Healthy Tiramisu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Tiramisu (literally “pick-me-up”, “tira-mi-su”) is a delightful dish that, in its traditional form, is also a trainwreck for the health, being loaded with inflammatory cream and sugar, not to mention the cholesterol content. Here we recreate the dish in healthy fashion, being loaded with protein, fiber, and healthy fats, not to mention that the optional sweetener is an essential amino acid. The coffee and cocoa, of course, are full of antioxidants too. All in all, what’s not celebrate?
You will need
- 2 cups silken tofu (no need to press it) (do not substitute with any firmer tofu or it will not work)
- 1 cup oat cream (you can buy this ready-made, or make it yourself by blending oats in water until you get the desired consistency) (you can also just use dairy cream, but that will be less healthy)
- 1 cup almond flour (also simply called “ground almonds”)
- 1 cup espresso ristretto, or otherwise the strongest black coffee you have facility to make
- ¼ cup unsweetened cocoa powder, plus more for dusting
- 1 pack savoiardi biscuits, also called “ladyfinger” biscuits (this was the only part we couldn’t make healthy—if you figure out a way to make it healthy, let us know!) (if vegan, obviously use a vegan substitute biscuit; this writer uses Lotus/Biscoff biscuits, which work well)
- 1 tsp vanilla essence
- ½ tsp almond essence
- Optional: glycine, per taste
- Garnish: roasted coffee beans
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add glycine to the coffee first if you want the overall dish to be sweeter. Glycine has approximately the same sweetness as sugar, and can be used as a 1:1 substitution. Use that information as you see fit.
2) Blend the tofu and the oat cream together in a high-speed blender until smooth. It should have a consistency like cake-batter; if it is too liquidy, add small amounts of almond flour until it is thicker. If it’s too thick, add oat cream until it isn’t. If you want it to be sweeter than it is, add glycine to taste. When happy with its taste and consistency, divide it evenly into two bowls.
3) Add the vanilla essence and almond essence to one bowl, and the cocoa powder to the other, mixing well (in a food processor, or just by using a whisk)
4) Coat the base of a glass dish (such as a Pyrex oven dish, but any dish is fine, and any glass dish will allow for viewing the pretty layers we’ll be making) with a very thin layer of almond flour (if you want sweetness there, you can mix some glycine in with the almond flour first).
4) One by one, soak the biscuits briefly in the coffee, and use them to line to base of the dish.
5) Add a thin layer of chocolate cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
6) Add a thin layer of vanilla-and-almond cream, ensuring the surface is as flat as possible. Dust it with cocoa powder, to increase the surface tension.
7) Stop and assess: do you have enough ingredients left to repeat these layers? It will depend on the size and shape dish you used. If you do, repeat them, finishing with a vanilla-and-almond cream layer.
8) Dust the final layer with cocoa powder if you haven’t already, and add the coffee bean garnish, if using.
9) Refrigerate for at least 8 hours, and if you have time to prepare it the day before you will eat it, that is best of all.
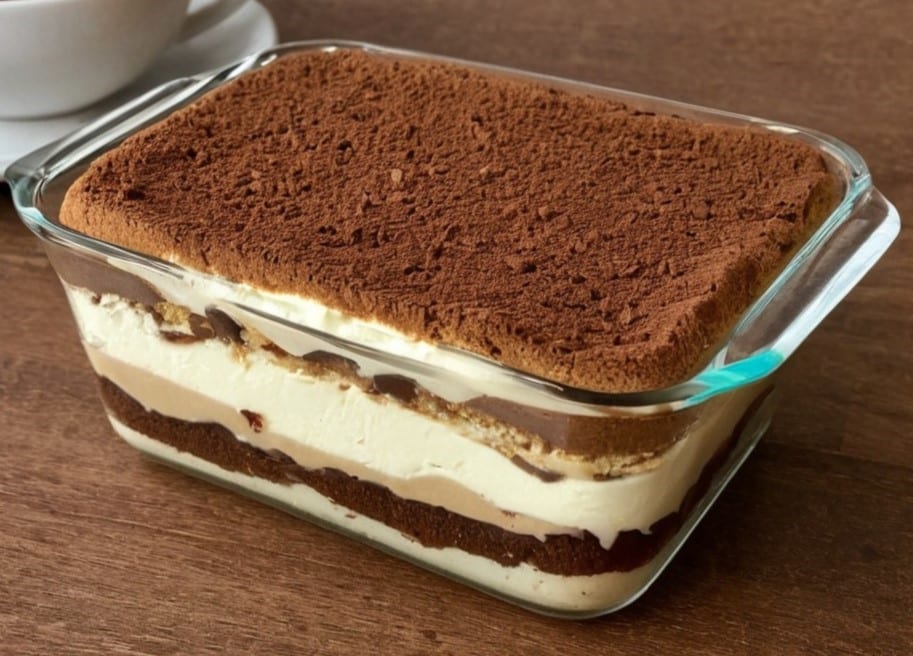

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Easily Digestible Vegetarian Protein Sources
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- The Sweet Truth About Glycine
- Tiramisu Crunch Bites ← craving tiramisu but not keen on all that effort? Enjoy these!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Which Style Of Yoga Is Best For You?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For you personally, that is—so let’s look at some options, their benefits, and what kind of person is most likely to benefit from each.
Yoga is, of course, an ancient practice, and like any ancient practice, especially one with so many practitioners (and thus also: so many teachers), there are very many branches to the tree of variations, that is to say, different schools and their offshoots.
Since we cannot possibly cover all of them, we’ll focus on five broad types that are popular (and thus, likely available near to you, unless you live in a very remote place):
Hatha Yoga
This is really the broadest of umbrella categories for yoga as a physical practice of the kind that most immediately comes to mind in the west:
- Purpose: energizes the practitioner through controlled postures and breath.
- Practice: non-heated, slow asanas held for about a minute with intentional transitions
- Benefits: reduces stress, improves flexibility, tones muscles, and boosts circulation.
- Best for: beginners with an active lifestyle.
Vinyasa Yoga
You may also have heard of this called simply “Flow”, without reference to the Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi sense of the word. Rather, it is about a flowing practice:
- Purpose: builds heat and strength through continuous, flowing movement paired with breath.
- Practice: dynamic sequences of the same general kind as the sun salutation, leading to a final resting pose.
- Benefits: enhances heart health, strengthens core, tones muscles, and improves flexibility.
- Best for: beginner to intermediate yogis seeking a cardio-based practice.
Hot Yoga
This one’s well-known and the clue is in the name; it’s yoga practised in a very hot room:
- Purpose: uses heat to increase heart rate, and loosen muscles.
- Practice: heated studio (32–42℃, which is 90–108℉), often with vinyasa flows, resulting in heavy sweating*
- Benefits: burns calories, improves mood, enhances skin, and builds bone density.
- Best for: intermediate yogis comfortable with heat; not recommended for certain health conditions.
*and also sometimes heat exhaustion / heat stroke. This problem arises most readily when the ambient temperature is higher than human body temperature, because that is the point at which sweating ceases to fulfil its biological function of cooling us down.
Noteworthily, a study found that doing the same series of yoga postures in the same manner, but without the heat, produced the same health benefits without the risk:
❝The primary finding from this investigation is that the hatha yoga postures in the Bikram yoga series produce similar enhancements in endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in healthy, middle-aged adults regardless of environmental temperature. These findings highlight the efficacy of yoga postures in producing improvements in vascular health and downplay the necessity of the heated practice environment in inducing vascular adaptations.❞
(“Bikram yoga” is simply the brand name of a particular school of hot yoga)
Yin Yoga
This is a Chinese variation, and is in some ways the opposite of the more vigorous forms, being gentler in pretty much all ways:
- Purpose: promotes deep tissue stretching and circulation by keeping muscles cool.
- Practice: passive, floor-based asanas held for 5–20 minutes in a calming environment.
- Benefits: increases flexibility, enhances circulation, improves mindfulness, and emotional release.
- Best for: all levels, regardless of health or flexibility.
Restorative Yoga
This is often tailored to a specific condition, but it doesn’t have to be:
- Purpose: encourages relaxation and healing through supported, restful poses.
- Practice: reclined, prop-supported postures in a soothing, low-lit setting.
- Benefits: relieves stress, reduces chronic pain, calms the nervous system, and supports healing.
- Best for: those recovering from illness/injury or managing emotional stress.
See for example: Yoga Therapy for Arthritis: A Whole-Person Approach to Movement and Lifestyle
Want to know more?
If you’re still unsure where to start, check out:
Yoga Teacher: “If I wanted to get flexible (from scratch) in 2025, here’s what I’d do”
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Strong At Every Age: 15 Habits To Level Up Your Health & Fitness
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not every increase in health and fitness needs to look like a training montage from the “Rocky” movies!
Making progress every day
We’ll not keep the 15 habits a secret; they are:
- Follow the one-minute rule: commit to just one minute of action—this makes starting easier, and often you’ll end up doing more once you’ve got started.
- Make the habit exciting: add fun elements to make the habit more enjoyable, like using new gear or accessories.
- Do it first: prioritize new habits by doing them early in the day to ensure they get done.
- Share the love: pair new habits with activities you already enjoy, where practical, to do “temptation bundling”.
- Embrace the uncomfortable: get used to discomfort daily to grow and build resilience for bigger changes.
- Do as little as possible: start small with habits, to minimize resistance and focus on consistency.
- Think how to be lazy: simplify processes and use shortcuts; there are no extra prizes for it having been difficult!
- Make the appointment: schedule habits with set dates and times, to increase accountability.
- Let habits evolve: adapt habits to fit current circumstances; that way you can still stay consistent over time.
- Plan ahead: prepare in advance to avoid setbacks—what could stop you from succeeding, and how can you pre-empt that?
- Pause to reflect: regularly evaluate what works and what doesn’t, to adjust and improve.
- Shut off your brain: avoid overthinking and start taking action now, not later, to build momentum.
- Question and learn: stay curious and open to learning, or else you will plateau quickly!
- Ask why: understand the deeper reasons behind any resistance, and make clear for yourself the value of the habit.
- Love your failures: embrace any setbacks as learning opportunities and, as such, stepping stones to success.
For more on all of each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Genetic Risk Factors For Long COVID
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people, after getting COVID, go on to have Long COVID. There are various contributing factors to this, including:
- Lifestyle factors that impact general disease-proneness
- Immune-specific factors such as being immunocompromised already
- Genetic factors
We looked at some modifiable factors to improve one’s disease-resistance, yesterday:
And we’ve taken a more big-picture look previously:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Along with some more systemic issues:
Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
But, for when the “don’t get COVID” ship has sailed, one of the big remaining deciding factors with regard to whether one gets Long COVID or not, is genetic
The Long COVID Genes
For those with their 23andMe genetic data to hand…
❝Study findings revealed that three specific genetic loci, HLA-DQA1–HLA-DQB1, ABO, and BPTF–KPAN2–C17orf58, and three phenotypes were at significantly heightened risk, highlighting high-priority populations for interventions against this poorly understood disease.❞
For those who don’t, then first: you might consider getting that! Here’s why:
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
But also, all is not lost meanwhile:
The same study also found that individuals with genetic predispositions to chronic fatigue, depression, and fibromyalgia, as well as other phenotypes such as autoimmune conditions and cardiometabolic conditions, are at significantly higher risk of long-COVID than individuals without these conditions.
Good news, bad news
Another finding was that women and non-smokers were more likely to get Long COVID, than men and smokers, respectively.
Does that mean that those things are protective against Long COVID, which would be very counterintuitive in the case of smoking?
Well, yes and no; it depends on whether you count “less likely to get Long COVID because of being more likely to just die” as protective against Long COVID.
(Incidentally, estrogen is moderately immune-enhancing, while testosterone is moderately immune-suppressing, so the sex thing was not too surprising. It’s also at least contributory to why women get more autoimmune disorders, while men get more respiratory infections such as colds and the like)
Want to know more?
You can read the paper itself, here:
*GWAS = Genome-Wide Association Study
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Inhaled Eucalyptus’s Immunomodulatory and Antimicrobial Effects
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝At the first hint of a cough or a cold, I resort to steam inhalation. Some people add herbs or aromatic oils to the boiling water. What do you recommend?❞
First of all, please do be careful:
Western science’s view is predominantly “this is popular and/but evidence for its usefulness is lacking”:
But! Traditional Chinese Medicine indicates shuanghuanglian, yuxingcao and qingkailing, which the China Food and Drug Administration has also approved:
Chinese Medicine in Inhalation Therapy: A Review of Clinical Application and Formulation Development
Indian scientists are also looking at modern scientific applications of certain Ayurvedic herbs:
Promising phytochemicals of traditional Indian herbal steam inhalation therapy to combat COVID-19
In terms of what is likely more available to you, there are several reasons to choose eucalyptus over popular alternatives:
Immune-modifying and antimicrobial effects of Eucalyptus oil and simple inhalation devices
For the sake of being methodical, here’s an example product on Amazon, though we’re sure you’d have no trouble finding this in your local pharmacy if you prefer.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Switchcraft – by Dr. Elaine Fox
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How do we successfully balance “a mind is like a parachute: it only works if it’s open”, with the importance of also actually having some kind of personal integrity and consistency?
Dr. Fox recommends that we focus on four key attributes:
- Mental agility
- Self-awareness
- Emotional awareness
- Situational awareness
If this sounds a little wishy-washy, it isn’t—she delineates and explains each in detail. And most importantly: how we can build and train each one.
Mental agility, for example, is not about being able to rapidly solve chess problems or “answer these riddles three”. It’s more about:
- Adaptability
- Balancing our life
- Challenging (and if appropriate, changing) our perspective
- Developing our mental competence
This sort of thing is the “meat” of the book. Meanwhile, self-awareness is more a foundational conscious knowledge of one’s own “pole star” values, while emotional awareness is a matter of identifying and understanding and accepting what we feel—anything less is self-sabotage! And situational awareness is perhaps most interesting:
Dr. Fox advocates for “trusting one’s gut feelings”. With a big caveat, though!
If we trust our gut feelings without developing their accuracy, we’re just going to go about being blindly prejudiced and often wrong. So, a whole section of the book is devoted to honing this and improving our ability to judge things as they really are—rather than as we expect.
Bottom line: this book is a great tool for not only challenging our preconceptions about how we think, but giving us the resources to be adaptable and resilient without sacrificing integrity.
Click here to check out Switchcraft on Amazon and level up your thinking!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Brain-Skin Doctor
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Of Brains And Breakouts
Today’s spotlight is on Dr. Claudia Aguirre. She’s a molecular neuroscientist, and today she’s going to be educating us about skin.
What? Why?
When we say “neuroscience”, we generally think of the brain. And indeed, that’s a very important part of it.
We might think about eyes, which are basically an extension of the brain.
We don’t usually think about skin, which (just like our eyes) is constantly feeding us a lot of information about our surroundings, via a little under three million nerve endings. Guess where the other ends of those nerves lead!
There’s a constant two-way communication going on between our brain and our skin.
What does she want us to know?
Psychodermatology
The brain and the skin talk to each other, and maladies of one can impact the other:
- Directly, e.g. stress prompting skin breakouts (actually this is a several-step process physiologically, but for the sake of brevity we’ll call this direct)
- Indirectly, e.g. nervous disorders that result in people scratching or picking at their skin, which prompts a whole vicious cycle of one thing making the other worse
Read more: Psychodermatology: The Brain-Skin Connection
To address both kinds of problems, clearly something beyond moisturizer is needed!
Mindfulness (meditation and beyond)
Mindfulness is a well-evidenced healthful practice for many reasons, and Dr. Aguirra argues the case for it being good for our skin too.
As she points out,
❝Cultural stress and anxiety can trigger or aggravate many skin conditions—from acne to eczema to herpes, psoriasis, and rosacea.
Conversely, a disfiguring skin condition can trigger stress, anxiety, depression, and even suicide.
Chronic, generalized anxiety can create chronic inflammation and exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions, such as those I mentioned previously.
Chronic stress can result in chronic anxiety, hypervigilance, poor sleep, and a whole cascade of effects resulting in a constant breakdown of tissues and organs, including the skin.❞
So, she recommends mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), for the above reasons, along with others!
Read more: Mind Matters
How to do it: No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
And as for “and beyond?”
Do you remember in the beginning of the pandemic, when people were briefly much more consciously trying to avoid touching their faces so much? That, too, is mindfulness. It may have been a stressed and anxious mindfulness for many*, but mindfulness nonetheless.
*which is why “mindfulness-based stress reduction” is not a redundant tautology repeated more than once unnecessarily, one time after another 😉
So: do try to keep aware of what you are doing to your skin, and so far as is reasonably practicable, only do the things that are good for it!
The skin as an endocrine organ
Nerves are not the only messengers in the body; hormones do a lot of our body’s internal communication too. And not just the ones everyone remembers are hormones (e.g. estrogen, testosterone, although yes, they do both have a big impact on skin too), but also many more, including some made in the skin itself!
Dr. Aguirra gives us a rundown of common conditions, the hormones behind them, and what we can do if we don’t want them:
Read more: Rethinking The Skin As An Endocrine Organ
Take-away advice:
For healthy skin, we need to do more than just hydrate, get good sleep, have good nutrition, and get a little sun (but not too much).
- We should also practice mindfulness-based stress reduction, and seek help for more serious mental health issues.
- We should also remember the part our hormones play in our skin, and not just the obvious ones.
Did you know that vitamin D is also a hormone, by the way? It’s not the only hormone at play in your skin by a long way, but it is an important one:
Society for Endocrinology | Vitamin D
Want to know more?
You might like this interview with Dr. Aguirre:
The Brain in Our Skin: An Interview with Dr. Claudia Aguirre
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: