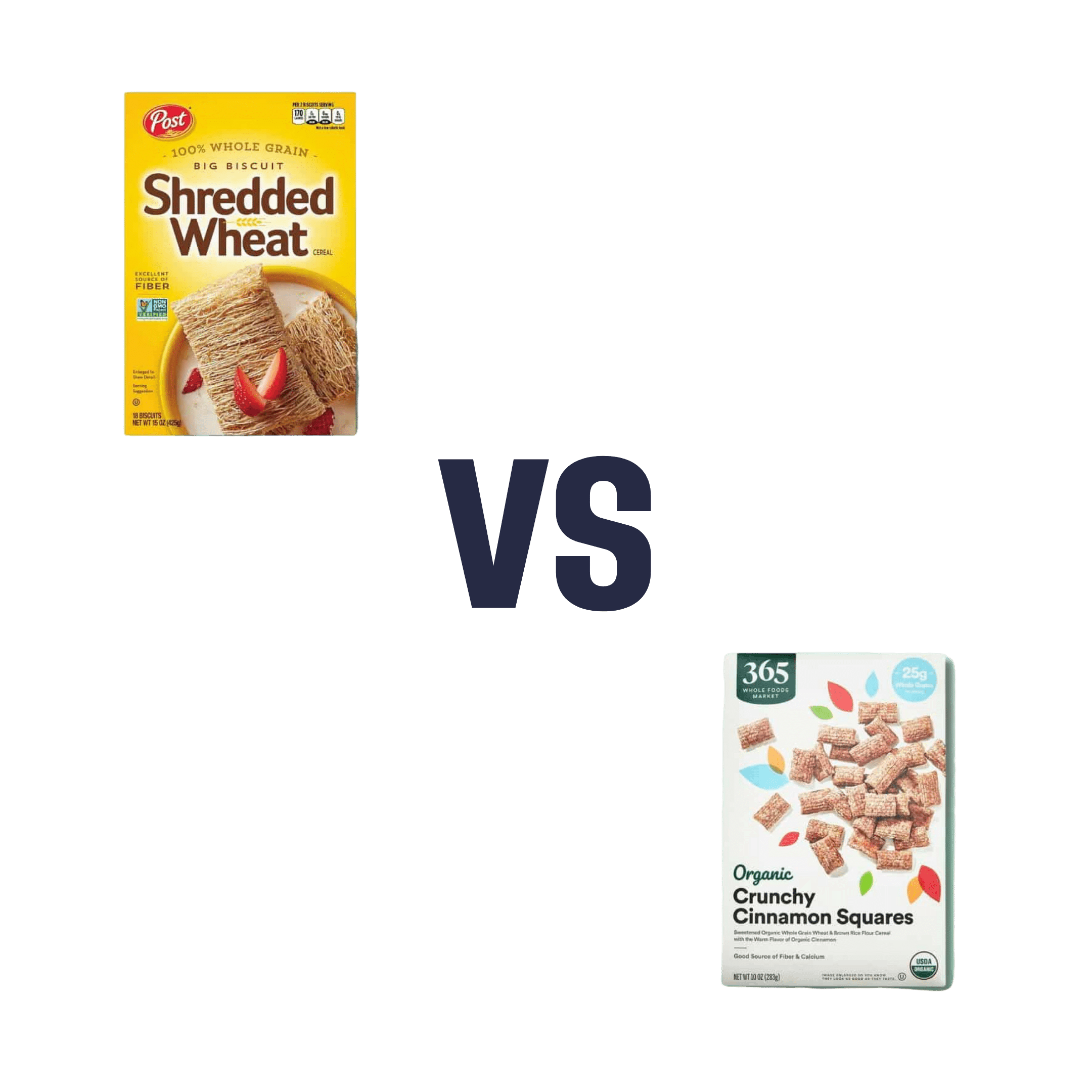
Shredded Wheat vs Organic Crunch – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing Shredded Wheat to Organic Crunch, we picked the Shredded Wheat.
Why?
In this battle of the cereals, it comes down to the ingredients:
- The Shredded Wheat cereal has two ingredients: wheat (shredded), and BHT. The latter is a phenolic compound and antioxidant.
- The Organic Crunch cereal has lots of ingredients, of which the first two are wheat flour, and sugar.
This means that, per serving…
- The Shredded Wheat cereal has 7g fiber and 0g sugar
- The Organic Crunch cereal has 3g fiber and 12g sugar
Quite a difference! Sometimes, the “Organic Crunch” of a product comes from crunchy sugar.
You can check them out side-by-side here:
Shredded Wheat | Organic Crunch
Want to know more?
There’s a popular view that the only way to get fiber is to eat things that look (and potentially taste) like cardboard. Not so! There are delicious options:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
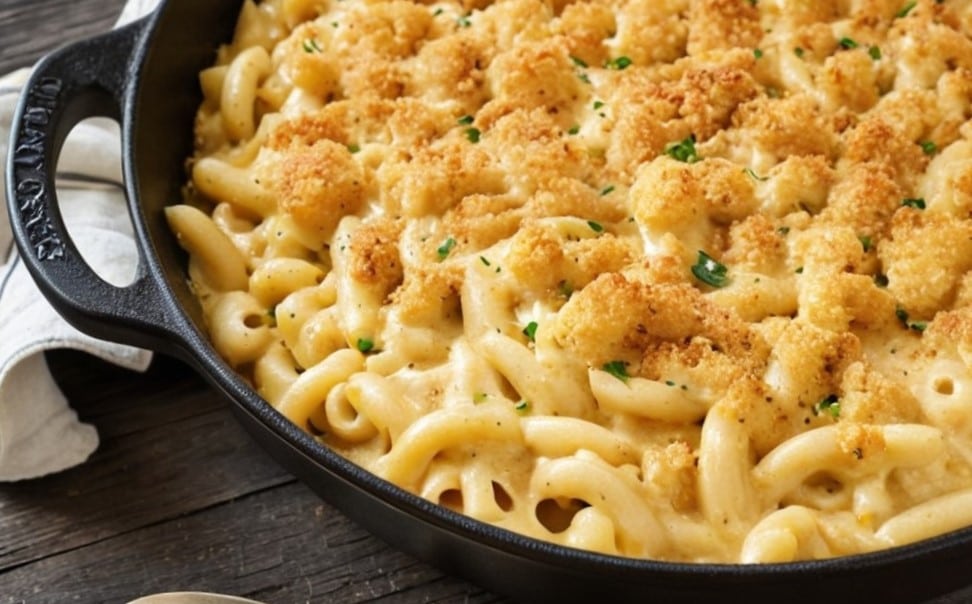
Healthy Butternut Macaroni Cheese
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A comfort food classic, healthy and plant-based, without skimping on the comfort.
You will need
- ½ butternut squash, peeled and cut into small pieces (if buying ready-chopped, this should be about 1 lb)
- 1 onion, chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 12 oz (or thereabouts) wholegrain macaroni, or similar pasta shape (even penne works fine—which is good, as it’s often easier to buy wholegrain penne than wholegrain macaroni) (substitute with a gluten-free pasta such as buckwheat pasta, if avoiding gluten)
- 6 oz (or thereabouts) cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 15 minutes (but longer is better)
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend hazelnut for its mellow nutty flavor)
- 3 tbsp nutritional yeast
- Juice of ½ lemon
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: smoked paprika, to serve
Note: if you are allergic to nuts, please accept our apologies that there’s no substitution available in this one. Simply put, removing the cashews would mean changing most of the rest of the recipe to compensate, so there’s no easy “or substitute with…” that we can mention. We’ll have to find/develop a good healthy plant-based no-nuts recipe for you at a later date.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the butternut squash, onion, and garlic with the olive oil, in a large roasting tin, tossing thoroughly to ensure an even coat of oil. Roast them for about 25 minutes until soft.
3) Cook the macaroni while you wait (this should take about 10 minutes or so in salted water), drain, and rinse thoroughly in cold water, before setting aside. This cooling increases the pasta’s resistant starch content (that’s good, for your gut and for your blood sugars, and thus also for your heart and brain), and it will maintain this benefit even when we reheat it later.
4) Drain the cashews, and tip them into a high-speed blender with the milk, and process until smooth. Add the roasted vegetables and the remaining ingredients apart from the pasta, and continue to process until again smooth. You can add a little more milk if you need to, but go easy with it.
5) Heat the sauce (that you just made in the food processor) gently in a saucepan, and refresh the pasta by pouring a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander.
6) Optional: combine the pasta and sauce in an ovenproof dish or cast iron pan, and give it a few minutes under the hottest grill (or browning iron, if you have such) your oven can muster. Alternatively, use a culinary blowtorch, if you have one.
7) Serve; and if you didn’t do the optional step above, this means combining the pasta and sauce. You can also dust the top with some extra seasonings if you like. Smoked paprika works well for this.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Butternut Squash vs Pumpkin – Which is Healthier?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
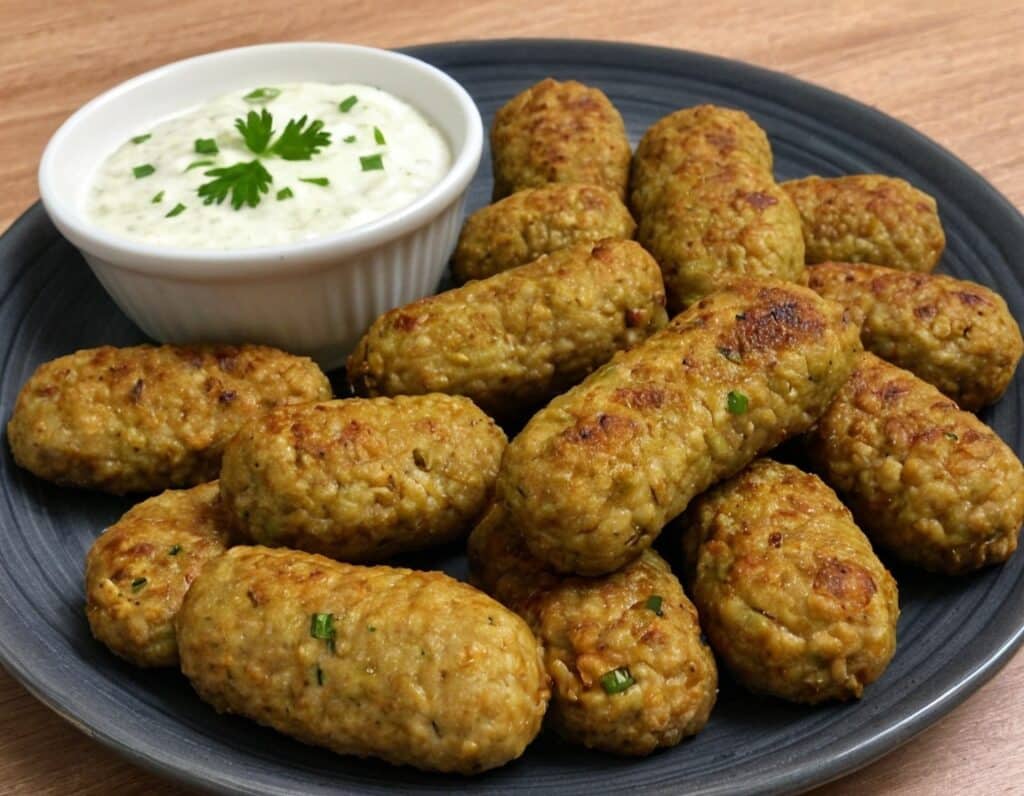
Zucchini & Oatmeal Koftas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
These vegetarian (and with one tweak, vegan) koftas are delicious as a snack, light lunch, or side to a larger meal. Healthwise, they contain the healthiest kind of fiber, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, and beneficial herbs and spices.
You will need
- ¼ cup oatmeal
- 1 large zucchini, grated
- 1 small carrot, grated
- ¼ cup cheese (your preference; vegan is also fine)
- 2 tbsp ground flaxseed
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Small handful fresh parsley, chopped
- Extra virgin olive oil, for frying
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the flaxseed in 2 oz hot water for at least 5 minutes
2) Combine all of the ingredients except the olive oil (and including the water that the flax has been soaking in) in a big bowl, mixing thoroughly
3) Shape into small balls, patties, or sausage shapes, and fry until the color is golden and the structural integrity is good. If doing patties, you’ll need to gently flip them to cook both sides; otherwise, rolling them to get all sides is fine.
4) Serve! Traditional is with some kind of yogurt dip, but we’re not the boss of you, so enjoy them how you like:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health? ← it’s β-glucan, as found in oats
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us ← as in the flax
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk? ← it’s healthier than table salt
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Mushrooms vs Eggplant – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mushrooms to eggplant, we picked the mushrooms.
Why?
First, you may be wondering: which mushrooms? Button mushrooms? White mushrooms? Chestnut mushrooms? Portobello mushrooms? And the answer is yes. Those (and more; it represents most mushrooms that are commonly sold fresh in western supermarkets) are all the same species at different ages; namely, Agaricus bisporus—not to be mistaken for fly agaric, which despite the name, is not even a member of the Agaricus genus, and is in fact Amanita muscari. This is an important distinction, because fly agaric is poisonous, though fatality is rare, and it’s commonly enjoyed recreationally (after some preparation, which reduces its toxicity) for its psychoactive effects. It’s the famous red one with white spots. Anyway, today we will be talking instead about Agaricus bisporus, which is most popular western varieties of “edible mushroom”.
With that in mind, let’s get down to it:
In terms of macros, mushrooms contain more than 3x the protein, while eggplant contains nearly 2x the carbs and 3x the fiber. We’ll call this a tie for macros.
As for vitamins, mushrooms contain more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, D, and choline, while eggplant contains more of vitamins A, E, and K. Most notably for vegans, mushrooms are a good non-animal source of vitamins B12 and D, which nutrients are not generally found in plants. Mushrooms, of course, are not technically plants. In any case, the vitamins category is an easy win for mushrooms.
When it comes to minerals, mushrooms have more copper, iron, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while eggplant has more calcium, magnesium, and manganese. Another easy win for mushrooms.
One final thing worth noting is that mushrooms are a rich source of the amino acid ergothioneine, which has been called a “longevity vitamin” for its healthspan-increasing effects (see our article below).
Meanwhile, in the category of mushrooms vs eggplant, mushrooms don’t leave much room for doubt and are the clear winner here.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
The Magic of Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
A Surprisingly Powerful Tool: Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing (EMDR)
What skeletons are in your closet? As life goes on, most of accumulate bad experiences as well as good ones, to a greater or lesser degree. From clear cases of classic PTSD, to the widely underexamined many-headed beast that is C-PTSD*, our past does affect our present. Is there, then, any chance for our future being different?
*PTSD is typically associated with military veterans, for example, or sexual assault survivors. There was a clear, indisputable, Bad Thing™ that was experienced, and it left a psychological scar. When something happens to remind us of that—say, there are fireworks, or somebody touches us a certain way—it’ll trigger an immediate strong response of some kind.
These days the word “triggered” has been popularly misappropriated to mean any adverse emotional reaction, often to something trivial.
But, not all trauma is so clear. If PTSD refers to the result of that one time you were smashed with a sledgehammer, C-PTSD (Complex PTSD) refers to the result of having been hit with a rolled-up newspaper every few days for fifteen years, say.
This might have been…
- childhood emotional neglect
- a parent with a hair-trigger temper
- bullying at school
- extended financial hardship as a young adult
- “just” being told or shown all too often that your best was never good enough
- the persistent threat (real or imagined) of doom of some kind
- the often-reinforced idea that you might lose everything at any moment
If you’re reading this list and thinking “that’s just life though”, you might be in the estimated 1 in 5 people with (often undiagnosed) C-PTSD.
For more on C-PTSD, see our previous main feature:
So, what does eye movement have to do with this?
Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing (EMDR) is a therapeutic technique whereby a traumatic experience (however small or large; it could be the memory of that one time you said something very regrettable, or it could be some horror we couldn’t describe here) is recalled, and then “detoothed” by doing a bit of neurological jiggery-pokery.
How the neurological jiggery-pokery works:
By engaging the brain in what’s called bilateral stimulation (which can be achieved in various ways, but a common one is moving the eyes rapidly from side to side, hence the name), the event can be re-processed, in much the same way that we do when dreaming, and relegated safely to the past.
This doesn’t mean you’ll forget the event; you’d need to do different exercises for that.
See also our previous main feature:
The Dark Side Of Memory (And How To Make Your Life Better)
That’s not the only aspect of EMDR, though…
EMDR is not just about recalling traumatic events while moving your eyes from side-to-side. What an easy fix that would be! There’s a little more to it.
The process also involves (ideally with the help of a trained professional) examining what other memories, thoughts, feelings, come to mind while doing that. Sometimes, a response we have today associated with, for example, a feeling of helplessness, or rage in conflict, or shame, or anything really, can be connected to previous instances of feeling the same thing. And, each of those events will reinforce—and be reinforced by—the others.
An example of this could be an adult who struggles with substance abuse (perhaps alcohol, say), using it as a crutch to avoid feelings of [insert static here; we don’t know what the feelings are because they’re being avoided], that were first created by, and gradually snowballed from, some adverse reaction to something they did long ago as a child, then reinforced at various times later in life, until finally this adult doesn’t know what to do, but they do know they must hide it at all costs, or suffer the adverse reaction again. Which obviously isn’t a way to actually overcome anything.
EMDR, therefore, seeks to not just “detooth” a singular traumatic memory, but rather, render harmless the whole thread of memories.
Needless to say, this kind of therapy can be quite an emotionally taxing experience, so again, we recommend trying it only under the guidance of a professional.
Is this an evidence-based approach?
Yes! It’s not without its controversy, but that’s how it is in the dog-eat-dog world of academia in general and perhaps psychotherapy in particular. To give a note to some of why it has some controversy, here’s a great freely-available paper that presents “both sides” (it’s more than two sides, really); the premises and claims, the criticisms, and explanations for why the criticisms aren’t necessarily actually problems—all by a wide variety of independent research teams:
Research on Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing (EMDR) as a Treatment for PTSD
To give an idea of the breadth of applications for EMDR, and the evidence of the effectiveness of same, here are a few additional studies/reviews (there are many):
- An Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) Group Intervention for Syrian Refugees With Post-traumatic Stress Symptoms: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing for Treating Panic Disorder: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) therapy in the treatment of depression: a matched pairs study in an inpatient setting
- Emergency room intervention to prevent post concussion-like symptoms and post-traumatic stress disorder. A pilot randomized controlled study of a brief eye movement desensitization and reprocessing intervention versus reassurance or usual care
As for what the American Psychiatric Association says about it:
❝After assessing the 120 outcome studies pertaining to the focus areas, we conclude that for two of the areas (i.e., PTSD in children and adolescents and EMDR early interventions research) the strength of the evidence is rated at the highest level, whereas the other areas obtain the second highest level.❞
Source: The current status of EMDR therapy, specific target areas, and goals for the future
Want to learn more?
To learn a lot more than we could include here, check out the APA’s treatment guidelines (they are written in a fashion that is very accessible to a layperson):
APA | Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) Therapy
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Daily, Weekly, Monthly: Habits Against Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Anil Rajani has advice on restoring/retaining youthfulness. Two out of three of the sections are on skincare specifically, which may seem a vanity, but it’s also worth remembering that our skin is a very large and significant organ, and makes a big difference for the rest of our physical health, as well as our mental health. So, it’s worthwhile to look after it:
The recommendations
Daily: meditation practice
Meditation reduces stress, which reduction in turn protects telomere length, slowing the overall aging process in every living cell of the body.
Weekly: skincare basics
Dr. Rajani recommends a combination of retinol and glycolic acid. The former to accelerate cell turnover, stimulate collagen production, and reduce wrinkles; the latter, to exfoliate dead cells, allowing the retinol to do its job more effectively.
We at 10almonds would like to add: wearing sunscreen with SPF50 is a very good thing to do on any day that your phone’s weather app says the UV index is “moderate” or higher.
Monthly: skincare extras
Here are the real luxuries; spa visits, microneedling (stimulates collagen production), and non-ablative laser therapy. He recommends creating a home spa if possible for monthly skincare treatments, investing in high-quality devices for long-term benefits.
For more on all of these things, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Age & Aging: What Can (And Can’t) We Do About It?
- No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
- The Evidence-Based Skincare That Beats Product-Specific Hype
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Mindgym: Wake Your Mind Up – by Dr. Sebastian Bailey and Octavius Black
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Since this reviewer got her copy, the subtitle and marketing of the book have changed, but the content has not. It’s now being marketed as “achieve more by thinking differently” like a pop-psychology business book. But it’s not that. What, then, is it?
It’s 20 chapters of exercises for different kinds of thinking. And yes, the exercises will help those hungry 25–35-year-old MBAs too, but it’s more of a complete how-to-think overhaul.
Its exercises cover psychology and philosophy, creativity and communication, logic and relaxation, cognition and motivation, and lots more.
The style of the book is that of a workbook, and as such, it’s very clearly laid-out; one can go through them methodically, or get an overview and then dive in to whatever one wants/needs most at the moment.
Bottom line: if you’d like a book that’s a one-stop shop for honing many different kinds of thinking, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out The Mindgym, and get training yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: