber ratio, are best if we’re going to eat nearer to bedtime. We know, eating before bed is often considered a bit of a no-no, but Badiei bids us indulge if we so desire, as the quicker-absorbed carbohydrates support tryptophan reaching our brain more efficiently, and thus promote sleep onset.
See also: Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
About that fat
We mentioned (or rather, Badiei’s citation mentioned) saturated fat. It is indeed linked with difficulty falling asleep, and/but omega-3 fatty acids, on the other hand, promote better sleep.
She cites: The relationship between sleep duration, sleep quality and dietary intake in adults
While you’re enjoying those nuts and seeds (for the omega-3 fatty acids), you might also note that several also star in Badiei’s list of plant-based foods that are rich in tryptophan, such as soy, cashews, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, beans, green vegetables, and mushrooms.
Micronutrients
Badiei’s focus here is on B-vitamins, iron, magnesium, selenium, and zinc. We imagine most of our readers here are taking steps to ensure to get a full daily coverage of vitamins and minerals anyway, but you might want to read what she has to say about iron on a plant-based diet, because the numbers may be different than you think.
The reason for this is that while animal products contain mostly heme iron, which is easier to absorb but associated with a risk increase in some diseases, plant-based foods usually* contain only non-heme iron, which is healthier but not as bioavailable, so if eating only plants, we need more of it:
Pick Up Limes | Iron on a Plant-Based Diet
*If you eat a carnivorous plant, guess what, it’ll have heme iron in it, tangling that food web.
“What if I know I have chronic fatigue for non-dietary reasons?”
Well, that sucks, and we’re not going to pretend the above will magically fix it. However, there are still things that can at least relatively improve your experience:
Eat To Beat Chronic Fatigue! Yes, Even When Fatigued Chronically
(it’s a good guide to being able to consistently eat healthily when your energy levels are consistently at minimal, meaning that a lot of common advice becomes unusable)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Why You Can’t Just “Get Over” Trauma
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Time does not, in fact, heal all wounds. Sometimes they even compound themselves over time. Dr. Tracey Marks explains the damage that trauma does—the physiological presentation of “the axe forgets but the tree remembers”—and how to heal from that actual damage.
The science of healing
Trauma affects the mind and body (largely because the brain is, of course, both—and affects pretty much everything else), which can ripple out into all areas of life.
On the physical level, brain areas affected by trauma include:
- Amygdalae: becomes hyperactive, keeping a person in a heightened state of vigilance.
- Hippocampi: can shrink, causing fragmented or missing memories.
- Prefrontal cortex: reduces in activity, impairing decision-making and emotional regulation.
Trauma also activates the body’s fight or flight response, releasing stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These are great things to have a pinch, but having them elevated all the time is equivalent to only ever driving your car at top speed—the only question becomes whether you’ll crash and burn before you break down.
However, there is hope! Neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to rewire itself) can make trauma recovery possible through various interventions.
Evidence-based therapies for trauma include:
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): this can help reprocess traumatic memories and reduce emotional intensity.
- Trauma-focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): this can help change unhelpful thought patterns and includes exposure therapy.
- Somatic therapies: these focus on the body and nervous system to release stored tension.
In this latter category, embodiment is key to trauma recovery—this may sound “wishy-washy”, but the evidence shows that reconnecting with the body does help manage emotional stress responses. Mind-body practices like mindfulness, yoga, and breathwork help cultivate embodiment and reduce trauma-related stress.
In short: you can’t just “get over” it, but with the right support and interventions, it’s possible to rewire the brain and body toward resilience and healing.
For more on all of this from Dr. Marks, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- PTSD, But, Well…. Complex.
- Undoing The Damage Of Life’s Hard Knocks
- A Surprisingly Powerful Tool: Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Tuna vs Catfish – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tuna to catfish, we picked the tuna.
Why?
Today in “that which is more expensive and/or harder to get is not necessarily healthier”…
Looking at their macros, tuna has more protein and less fat (and overall, less saturated fat, and also less cholesterol).
In the category of vitamins, both are good but tuna distinguishes itself: tuna has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, and D, while catfish has more of vitamins B5, B9, B12, E, and K. They are both approximately equal in choline, and as an extra note in tuna’s favor (already winning 6:5), tuna is a very good source of vitamin D, while catfish barely contains any. All in all: a moderate, but convincing, win for tuna.
When it comes to minerals, things are clearer still: tuna has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while catfish has more calcium, manganese, and zinc. Oh, and catfish is also higher in one other mineral: sodium, which most people in industrialized countries need less of, on average. So, a 6:3 win for tuna, before we even take into account the sodium content (which makes the win for tuna even stronger).
In short: tuna wins the day in every category!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught (It Makes Quite A Difference)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The 5 Resets – by Dr. Aditi Nerurkar
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What this book isn’t: an advice to go on a relaxing meditation retreat, or something like that.
What this is: a science-based guide to what actually works.
There’s no need to be mysterious, so we’ll mention that the titular “5 resets” are:
- What matters most
- Quiet in a noisy world
- Leveraging the brain-body connection
- Coming up for air (regaining perspective)
- Bringing your best self forward
All of these are things we can easily lose sight of in the hustle and bustle of daily life, so having a system for keeping them on track can make a huge difference!
The style is personable and accessible, while providing a lot of strongly science-backed tips and tricks along the way.
Bottom line: if life gets away from you a little too often for comfort, this book can help you keep on top of things with a lot less stress.
Click here to check out “The 5 Resets”, and take control with conscious calm!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Just Be Well – by Dr. Thomas Sult
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, what this is not: a “think yourself well” book. It’s not about just deciding to be well.
Rather, it’s about ensuring the foundations of wellness, from which the rest of good health can spring, and notably, an absence of chronic illness. In essence: enjoying chronic good health.
The prescription here is functional medicine, which stands on the shoulders of lifestyle medicine. This latter is thus briefly covered and the basics presented, but most of the book is about identifying the root causes of disease and eliminating them one by one, by taking into account the functions of the body’s processes, both in terms of pathogenesis (and thus, seeking to undermine that) and in terms of correct functioning (i.e., good health).
While the main focus of the book is on health rather than disease, he does cover a number of very common chronic illnesses, and how even in those cases where they cannot yet be outright cured, there’s a lot more that can be done for them than “take two of these and call your insurance company in the morning”, when the goal is less about management of symptoms (though that is also covered) and more about undercutting causes, and ensuring that even if one thing goes wrong, it doesn’t bring the entire rest of the system down with it (something that often happens without functional medicine).
The style is clear, simple, and written for the layperson without unduly dumbing things down.
Bottom line: if you would like glowingly good health regardless of any potential setbacks, this book can help your body do what it needs to for you.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: