Dopamine Nation – by Dr. Anna Lembke
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We live in an age of abundance, though it often doesn’t feel like it. Some of that is due to artificial scarcity, but a lot of it is due to effectively whiting out our dopamine circuitry through chronic overuse.
Psychiatrist Dr. Anna Lembke explores the neurophysiology of pleasure and pain, and how each can (and does) lead to the other. Is the answer to lead a life of extreme neutrality? Not quite.
Rather, simply by being more mindful of how we seek each (yes, both pleasure and pain), we can leverage our neurophysiology to live a better, healthier life—and break/avoid compulsive habits, while we’re at it.
That said, the book itself is quite compelling reading, but as Dr. Lembke shows us, that certainly doesn’t have to be a bad thing.
Bottom line: if you sometimes find yourself restlessly cycling through the same few apps (or TV channels) looking for dopamine that you’re not going to find there, this is the book for you.
Click here to check out Dopamine Nation, and get a handle on yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Worst Way to Wake Up (and What to Do Instead)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not everyone is naturally inclined to be a morning person, but there are things we can do to make things go more easily for our brains!
Cause for alarm?
Dr. Tracey Marks, psychiatrist, explains the impact of our first moments upon awakening, and what that can do to/for us in terms of sleep inertia (i.e. grogginess).
Sleep inertia is worse when waking from deep sleep—and notably, we don’t naturally wake directly from deep sleep unless we are externally aroused (e.g. by an alarm clock).
Dr. Marks suggests the use of more gradual alarms, including those with soft melodies, perhaps birdsong or other similarly gentle things (artificial sunlight alarms are also good), to ease our transition from sleeping to waking. It might take us a few minutes longer to be woken from sleep, but we’re not going to spend the next hour in a bleary-eyed stupor.
For more details on these things and more (including why not to hit “snooze”), enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Apple vs Pineapple – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple to pineapple, we picked the pineapple.
Why?
An apple a day may keep the doctor away, but pineapples are heavier and armored and spiky and generally much more intimidating.
More seriously, apples are great but we say pineapples have the better nutritional and phytochemical properties overall:
In terms of macros, actually apples win this first round, albeit marginally; the two fruits are equal on carbs, while apple has a little more fiber and pineapple has a (very) little more protein. This makes the fiber content the deciding factor, so apples do win this one, even if by just 1g/100g difference.
When it comes to vitamins, however, apples have more of vitamins E and K, while pineapple has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, and choline. The margins of difference are equally generous on both sides, so this is a clear and overwhelming win for pineapple (including 10x more vitamin C than apples, which are themselves considered a good source of vitamin C)
In the category of minerals, apples have slightly more phosphorus, and pineapple has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, potassium, selenium, and zinc. Another easy win for pineapple.
Pineapples are not only also higher in polyphenols, but also contain bromelain, a powerful anti-inflammatory group of enzymes that are unique to pineapple—you can read about it in the link below!
Meanwhile, pineapple wins the day in our head-to-head here, but as ever when it comes to a plurality of healthy things, do enjoy either or both! Diversity is good.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
I’m feeling run down. Why am I more likely to get sick? And how can I boost my immune system?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It has been a long winter, filled with many viruses and cost-of-living pressures, on top of the usual mix of work, study, life admin and caring responsibilities.
Stress is an inevitable part of life. In short bursts, our stress response has evolved as a survival mechanism to help us be more alert in fight or flight situations.
But when stress is chronic, it weakens the immune system and makes us more vulnerable to illnesses such as the common cold, flu and COVID.
Pexels/Ketut Subiyanto Stress makes it harder to fight off viruses
When the immune system starts to break down, a virus that would normally have been under control starts to flourish.
Once you begin to feel sick, the stress response rises, making it harder for the immune system to fight off the disease. You may be sick more often and for longer periods of time, without enough immune cells primed and ready to fight.
In the 1990s, American psychology professor Sheldon Cohen and his colleagues conducted a number of studies where healthy people were exposed to an upper respiratory infection, through drops of virus placed directly into their nose.
These participants were then quarantined in a hotel and monitored closely to determine who became ill.
One of the most important factors predicting who got sick was prolonged psychological stress.
Cortisol suppresses immunity
“Short-term stress” is stress that lasts for a period of minutes to hours, while “chronic stress” persists for several hours per day for weeks or months.
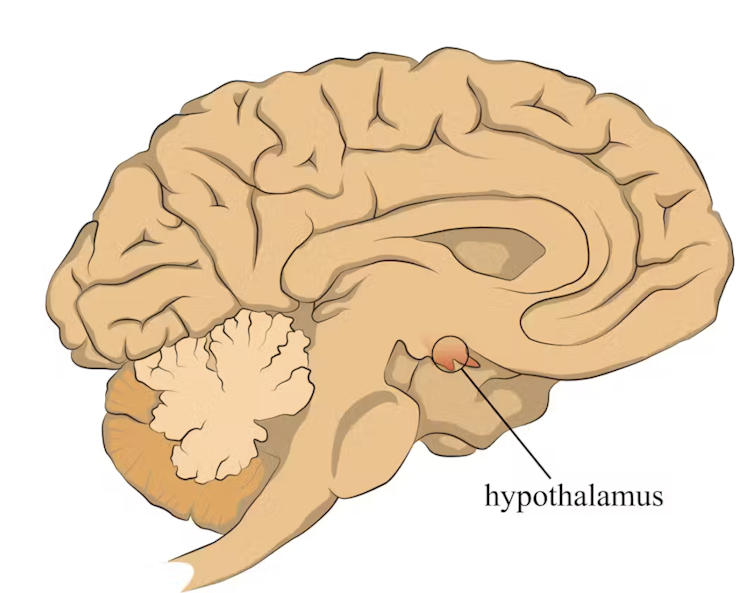
When faced with a perceived threat, psychological or physical, the hypothalamus region of the brain sets off an alarm system. This signals the release of a surge of hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol.
The hypothalamus sets off an alarm system in response to a real or perceived threat. stefan3andrei/Shutterstock In a typical stress response, cortisol levels quickly increase when stress occurs, and then rapidly drop back to normal once the stress has subsided. In the short term, cortisol suppresses inflammation, to ensure the body has enough energy available to respond to an immediate threat.
But in the longer term, chronic stress can be harmful. A Harvard University study from 2022 showed that people suffering from psychological distress in the lead up to their COVID infection had a greater chance of experiencing long COVID. They classified this distress as depression, probable anxiety, perceived stress, worry about COVID and loneliness.
Those suffering distress had close to a 50% greater risk of long COVID compared to other participants. Cortisol has been shown to be high in the most severe cases of COVID.
Stress causes inflammation
Inflammation is a short-term reaction to an injury or infection. It is responsible for trafficking immune cells in your body so the right cells are present in the right locations at the right times and at the right levels.
The immune cells also store a memory of that threat to respond faster and more effectively the next time.
Initially, circulating immune cells detect and flock to the site of infection. Messenger proteins, known as pro-inflammatory cytokines, are released by immune cells, to signal the danger and recruit help, and our immune system responds to neutralise the threat.
During this response to the infection, if the immune system produces too much of these inflammatory chemicals, it can trigger symptoms such as nasal congestion and runny nose.
Our immune response can trigger symptoms such as a runny nose. Alyona Mandrik/Shutterstock What about chronic stress?
Chronic stress causes persistently high cortisol secretion, which remains high even in the absence of an immediate stressor.
The immune system becomes desensitised and unresponsive to this cortisol suppression, increasing low-grade “silent” inflammation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (the messenger proteins).
Immune cells become exhausted and start to malfunction. The body loses the ability to turn down the inflammatory response.
Over time, the immune system changes the way it responds by reprogramming to a “low surveillance mode”. The immune system misses early opportunities to destroy threats, and the process of recovery can take longer.
So how can you manage your stress?
We can actively strengthen our immunity and natural defences by managing our stress levels. Rather than letting stress build up, try to address it early and frequently by:
1) Getting enough sleep
Getting enough sleep reduces cortisol levels and inflammation. During sleep, the immune system releases cytokines, which help fight infections and inflammation.
2) Taking regular exercise
Exercising helps the lymphatic system (which balances bodily fluids as part of the immune system) circulate and allows immune cells to monitor for threats, while sweating flushes toxins. Physical activity also lowers stress hormone levels through the release of positive brain signals.
3) Eating a healthy diet
Ensuring your diet contains enough nutrients – such as the B vitamins, and the full breadth of minerals like magnesium, iron and zinc – during times of stress has a positive impact on overall stress levels. Staying hydrated helps the body to flush out toxins.
4) Socialising and practising meditation or mindfulness
These activities increase endorphins and serotonin, which improve mood and have anti-inflammatory effects. Breathing exercises and meditation stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which calms down our stress responses so we can “reset” and reduce cortisol levels.
Sathana Dushyanthen, Academic Specialist & Lecturer in Cancer Sciences & Digital Health| Superstar of STEM| Science Communicator, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Clean Your Brain (Glymphatic Health Primer)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
That’s not a typo! The name “glymphatic system” was coined by the Danish neuroscientist Dr. Maiken Nedergaard, and is a nod to its use of glial cells to do a similar job to that of the peripheral lymphatic system—but this time, in the CNS. Today, we have Dr. Jin Sung to tell us more:
Brainwashing (but not like that)
The glymphatic system may sound like a boring job, but so does “sanitation worker” in a city—yet the city would grind to a messy halt very very quickly without them. Same goes for your brain.
Diseases that are prevalent when this doesn’t happen the way it should include Alzheimer’s (beta-amyloid clearance) and Parkinson’s (alpha-synuclein clearance) amongst others.
Things Dr. Sung recommends for optimal glymphatic function include: sleep (7–9 hours), exercise (30–45 minutes daily), hydration (half your bodyweight in pounds, in ounces, so if your body weighs 150 lbs, that means 75 oz of water), good posture (including the use of good ergonomics, e.g. computer monitor at right height, car seat correct, etc), stress reduction (reduces inflammatory cytokines), getting enough omega-3 (the brain needs certain fats to work properly, and this is the one most likely to see a deficit), vagal stimulation (methods include humming, gargling, and gagging—please note we said vagal stimulation; easy to misread at a glance!), LED light therapy, and fasting (intermittent or prolonged).
For more on each of these, including specific tips, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- Ask Not What Your Lymphatic System Can Do For You…
- The Vagus Nerve (And How You Can Make Use Of It)
- Casting Yourself In A Healthier Light
- Intermittent Fasting: How Does It Work?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
NADᐩ Against Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or “NAD” to its friends, is a coenzyme produced in the human body (amongst other places), and it is critical for cellular energy metabolism, but there’s more to it than that.
Today we’ll be looking mostly at NAD+, of which the + indicates the positive formal charge of one of its nitrogen atoms. We won’t get too much into the chemistry of this, but we will mention that it’s a cofactor with NADH—the former accepting electrons and the latter donating electrons.
Both NAD+ and NADH are critical to good health, but we’re going to focus on NAD+ for the simple reason that it gets depleted with aging.
Note: it gets depleted with aging.
Chronological age is not so important here, but there is a direct relationship between biological aging and NAD+ depletion.
For example, healthy centenarians tend not to have depleted NAD+ levels. Further, its depletion (in those in whom it is depleted) is then a causal factor for many age-related diseases:
❝Remarkably, ageing is accompanied by a gradual decline in tissue and cellular NAD+ levels in multiple model organisms, including rodents and humans.
This decline in NAD+ levels is linked causally to numerous ageing-associated diseases, including cognitive decline, cancer, metabolic disease, sarcopenia and frailty.
Many of these ageing-associated diseases can be slowed down and even reversed by restoring NAD+ levels.❞
~ Dr. Rosalba Perrone et al.
Read in full: NAD+ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing
As for restoring those NADᐩ levels, that does help in interventional trials, whether by supplementing directly, or with NAD precursors*:
❝NAD+ levels steadily decline with age, resulting in altered metabolism and increased disease susceptibility.
Restoration of NAD+ levels in old or diseased animals can promote health and extend lifespan, prompting a search for safe and efficacious NAD-boosting molecules that hold the promise of increasing the body’s resilience, not just to one disease, but to many, thereby extending healthy human lifespan.❞
~ Dr. David Sinclair et al.
Read more: Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The In Vivo Evidence
*There are actually also other NAD-boosting molecules besides NAD itself and its precursors. For example, the liver will not produce NADᐩ unless it has aminocarboxymuconate-semialdehyde decarboxylase (or “ACMSD”, to its friends), which limits the production of NADᐩ. Why, you ask? The theory is that it is a kind of evolutionary conservativism, much like not lighting a fire without the ability to put it out. In any case, taking ACMSD-blockers will thus result in an increased endogenous production of NADᐩ.
You can read about this here:
De novo NAD+ synthesis enhances mitochondrial function and improves health
Nor is taking supplements or drugs the only way to get more of it; there’s an enzyme nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (“NAMPT”, to its friends) involved in the synthesis of NADᐩ, and exercise boosts levels by 127% (i.e., it more than doubles the levels), based on a modest three-week exercise bike regimen:
Skeletal muscle NAMPT is induced by exercise in humans
And to underline that point, another study found that resistance training (so, a different kind of exercise from that of the previous study) boosts levels of NADᐩ itself by the same 127%:
One way to get more out of NADᐩ
We’ll get straight to the point: it works very well paired with a senolytic agent, i.e. something that kills aging cells so that they get recycled sooner:
NAD+, Senolytics, or Pyruvate for Healthy Aging?
To read more about senolytics, check out:
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Codependency Isn’t What Most People Think It Is
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Codependency isn’t what most people think it is
In popular parlance, people are often described as “codependent” when they rely on each other to function normally. That’s interdependent mutualism, and while it too can become a problem if a person is deprived of their “other half” and has no idea how to do laundry and does not remember to take their meds, it’s not codependency.
Codependency finds its origins in the treatment and management of alcoholism, and has been expanded to encompass other forms of relationships with dependence on substances and/or self-destructive behaviors—which can be many things, including the non-physical, for example a pattern of irresponsible impulse-spending, or sabotaging one’s own relationship(s).
We’ll use the simplest example, though:
- Person A is (for example) an alcoholic. They have a dependency.
- Person B, married to A, is not an alcoholic. However, their spouse’s dependency affects them greatly, and they do what they can to manage that, and experience tension between wanting to “save” their spouse, and wanting their spouse to be ok, which latter, superficially, often means them having their alcohol.
Person B is thus said to be “codependent”.
The problem with codependency
The problems of codependency are mainly twofold:
- The dependent partner’s dependency is enabled and thus perpetuated by the codependent partner—they might actually have to address their dependency, if it weren’t for their partner keeping them from too great a harm (be it financially, socially, psychologically, medically, whatever)
- The codependent partner is not having a good time of it either. They have the stress of two lives with the resources (e.g. time) of one. They are stressing about something they cannot control, understandably worrying about their loved one, and, worse: every action they might take to “save” their loved one by reducing the substance use, is an action that makes their partner unhappy, and causes conflict too.
Note: codependency is often a thing in romantic relationships, but it can appear in other relationships too, e.g. parent-child, or even between friends.
See also: Development and validation of a revised measure of codependency
How to deal with this
If you find yourself in a codependent position, or are advising someone who is, there are some key things that can help:
- Be a nurturer, not a rescuer. It is natural to want to “rescue” someone we care about, but there are some things we cannot do for them. Instead, we must look for ways to build their strength so that they can take the steps that only they can take to fix the problem.
- Establish boundaries. Practise saying “no”, and also be clear over what things you can and cannot control—and let go of the latter. Communicate this, though. An “I’m not the boss of you” angle can prompt a lot of people to take more personal responsibility.
- Schedule time for yourself. You might take some ideas from our previous tangentially-related article:
How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
Want to read more?
That’s all we have space for today, but here’s a very useful page with a lot of great resources (including questionnaires and checklist and things, in case you’re thinking “is it, or…?”)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: