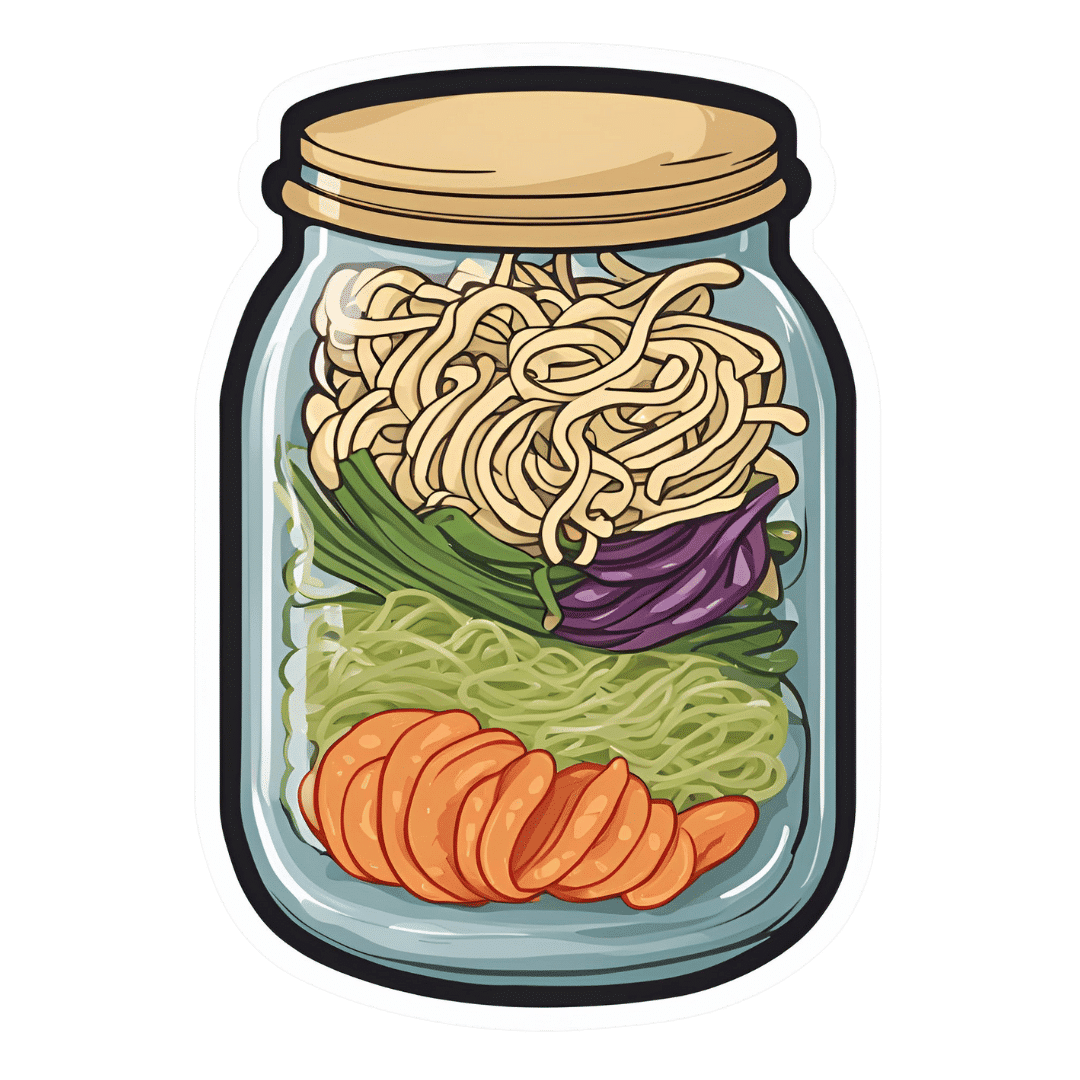
Gut-Positive Pot Noodles
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everything we consume either improves our health a little or worsens it. Pot noodles aren’t generally the healthiest foods, but these ones sure are! There’s quite a range of fiber in this, including the soluble fiber of the noodles themselves (which are, in fact, mostly fiber and water). As a bonus, the glucomannan in the noodles promotes feelings of fullness, notwithstanding its negligible carb count. Of course, the protein in the edamame beans also counts for satiety!
You will need
- ½ cup konjac noodles (also called shirataki), tossed in 1 tsp avocado oil (or sesame oil, if you don’t have avocado)
- 2 oz mangetout, thinly sliced
- 1 oz edamame beans
- ¼ carrot, grated
- 2 baby sweetcorn, cut in half lengthways
- 1 scallion, finely diced
- 1 heaped tsp crunchy peanut butter (omit if allergic)
- 1 tsp miso paste
- 1 tsp chili oil
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp peeled-and-grated ginger
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Layer a heat-resistant jar (mason jars are usually quite resistant to temperature changes) with the noodles and vegetables.
2) Combine the peanut butter, miso paste, and chili oil, black pepper, and ginger in a small bowl. Pour this dressing over the layered vegetables and noodles, and screw the lid on. Refrigerate until needed.
3) Add hot water to the jar and stir, to serve. If you prefer the vegetables to be more cooked, you can microwave (without the lid!) for a minute or two.
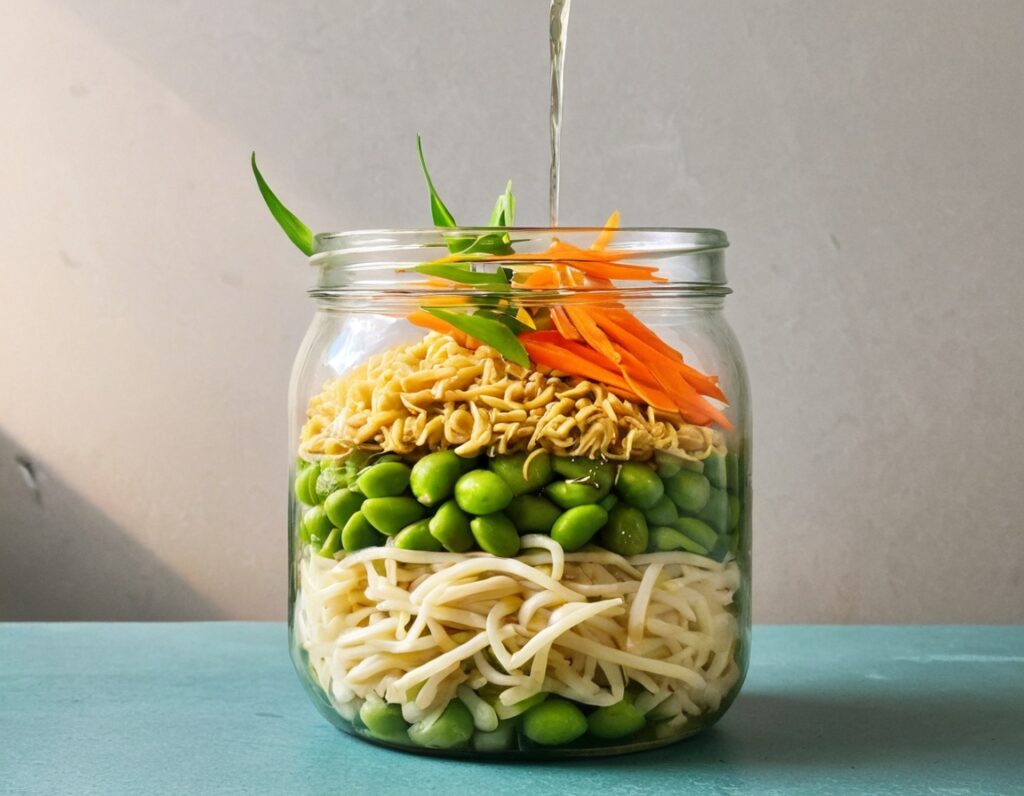

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars ← today’s recipe makes a perfect high-fiber, low-carb starter, per the hacks here
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Ginger Does A Lot More Than You Think
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sun-dried Tomatoes vs Black Olives – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sun-dried tomatoes to black olives, we picked the sun-dried tomatoes.
Why?
These common snack-salad items may seem similar in consistency, but their macros are very different: the tomatoes, being dried, have proportionally a lot more protein, carbs, and fiber. The olives, meanwhile, have more fat (and/but yes, a very healthy blend of fats). Note that these comments are true for the things themselves; be aware that sun-dried tomatoes are often sold in vegetable oil, which would obviously change the macros considerably and be much less healthy. So, for the sake of statistics, we’re assuming you got sun-dried tomatoes that aren’t soaked in oil. All in all, we’re calling this category a win for the tomatoes, but those fats from the olives are very good too.
In terms of vitamins, the sun-dried tomatoes being dried again means that the loss of water weight means the vitamin content is proportionally much higher; the tomatoes are higher in vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and K, while olives are higher only in vitamin E (but in their defence, olives have 165x more vitamin E than sun-dried tomatoes). Still, a win for sun-dried tomatoes here.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a similar story for the same reason; the loss of water weight in the sun-dried tomatoes makes them much more nutritionally dense; they are higher in calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while the olives are higher only in sodium. Note, we’re looking at black olives today; green olives would be even higher in sodium than black ones, as they are “cured” for longer.
Lastly, in terms of polyphenols, they both have a lot of great things to bring, but sun-dried tomatoes are pretty much the richest natural source of lycopene, which itself a very powerful polyphenol even my general polyphenol standards, so we’d call this one a win for the sun-dried tomatoes too.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Smart Sex – by Dr. Emily Morse
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this isn’t: this isn’t a mere book of sex positions and party tricks, nor is it a book of Cosmo-style “drive your man wild by using hot sauce as lube” advice.
What it offers instead, is a refreshingly mature take on sex, free from the “teehee” titillations and blushes that many books of the genre go for.
Dr. Emily Morse outlines five pillars of sex:
- Embodiment
- Health
- Collaboration
- Self-knowledge
- Self-acceptance
…and talks about each of them in detail, and how we can bring them together. And, of course, how we or our partner(s) could accidentally sabotage ourselves or each other, and the conversations we can (and should!) have, to work past that.
She also, critically, and this is a big source of value in the book, looks at “pleasure thieves”: stress, trauma, and shame. The advice for overcoming these is not “don’t worry; be happy” but rather is actual practical steps one can take.
The style throughout is direct and unpatronizing. Since the advice within pertains to everyone who has and/or wants an active sex life, very little is divided by gender etc.
There is some attention given to anatomy and physiology, complete with clear diagrams. Honestly, most people could benefit from these, because most people’s knowledge of the relevant anatomy stopped with a very basic high school text book diagram that missed a lot out.
Bottom line: this book spends more time on what’s between your ears than what’s between your legs, and yet is very comprehensive in all areas. Everyone has something to gain from this one.
Share This Post
-
Melatonin: A Safe, Natural Sleep Aid?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Melatonin: A safe sleep supplement?
Melatonin is a hormone normally made in our pineal gland. It helps regulate our circadian rhythm, by making us sleepy.
It has other roles too—it has a part to play in regulating immune function, something that also waxes and wanes as a typical day goes by.
Additionally, since melatonin and cortisol are antagonistic to each other, a sudden increase in either will decrease the other. Our brain takes advantage of this, by giving us a cortisol spike in the morning to help us wake up.
As a supplement, it’s generally enjoyed with the intention of inducing healthy, natural, restorative sleep.
Does it really induce healthy, natural, restorative, sleep?
Yes! Well, “natural” is a little subject and relative, if you’re taking it as a supplement, but it’s something your body produces naturally anyway.
Contrast with, for example, benzodiazepines (that whole family of medications with names ending in -azopan or -alozam), or other tranquilizing drugs that do not so much induce healthy sleep, but rather reduce your brain function and hopefully knock you out, and/but often have unwanted side effects, and a tendency to create dependency.
Melatonin, unlike most of those drugs, does not create dependency, and furthermore, we don’t develop tolerance to it. In other words, the same dose will continue working (we won’t need more and more).
In terms of benefits, melatonin not only reduces the time to fall asleep and increases total sleep time, but also (quite a bonus) improves sleep quality, too:
Meta-Analysis: Melatonin for the Treatment of Primary Sleep Disorders
Because it is a natural hormone rather than a drug with many side effects and interactions, it’s also beneficial for those who need good sleep and/but don’t want tranquilizing:
Any other benefits?
Yes! It can also help guard against Seasonal Affective Disorder, also called seasonal depression. Because SAD is not just about “not enough light = not enough serotonin”, but also partly about circadian rhythm and (the body is not so sure what time of day it is when there are long hours of darkness, or even, in the other hemisphere / other time of year, long hours of daylight), melatonin can help, by giving your brain something to “anchor” onto, provided you take it at the same time each day. See:
- Is seasonal affective disorder a disorder of circadian rhythms?
- The circadian basis of winter depression: the case for low-dose melatonin use
As a small bonus, melatonin also promotes HGH production (important for maintaining bone and muscle mass, especially in later life):
Anything we should worry about?
Assuming taking a recommended dose only (0.5mg–10mg per day), toxicity is highly unlikely, especially given that it has a half-life of only 40–60 minutes, so it’ll be eliminated quite quickly.
However! It does indeed induce sleepiness, so for example, don’t take melatonin and then try to drive or operate heavy machinery—or, ideally, do anything other than go to bed.
It can interfere with some medications. We mentioned that melatonin helps regulate immune function, so for example that’s something to bear in mind if you’re on immunosuppressants or otherwise have an autoimmune disorder. It can also interfere with blood pressure medications and blood thinners, and may make epilepsy meds less effective.
As ever, if in doubt, please speak with your doctor and/or pharmacist.
Where to get it?
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here is an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
International Day of Women and Girls in Science
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Today is the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, so we’ve got a bunch of content for the ladies out there. Let’s start with the statement Sima Bahous (the Executive Director of UN Women) made:
❝This year, the sixty-seventh session of the Commission on the Status of Women (CSW67) will consider as its priority theme “Innovation and technological change, and education in the digital age for achieving gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls”.
This is an unprecedented opportunity for the Commission to develop a definitive agenda for progress towards women’s full and equal participation and representation in STEM. Its implementation will require bold, coordinated, multi-stakeholder action.❞
Here at 10almonds, we are just one newsletter, and maybe we can’t change the world (…yet), but we’re all for this!
We’re certainly all in favour of education in the digital age, and more of our subscribers are women and girls than not (highest of fives from your writer today, also a woman—and I do bring most of the sciency content).
Medical News Today asks “Why Are Women Less Likely To Survive Cardiac Arrest Than Men?”
You can read the full article here, but the short version is:
- People (bystanders and EMS professionals alike!) are less likely to intervene to give CPR when the patient is a woman (we appreciate that “your hands on an unknown woman’s chest” is a social taboo, but there’s a time and a place!)
- People trained to give CPR (volunteers or professionals!) are often less confident about how to do so with female anatomy—training is almost entirely on “male” dummies.
A quick take-away from this is: to give effective CPR, you need to be giving two-inch compressions!
On a side note, do you want to learn how to correctly do chest compressions on female anatomy? This short (1:55) video could save a woman’s life!
As a science-based health and productivity newsletter, we make no apologies if occasional issues sometimes have a slant to women’s health! Heaven help us, the bias in science at large is certainly the opposite:
The list of examples is far too long for us to include here, but two that spring immediately to mind are:
- PCOS (Polycystic ovary syndrome), which affects nearly 1 in 5 women, can lead to infertility, never mind the inconvenience of irregular bleeding, chronic pain, and diabetes (amongst other things), and… nobody knows what causes it, or what to do about it.
- Endometriosis (the lining of the womb starts growing in other places), meanwhile, affects around 1 in 10 women. It causes chronic pain and fatigue, and again, nobody knows what causes it or how to cure it.
Maybe if women in STEM weren’t on the receiving end of rampant systemic misogyny, we’d have more women in science, and some answers by now!
❗️NOT-SO-FUN FACT:
Women make up only 28% of the workforce in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM), and men vastly outnumber women majoring in most STEM fields in college. The gender gaps are particularly high in some of the fastest-growing and highest-paid jobs of the future, like computer science and engineering.
Source: AAUW
The US census suggests change is happening, but is a very long way from equality!
WHAT OUR SUBSCRIBERS SAY:
❝Women are slowly gaining more of a place in academia, and slowly making more of a difference when they get there, and start doing research that reflects ourselves. But I still think that it’s a struggle to get there, and it’s a struggle to be heard and be respected.
It’s a matter of pride, it’s a matter of proving yourself, being in STEM, and [women in STEM] still report being extremely disrespected, not taken seriously all, despite being very very good.
It’s worth noting as well, that we’ve had women in STEM for a while and there are so many things we appreciate nowadays that they were a part of, but they were never given credit for—it’s still a problem today and something we need to more actively fight.❞
Isabella F. Lima, Occupational Psychologist
Are you a woman in STEM, and have a story to tell? We’d love to hear it! Just reply to this email 🙂
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Science Of New Year’s Pre-Resolutions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Science Of New Year’s Pre-Resolutions
There’s a military dictum that “prior preparation and planning prevents piss-poor performance”.
Would it surprise you to know that soldiers going on the attack are not focused on the goal? Rather, they are focused on the process.
With drills and mnemonics, everything that can be controlled for in advance is; every action, every reaction, everything that can go wrong, and all the “if x then y” decisions in between pre-battle PREWAR and PAWPERSO and post-battle PACESDO (all mnemonic acronyms; the content is not important here but the principle is).
In short: take Murphy’s Law into account now, and plan accordingly!
The same goes for making your plans the winning kind
If you want your resolutions to work, you may need to make pre-resolutions now, so that you’re properly prepared:
- Do you want to make an exercise habit? Make sure now that you have the right clothes/shoes/etc, make sure that they fit you correctly, make sure you have enough of them that you can exercise when one set’s in the wash, etc.
- What grace will you allow yourself if tired, unwell, busy? What’s your back-up plan so that you still do what you can at those times when “what you can” is legitimately a bit less?
- If it’s an outdoors plan, what’s your plan for when it’s rainy? Snowy? Dangerously hot?
- What are the parameters for what counts? Make it measurable. How many exercise sessions per week, what duration?
- Do you want to make a diet habit? Make sure that you have in the healthy foods that you want to eat; know where you can and will get things. We’re often creatures of habit when it comes to shopping, so planning will be critical here!
- Do you want to cut some food/drink/substance out? Make sure you have a plan to run down or otherwise dispose of your current stock first. And make sure you have alternatives set up, and if it was something you were leaning on as a coping strategy of some kind (e.g. alcohol, cannabis, comfort-eating, etc), make sure you have an alternative coping strategy, too!
See also: How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
We promised science, so here it comes
Approach-oriented resolutions work better than avoidance-oriented ones.
This means: positively-framed resolutions work better than negatively-framed ones.
On a simple level, this means that, for example, resolving to exercise three times per week is going to work better than resolving to not consume alcohol.
But what if you really want to quit something? Just frame it positively. There’s a reason that Alcoholics Anonymous (and similar Thing Anonymous groups) measure days sober, not relapses.
So it’s not “I will not consume alcohol” but “I will get through each day alcohol-free”.
Semantics? Maybe, but it’s also science:
Why January the 1st? It’s a fresh start
Resolutions started on the 1st of January enjoy a psychological boost of a feeling of a fresh start, a new page, a new chapter.
Similar benefits can be found from starting on the 1st of a month in general, or on a Monday, or on some date that is auspicious to the person in question (religious fasts tied to calendar dates are a fine example of this).
Again, this is borne-out by science:
The Fresh Start Effect: Temporal Landmarks Motivate Aspirational Behavior
Make it a habit
Here be science:
How do people adhere to goals when willpower is low? The profits (and pitfalls) of strong habits
As for how to do that?
How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Trim the middle
No, we’re not talking about your waistline. Rather, what Dr. Ayelet Fischbach refers to as “the middle problem”:
❝We’re highly motivated at the beginning. Over time, our motivation declines as we lose steam. To the extent that our goal has a clear end point, our motivation picks up again toward the end.
Therefore, people are more likely to adhere to their standards at the beginning and end of goal pursuit—and slack in the middle. We demonstrate this pattern of judgment and behavior in adherence to ethical standards (e.g., cheating), religious traditions (e.g., skipping religious rituals), and performance standards (e.g., “cutting corners” on a task).
We also show that the motivation to adhere to standards by using proper means is independent and follows a different pattern from the motivation to reach the end state of goal pursuit❞
Read: The end justifies the means, but only in the middle
How to fix this, then?
Give yourself consistent, recurring, short-term goals, with frequent review points. That way, it’s never “the middle” for long:
The fresh start effect: temporal landmarks motivate aspirational behavior
See also:
How do people protect their long-term goals from the influence of short-term motives or temptations?
Finally…
You might like this previous main feature of ours that was specifically about getting oneself through those “middle” parts:
How To Keep On Keeping On… Long Term!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- Do you want to make an exercise habit? Make sure now that you have the right clothes/shoes/etc, make sure that they fit you correctly, make sure you have enough of them that you can exercise when one set’s in the wash, etc.
-
But First, Inner Peace – by Case Kenny
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Thinking positively and vividly imagining a Ferrari parked in your driveway will not, in fact, cause it to manifest there.
You know what that method does work for, though? Feelings.
This book is essentially a guided thought-and-feeling modelling system that, consisting of 60 chapters to be taken one-per-day, aims to rewire your mind for inner peace.
This is not, however, just a matter of “imagine peacefulness”, or nice-sounding platitudes. Rather, at the end of each chapter there is an exercise and journaling prompts; effectively, work to do along the way.
Weighing in at 438 pages, this is a sizeable book, but part of that is because of the space to write answers to journaling prompts. Still, it’s not exactly a pamphlet, either—there is serious and extensive content here too.
Like any daily reader, you can zip through it all at once if you like, but a benefit to doing the chapter-a-day approach is that it sets a habit of mindful reflection, and gives you a chance to implement each thing, one per day, building up new habits in that regard, too. In contrast, reading it all in one sitting wouldn’t give that.
Bottom line: without inner peace, we don’t have much. Treat yourself—you deserve it.
Click here to check out But First, Inner Peace, and enjoy inner peace!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: