Fix Chronic Fatigue & Regain Your Energy, By Science
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Chronic fatigue is on the rise. A lot of it appears to be Long COVID-related, but whether that’s the case for you or not, one thing that will make a big difference to your energy levels is something that French biochemist Jessie Inchauspé is here to explain:
Mitochondrial management
Inchauspé explains it in terms of a steam train; to keep running, it must have coal burning in its furnace. However, if more coal is delivered to the engine room faster than it can be put in the furnace and burned, and the coal just keeps on coming, the worker there will soon be overwhelmed trying to find places to put it all; the engine room will be full of coal, and the furnace will sputter and go out because the worker can’t even reach it on account of being buried in coal.
So it is with our glucose metabolism also. If we get spikes of glucose faster than our body can deal with them, it will overload the body’s ability to process that energy at all. Just like the steam train worker, our body will try! It’ll stuff that extra glucose wherever it can (storing as glycogen in the liver is a readily available option that’s easy to do and/but also gives you non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and isn’t quickly broken down into useable energy), and meanwhile, your actual mitochondria aren’t getting what they need (which is: a reliable, but gentle, influx of glucose).
You can imagine that the situation we described in the steam train isn’t good for the engine’s longevity, and the corresponding situation in the human body isn’t good for our mitochondria either (or our pancreas, or our liver, or… the list goes on). Indeed, damaged mitochondria affect exercise capacity and stress resilience—as well as being a long-term driver of cancer.
The remedy, of course, is blood sugar management. Specifically, avoiding glucose spikes. She has a list of 10 ways to do this (small changes to how we eat; what things to eat with what, in which order, etc) that make a huge measurable difference. For your convenience, we’ve linked those ten ways below; first though, if you’d like to hear it from Inchauspé directly (her style is very pleasant), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- 10 Ways To Balance Your Blood Sugars ← this is the longer list she’s referring to in the video!
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver ← also relevant
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
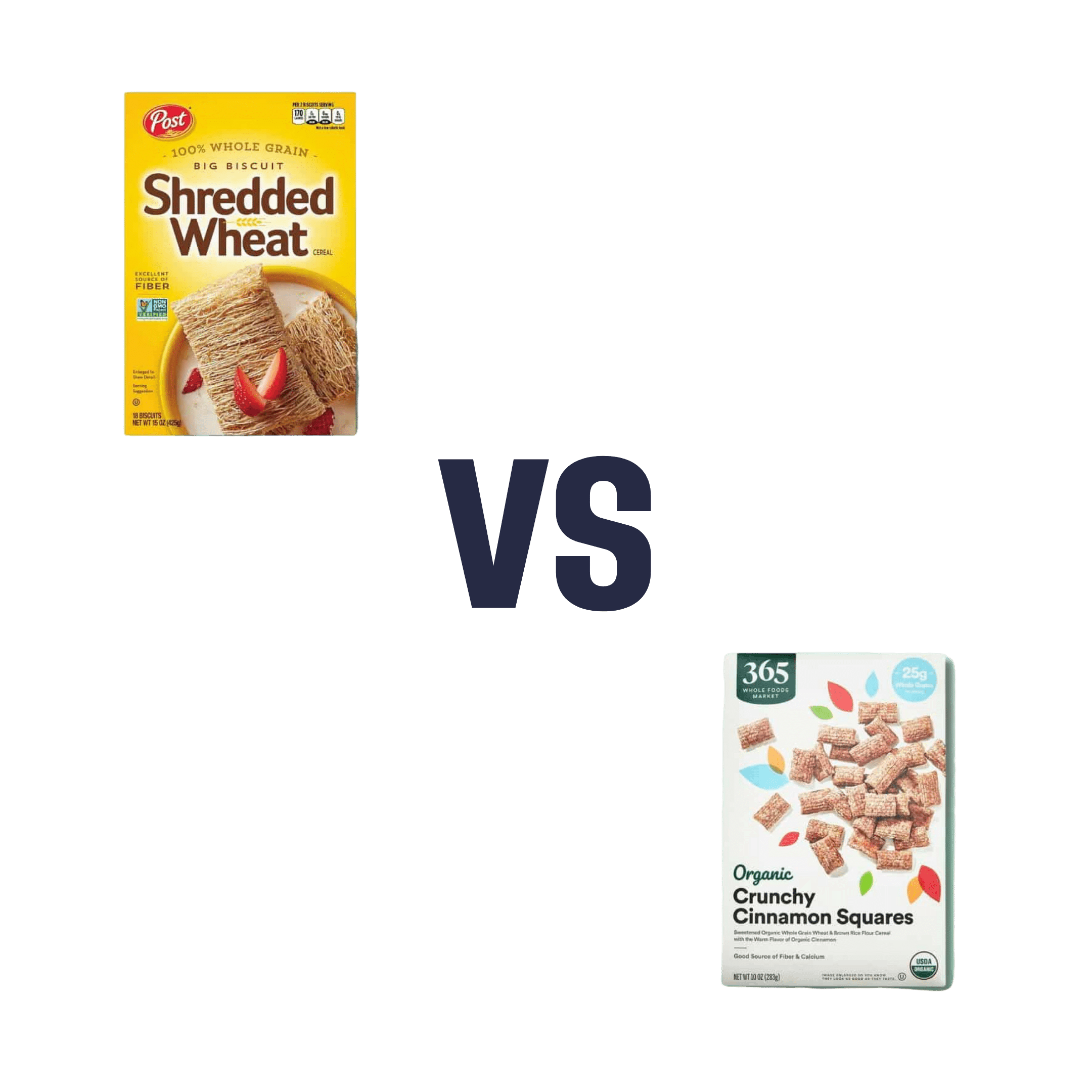
Shredded Wheat vs Organic Crunch – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Shredded Wheat to Organic Crunch, we picked the Shredded Wheat.
Why?
In this battle of the cereals, it comes down to the ingredients:
- The Shredded Wheat cereal has two ingredients: wheat (shredded), and BHT. The latter is a phenolic compound and antioxidant.
- The Organic Crunch cereal has lots of ingredients, of which the first two are wheat flour, and sugar.
This means that, per serving…
- The Shredded Wheat cereal has 7g fiber and 0g sugar
- The Organic Crunch cereal has 3g fiber and 12g sugar
Quite a difference! Sometimes, the “Organic Crunch” of a product comes from crunchy sugar.
You can check them out side-by-side here:
Shredded Wheat | Organic Crunch
Want to know more?
There’s a popular view that the only way to get fiber is to eat things that look (and potentially taste) like cardboard. Not so! There are delicious options:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
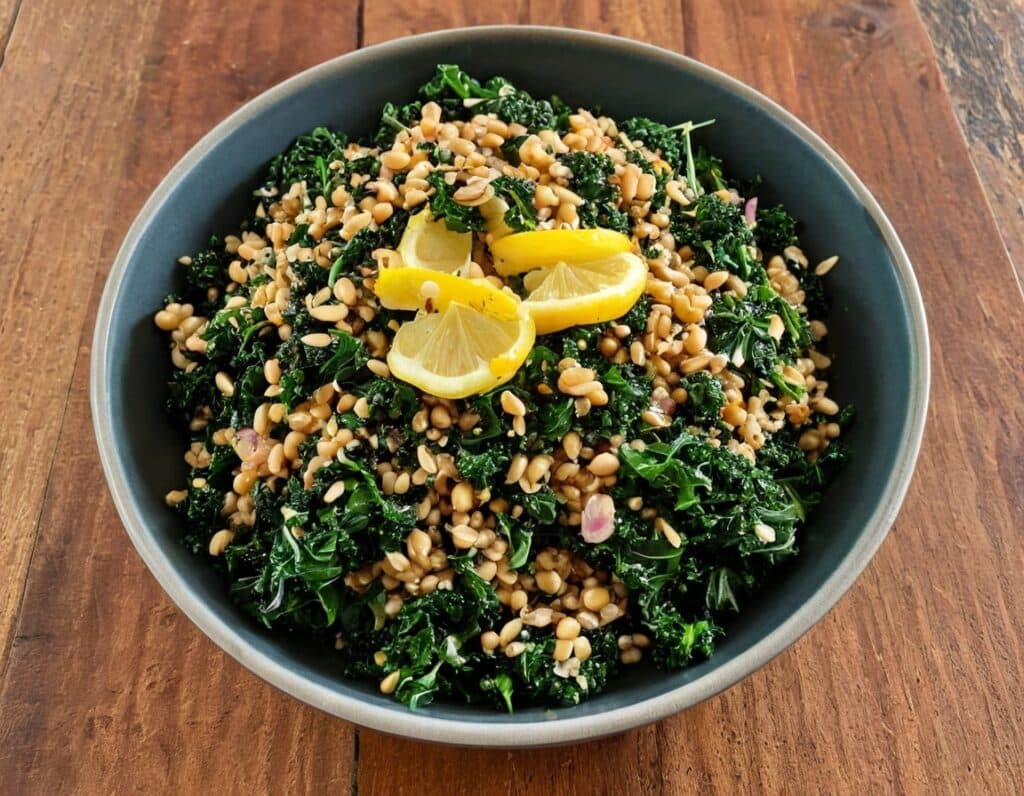
SMOL Bowl With Sautéed Greens
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Whole grains are good, and gluten is bad for some people. Today’s dish has four whole grains, and no gluten (assuming no cross-contamination, so look for the gluten-free label if that’s important to you). Breafast? Brunch? Lunch? Supper, even? This is good at any time of day, packed with nutrients and full of flavor!
You will need (per person)
- 1 cup mixed cooked grains of equal parts sorghum, millet, oats, lentils (SMOL)—these can be cooked in bulk in advance and frozen in portions, as it’s often good to used mixed grains, and these four are a great combination for many purposes.
- ½ cup low sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made this yourself from vegetable offcuts you kept in the freezer until you had enough for this purpose, but failing that, low-sodium stock cubes can be bought at most large supermarkets).
- ½ cup finely chopped red onion
- 6 oz cavolo nero, finely chopped
- 1 small carrot, finely chopped
- 3 cloves garlic, finely chopped
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- To serve: 1 lemon wedge
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Add the stock to a sauté pan over a medium heat, and add the onion, garlic, and carrot. Stir frequently for about 7 minutes.
2) Add the cavolo nero and miso paste, stirring for another 4 minutes. If there is any liquid remaining, drain it off now.
3) Warm the SMOL mixture (microwave is fine) and spoon it into a bowl, topping with the nutritional yeast and black pepper. Finally, add the hot cavolo nero mixture.
4) Serve with the lemon wedge on the side, to add a dash of lemon at will.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
We’re only using a fraction of health workers’ skills. This needs to change
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Roles of health professionals are still unfortunately often stuck in the past. That is, before the shift of education of nurses and other health professionals into universities in the 1980s. So many are still not working to their full scope of practice.
There has been some expansion of roles in recent years – including pharmacists prescribing (under limited circumstances) and administering a wider range of vaccinations.
But the recently released paper from an independent Commonwealth review on health workers’ “scope of practice” identifies the myriad of barriers preventing Australians from fully benefiting from health professionals’ skills.
These include workforce design (who does what, where and how roles interact), legislation and regulation (which often differs according to jurisdiction), and how health workers are funded and paid.
There is no simple quick fix for this type of reform. But we now have a sensible pathway to improve access to care, using all health professionals appropriately.
A new vision for general practice
I recently had a COVID booster. To do this, I logged onto my general practice’s website, answered the question about what I wanted, booked an appointment with the practice nurse that afternoon, got jabbed, was bulk-billed, sat down for a while, and then went home. Nothing remarkable at all about that.
But that interaction required a host of facilitating factors. The Victorian government regulates whether nurses can provide vaccinations, and what additional training the nurse requires. The Commonwealth government has allowed the practice to be paid by Medicare for the nurse’s work. The venture capitalist practice owner has done the sums and decided allocating a room to a practice nurse is economically rational.
The future of primary care is one involving more use of the range of health professionals, in addition to GPs.
It would be good if my general practice also had a physiotherapist, who I could see if I had back pain without seeing the GP, but there is no Medicare rebate for this. This arrangement would need both health professionals to have access to my health record. There also needs to be trust and good communication between the two when the physio might think the GP needs to be alerted to any issues.
This vision is one of integrated primary care, with health professionals working in a team. The nurse should be able to do more than vaccination and checking vital signs. Do I really need to see the GP every time I need a prescription renewed for my regular medication? This is the nub of the “scope of practice” issue.
How about pharmacists?
An integrated future is not the only future on the table. Pharmacy owners especially have argued that pharmacists should be able to practise independently of GPs, prescribing a limited range of medications and dispensing them.
This will inevitably reduce continuity of care and potentially create risks if the GP is not aware of what other medications a patient is using.
But a greater role for pharmacists has benefits for patients. It is often easier and cheaper for the patient to see a pharmacist, especially as bulk billing rates fall, and this is one of the reasons why independent pharmacist prescribing is gaining traction.
It’s often easier for a patient to see a pharmacist than a GP. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock Every five years or so the government negotiates an agreement with the Pharmacy Guild, the organisation of pharmacy owners, about how much pharmacies will be paid for dispensing medications and other services. These agreements are called “Community Pharmacy Agreements”. Paying pharmacists independent prescribing may be part of the next agreement, the details of which are currently being negotiated.
GPs don’t like competition from this new source, even though there will be plenty of work around for GPs into the foreseeable future. So their organisations highlight the risks of these changes, reopening centuries old turf wars dressed up as concerns about safety and risk.
Who pays for all this?
Funding is at the heart of disputes about scope of practice. As with many policy debates, there is merit on both sides.
Clearly the government must increase its support for comprehensive general practice. Existing funding of fee-for-service medical benefits payments must be redesigned and supplemented by payments that allow practices to engage a range of other health professionals to create health-care teams.
This should be the principal direction of primary care reform, and the final report of the scope of practice review should make that clear. It must focus on the overall goal of better primary care, rather than simply the aspirations of individual health professionals, and working to a professional’s full scope of practice in a team, not a professional silo.
In parallel, governments – state and federal – must ensure all health professionals are used to their best of their abilities. It is a waste to have highly educated professionals not using their skills fully. New funding arrangements should facilitate better access to care from all appropriately qualified health professionals.
In the case of prescribing, it is possible to reconcile the aspirations of pharmacists and the concerns of GPs. New arrangements could be that pharmacists can only renew medications if they have agreements with the GP and there is good communication between them. This may be easier in rural and suburban areas, where the pharmacists are better known to the GPs.
The second issues paper points to the complexity of achieving scope of practice reforms. However, it also sets out a sensible path to improve access to care using all health professionals appropriately.
Stephen Duckett, Honorary Enterprise Professor, School of Population and Global Health, and Department of General Practice and Primary Care, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Why Your Brain Blinds You For 2 Hours Every Day
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
…and then covers its tracks so that you don’t notice:
Now you see it…
The world you experience is not an accurate representation of reality. Your brain actively constructs your perception, editing your memories as they happen and manipulating your sense of time. What you perceive as the present moment is actually a processed and reconstructed version of past events.
Nor is your vision anywhere near as detailed as it seems. Only a small central portion is in high resolution, while the rest is blurry. Your brain compensates for this by filling in the gaps with its best guess and/or what it believes is there from the last time you saw it. Your eyes constantly make rapid movements called saccades, and during these (i.e. when your eyes are moving), your vision momentarily shuts down—making you effectively blind for (in total, if we add them all up) about two hours every day (according to this video, anyway; our calculations find it to be more than that, but you get the idea). Your brain stitches together the visual input, creating a seamless experience that feels continuous (much like an animation reel composed of still images).
Why does it do this?
It’s because your senses operate at different speeds—light reaches your eyes in nanoseconds, sound in milliseconds, and touch signals in tens of milliseconds. However, your brain processes these inputs together, creating the illusion of a smooth and simultaneous experience. In reality, what you perceive as the present is actually a delayed and selectively edited version of the past.
Instead of showing you the world as it is, your brain predicts what will happen next. In high-speed situations, such as playing table tennis, if your brain relied on past sensory data, you wouldn’t react in time. Instead, it estimates an object’s future position and presents that prediction as your visual reality.
This also means that because your brain effectively sees things slightly sooner than you do, your brain has already prepared multiple possible responses and when an event occurs, it quickly selects the most likely course of action, deleting the alternatives before you are even aware of them. By the time you think you’ve made a decision, your body has already acted.
This goes for more than just the things we think of as requiring quick reactions!
Walking is a complex task that involves multiple time layers—your brain processes past feedback, assesses your current state, and predicts future movements. That’s why it was something that cyberneticists found difficult to recreate for a very long time. If something unexpected happens, like slipping cartoon-style on a banana peel, your body reacts before you consciously notice the danger. Your spinal cord and brainstem trigger emergency reflexes to stabilize you before your conscious mind even catches up.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
This Main Feature Should Take You Two Minutes (and 18 Seconds) To Read ← There’s a problem nobody wants to talk about when it comes to speed-reading; can you guess what it is based on what we just talked about above?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Happy Mind, Happy Life – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s start with a “why”. If happiness doesn’t strike you as a worthwhile goal in and of itself, Dr. Chatterjee discusses the health implications of happiness/unhappiness.
And, yes, including in studies where other factors were controlled for, so he shows how happiness/unhappiness does really have a causal role in health—it’s not just a matter of “breaking news: sick people are less happy”.
The author, a British GP (General Practitioner, the equivalent of what the US calls a “family doctor”) with decades of experience, has found a lot of value in the practice of holistic medicine. For this reason, it’s what he recommends to his patients at work, in his books, his blog, and his regular spot on a popular BBC breakfast show.
The writing style is relaxed and personable, without skimping on information density. Indeed, Dr. Chatterjee offers many pieces of holistic health advice, and dozens of practical exercises to boost your happiness and proof you against adversity.
Because, whatever motivational speakers may say, we can’t purely “think ourselves happy”; sometimes we have real external threats and bad things in life. But, we can still improve our experience of even these things, not to mention suffer less, and get through it in better shape with a smile at the end of it.
Bottom line: if you’d like to be happier and healthier (who wouldn’t?), then this book is a sure-fire way to set you on that path.
Click here to check out Happy Mind, Happy Life and upgrade yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes – by Dr. Marie Feldman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book doesn’t assume prior knowledge, and does explain the science of diabetes, prediabetes, the terms and the symptoms, what’s going on inside, etc—before getting onto the main meat of the book, the tips.
The promised 100 tips are varied in their application; they range from diet and exercise, to matters of sleep, stress, and even love.
There are bonus tips too! For example, an appendix covers “tips for healthier eating out” (i.e. in restaurants etc) and a grocery list to ensure your pantry is good for defending you against prediabetes.
The writing style is very accessible pop-science; this isn’t like reading some dry academic paper—though it does cite its sources for claims, which we always love to see.
Bottom line: if you’d like to proof yourself against prediabetes, and are looking for “small things that add up” habits to get into to achieve that, this book is an excellent first choice.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: