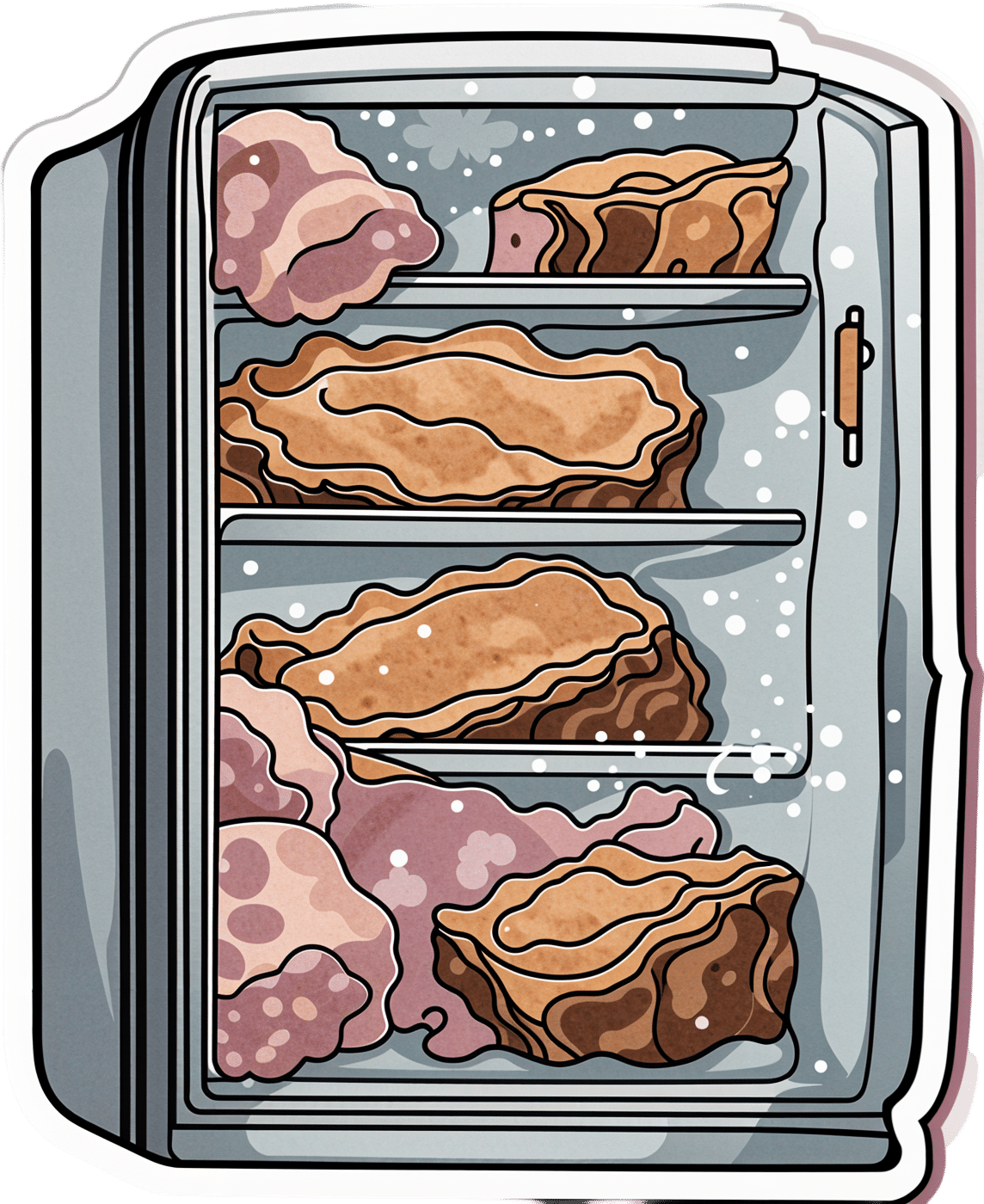
Frozen/Thawed/Refrozen Meat: How Much Is Safety, And How Much Is Taste?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What You Can (And Can’t) Safely Do With Frozen Meat
Yesterday, we asked you:
❝You have meat in the freezer. How long is it really safe to keep it?❞
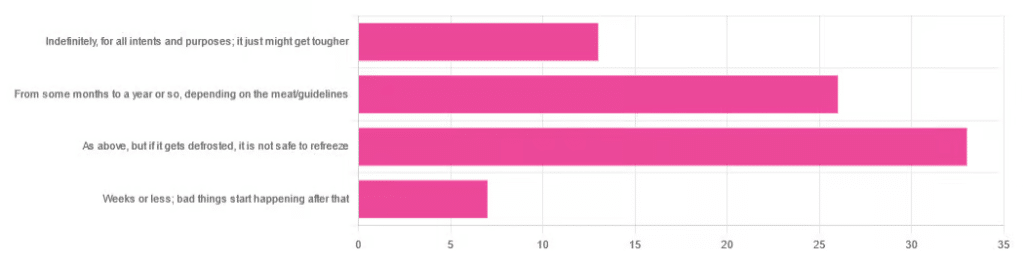
…and got a range of answers, mostly indicating to a) follow the instructions (a very safe general policy) and b) do not refreeze if thawed because that would be unsafe. Fewer respondents indicated that meat could be kept for much longer than guidelines say, or conversely, that it should only be kept for weeks or less.
So, what does the science say?
Meat can be kept indefinitely (for all intents and purposes) in a freezer; it just might get tougher: True or False?
False, assuming we are talking about a normal household electrical freezer that bottoms out at about -18℃ / 0℉.
Fun fact: cryobiologists cryopreserve tissue samples (so basically, meat) at -196℃ / -320℉, and down at those temperatures, the tissues will last a lot longer than you will (and, for all practical purposes: indefinitely). There are other complications with doing so (such as getting the sample through the glass transition point without cracking it during the vitrification process) but those are beyond the scope of this article.
If you remember back to your physics or perhaps chemistry classes at school, you’ll know that molecules move more quickly at higher temperatures, and more slowly at lower ones, only approaching true stillness as they near absolute zero (-273℃ / -459℉ / 0K ← we’re not saying it’s ok, although it is; rather, that is zero kelvin; no degree sign is used with kelvins)
That means that when food is frozen, the internal processes aren’t truly paused; it’s just slowed to a point of near imperceptibility.
So, all the way up at the relatively warm temperatures of a household freezer, a lot of processes are still going on.
What this means in practical terms: those guidelines saying “keep in the freezer for up to 4 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 9 months”, “keep in the freezer for up to 12 months” etc are being honest with you.
More or less, anyway! They’ll usually underestimate a little to be on the safe side—but so should you.
Bad things start happening within weeks at most: True or False?
False, for all practical purposes. Again, assuming a normal and properly-working household freezer as described above.
(True, technically but misleadingly: the bad things never stopped; they just slowed down to a near imperceptible pace—again, as described above)
By “bad” here we should clarify we mean “dangerous”. One subscriber wrote:
❝Meat starts losing color and flavor after being in the freezer for too long. I keep meat in the freezer for about 2 months at the most❞
…and as a matter of taste, that’s fair enough!
It is unsafe to refreeze meat that has been thawed: True or False?
False! Assuming it has otherwise been kept chilled, just the same as for fresh meat.
Food poisoning comes from bacteria, and there is nothing about the meat previously having been frozen that will make it now have more bacteria.
That means, for example…
- if it was thawed (but chilled) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been chilled for that period of time (so probably: use it or freeze it, unless it’s been more than a few days)
- if it was thawed (and at room temperature) for a period of time, treat it like you would any other meat that has been at room temperature for that period of time (so probably: throw it out, unless the period of time is very small indeed)
The USDA gives for 2 hours max at room temperature before considering it unsalvageable, by the way.
However! Whenever you freeze meat (or almost anything with cells, really), ice crystals will form in and between cells. How much ice crystallization occurs depends on several variables, with how much water there is present in the food is usually the biggest factor (remember that animal cells are—just like us—mostly water).
Those ice crystals will damage the cell walls, causing the food to lose structural integrity. When you thaw it out, the ice crystals will disappear but the damage will be left behind (this is what “freezer burn” is).
So if your food seems a little “squishy” after having been frozen and thawed, that’s why. It’s not rotten; it’s just been stabbed countless times on a microscopic level.
The more times you freeze and thaw and refreeze food, the more this will happen. Your food will degrade in structural integrity each time, but the safety of it won’t have changed meaningfully.
Want to know more?
Further reading:
You can thaw and refreeze meat: five food safety myths busted
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Morning Routines That Just FLOW
“If the hardest thing you have to do in your day is eat a frog, eat that frog first!”, they say.
And, broadly speaking, it is indeed good to get anything stressful out of the way early, so that we can relax afterwards. But…
- Are we truly best at frog-eating when blurry-eyed and sleepy?
- Is there a spoonful of sugar that could make the medicine go down better?
- What do we need to turn eating the frog into an enjoyable activity?
Flow
“Flow” is a concept brought to public consciousness by psychologist Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi, and it refers to a state in which we feel good about what we’re doing, and just keep doing, at a peak performance level.
Writer’s note: as a writer, for example…
Sometimes I do not want to write, I pace to and fro near my computer, going on side-quests like getting a coffee or gazing out of the window into my garden. But once I get going, suddenly, something magical happens and before I know it, I have to trim my writing down because I’ve written too much. That magical window of effortless productivity was a state of flow.
Good morning!
What is a good morning, to you? Build that into your morning! Set parameters around it so you don’t get carried away timewise and find yourself in the afternoon (unless that would work for you!), but first thing in the morning is the time to light up each part of your brain with appropriate neurotransmitters.
Getting the brain juices flowing
Cortisol
When we wake up, we (unless we have some neurochemical imbalance, such as untreated depression) get a spike of cortisol. Cortisol is much-maligned and feared, and indeed it can be very much deleterious to the health in cases of chronic stress. But a little spike now and again is actually beneficial for us.
Quick Tip: if you want to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning cortisol spike, a cold shower is the way to go. Or even just a face-plunge into a bowl of ice-water (put ice in it, give it a couple of minutes to chill the water, then put your face in for a count of 30 seconds, or less if you can’t hold your breath that long).
Serotonin
Serotonin is generally thought of as “the happy chemical”, and it’s stimulated by blue/white light, and also by seeing greenery.
Quick tip: to artificially stimulate (or enhance) a morning serotonin boost, your best friend is sunlight. Even sun through a partly-clouded sky will tend to outperform artificial lighting, including artificial sunlight lighting. Try to get sun between 08:30 and 09:00, if you can. Best of all, do it in your garden or nearby park, as the greenery will be an extra boost!
Dopamine
Generally thought of as “the reward chemical”, but it’s also critical for a lot of kinds of brainwork, including language processing and problem-solving.
Quick Tip: to artificially stimulate* a dopamine surge to get you going, do something that you and/or your body finds rewarding. Examples include:
- Exercise, especially in a vigorous burst
- A good breakfast, a nice coffee, whatever feels right to you
- An app that has motivational bells and whistles, a streak for you to complete, etc
Note: another very enjoyable activity might come to mind that doesn’t even require you getting out of bed. Be aware, however, gentleman-readers specifically, that if you complete that activity, you’ll get a prolactin spike that will wipe out the dopamine you just worked up (because prolactin is antagonistic to dopamine). So that one’s probably better for a lazy morning when you can go back to sleep, than a day when you want to get up and go! Ladies, this is less of a worry for us as the physiology an orgasm driven by estrogen+progesterone rather than testosterone is different; there will not usually be a prolactin spike following the spike of dopamine; our orgasm-related dopamine spike is followed by a wave of oxytocin instead (“the cuddle chemical”), which is much more pleasant than prolactin.
*there’s no “(or enhance)” for this one; you won’t get dopamine from doing nothing, that’s just not how “the reward chemical” works
Flow-building in a stack
When you’ve just woken up and are in a blurry morning haze, that’s not the time to be figuring out “what should I be doing next?”, so instead:
- Work out the things you want to incorporate into your morning routine
- Put them in the order that will be easiest to perform—some things will go a lot better after others!
- Remember to also include things that are simply necessary—morning bathroom ablutions, for example
The goal here is to have a this-and-this-and-this-and-this list of items that you can go through without any deviations, and get in the habit of “after item 1 I automatically do item 2, after which I automatically do item 3, after which…”
Implement this, and your mornings will become practically automated, but in a joyous, life-enhancing way that sets you up in good order for whatever you want/need to do!
Share This Post
-
Self-Compassion – by Dr. Kristin Neff
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of people struggle with self-esteem, and depending on one’s surrounding culture, it can even seem socially obligatory to be constantly valuing oneself highly (or else, who else will if we do not?). But, as Dr. Neff points out, there’s an inherent problem with reinforcing for oneself even a positive message like “I am smart, strong, and capable!” because sometimes all of us have moments of being stupid, weak, and incapable (occasionally all three at once!), which places us in a position of having to choose between self-deceit and self-deprecation, neither of which are good.
Instead, Dr. Neff advocates for self-compassion, for treating oneself as one (hopefully) would a loved one—seeing their/our mistakes, weaknesses, failures, and loving them/ourself anyway.
She does not, however, argue that we should accept just anything from ourselves uncritically, but rather, we identify our mistakes, learn, grow, and progress. So not “I should have known better!”, nor even “How was I supposed to know?!”, but rather, “Now I have learned a thing”.
The style of the book is quite personal, as though having a heart-to-heart over a hot drink perhaps, but the format is organized and progresses naturally from one idea to the next, taking the reader to where we need to be.
Bottom line: if you have trouble with self-esteem (as most people do), then that’s a trap that there is a way out of, and it doesn’t require being perfect or lowering one’s standards, just being kinder to oneself along the way—and this book can help inculcate that.
Click here to check out Self-Compassion, and indeed be kind to yourself!
Share This Post
-
Policosanol: A Rival To Statins, Without The Side Effects?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Policosanol (which can be extracted from various sources, but is mostly made from sugar cane extract) is marketed as lipid-lowering agent for improving cholesterol levels, but its research history has not been without controversy:
2001: it works!
After a lot of research in the 1990s, it came out of the gate strong in 2001, with:
❝Policosanol (5 and 10 mg/day) significantly decreased LDL-cholesterol (17.3% and 26.7%, respectively), total cholesterol (12.9% and 19.5%), as well as the ratios of LDL-cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol (17.2% and 26.5%) and total cholesterol to HDL-cholesterol (16.3% and 21.0%) compared with baseline and placebo❞
This, by the way, is comparable in efficacy to the most powerful statins, but without the adverse side effects.
Source: Efficacy and tolerability of policosanol in hypercholesterolemic postmenopausal women
Furthermore, its effects were not limited to postmenopausal women, and additionally, it was found that 20mg/day was sufficient for optimal effects; 40mg worked exactly the same as 20mg:
2006–2010: we do not trust the Cubans!
After it had been marketed and used in much of the world for some years, extra scrutiny was brought upon it, because the initial studies had been performed by the same lab in Cuba, a commercial lab that had tested them for a private interest (i.e., a company selling the supplement):
Heart Beat: Policosanol: A sweet nothing for high cholesterol
And furthermore, US-based labs were unable to replicate the results:
Policosanols as Nutraceuticals: Fact or Fiction
The Cuban researchers countered that the composition of policosanol as produced in their lab was different than the composition of the policosanol as produced in the US labs, because of the purity of the ingredients used in the Cuban lab.
Which, on the face of it, could be true or could just be the claim of a commercial lab with an association with a company selling a product.
Of course, importing Cuban ingredients to test them in the US was not a reasonably accessible option for the US-based labs, because of the US’s embargo of Cuba. In principle it could be done, but unless there is already a huge clear profit incentive, research scientists are usually on their hands and knees begging for grants already, so getting extra funding for specially-important Cuban ingredients was not going to be likely.
2012: never mind, it does work after all!
An American meta-analysis of 4596 patients from 52 eligible studies (from around the world, so many of them not affected by the US’s embargo; some were from within the US using non-Cuban ingredients, though), found:
❝policosanol is more effective than plant sterols and stanols for LDL level reduction and more favorably alters the lipid profile, approaching antilipemic drug efficacy❞
Those last words there, to be clear, mean “yes, the original claim of being on a par with statins is at least more or less true”.
Source: Meta-Analysis of Natural Therapies for Hyperlipidemia: Plant Sterols and Stanols versus Policosanol
2018: also yes, the Cuban kind does get those extra-effective results, even when tested outside of Cuba
A Korean research team verified this; it’s quite straightforward so for brevity we’ll just drop links:
- Consumption of Cuban Policosanol Improves Blood Pressure and Lipid Profile via Enhancement of HDL Functionality in Healthy Women Subjects: Randomized, Double-Blinded, and Placebo-Controlled Study
- Long-Term Consumption of Cuban Policosanol Lowers Central and Brachial Blood Pressure and Improves Lipid Profile With Enhancement of Lipoprotein Properties in Healthy Korean Participants
Mystery resolved!
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon—it’s not the Cuban kind, because the US’s trade embargo makes it difficult for the US to import even things that are theoretically now exempt from the embargo such as food and medicines. In principle they can now be imported, but in practice, the extra regulations added to Cuban imports make it nearly impossible, especially for small sellers.
Still, it’s 40mg/tablet policosanol from sugar cane extract, and 3rd party lab tested, so it’s the next best thing 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Syringe Exchange Fears Hobble Fight Against West Virginia HIV Outbreak
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
CHARLESTON, http://w.va/. — More than three years have passed since federal health officials arrived in central Appalachia to assess an alarming outbreak of HIV spread mostly between people who inject opioids or methamphetamine.
Infectious disease experts from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention made a list of recommendations following their visit, including one to launch syringe service programs to stop the spread at its source. But those who’ve spent years striving to protect people who use drugs from overdose and illness say the situation likely hasn’t improved, in part because of politicians who contend that such programs encourage illegal drug use.
Joe Solomon is a Charleston City Council member and co-director of SOAR WV, a group that works to address the health needs of people who use drugs. He’s proud of how his close-knit community has risen to this challenge but frustrated with the restraints on its efforts.
“You see a city and a county willing to get to work at a scale that’s bigger than ever before,” Solomon said, “but we still have one hand tied behind our back.”
The hand he references is easier access to clean syringes.
In April 2021, the CDC came to Charleston — the seat of Kanawha County and the state capital, tucked into the confluence of the Kanawha and Elk rivers — to investigate dozens of newly detected HIV infections. The CDC’s HIV intervention chief called it “the most concerning HIV outbreak in the United States” and warned that the number of reported diagnoses could be just “the tip of the iceberg.”
Now, despite attention and resources directed toward the outbreak, researchers and health workers say HIV continues to spread. In large part, they say, the outbreak lingers because of restrictions state and local policymakers have placed on syringe exchange efforts.
Research indicates that syringe service programs are associated with an estimated 50% reduction in HIV and hepatitis C, and the CDC issued recommendations to steer a response to the outbreak that emphasized the need for improved access to those services.
That advice has thus far gone unheeded by local officials.
In late 2015, the Kanawha-Charleston Health Department launched a syringe service program but shuttered it in 2018 under pressure, with then-Mayor Danny Jones calling it a “mini-mall for junkies and drug dealers.”
SOAR stepped in, hosting health fairs at which it distributed naloxone, an opioid overdose reversal drug; offered treatment and referrals; provided HIV testing; and exchanged clean syringes for used ones.
But in April 2021, the state legislature passed a bill limiting the number of syringes people could exchange and made it mandatory to present a West Virginia ID. The Charleston City Council subsequently added guidelines of its own, including requiring individual labeling of syringes.
As a result of these restrictions, SOAR ceased exchanging syringes. West Virginia Health Right now operates an exchange program in the city under the restrictions.
Robin Pollini is a West Virginia University epidemiologist who conducts community-based research on injection drug use. “Anyone I’ve talked to who’s used that program only used it once,” she said. “And the numbers they report to the state bear that out.”
A syringe exchange run by the health department in nearby Cabell County — home to Huntington, the state’s largest city after Charleston — isn’t so constrained. As Solomon notes, that program exchanges more than 200 syringes for every one exchanged in Kanawha.
A common complaint about syringe programs is that they result in discarded syringes in public spaces. Jan Rader, director of Huntington’s Mayor’s Office of Public Health and Drug Control Policy, is regularly out on the streets and said she seldom encounters discarded syringes, pointing out that it’s necessary to exchange a used syringe for a new one.
In August 2023, the Charleston City Council voted down a proposal from the Women’s Health Center of West Virginia to operate a syringe exchange in the city’s West Side community, with opponents expressing fears of an increase in drug use and crime.
Pollini said it’s difficult to estimate the number of people in West Virginia with HIV because there’s no coordinated strategy for testing; all efforts are localized.
“You would think that in a state that had the worst HIV outbreak in the country,” she said, “by this time we would have a statewide testing strategy.”
In addition to the testing SOAR conducted in 2021 at its health fairs, there was extensive testing during the CDC’s investigation. Since then, the reported number of HIV cases in Kanawha County has dropped, Pollini said, but it’s difficult to know if that’s the result of getting the problem under control or the result of limited testing in high-risk groups.
“My inclination is the latter,” she said, “because never in history has there been an outbreak of injection-related HIV among people who use drugs that was solved without expanding syringe services programs.”
“If you go out and look for infections,” Pollini said, “you will find them.”
Solomon and Pollini praised the ongoing outreach efforts — through riverside encampments, in abandoned houses, down county roads — of the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program to test those at highest risk: people known to be injecting drugs.
“It’s miracle-level work,” Solomon said.
But Christine Teague, Ryan White Program director at the Charleston Area Medical Center, acknowledged it hasn’t been enough. In addition to HIV, her concerns include the high incidence of hepatitis C and endocarditis, a life-threatening inflammation of the lining of the heart’s chambers and valves, and the cost of hospital resources needed to address them.
“We’ve presented that data to the legislature,” she said, “that it’s not just HIV, it’s all these other lengthy hospital admissions that, essentially, Medicaid is paying for. And nothing seems to penetrate.”
Frank Annie is a researcher at CAMC specializing in cardiovascular diseases, a member of the Charleston City Council, and a proponent of syringe service programs. Research he co-authored found 462 cases of endocarditis in southern West Virginia associated with injection drug use, at a cost to federal, state, and private insurers of more than $17 million, of which less than $4 million was recovered.
Teague is further concerned for West Virginia’s rural counties, most of which don’t have a syringe service program.
Tasha Withrow, a harm reduction advocate in bordering rural Putnam County, said her sense is that HIV numbers aren’t alarmingly high there but said that, with little testing and heightened stigma in a rural community, it’s difficult to know.
In a January 2022 follow-up report, the CDC recommended increasing access to harm reduction services such as syringe service programs through expansion of mobile services, street outreach, and telehealth, using “patient-trusted” individuals, to improve the delivery of essential services to people who use drugs.
Teague would like every rural county to have a mobile unit, like the one operated by her organization, offering harm reduction supplies, medication, behavioral health care, counseling, referrals, and more. That’s an expensive undertaking. She suggested opioid settlement money through the West Virginia First Foundation could pay for it.
Pollini said she hopes state and local officials allow the experts to do their jobs.
“I would like to see them allow us to follow the science and operate these programs the way they’re supposed to be run, and in a broader geography,” she said. “Which means that it shouldn’t be a political decision; it should be a public health decision.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
This article first appeared on KFF Health News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How a Friend’s Death Turned Colorado Teens Into Anti-Overdose Activists
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Gavinn McKinney loved Nike shoes, fireworks, and sushi. He was studying Potawatomi, one of the languages of his Native American heritage. He loved holding his niece and smelling her baby smell. On his 15th birthday, the Durango, Colorado, teen spent a cold December afternoon chopping wood to help neighbors who couldn’t afford to heat their homes.
McKinney almost made it to his 16th birthday. He died of fentanyl poisoning at a friend’s house in December 2021. His friends say it was the first time he tried hard drugs. The memorial service was so packed people had to stand outside the funeral home.
Now, his peers are trying to cement their friend’s legacy in state law. They recently testified to state lawmakers in support of a bill they helped write to ensure students can carry naloxone with them at all times without fear of discipline or confiscation. School districts tend to have strict medication policies. Without special permission, Colorado students can’t even carry their own emergency medications, such as an inhaler, and they are not allowed to share them with others.
“We realized we could actually make a change if we put our hearts to it,” said Niko Peterson, a senior at Animas High School in Durango and one of McKinney’s friends who helped write the bill. “Being proactive versus being reactive is going to be the best possible solution.”
Individual school districts or counties in California, Maryland, and elsewhere have rules expressly allowing high school students to carry naloxone. But Jon Woodruff, managing attorney at the Legislative Analysis and Public Policy Association, said he wasn’t aware of any statewide law such as the one Colorado is considering. Woodruff’s Washington, D.C.-based organization researches and drafts legislation on substance use.
Naloxone is an opioid antagonist that can halt an overdose. Available over the counter as a nasal spray, it is considered the fire extinguisher of the opioid epidemic, for use in an emergency, but just one tool in a prevention strategy. (People often refer to it as “Narcan,” one of the more recognizable brand names, similar to how tissues, regardless of brand, are often called “Kleenex.”)
The Biden administration last year backed an ad campaign encouraging young people to carry the emergency medication.
Most states’ naloxone access laws protect do-gooders, including youth, from liability if they accidentally harm someone while administering naloxone. But without school policies explicitly allowing it, the students’ ability to bring naloxone to class falls into a gray area.
Ryan Christoff said that in September 2022 fellow staff at Centaurus High School in Lafayette, Colorado, where he worked and which one of his daughters attended at the time, confiscated naloxone from one of her classmates.
“She didn’t have anything on her other than the Narcan, and they took it away from her,” said Christoff, who had provided the confiscated Narcan to that student and many others after his daughter nearly died from fentanyl poisoning. “We should want every student to carry it.”
Boulder Valley School District spokesperson Randy Barber said the incident “was a one-off and we’ve done some work since to make sure nurses are aware.” The district now encourages everyone to consider carrying naloxone, he said.
Community’s Devastation Turns to Action
In Durango, McKinney’s death hit the community hard. McKinney’s friends and family said he didn’t do hard drugs. The substance he was hooked on was Tapatío hot sauce — he even brought some in his pocket to a Rockies game.
After McKinney died, people started getting tattoos of the phrase he was known for, which was emblazoned on his favorite sweatshirt: “Love is the cure.” Even a few of his teachers got them. But it was classmates, along with their friends at another high school in town, who turned his loss into a political movement.
“We’re making things happen on behalf of him,” Peterson said.
The mortality rate has spiked in recent years, with more than 1,500 other children and teens in the U.S. dying of fentanyl poisoning the same year as McKinney. Most youth who die of overdoses have no known history of taking opioids, and many of them likely thought they were taking prescription opioids like OxyContin or Percocet — not the fake prescription pills that increasingly carry a lethal dose of fentanyl.
“Most likely the largest group of teens that are dying are really teens that are experimenting, as opposed to teens that have a long-standing opioid use disorder,” said Joseph Friedman, a substance use researcher at UCLA who would like to see schools provide accurate drug education about counterfeit pills, such as with Stanford’s Safety First curriculum.
Allowing students to carry a low-risk, lifesaving drug with them is in many ways the minimum schools can do, he said.
“I would argue that what the schools should be doing is identifying high-risk teens and giving them the Narcan to take home with them and teaching them why it matters,” Friedman said.
Writing in The New England Journal of Medicine, Friedman identified Colorado as a hot spot for high school-aged adolescent overdose deaths, with a mortality rate more than double that of the nation from 2020 to 2022.
“Increasingly, fentanyl is being sold in pill form, and it’s happening to the largest degree in the West,” said Friedman. “I think that the teen overdose crisis is a direct result of that.”
If Colorado lawmakers approve the bill, “I think that’s a really important step,” said Ju Nyeong Park, an assistant professor of medicine at Brown University, who leads a research group focused on how to prevent overdoses. “I hope that the Colorado Legislature does and that other states follow as well.”
Park said comprehensive programs to test drugs for dangerous contaminants, better access to evidence-based treatment for adolescents who develop a substance use disorder, and promotion of harm reduction tools are also important. “For example, there is a national hotline called Never Use Alone that anyone can call anonymously to be supervised remotely in case of an emergency,” she said.
Taking Matters Into Their Own Hands
Many Colorado school districts are training staff how to administer naloxone and are stocking it on school grounds through a program that allows them to acquire it from the state at little to no cost. But it was clear to Peterson and other area high schoolers that having naloxone at school isn’t enough, especially in rural places.
“The teachers who are trained to use Narcan will not be at the parties where the students will be using the drugs,” he said.
And it isn’t enough to expect teens to keep it at home.
“It’s not going to be helpful if it’s in somebody’s house 20 minutes outside of town. It’s going to be helpful if it’s in their backpack always,” said Zoe Ramsey, another of McKinney’s friends and a senior at Animas High School.
“We were informed it was against the rules to carry naloxone, and especially to distribute it,” said Ilias “Leo” Stritikus, who graduated from Durango High School last year.
But students in the area, and their school administrators, were uncertain: Could students get in trouble for carrying the opioid antagonist in their backpacks, or if they distributed it to friends? And could a school or district be held liable if something went wrong?
He, along with Ramsey and Peterson, helped form the group Students Against Overdose. Together, they convinced Animas, which is a charter school, and the surrounding school district, to change policies. Now, with parental permission, and after going through training on how to administer it, students may carry naloxone on school grounds.
Durango School District 9-R spokesperson Karla Sluis said at least 45 students have completed the training.
School districts in other parts of the nation have also determined it’s important to clarify students’ ability to carry naloxone.
“We want to be a part of saving lives,” said Smita Malhotra, chief medical director for Los Angeles Unified School District in California.
Los Angeles County had one of the nation’s highest adolescent overdose death tallies of any U.S. county: From 2020 to 2022, 111 teens ages 14 to 18 died. One of them was a 15-year-old who died in a school bathroom of fentanyl poisoning. Malhotra’s district has since updated its policy on naloxone to permit students to carry and administer it.
“All students can carry naloxone in our school campuses without facing any discipline,” Malhotra said. She said the district is also doubling down on peer support and hosting educational sessions for families and students.
Montgomery County Public Schools in Maryland took a similar approach. School staff had to administer naloxone 18 times over the course of a school year, and five students died over the course of about one semester.
When the district held community forums on the issue, Patricia Kapunan, the district’s medical officer, said, “Students were very vocal about wanting access to naloxone. A student is very unlikely to carry something in their backpack which they think they might get in trouble for.”
So it, too, clarified its policy. While that was underway, local news reported that high school students found a teen passed out, with purple lips, in the bathroom of a McDonald’s down the street from their school, and used Narcan to revive them. It was during lunch on a school day.
“We can’t Narcan our way out of the opioid use crisis,” said Kapunan. “But it was critical to do it first. Just like knowing 911.”
Now, with the support of the district and county health department, students are training other students how to administer naloxone. Jackson Taylor, one of the student trainers, estimated they trained about 200 students over the course of three hours on a recent Saturday.
“It felt amazing, this footstep toward fixing the issue,” Taylor said.
Each trainee left with two doses of naloxone.
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wise Old Fool
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
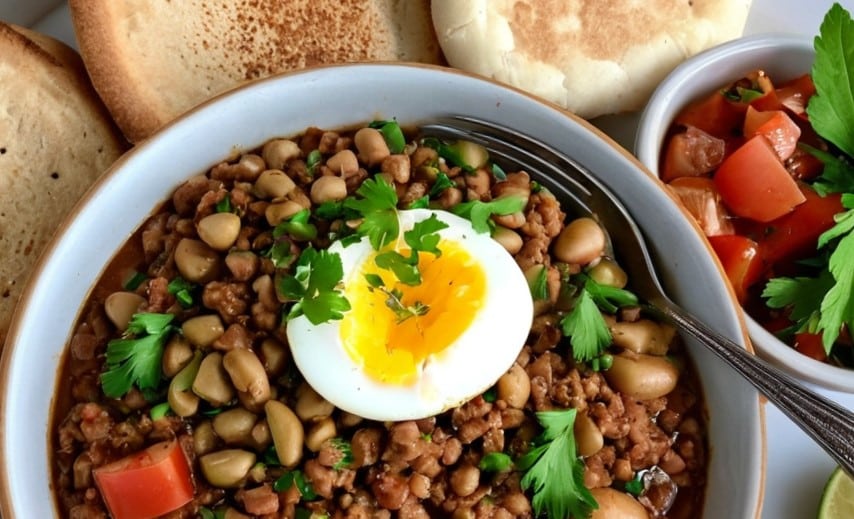
How old is this dish? Well, let’s put it this way, it used to be called “𓅮𓏏𓈖” and remnants of it have been found at neolithic burial sites in Egypt. Nowadays it’s called “فول مدمس”, which gets rendered a lot of different ways in the Latin alphabet, but “fūl mudammas” is one option. For short, it’s just called “fūl”, which is pronounced like the English word “fool”, and it’s about the beans.
From chana masala with poori to frijoles refritos to beans on toast, lots of cultures have some version of this breakfast food, and all can be great (yes, even the beans on toast). But today we’re about this particular kind of morning protein, fiber, fats, and healthful spices.
You will need
- 2x 14 oz cans fava beans (other kinds of beans work as substitute; kidney beans are common substitution, but this writer prefers black beans personally if she doesn’t have fava in), drained
- 4 garlic cloves, crushed
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 teaspoon sweet cinnamon (or ½ sweet cinnamon stick)
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 tsp paprika
- 1 tsp black pepper
- Juice of ½ lemon
- For the relish: 1 medium tomato, finely chopped; 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil; 2 tbsp parsley, finely chopped
- To serve: 4 pitta breads, 2 eggs (omit if vegan), and a selection of pickled vegetables, drained
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the olive oil to a saucepan over a medium heat; add the garlic, cumin seeds, and cinnamon. Keep these moving for a minute or two before moving to the next step.
2) Add the fava beans, as well as the other seasonings (chili flakes, paprika, black pepper), and mix thoroughly
3) Add 1 cup boiling water, and keep everything on a simmer for about 20 minutes, stirring often. Add the lemon juice while it’s simmering; when the beans start to break down and the mixture starts to thicken, it’s ready.
4) Mix the relish ingredients (finely chopped tomato, olive oil, parsley) thoroughly in a small bowl
5) Toast the pitta breads, and if using, soft-boil the eggs.
6) Serve! We suggest: fūl in a bowl, with one half of a soft-boiled egg per bowl, topped with the relish, and served with the pitta bread and pickled vegetables on the side.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Less Obvious Probiotic Benefits ← the pickled vegetables contain the probiotics here, while the beans are a great source of prebiotic fiber; this is why they work so well together
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- A Tale Of Two Cinnamons
- Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: