How to Boost Your Metabolism When Over 50
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Dawn Andalon, a physiotherapist, explains the role of certain kinds of exercise in metabolism; here’s what to keep in mind:
Work with your body
Many people make the mistake of thinking that it is a somehow a battle of wills, and they must simply will their body to pick up the pace. That’s not how it works though, and while that can occasionally get short-term results, at best it’ll quickly result in exhaustion. So, instead:
- Strength training: engage in weight training 2–3 times per week; build muscle and combat bone loss too. Proper guidance from trainers familiar with older adults is recommended. Pilates (Dr. Andalon is a Pilates instructor) can also complement strength training by enhancing core stability and preventing injuries. The “building muscle” thing is important for metabolism, because muscle increases the body’s metabolic base rate.
- Protein intake: Dr. Andalon advises to consume 25–30 grams of lean protein per meal to support muscle growth and repair (again, important for the same reason as mentioned above re exercise). Dr. Andalon’s recommendation is more protein per meal than is usually advised, as it is generally held that the body cannot use more than about 20g at once.
- Sleep quality: prioritize good quality sleep, by practising good sleep hygiene, and also addressing any potential hormonal imbalances affecting sleep. If you do not get good quality sleep, your metabolism will get sluggish in an effort to encourage you to sleep more.
- Exercise to manage stress: regular walking (such as the popular 10,000 steps daily) helps manage stress and improve metabolism. Zone two cardio (low-intensity movement) also supports joint health, blood flow, and recovery—but the main issue about stress here is that if your body experiences unmanaged stress, it will try to save you from whatever is stressing you by reducing your metabolic base rate so that you can out-survive the bad thing. Which is helpful if the stressful thing is that the fruit trees got stripped by giraffes and hunting did not yield a kill, but not so helpful if the stressful thing is the holiday season.
- Hydration: your body cannot function properly without adequate hydration; water is needed (directly or indirectly) for all bodily processes, and your metabolism will also “dry up” without it.
- Antidiabetic & anti-inflammatory diet: minimize sugar intake and reduce processed foods, especially those with inflammatory refined oils (esp. canola & sunflower) and the like. This has very directly to do with your body’s energy metabolism, and as they say in computing, “garbage in; garbage out”.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Forks Over Knives: Flavor! – by Darshana Thacker
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s important to not have to choose too much between health and flavor, because the outcome will never be a good one, either for your health or your happiness. And what’s bad for your happiness will ultimately not work out and thus will be bad for your general health, so, the question becomes: how to get both?
This book handles that nicely, delivering plant-based dishes that are also incidentally oil-free, and also either gluten-free or else there’s an obvious easy substitution to make it such. The flavor here comes from the ingredients as a whole, including the main ingredients as well as seasonings.
On the downside, occasionally those ingredients may be a little obscure if you don’t live in, say, San Francisco, and the ingredients weren’t necessarily chosen for cooking on a budget, either.
However, in most cases for most people it will, at worse, inspire you to try using an ingredient you don’t usually use—so that’s a good result.
The recipes are very clear and easy to follow, although not all are illustrated, and the “ready in…” times are about as accurate as they are for any cookbook, that is to say, it’s the time in which it conceivably can be done if (like the author, a head chef) you have a team of sous-chefs who have done a bunch of prep for you (e.g. sweet potato does not normally come in ½” dice; it comes in sweet potatoes) and laid everything out in little bowls mise-en-place style, and also you know the procedure well enough to not have to stop, hesitate, check anything, wash anything, wait for water to boil or anything else to heat up, or so forth. In other words, if you’re on your own in your home kitchen with normal domestic appliances, it’s going to take a little longer than for a professional in a professional kitchen with professional help.
But don’t let that detract from the honestly very good recipes.
Bottom line: if you’d like to level-up your plant-based cooking, this will definitely make your dishes that bit better!
Click here to check out Forks Over Knives: Flavor!, and dig in!
Share This Post
-
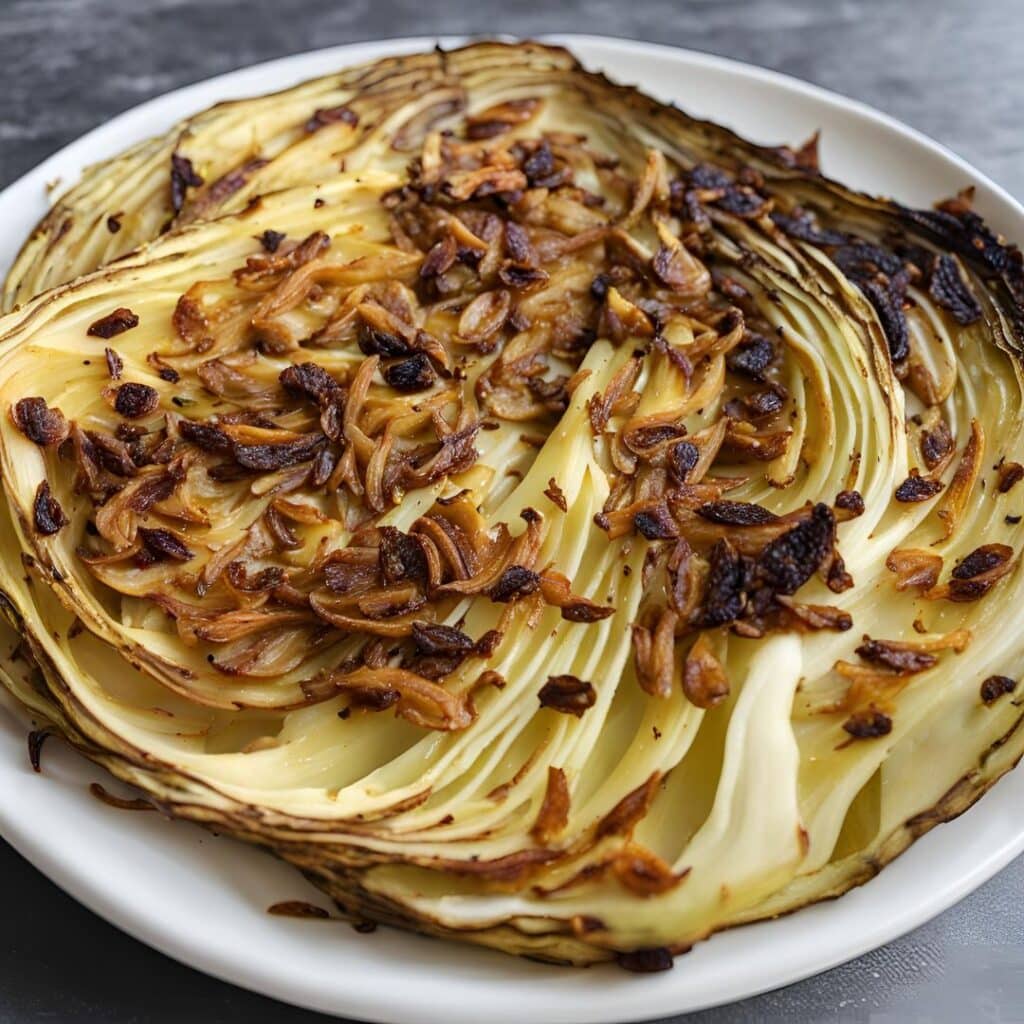
Caramelized Caraway Cabbage
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cabbage is an underrated vegetable for its many nutrients and its culinary potential—here’s a great way to make it a delectable starter or respectable side.
You will need
- 1 medium white cabbage, sliced into 1″ thick slabs
- 1 tbsp extra-virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp caraway seeds
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp turmeric
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the non-cabbage ingredients in a small bowl, whisking to mix thoroughly—with a tiny whisk if you have one, but a fork will work if necessary.
3) Arrange the cabbage slices on a lined baking tray and brush the seasoning-and-oil mixture over both sides of each slice.
4) Roast for 20–25 minutes until the cabbage is tender and beginning to caramelize.
5) Serve warm.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Curcumin (Turmeric) is worth its weight in gold
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Here’s how to help protect your family from norovirus
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- Norovirus is a very contagious infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea.
- The best way to help protect against norovirus is to wash your hands often with soap and warm water, since hand sanitizer may not be effective at killing the virus.
- If someone in your household has symptoms of norovirus, isolate them away from others, watch for signs of dehydration, and take steps to help prevent it from spreading.
If you feel like everyone is sick right now, you’re not alone. Levels of respiratory illnesses like COVID-19, flu, and RSV remain remain high in many states, and the U.S. is also battling a wave of norovirus, one of several viruses that cause a very contagious infection of the stomach and intestines.
Although norovirus infections are more common during the colder months—it’s also called the “winter vomiting disease”—the virus can spread at any time. Right now, however, cases have more than doubled since last year’s peak.
Read on to learn about the symptoms of norovirus, how it spreads, and what to do if someone in your household gets sick.
What are the symptoms of norovirus?
Norovirus is a very contagious infection that causes vomiting and diarrhea, which typically begins 12 to 48 hours after exposure to the virus. Additional symptoms may include stomach pain, body aches, headaches, and a fever. Norovirus typically resolves within three days, but people who are infected may still be contagious for up to two days after symptoms resolve.
Norovirus may cause dehydration, or a dangerous loss of fluids, especially in young children and older adults. See a health care provider if you or someone in your household shows signs of dehydration, which may include decreased urination, dizziness, a dry mouth and throat, sleepiness, and crying without tears.
How can you help protect against norovirus?
You can get norovirus if you have close contact with someone who is infected, touch a contaminated surface and then touch your mouth or nose, or consume contaminated food or beverages.
The best way to help protect yourself and others against norovirus is to wash your hands often with soap and warm water, since hand sanitizer may not be effective at killing the virus. Other ways to help protect yourself may include cooking food thoroughly and washing fruits and vegetables before eating them.
You can get sick with norovirus even if you’ve had it before, since there are many different strains.
How can families help protect against the spread of norovirus at home?
If someone in your household has symptoms of norovirus, isolate them away from others and watch for signs of dehydration. If you are sick with norovirus, do not prepare food for others in your household and use a separate bathroom, if possible.
When cleaning up after someone who has norovirus, wear rubber, latex, or nitrile gloves. Then wash your hands thoroughly.
Clean surfaces using a solution containing five to 25 tablespoons of bleach (that’s 12.5 fluid ounces, or just over ¾ cup), per gallon of water. Leave the bleach-water mix on surfaces for at least five minutes before wiping it off.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Tilapia vs Cod – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing tilapia to cod, we picked the tilapia.
Why?
Another case of “that which is more expensive is not necessarily the healthier”!
In terms of macros, tilapia has more protein and fats, as well as more omega-3 (and omega-6). On the downside, tilapia does have relatively more saturated fat, but at 0.94g/100g, it’s not exactly butter.
The vitamins category sees that tilapia has more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B12, D, and K, while cod has more of vitamins B6, B9, and choline. A moderate win for tilapia.
When it comes to minerals, things are most divided; tilapia has more copper, iron, phosphorus, potassium, manganese, and selenium, while cod has more magnesium and zinc. An easy win for tilapia.
One other thing to note is that both of these fish contain mercury these days (and it’s worth noting: cod has nearly 10x more mercury). Mercury is, of course, not exactly a health food.
So, excessive consumption of either is not recommended, but out of the two, tilapia is definitely the one to pick.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Farmed Fish vs Wild Caught: Know The Health Differences
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How To Get Your First Pull-Up
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Pull-ups are a great compound exercise that works most of the upper body. However, it can be frustrating for many, if unable to do more than dangle and struggle while not going anywhere. That’s not actually bad, by the way! Of course it’s not great athletic performance, but in terms of exercise, “dangling and struggling while not going anywhere” is an isometric exercise that has plenty of benefits of its own. However, for those who would rather go up in the world, personal trainer Meg Gallagher shows the way:
The Only Way Is Up?
Gallagher offers a few methods; the first is simply an improvement on the “dangling and struggling while not going anywhere” method, but doing it with good form. It’s called the…
Hollow body hold:
- Hang from the bar with legs and feet together.
- Maintain a posterior pelvic tilt (i.e. don’t let your hips roll forwards, and don’t let your butt stick out more than is necessary by mere virtue of having a butt)
- Engage your core by shortening the space between your ribs and pelvis.
- Turn on your abs and lats, with your head slightly behind the bar.
- Practice the hollow body hang instead of dead hangs to build grip and core strength.
Another method is now moving on from the hollow body hold, and shows that in fact, up is not the only way. It’s called…
Negative pull-ups:
- Jump up to get your chin over the bar, then slowly lower yourself in a controlled manner.
- Prioritize negative pull-ups over other exercises to build strength.
- You can use modifications like resistance bands or feet assistance if necessary to extend the duration of your negative pull-up, but these are “crutches”, so try to move on from them as soon as you reasonably can—same if your gym has an “assisted pull-up” machine, consisting of a moving platform with a variable counterweight, mimicking how a pull-up would feel if your body were lighter.
- Practice resisting throughout the entire range of motion.
To give a sense of direction, Gallagher offers the following program:
- On day 1, test how long you can resist the negative pull-up (e.g., 10 seconds).
- For each session, multiply your time by 2 (e.g., 10 seconds × 2 = 20 seconds total).
- Break the total volume into as many sets as needed (e.g., 2 sets of 10 seconds or 4 sets of 5 seconds).
- After each session, add 2 seconds to the total volume for the next session.
- Aim for 3 sessions per week for 3–4 weeks, increasing by 2 seconds each session.
- When you reach about 25 seconds, you should be close to performing your first pull-up.
For more on all of this, plus a few other things to try, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Early Detection May Help Kentucky Tamp Down Its Lung Cancer Crisis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Anthony Stumbo’s heart sank after the doctor shared his mother’s chest X-ray.
“I remember that drive home, bringing her back home, and we basically cried,” said the internal medicine physician, who had started practicing in eastern Kentucky near his childhood home shortly before his mother began feeling ill. “Nobody wants to get told they’ve got inoperable lung cancer. I cried because I knew what this meant for her.”
Now Stumbo, whose mother died the following year, in 1997, is among a group of Kentucky clinicians and researchers determined to rewrite the script for other families by promoting training and boosting awareness about early detection in the state with the highest lung cancer death rate. For the past decade, Kentucky researchers have promoted lung cancer screening, first recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in 2013. These days the Bluegrass State screens more residents who are at high risk of developing lung cancer than any state except Massachusetts — 10.6% of eligible residents in 2022, more than double the national rate of 4.5% — according to the most recent American Lung Association analysis.
The effort has been driven by a research initiative called the Kentucky LEADS (Lung Cancer Education, Awareness, Detection, and Survivorship) Collaborative, which in 2014 launched to improve screening and prevention, to identify more tumors earlier, when survival odds are far better. The group has worked with clinicians and hospital administrators statewide to boost screening rates both in urban areas and regions far removed from academic medical centers, such as rural Appalachia. But, a decade into the program, the researchers face an ongoing challenge as they encourage more people to get tested, namely the fear and stigma that swirl around smoking and lung cancer.
Lung cancer kills more Americans than any other malignancy, and the death rates are worst in a swath of states including Kentucky and its neighbors Tennessee and West Virginia, and stretching south to Mississippi and Louisiana, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
It’s a bit early to see the impact on lung cancer deaths because people may still live for years with a malignancy, LEADS researchers said. Plus, treatment improvements and other factors may also help reduce death rates along with increased screening. Still, data already shows that more cancers in Kentucky are being detected before they become advanced, and thus more difficult to treat, they said. Of total lung cancer cases statewide, the percentage of advanced cases — defined as cancers that had spread to the lymph nodes or beyond — hovered near 81% between 2000 and 2014, according to Kentucky Cancer Registry data. By 2020, that number had declined to 72%, according to the most recent data available.
“We are changing the story of families. And there is hope where there has not been hope before,” said Jennifer Knight, a LEADS principal investigator.
Older adults in their 60s and 70s can hold a particularly bleak view of their mortality odds, given what their loved ones experienced before screening became available, said Ashley Shemwell, a nurse navigator for the lung cancer screening program at Owensboro Health, a nonprofit health system that serves Kentucky and Indiana.
“A lot of them will say, ‘It doesn’t matter if I get lung cancer or not because it’s going to kill me. So I don’t want to know,’” said Shemwell. “With that generation, they saw a lot of lung cancers and a lot of deaths. And it was terrible deaths because they were stage 4 lung cancers.” But she reminds them that lung cancer is much more treatable if caught before it spreads.
The collaborative works with several partners, including the University of Kentucky, the University of Louisville, and GO2 for Lung Cancer, and has received grant funding from the Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation. Leaders have provided training and other support to 10 hospital-based screening programs, including a stipend to pay for resources such as educational materials or a nurse navigator, Knight said. In 2022, state lawmakers established a statewide lung cancer screening program based in part on the group’s work.
Jacob Sands, a lung cancer physician at Boston’s Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, credits the LEADS collaborative with encouraging patients to return for annual screening and follow-up testing for any suspicious nodules. “What the Kentucky LEADS program is doing is fantastic, and that is how you really move the needle in implementing lung screening on a larger scale,” said Sands, who isn’t affiliated with the Kentucky program and serves as a volunteer spokesperson for the American Lung Association.
In 2014, Kentucky expanded Medicaid, increasing the number of lower-income people who qualified for lung cancer screening and any related treatment. Adults 50 to 80 years old are advised to get a CT scan every year if they have accumulated at least 20 pack years and still smoke or have quit within the past 15 years, according to the latest task force recommendation, which widened the pool of eligible adults. (To calculate pack years, multiply the packs of cigarettes smoked daily by years of smoking.) The lung association offers an online quiz, called “Saved By The Scan,” to figure out likely eligibility for insurance coverage.
Half of U.S. patients aren’t diagnosed until their cancer has spread beyond the lungs and lymph nodes to elsewhere in the body. By then, the five-year survival rate is 8.2%.
But regular screening boosts those odds. When a CT scan detects lung cancer early, patients have an 81% chance of living at least 20 years, according to data published in November in the journal Radiology.
Some adults, like Lisa Ayers, didn’t realize lung cancer screening was an option. Her family doctor recommended a CT scan last year after she reported breathing difficulties. Ayers, who lives in Ohio near the Kentucky border, got screened at UK King’s Daughters, a hospital in far eastern Kentucky. The scan didn’t take much time, and she didn’t have to undress, the 57-year-old said. “It took me longer to park,” she quipped.
She was diagnosed with a lung carcinoid tumor, a type of neuroendocrine cancer that can grow in various parts of the body. Her cancer was considered too risky for surgery, Ayers said. A biopsy showed the cancer was slow-growing, and her doctors said they would monitor it closely.
Ayers, a lifelong smoker, recalled her doctor said that her type of cancer isn’t typically linked to smoking. But she quit anyway, feeling like she’d been given a second chance to avoid developing a smoking-related cancer. “It was a big wake-up call for me.”
Adults with a smoking history often report being treated poorly by medical professionals, said Jamie Studts, a health psychologist and a LEADS principal investigator, who has been involved with the research from the start. The goal is to avoid stigmatizing people and instead to build rapport, meeting them where they are that day, he said.
“If someone tells us that they’re not ready to quit smoking but they want to have lung cancer screening, awesome; we’d love to help,” Studts said. “You know what? You actually develop a relationship with an individual by accepting, ‘No.’”
Nationally, screening rates vary widely. Massachusetts reaches 11.9% of eligible residents, while California ranks last, screening just 0.7%, according to the lung association analysis.
That data likely doesn’t capture all California screenings, as it may not include CT scans done through large managed care organizations, said Raquel Arias, a Los Angeles-based associate director of state partnerships at the American Cancer Society. She cited other 2022 data for California, looking at lung cancer screening for eligible Medicare fee-for-service patients, which found a screening rate of 1%-2% in that population.
But, Arias said, the state’s effort is “nowhere near what it needs to be.”
The low smoking rate in California, along with its image as a healthy state, “seems to have come with the unintended consequence of further stigmatizing people who smoke,” said Arias, citing one of the findings from a 2022 report looking at lung cancer screening barriers. For instance, eligible patients may be reluctant to share prior smoking habits with their health provider, she said.
Meanwhile, Kentucky screening efforts progress, scan by scan.
At Appalachian Regional Healthcare, 3,071 patients were screened in 2023, compared with 372 in 2017. “We’re just scratching the surface of the potential lives that we can have an effect on,” said Stumbo, a lung cancer screening champion at the health system, which includes 14 hospitals, most located in eastern Kentucky.
The doctor hasn’t shed his own grief about what his family missed after his mother died at age 51, long before annual screening was recommended. “Knowing that my children were born, and never knowing their grandmother,” he said, “just how sad is that?”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: