In Crisis, She Went to an Illinois Facility. Two Years Later, She Still Isn’t Able to Leave.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Series: Culture of Cruelty:Inside Illinois’ Mental Health System
State-run facilities in Illinois are supposed to care for people with mental and developmental disabilities. But patients have been subjected to abuse, neglect and staff misconduct for decades, despite calls for change.
Kaleigh Rogers was in crisis when she checked into a state-run institution on Illinois’ northern border two years ago. Rogers, who has cerebral palsy, had a mental health breakdown during the pandemic and was acting aggressively toward herself and others.
Before COVID-19, she had been living in a small group home; she had been taking college classes online and enjoyed going out with friends, volunteering and going to church. But when her aggression escalated, she needed more medical help than her community setting could provide.
With few viable options for intervention, she moved into Kiley Developmental Center in Waukegan, a much larger facility. There, she says she has fewer freedoms and almost nothing to do, and was placed in a unit with six other residents, all of whom are unable to speak. Although the stay was meant to be short term, she’s been there for two years.
The predicament facing Rogers and others like her is proof, advocates say, that the state is failing to live up to the promise it made in a 13-year-old federal consent decree to serve people in the community.
Rogers, 26, said she has lost so much at Kiley: her privacy, her autonomy and her purpose. During dark times, she cries on the phone to her mom, who has reduced the frequency of her visits because it is so upsetting for Rogers when her mom has to leave.
The 220-bed developmental center about an hour north of Chicago is one of seven in the state that have been plagued by allegations of abuse and other staff misconduct. The facilities have been the subject of a monthslong investigation by Capitol News Illinois and ProPublica about the state’s failures to correct poor conditions for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. The news organizations uncovered instances of staff who had beaten, choked, thrown, dragged and humiliated residents inside the state-run facilities.
Advocates hoped the state would become less reliant on large institutions like these when they filed a lawsuit in 2005, alleging that Illinois’ failure to adequately fund community living options ended up segregating people with intellectual and developmental disabilities from society by forcing them to live in institutions. The suit claimed Illinois was in direct violation of a 1999 U.S. Supreme Court decision in another case, which found that states had to serve people in the most integrated setting of their choosing.
Negotiations resulted in a consent decree, a court-supervised improvement plan. The state agreed to find and fund community placements and services for individuals covered by the consent decree, thousands of adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities across Illinois who have put their names on waiting lists to receive them.
Now, the state has asked a judge to consider ending the consent decree, citing significant increases in the number of people receiving community-based services. In a court filing in December, Illinois argued that while its system is “not and never will be perfect,” it is “much more than legally adequate.”
But advocates say the consent decree should not be considered fulfilled as long as people with disabilities continue to live without the services and choices that the state promised.
Across the country, states have significantly downsized or closed their large-scale institutions for people with developmental and intellectual disabilities in favor of smaller, more integrated and more homelike settings.
But in Illinois, a national outlier, such efforts have foundered. Efforts to close state-operated developmental centers have been met with strong opposition from labor unions, the communities where the centers are located, local politicians and some parents.
U.S. District Judge Sharon Johnson Coleman in Chicago is scheduled in late summer to decide whether the state has made enough progress in building up community supports to end the court’s oversight.
For some individuals like Rogers, who are in crisis or have higher medical or behavioral challenges, the state itself acknowledges that it has struggled to serve them in community settings. Rogers said she’d like to send this message on behalf of those in state-operated developmental centers: “Please, please get us out once and for all.”
“Living Inside a Box”
Without a robust system of community-based resources and living arrangements to intervene during a crisis, state-operated developmental centers become a last resort for people with disabilities. But under the consent decree agreement, the state, Equip for Equality argues, is expected to offer sufficient alternative crisis supports to keep people who want them out of these institutions.
In a written response to questions, Rachel Otwell, a spokesperson for the Illinois Department of Human Services, said the state has sought to expand the menu of services it offers people experiencing a crisis, in an effort to keep them from going into institutions. But Andrea Rizor, a lawyer with Equip for Equality, said, “They just don’t have enough to meet the demand.”
For example, the state offers stabilization homes where people can live for 90 days while they receive more intensive support from staff serving the homes, including medication reviews and behavioral interventions. But there are only 32 placements available — only four of them for women — and the beds are always full, Rizor said.
Too many people, she said, enter a state-run institution for short-term treatment and end up stuck there for years for various reasons, including shortcomings with the state’s discharge planning and concerns from providers who may assume those residents to be disruptive or difficult to serve without adequate resources.
That’s what happened to Rogers. Interruptions to her routine and isolation during the pandemic sent her anxiety and aggressive behaviors into overdrive. The staff at her community group home in Machesney Park, unsure of what to do when she acted out, had called the police on several occasions.
Doctors also tried to intervene, but the cocktail of medications she was prescribed turned her into a “zombie,” Rogers said. Stacey Rogers, her mom and legal guardian, said she didn’t know where else to turn for help. Kiley, she said, “was pretty much the last resort for us,” but she never intended for her daughter to be there for this long. She’s helped her daughter apply to dozens of group homes over the past year. A few put her on waitlists; most have turned her down.
“Right now, all she’s doing is living inside a box,” Stacey Rogers said.
Although Rogers gave the news organizations permission to ask about her situation, IDHS declined to comment, citing privacy restrictions. In general, the IDHS spokesperson said that timelines for leaving institutions are “specific to each individual” and their unique preferences, such as where they want to live and speciality services they may require in a group home.
Equip for Equality points to people like Rogers to argue that the consent decree has not been sufficiently fulfilled. She’s one of several hundred in that predicament, the organization said.
“If the state doesn’t have capacity to serve folks in the community, then the time is not right to terminate this consent decree, which requires community capacity,” Rizor said.
Equip for Equality has said that ongoing safety issues in these facilities make it even more important that people covered by the consent decree not be placed in state-run institutions. In an October court brief, citing the news organizations’ reporting, Equip for Equality said that individuals with disabilities who were transferred from community to institutional care in crisis have “died, been raped, and been physically and mentally abused.”
Over the summer, an independent court monitor assigned to provide expert opinions in the consent decree, in a memo to the court, asked a judge to bar the state from admitting those individuals into its institutions.
In its December court filing, the state acknowledged that there are some safety concerns inside its state-run centers, “which the state is diligently working on,” as well as conditions inside privately operated facilities and group homes “that need to be addressed.” But it also argued that conditions inside its facilities are outside the scope of the consent decree. The lawsuit and consent decree specifically aimed to help people who wanted to move out of large private institutions, but plaintiffs’ attorneys argue that the consent decree prohibits the state from using state-run institutions as backup crisis centers.
In arguing to end the consent decree, the state pointed to significant increases in the number of people served since it went into effect. There were about 13,500 people receiving home- and community-based services in 2011 compared with more than 23,000 in 2023, it told the court.
The state also said it has significantly increased funding that is earmarked to pay front-line direct support professionals who assist individuals with daily living needs in the community, such as eating and grooming.
In a statement to reporters, the human services department called these and other improvements to the system “extraordinary.”
Lawyers for the state argued that those improvements are enough to end court oversight.
“The systemic barriers that were in place in 2011 no longer exist,” the state’s court filing said.
Among those who were able to find homes in the community is Stanley Ligas, the lead plaintiff in the lawsuit that led to the consent decree. When it was filed in 2005, he was living in a roughly 100-bed private facility but wanted to move into a community home closer to his sister. The state refused to fund his move.
Today, the 56-year-old lives in Oswego with three roommates in a house they rent. All of them receive services to help their daily living needs through a nonprofit, and Ligas has held jobs in the community: He previously worked in a bowling alley and is now paid to make public appearances to advocate for others with disabilities. He lives near his sister, says he goes on family beach vacations and enjoys watching professional wrestling with friends. During an interview with reporters, Ligas hugged his caregiver and said he’s “very happy” and hopes others can receive the same opportunities he’s been given.
While much of that progress has come only in recent years, under Gov. JB Pritzker’s administration, it has proven to be vulnerable to political and economic changes. After a prolonged budget stalemate, the court in 2017 found Illinois out of compliance with the Ligas consent decree.
At the time, late and insufficient payments from the state had resulted in a staffing crisis inside community group homes, leading to escalating claims of abuse and neglect and failures to provide routine services that residents relied on, such as help getting to work, social engagements and medical appointments in the community. Advocates worry about what could happen under a different administration, or this one, if Illinois’ finances continue to decline as projected.
“I acknowledge the commitments that this administration has made. However, because we had so far to come, we still have far to go,” said Kathy Carmody, chief executive of The Institute on Public Policy for People with Disabilities, which represents providers.
While the wait for services is significantly shorter than it was when the consent decree went into effect in 2011, there are still more than 5,000 adults who have told the state they want community services but have yet to receive them, most of them in a family home. Most people spend about five years waiting to get the services they request. And Illinois continues to rank near the bottom in terms of the investment it makes in community-based services, according to a University of Kansas analysis of states’ spending on services for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities.
Advocates who believe the consent decree has not been fulfilled contend that Illinois’ continued reliance on congregate settings has tied up funds that could go into building up more community living options. Each year, Illinois spends about $347,000 per person to care for those in state-run institutions compared with roughly $91,000 per person spent to support those living in the community.
For Rogers, the days inside Kiley are long, tedious and sometimes chaotic. It can be stressful, but Rogers told reporters that she uses soothing self-talk to calm herself when she feels sad or anxious.
“I tell myself: ‘You are doing good. You are doing great. You have people outside of here that care about you and cherish you.’”
This article is republished from ProPublica under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Drug companies pay doctors over A$11 million a year for travel and education. Here’s which specialties received the most
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Drug companies are paying Australian doctors millions of dollars a year to fly to overseas conferences and meetings, give talks to other doctors, and to serve on advisory boards, our research shows.
Our team analysed reports from major drug companies, in the first comprehensive analysis of its kind. We found drug companies paid more than A$33 million to doctors in the three years from late 2019 to late 2022 for these consultancies and expenses.
We know this underestimates how much drug companies pay doctors as it leaves out the most common gift – food and drink – which drug companies in Australia do not declare.
Due to COVID restrictions, the timescale we looked at included periods where doctors were likely to be travelling less and attending fewer in-person medical conferences. So we suspect current levels of drug company funding to be even higher, especially for travel.
Monster Ztudio/Shutterstock What we did and what we found
Since 2019, Medicines Australia, the trade association of the brand-name pharmaceutical industry, has published a centralised database of payments made to individual health professionals. This is the first comprehensive analysis of this database.
We downloaded the data and matched doctors’ names with listings with the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (Ahpra). We then looked at how many doctors per medical specialty received industry payments and how much companies paid to each specialty.
We found more than two-thirds of rheumatologists received industry payments. Rheumatologists often prescribe expensive new biologic drugs that suppress the immune system. These drugs are responsible for a substantial proportion of drug costs on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS).
The specialists who received the most funding as a group were cancer doctors (oncology/haematology specialists). They received over $6 million in payments.
This is unsurprising given recently approved, expensive new cancer drugs. Some of these drugs are wonderful treatment advances; others offer minimal improvement in survival or quality of life.
A 2023 study found doctors receiving industry payments were more likely to prescribe cancer treatments of low clinical value.
Our analysis found some doctors with many small payments of a few hundred dollars. There were also instances of large individual payments.
Why does all this matter?
Doctors usually believe drug company promotion does not affect them. But research tells a different story. Industry payments can affect both doctors’ own prescribing decisions and those of their colleagues.
A US study of meals provided to doctors – on average costing less than US$20 – found the more meals a doctor received, the more of the promoted drug they prescribed.
Pizza anyone? Even providing a cheap meal can influence prescribing. El Nariz/Shutterstock Another study found the more meals a doctor received from manufacturers of opioids (a class of strong painkillers), the more opioids they prescribed. Overprescribing played a key role in the opioid crisis in North America.
Overall, a substantial body of research shows industry funding affects prescribing, including for drugs that are not a first choice because of poor effectiveness, safety or cost-effectiveness.
Then there are doctors who act as “key opinion leaders” for companies. These include paid consultants who give talks to other doctors. An ex-industry employee who recruited doctors for such roles said:
Key opinion leaders were salespeople for us, and we would routinely measure the return on our investment, by tracking prescriptions before and after their presentations […] If that speaker didn’t make the impact the company was looking for, then you wouldn’t invite them back.
We know about payments to US doctors
The best available evidence on the effects of pharmaceutical industry funding on prescribing comes from the US government-run program called Open Payments.
Since 2013, all drug and device companies must report all payments over US$10 in value in any single year. Payment reports are linked to the promoted products, which allows researchers to compare doctors’ payments with their prescribing patterns.
Analysis of this data, which involves hundreds of thousands of doctors, has indisputably shown promotional payments affect prescribing.
Medical students need to know about this. LightField Studios/Shutterstock US research also shows that doctors who had studied at medical schools that banned students receiving payments and gifts from drug companies were less likely to prescribe newer and more expensive drugs with limited evidence of benefit over existing drugs.
In general, Australian medical faculties have weak or no restrictions on medical students seeing pharmaceutical sales representatives, receiving gifts, or attending industry-sponsored events during their clinical training. They also have no restrictions on academic staff holding consultancies with manufacturers whose products they feature in their teaching.
So a first step to prevent undue pharmaceutical industry influence on prescribing decisions is to shelter medical students from this influence by having stronger conflict-of-interest policies, such as those mentioned above.
A second is better guidance for individual doctors from professional organisations and regulators on the types of funding that is and is not acceptable. We believe no doctor actively involved in patient care should accept payments from a drug company for talks, international travel or consultancies.
Third, if Medicines Australia is serious about transparency, it should require companies to list all payments – including those for food and drink – and to link health professionals’ names to their Ahpra registration numbers. This is similar to the reporting standard pharmaceutical companies follow in the US and would allow a more complete and clearer picture of what’s happening in Australia.
Patients trust doctors to choose the best available treatments to meet their health needs, based on scientific evidence of safety and effectiveness. They don’t expect marketing to influence that choice.
Barbara Mintzes, Professor, School of Pharmacy and Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney and Malcolm Forbes, Consultant psychiatrist and PhD candidate, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
We’re aware that very many of our readers are women, who do not have a prostate.
However, dear reader: if you do have one, and/or love someone who has one, this is a good thing to know about.
The prostate gland is a (hopefully) walnut-sized gland (it actually looks a bit like a walnut too), that usually sits just under the bladder.
See also: How to Locate Your Prostate*
*The scale is not great in these diagrams, but they’ll get the job done. Besides, everyone is different on the inside, anyway. Not in a “special unique snowflake” way, but in a “you’d be surprised how much people’s insides move around” way.
Fun fact: did you ever feel like your intestines are squirming? That’s because they are.
You can’t feel it most of the time due to the paucity of that kind of nervous sensation down there, but the peristaltic motion that they use to move food along them on the inside, also causes them push against the rest of your guts, on the outside of them. This is the exact same way that many snakes move about.
If someone has to perform an operation in that region, sometimes it will be necessary to hang the intestines on a special rack, to keep them in one place for the surgery.
What can go wrong?
There are two very common things that can go wrong with the prostate:
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH), otherwise known as an enlarged prostate
- Prostate cancer
For most men, the prostate gland continues to grow with age, which is how the former comes about so frequently.
For everyone, due to the nature of the mathematics involved in cellular mutation and replication, we will eventually get cancer if something else doesn’t kill us first.
- Prostate cancer affects 12% of men overall, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing each year thereafter.
- Prostate cancer can look like BPH in the early stages (and/or, an enlarged prostate can turn cancerous) so it’s important to not shrug off the symptoms of BPH.
How can BPH be avoided/managed?
There are prescription medications that can help reduce the size of the prostate, including testosterone blockers (such as spironolactone and bicalutamide) and 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride. Each have their pros and cons:
- Testosterone-blockers are the heavy-hitters, and work very well… but have more potential adverse side effects (your body is used to running on testosterone, after all)
- 5α-reductase inhibitors aren’t as powerful, but they block the conversion of free testosterone to dihydrogen testosterone (DHT), and it’s primarily DHT that causes the problems. By blocking the conversion of T to DHT, you may actually end up with higher serum testosterone levels, but fewer ill-effects. Exact results will vary depending on your personal physiology, and what else you are taking, though.
There are also supplements that can help, including saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil. Here’s a good paper that covers both:
We have recommended saw palmetto before for a variety of uses, including against BPH:
Too much or too little testosterone? This one supplement may fix that
You might want to avoid certain medications that can worsen BPH symptoms (but not actually the size of the prostate itself). They include:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (most modern antidepressants aren’t this kind; ask your pharmacist/doctor if unsure)
You also might want to reduce/skip:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
In all the above cases, it’s because of how they affect the bladder, not the prostate, but given their neighborliness, each thing affects the other.
What if it’s cancer? How do I know and what do I do?
The creator of the Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test has since decried it as “a profit-driven health disaster” that is “no better than a coin toss”, but it remains the first go-to of many medical services.
However, there’s a newer, much more accurate test, called the Prostate Screening Episwitch (PSE) test, which is 94% accurate, so you might consider asking your healthcare provider whether that’s an option:
The new prostate cancer blood test with 94 per cent accuracy
As for where to go from there, we’re out of space for today, but we previously reviewed a very good book about this, Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer, and we highly recommend it—it could easily be a literal lifesaver.
Share This Post
-
Not quite an introvert or an extrovert? Maybe you’re an ambivert
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
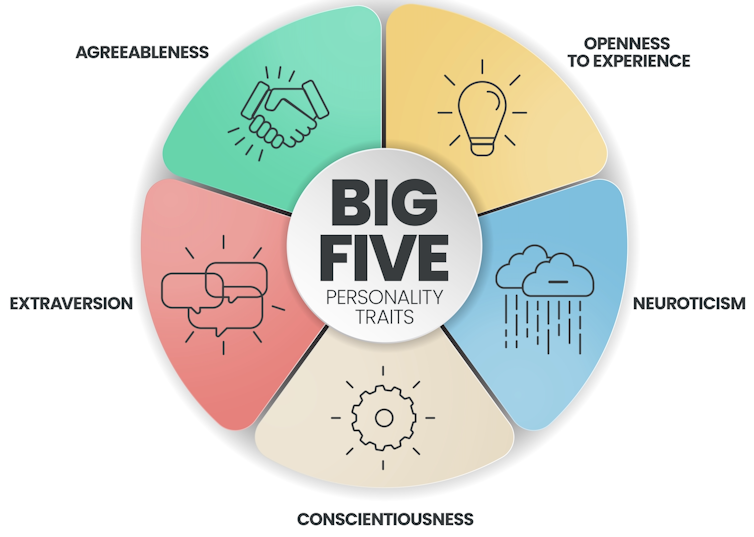
Our personalities are generally thought to consist of five primary factors: openness to experience, conscientiousness, extroversion, agreeableness and neuroticism, with each of us ranking low to high for each.
Extroversion is one of the Big Five personality traits. Big 5 personality traits graphic Those who rank high in extroversion, known as extroverts, typically focus on their external world. They tend to be more optimistic, recharge by socialising and enjoy social interaction.
On the other end of the spectrum, introverts are more likely to be quiet, deep thinkers, who recharge by being alone and learn by observing (but aren’t necessarily shy).
But what if you’re neither an introvert or extrovert – or you’re a bit of both? Another category might fit better: ambiverts. They’re the middle of the spectrum and are also called “social introverts”.
What exactly is an ambivert?
The term ambivert emerged in 1923. While it was not initially embraced as part of the introvert-extrovert spectrum, more recent research suggests ambiverts are a distinct category.
Ambiverts exhibit traits of both extroverts and introverts, adapting their behaviour based on the situation. It may be that they socialise well but need solitude and rest to recharge, and they intuitively know when to do this.
Ambiverts seems to have the following characteristics:
- good communication skills, as a listener and speaker
- ability to be a peacemaker if conflict occurs
- leadership and negotiation skills, especially in teams
- compassion and understanding for others.
Some research suggests ambiverts make up a significant portion of the population, with about two-thirds of people falling into this category.
What makes someone an ambivert?
Personality is thought to be 50% inherited, with the remaining being influenced by environmental factors and individual experiences.
Emerging research has found physical locations of genes on chromosomes closely aligned with extroversion-introversion traits.
So, chances are, if you are a blend of the two styles as an ambivert, one of your parents may be too.
What do ambiverts tend to be good at?
Ambiverts are flexible with talking and also listening. Cotton Bro Studios/Pexels One area of research focus in recent decades has been personality type and job satisfaction. One study examined 340 introverts, extroverts and ambiverts in sales careers.
It has always been thought extroverts were more successful with sales. However, the author found ambiverts were more influential and successful.
They may have a sales advantage because of their ability to read the situation and modify their behaviour if they notice a customer is not interested, as they’re able to reflect and adapt.
Ambiverts stress less than introverts
Generally, people lower in extroversion have higher stress levels. One study found introverts experience more stress than both ambiverts and extroverts.
It may be that highly sensitive or introverted individuals are more susceptible to worry and stress due to being more perfectionistic.
Ambiverts are adept at knowing when to be outgoing and when to be reflective, showcasing a high degree of situational awareness. This may contribute to their overall wellbeing because of how they handle stress.
What do ambiverts tend to struggle with?
Ambiverts may overextend themselves attempting to conform or fit in with many social settings. This is termed “overadaptation” and may force ambiverts to feel uncomfortable and strained, ultimately resulting in stress or burnout.
Ambiverts tend to handle stress well but feel strained when overadapting. Cottonbro Studios/Pexels But personality traits aren’t fixed
Regardless of where you sit on the scale of introversion through to extroversion, the reality is it may not be fixed. Different situations may be more comfortable for introverts to be social, and extroverts may be content with quieter moments.
And there are also four other key personality traits – openness to experience, conscientiousness, agreeableness and neuroticism – which we all possess in varying levels, and are expressed in different ways, alongside our levels of extroversion.
There is also evidence our personality traits can change throughout our life spans are indeed open to change.
Peta Stapleton, Associate Professor in Psychology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Longans vs Lychees – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing longans to lychees, we picked the lychees.
Why?
These two fruits are more closely related than they look from the outside, both being members of the soapberry family. However, there are some differences:
In terms of macros, longans have more protein while lychees have more carbs, and they are equal on fiber, giving longans the lower glycemic index. They’re both good, but longans nominally take the win on this one.
When it comes to vitamins, longans have more of vitamins B1, B2, and C, while lychees have more of vitamins B3, B6, B9, E, K, and choline, making for a respectable win for lychees in this category.
In the category of minerals, longans have more copper and potassium, while lychees have more calcium, iron, manganese phosphorus, and zinc. Thus, a win for lychees here too.
It’s worth looking at polyphenols too—lychees have around 10x more, which is notable.
Adding up the categories makes for an overall win for lychees, but by all means enjoy either or both! Diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods ← longans and lychees both make the list
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Your Mucus Says About Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s not a sexy topic (unless perhaps you have a fetish), but it is a useful topic to know about.
So, let’s get down to business with this much-maligned bodily fluid:
What is mucus? And why?
Sometimes, it can seem that mucus only exists to be an inconvenience, and to convey disease.
And… Actually, that’s mostly true.
While some kinds of mucus have other jobs beyond the scope of today’s article (did you know semen is mostly mucus? If not, now you do), the primary job of most of our mucus is to stop things (especially pathogens) going where they shouldn’t.
So, in essence, it really does exist to be an inconvenience—to pathogens. And to convey those pathogens to where they can be disposed of safely, either outside of the body, or to be an easy meal (what with being stuck in mucus, and thus at least moderately immobilized) for our various active immune cells. To make matters worse for the pathogens, there are (usually) enzymes in our mucus that have antimicrobial properties, too.
Some of mucus’s protective role can be in other ways too, such as by lining our stomach. You know, the stomach that contains the acid that can dissolve meat, despite us also being made of meat.
The slimiest rainbow
Ok, maybe not the slimiest rainbow—there’s probably a YouTube slime channel producing more colors. But, our noses are capable of dispensing astonishing quantities of mucus sometimes, and the color can vary widely, so here’s what we can know from that:
Clear
This is as it should be, in good health. If you’re getting lots of it but it’s clear, then it’s usually allergies, but watch out in case it changes color, heralding an infection. This “clear is how it looks when in ideal health”, by the way, is why when someone is sobbing in abject grief, any mucus that shows up to add to that picture will generally be clear.
White
As above, but now inflamed. Inflammation is usually something we don’t want, but in the case of a threat from a pathogen, we actually do want acute inflammation like this—the body is assembling its armies, of which, the most visible (when they appear in mass) are white blood cells. Because of their abundant presence at this stage, the mucus will also become thicker.
Yellow
As above, but the battle is now truly underway, and the yellow color comes from dead white blood cells. This does not, however, mean the battle is necessarily going badly—the body treats its white blood cells as very disposable fighters, and their deaths in large numbers are expected and normal when doing battle.
Green
As above, but neutrophils (a specific kind of white blood cell) have joined the party. They release an enzyme that colors the mucus green—and kills a lot of pathogens. Popular lore says that green mucus means a bacterial infection, but it’s not always so; these can be deployed against viruses too, depending on various factors beyond the scope of this article (but generally pertaining to severity). In any case, this too does not mean the battle is necessarily going badly, but it does express that your body is taking it very seriously—and you should, too.
Red
Nothing to do with infections, usually—it’s just a little blood (the red kind, this time). Usually it got into the mucus because the mucus membrane got damaged, usually due to some kind of physical trauma (e.g. very vigorous nose-blowing, poking things up the nose, etc) or sometimes if the air is very dry (then the mucus itself can dry out, and become stabby inside the nose; when more mucus is produced, it gets infused with blood from the injury).
Pink
As above, but combined with the “white” stage of infection response.
Orange
As above, but combined with the “yellow” stage of infection response.
Brown
As above, but the blood has oxidized—or, as a completely alterative possibility, it could mean you have been breathing a lot of pollutants. Smoke of various kinds (from fires, from smoking, etc) can cause this.
Black
There are various possible explanations here and all of them are bad. Get thee to a doctor. Superficial examples include:
- Fungal infection (you thought toxic black mold was bad when it was on the wall of the house, wait until it’s on the walls of your respiratory system)
- Blood, in abundance, oxidized (which begs the question of what caused that, but certainly: something wrong is not right)
- Pollutants again, but this time at absurd levels of exposure
That last one might sound very transient and self-correcting, but it’s not, and it comes with many increased short- and long-term health risks.
Want to know more?
Knowledge is power, so read up, and stay well:
- Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
- The Cold Truth About Respiratory Infections
- Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lyme Disease At-A-Glance
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Good info as always…was wondering if you have any recommendations for fighting Lyme disease naturally along wDr advice? Dr’s aren’t real keen on alternatives so always interested. Thanks❞
That depends on whether we’re looking at prevention or cure!
Prevention:
- Try not to get bitten by Lyme-disease-carrying ticks. Boots and long socks are your friends. As are long-gauntletted gloves for gardening.
- If you are in a high-risk area and/or engage in high-risk activities, check your body daily.
- This is because it usually takes 36–48 hours of being attached for a tick to cause an infection
- Obviously best if you can get a partner or close friend to help you with this, unless you have mastered some advanced pretzel positions of yoga.
- Contrary to many folk remedies, the safest way to remove a tick is with tweezers (carefully!).
- If you find and remove a tick, or otherwise suspect you have developed symptoms, go to your doctor immediately (not next week; today; time really counts for this).
Cure:
- No. Sorry. Regretfully, antibiotics are the only known effective treatment.
However! As with almost any kind of recovery, getting good rest, including good quality sleep, will hasten things. Also sensible is reducing stress if possible, and anything that could worsen inflammation.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: