Healthy Harissa Falafel Patties
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You can make these as regular falafel balls if you prefer, but patties are quicker and easier to cook, and are great for popping in a pitta.
You will need
For the falafels:
- 1 can chickpeas, drained, keep the chickpea water (aquafaba)
- 1 red onion, roughly chopped
- 2 tbsp chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- 1 bunch parsley
- 1 tbsp harissa paste
- Extra virgin olive oil for frying
For the harissa sauce:
- ½ cup crème fraîche or plant-based equivalent (you can use our Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese recipe and add the juice of 1 lemon)*
- 1 tbsp harissa paste (or adjust this quantity per your heat preference)
*if doing this, rather than waste the zest of the lemon, you can add the zest to the falafels if you like, but it’s by no means necessary, just an option
For serving:
- Wholegrain pitta or other flatbread (you can use our Healthy Homemade Flatbreads recipe)
- Salad (your preference; we recommend some salad leaves, sliced tomato, sliced cucumber, maybe some sliced onion, that sort of thing)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Blend the chickpeas, 1 oz of the aquafaba, the onion, the parsley, and the harissa paste, until smooth. Then add in the chickpea flour until you get a thick batter. If you overdo it with the chickpea flour, add a little more of the aquafaba to equalize. Refrigerate the mixture for at least 30 minutes.
2) Heat some oil in a skillet, and spoon the falafel mixture into the pan to make the patties, cooking on both sides (you can use a spatula to gently turn them), and set them aside.
3) Mix the harissa sauce ingredients in a small bowl.
4) Assemble; best served warm, but enjoy it however you like!
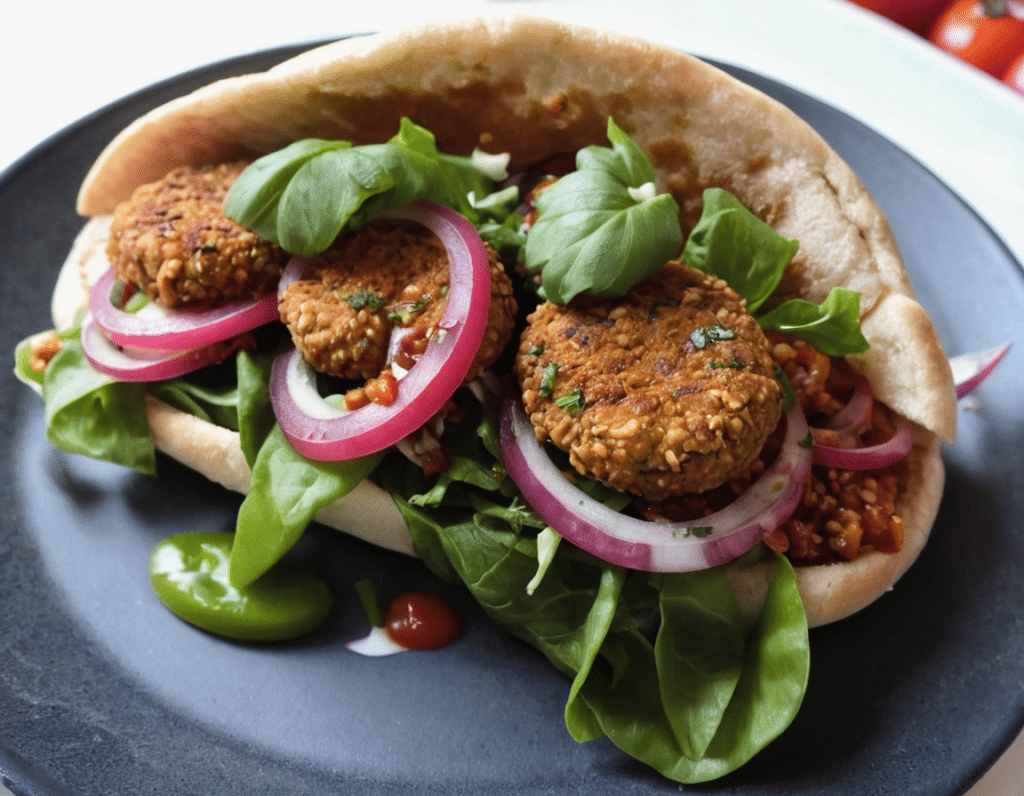

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in more of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Hero Homemade Hummus ← another great option
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Genetic Risk Factors For Long COVID
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Some people, after getting COVID, go on to have Long COVID. There are various contributing factors to this, including:
- Lifestyle factors that impact general disease-proneness
- Immune-specific factors such as being immunocompromised already
- Genetic factors
We looked at some modifiable factors to improve one’s disease-resistance, yesterday:
And we’ve taken a more big-picture look previously:
Beyond Supplements: The Real Immune-Boosters!
Along with some more systemic issues:
Why Some People Get Sick More (And How To Not Be One Of Them)
But, for when the “don’t get COVID” ship has sailed, one of the big remaining deciding factors with regard to whether one gets Long COVID or not, is genetic
The Long COVID Genes
For those with their 23andMe genetic data to hand…
❝Study findings revealed that three specific genetic loci, HLA-DQA1–HLA-DQB1, ABO, and BPTF–KPAN2–C17orf58, and three phenotypes were at significantly heightened risk, highlighting high-priority populations for interventions against this poorly understood disease.❞
For those who don’t, then first: you might consider getting that! Here’s why:
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
But also, all is not lost meanwhile:
The same study also found that individuals with genetic predispositions to chronic fatigue, depression, and fibromyalgia, as well as other phenotypes such as autoimmune conditions and cardiometabolic conditions, are at significantly higher risk of long-COVID than individuals without these conditions.
Good news, bad news
Another finding was that women and non-smokers were more likely to get Long COVID, than men and smokers, respectively.
Does that mean that those things are protective against Long COVID, which would be very counterintuitive in the case of smoking?
Well, yes and no; it depends on whether you count “less likely to get Long COVID because of being more likely to just die” as protective against Long COVID.
(Incidentally, estrogen is moderately immune-enhancing, while testosterone is moderately immune-suppressing, so the sex thing was not too surprising. It’s also at least contributory to why women get more autoimmune disorders, while men get more respiratory infections such as colds and the like)
Want to know more?
You can read the paper itself, here:
*GWAS = Genome-Wide Association Study
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Parent Effectiveness Training – by Dr. Thomas Gordon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you want your home (or workplace, for that matter) to be a place of peace? This book literally got the author nominated for a Nobel Peace Prize. Can’t really get much higher praise than that.
The title is “Parent Effectiveness Training”, but in reality, the advice in the book is applicable to all manner of relationships, including:
- romantic relationships
- friends
- colleagues
- …and really any human interaction.
It covers some of the same topics we did today (and more) in much more detail than we ever could in a newsletter. It lays out formulae to use, gives plenty of examples, and/but is free from undue padding.
- Pros: this isn’t one of those “should have been an article” books. It has so much valuable content.
- Cons: It is from the 1970s* so examples may feel “dated” now.
In addition to going into much more detail on some of the topics covered in today’s issue of 10almonds, Dr. Gordon also talks in-depth about the concept of “problem-ownership”.
In a nutshell, that means: whose problem is a given thing? Who “has” what problem? Everyone needs to be on the same page about everyone else’s problems in the situation… as well as their own, which is not always a given!
Dr. Gordon presents, in short, tools not just to resolve conflict, but also to pre-empt it entirely. With these techniques, we can identify and deal with problems (together!) well before they arise.
Everybody wins.
Get your copy of “Parent Effectiveness Training” from Amazon today!
*Note: There is an updated edition on the market, and that’s what you’ll find upon following the above link. This reviewer (hi!) has a battered old paperback from the 1970s and cannot speak for what was changed in the new edition. However: if the 70s one is worth more than its weight in gold (and it is), the new edition is surely just as good, if not better!
Share This Post
-
Cherries’ Very Healthy Wealth Of Benefits!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cherries’ Health Benefits Simply Pop
First, be aware, there are different kinds:
Sweet & Sour
Cherries can be divided into sweet vs sour. These are mostly nutritionally similar, though sour ones do have some extra benefits.
Sweet and sour cherries are closely related but botanically different plants; it’s not simply a matter of ripeness (or preparation).
These can mostly be sorted into varieties of Prunus avium and Prunus cerasus, respectively:
Cherry Antioxidants: From Farm to Table
Sour cherry varieties include morello and montmorency, so look out for those names in particular when doing your grocery-shopping.
You may remember that it’s a good rule of thumb that foods that are more “bitter, astringent, or pungent” will tend to have a higher polyphenol content (that’s good):
Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Juiced up
Almost certainly for reasons of budget and convenience, as much as for standardization, most studies into the benefits of cherries have been conducted using concentrated cherry juice as a supplement.
At home, we need not worry so much about standardization, and our budget and convenience are ours to manage. To this end, as a general rule of thumb, whole fruits are pretty much always better than juice:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Antioxidant & anti-inflammatory!
Cherries are a very good source of antioxidants, and as such they also reduce inflammation, which in turn means ameliorating autoimmune diseases, from common things like arthritis…
…to less common things like gout:
Cherry Consumption and the Risk of Recurrent Gout Attacks
This can also be measured by monitoring uric acid metabolites:
Consumption of cherries lowers plasma urate in healthy women
Anti-diabetic effect
Most of the studies on this have been rat studies, and the human studies have been less “the effect of cherry consumption on diabetes” and more a matter of separate studies adding up to this conclusion in, the manner of “cherries have this substance, this substance has this effect, therefore cherries will have this effect”. You can see an example of this discussed over the course of 15 studies, here:
A Review of the Health Benefits of Cherries ← skip to section 2.2.1: “Cherry Intake And Diabetes”
In short, the jury is out on cherry juice, but eating cherries themselves (much like getting plenty of fruit in general) is considered good against diabetes.
Good for healthy sleep
For this one, the juice suffices (actual cherries are still recommended, but the juice gave clear significant positive results):
Pilot Study of the Tart Cherry Juice for the Treatment of Insomnia and Investigation of Mechanisms ← this was specifically in people over the age of 50
Importantly, it’s not that cherries have a sedative effect, but rather they support the body’s ability to produce melatonin adequately when the time comes:
Effect of tart cherry juice (Prunus cerasus) on melatonin levels and enhanced sleep quality
Post-exercise recovery
Cherries are well-known for boosting post-exercise recovery, though they may actually improve performance during exercise too, if eaten beforehand/
For example, these marathon-runners who averaged 13% compared to placebo control:
As for its recovery benefits, we wrote about this before:
How To Speed Up Recovery After A Workout (According To Actual Science)
Want to get some?
We recommend your local supermarket (or farmer’s market!), but if for any reason you prefer to take a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
People on Ozempic may have fewer heart attacks, strokes and addictions – but more nausea, vomiting and stomach pain
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Ozempic and Wegovy are increasingly available in Australia and worldwide to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity.
The dramatic effects of these drugs, known as GLP-1s, on weight loss have sparked huge public interest in this new treatment option.
However, the risks and benefits are still being actively studied.
In a new study in Nature Medicine, researchers from the United States reviewed health data from about 2.4 million people who have type 2 diabetes, including around 216,000 people who used a GLP-1 drug, between 2017 and 2023.
The researchers compared a range of health outcomes when GLP-1s were added to a person’s treatment plan, versus managing their diabetes in other ways, often using glucose-lowering medications.
Overall, they found people who used GLP-1s were less likely to experience 42 health conditions or adverse health events – but more likely to face 19 others.
myskin/Shutterstock What conditions were less common?
Cardiometabolic conditions
GLP-1 use was associated with fewer serious cardiovascular and coagulation disorders. This includes deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, stroke, cardiac arrest, heart failure and myocardial infarction.
Neurological and psychiatric conditions
GLP-1 use was associated with fewer reported substance use disorders or addictions, psychotic disorders and seizures.
Infectious conditions
GLP-1 use was associated with fewer bacterial infections and pneumonia.
What conditions were more common?
Gastrointestinal conditions
Consistent with prior studies, GLP-1 use was associated with gastrointestinal conditions such as nausea, vomiting, gastritis, diverticulitis and abdominal pain.
Other adverse effects
Increased risks were seen for conditions such as low blood pressure, syncope (fainting) and arthritis.
People who took Ozempic were more likely to experience stomach upsets than those who used other type 2 diabetes treatments. Douglas Cliff/Shutterstock How robust is this study?
The study used a large and reputable dataset from the US Department of Veterans Affairs. It’s an observational study, meaning the researchers tracked health outcomes over time without changing anyone’s treatment plan.
A strength of the study is it captures data from more than 2.4 million people across more than six years. This is much longer than what is typically feasible in an intervention study.
Observational studies like this are also thought to be more reflective of the “real world”, because participants aren’t asked to follow instructions to change their behaviour in unnatural or forced ways, as they are in intervention studies.
However, this study cannot say for sure that GLP-1 use was the cause of the change in risk of different health outcomes. Such conclusions can only be confidently made from tightly controlled intervention studies, where researchers actively change or control the treatment or behaviour.
The authors note the data used in this study comes from predominantly older, white men so the findings may not apply to other groups.
Also, the large number of participants means that even very small effects can be detected, but they might not actually make a real difference in overall population health.
Observational studies track outcomes over time, but can’t say what caused the changes. Jacob Lund/Shutterstock Other possible reasons for these links
Beyond the effect of GLP-1 in the body, other factors may explain some of the findings in this study. For example, it’s possible that:
- people who used GLP-1 could be more informed about treatment options and more motivated to manage their own health
- people who used GLP-1 may have received it because their health-care team were motivated to offer the latest treatment options, which could lead to better care in other areas that impact the risk of various health outcomes
- people who used GLP-1 may have been able to do so because they lived in metropolitan centres and could afford the medication, as well as other health-promoting services and products, such as gyms, mental health care, or healthy food delivery services.
Did the authors have any conflicts of interest?
Two of the study’s authors declared they were “uncompensated consultants” for Pfizer, a global pharmaceutical company known for developing a wide range of medicines and vaccines. While Pfizer does not currently make readily available GLP-1s such as Ozempic or Wegovy, they are attempting to develop their own GLP-1s, so may benefit from greater demand for these drugs.
This research was funded by the US Department of Veterans Affairs, a government agency that provides a wide range of services to military veterans.
No other competing interests were reported.
Diabetes vs weight-loss treatments
Overall, this study shows people with type 2 diabetes using GLP-1 medication generally have more positive health outcomes than negative health outcomes.
However, the study didn’t include people without type 2 diabetes. More research is needed to understand the effects of these medications in people without diabetes who are using them for other reasons, including weight loss.
While the findings highlight the therapeutic benefits of GLP-1 medications, they also raise important questions about how to manage the potential risks for those who choose to use this medication.
The findings of this study can help many people, including:
- policymakers looking at ways to make GLP-1 medications more widely available for people with various health conditions
- health professionals who have regular discussions with patients considering GLP-1 use
- individuals considering whether a GLP-1 medication is right for them.
Lauren Ball, Professor of Community Health and Wellbeing, The University of Queensland and Emily Burch, Accredited Practising Dietitian and Lecturer, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Do we really need to burp babies? Here’s what the research says
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Parents are often advised to burp their babies after feeding them. Some people think burping after feeding is important to reduce or prevent discomfort crying, or to reduce how much a baby regurgitates milk after a feed.
It is true babies, like adults, swallow air when they eat. Burping releases this air from the top part of our digestive tracts. So when a baby cries after a feed, many assume it’s because the child needs to “be burped”. However, this is not necessarily true.
Why do babies cry or ‘spit up’ after a feed?
Babies cry for a whole host of reasons that have nothing to do with “trapped air”.
They cry when they are hungry, cold, hot, scared, tired, lonely, overwhelmed, needing adult help to calm, in discomfort or pain, or for no identifiable reason. In fact, we have a name for crying with no known cause; it’s called “colic”.
“Spitting up” – where a baby gently regurgitates a bit of milk after a feed – is common because the muscle at the top of a newborn baby’s stomach is not fully mature. This means what goes down can all too easily go back up.
Spitting up frequently happens when a baby’s stomach is very full, there is pressure on their tummy or they are picked up after lying down.
Spitting up after feeding decreases as babies get older. Three-quarters of babies one month old spit up after feeding at least once a day. Only half of babies still spit up at five months and almost all (96%) stop by their first birthdays.
There’s not much research out there on ‘burping’ babies. antoniodiaz/Shutterstock Does burping help reduce crying or spitting up?
Despite parents being advised to burp their babies, there’s not much research evidence on the topic.
One study conducted in India encouraged caregivers of 35 newborns to burp their babies, while caregivers of 36 newborns were not given any information about burping.
For the next three months, mothers and caregivers recorded whether their baby would spit up after feeding and whether they showed signs of intense crying.
This study found burping did not reduce crying and actually increased spitting up.
When should I be concerned about spitting up or crying?
Most crying and spitting up is normal. However, these behaviours are not:
- refusing to feed
- vomiting so much milk weight gain is slow
- coughing or wheezing distress while feeding
- bloody vomit.
If your baby has any of these symptoms, see a doctor or child health nurse.
If your baby seems unbothered by vomiting and does not have any other symptoms it is a laundry problem rather than something that needs medical attention.
It is also normal for babies to cry and fuss quite a lot; two hours a day, for about the first six weeks is the average.
This has usually reduced to about one hour a day by the time they are three months of age.
Crying more than this doesn’t necessarily mean there is something wrong. The intense, inconsolable crying of colic is experienced by up to one-quarter of young babies but goes away with time on its own .
If your baby is crying more than average or if you are worried there might be something wrong, you should see your doctor or child health nurse.
If your baby likes being ‘burped’, then it’s OK to do it. But don’t stress if you skip it. Miljan Zivkovic/Shutterstock Not everyone burps their baby
Burping babies seems to be traditional practice in some parts of the world and not in others.
For example, research in Indonesia found most breastfeeding mothers rarely or never burped their babies after feeding.
One factor that may influence whether a culture encourages burping babies may be related to another aspect of infant care: how much babies are carried.
Carrying a baby in a sling or baby carrier can reduce the amount of time babies cry.
Babies who are carried upright on their mother or another caregiver’s front undoubtedly find comfort in that closeness and movement.
Babies in slings are also being held firmly and upright, which would help any swallowed air to rise up and escape via a burp if needed.
Using slings can make caring for a baby easier. Studies (including randomised controlled trials) have also shown women have lower rates of post-natal depression and breastfeed for longer when they use a baby sling.
It is important baby carriers and slings are used safely, so make sure you’re up to date on the latest advice on how to do it.
So, should I burp my baby?
The bottom line is: it’s up to you.
Gently burping a baby is not harmful. If you feel burping is helpful to your baby, then keep doing what you’re doing.
If trying to burp your baby after every feed is stressing you or your baby out, then you don’t have to keep doing it.
Karleen Gribble, Adjunct Associate Professor, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Western Sydney University and Nina Jane Chad, Research Fellow, University of Sydney School of Public Health, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
A new emergency procedure for cardiac arrests aims to save more lives – here’s how it works
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As of January this year, Aotearoa New Zealand became just the second country (after Canada) to adopt a groundbreaking new procedure for patients experiencing cardiac arrest.
Known as “double sequential external defibrillation” (DSED), it will change initial emergency response strategies and potentially improve survival rates for some patients.
Surviving cardiac arrest hinges crucially on effective resuscitation. When the heart is working normally, electrical pulses travel through its muscular walls creating regular, co-ordinated contractions.
But if normal electrical rhythms are disrupted, heartbeats can become unco-ordinated and ineffective, or cease entirely, leading to cardiac arrest.
Defibrillation is a cornerstone resuscitation method. It gives the heart a powerful electric shock to terminate the abnormal electrical activity. This allows the heart to re-establish its regular rhythm.
Its success hinges on the underlying dysfunctional heart rhythm and the proper positioning of the defibrillation pads that deliver the shock. The new procedure will provide a second option when standard positioning is not effective.
Using two defibrillators
During standard defibrillation, one pad is placed on the right side of the chest just below the collarbone. A second pad is placed below the left armpit. Shocks are given every two minutes.
Early defibrillation can dramatically improve the likelihood of surviving a cardiac arrest. However, around 20% of patients whose cardiac arrest is caused by “ventricular fibrillation” or “pulseless ventricular tachycardia” do not respond to the standard defibrillation approach. Both conditions are characterised by abnormal activity in the heart ventricles.
DSED is a novel method that provides rapid sequential shocks to the heart using two defibrillators. The pads are attached in two different locations: one on the front and side of the chest, the other on the front and back.
A single operator activates the defibrillators in sequence, with one hand moving from the first to the second. According to a recent randomised trial in Canada, this approach could more than double the chances of survival for patients with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia who are not responding to standard shocks.
The second shock is thought to improve the chances of eliminating persistent abnormal electrical activity. It delivers more total energy to the heart, travelling along a different pathway closer to the heart’s left ventricle.
Evidence of success
New Zealand ambulance data from 2020 to 2023 identified about 1,390 people who could potentially benefit from novel defibrillation methods. This group has a current survival rate of only 14%.
Recognising the potential for DSED to dramatically improve survival for these patients, the National Ambulance Sector Clinical Working Group updated the clinical procedures and guidelines for emergency medical services personnel.
The guidelines now specify that if ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia persist after two shocks with standard defibrillation, the DSED method should be administered. Two defibrillators need to be available, and staff must be trained in the new approach.
Though the existing evidence for DSED is compelling, until recently it was based on theory and a small number of potentially biased observational studies. The Canadian trial was the first to directly compare DSED to standard treatment.
From a total of 261 patients, 30.4% treated with this strategy survived, compared to 13.3% when standard resuscitation protocols were followed.
The design of the trial minimised the risk of other factors confounding results. It provides confidence that survival improvements were due to the defibrillation approach and not regional differences in resources and training.
The study also corroborates and builds on existing theoretical and clinical scientific evidence. As the trial was stopped early due to the COVID-19 pandemic, however, the researchers could recruit fewer than half of the numbers planned for the study.
Despite these and other limitations, the international group of experts that advises on best practice for resuscitation updated its recommendations in 2023 in response to the trial results. It suggested (with caution) that emergency medical services consider DSED for patients with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia who are not responding to standard treatment.
Training and implementation
Although the evidence is still emerging, implementation of DSED by emergency services in New Zealand has implications beyond the care of patients nationally. It is also a key step in advancing knowledge about optimal resuscitation strategies globally.
There are always concerns when translating an intervention from a controlled research environment to the relative disorder of the real world. But the balance of evidence was carefully considered before making the decision to change procedures for a group of patients who have a low likelihood of survival with current treatment.
Before using DSED, emergency medical personnel undergo mandatory education, simulation and training. Implementation is closely monitored to determine its impact.
Hospitals and emergency departments have been informed of the protocol changes and been given opportunities to ask questions and give feedback. As part of the implementation, the St John ambulance service will perform case reviews in addition to wider monitoring to ensure patient safety is prioritised.
Ultimately, those involved are optimistic this change to cardiac arrest management in New Zealand will have a positive impact on survival for affected patients.
Vinuli Withanarachchie, PhD candidate, College of Health, Massey University; Bridget Dicker, Associate Professor of Paramedicine, Auckland University of Technology, and Sarah Maessen, Research Associate, Auckland University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: