How To Avoid Carer Burnout (Without Dropping Care)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How To Avoid Carer Burnout
Sometimes in life we find ourselves in a caregiving role.
Maybe we chose it. For example, by becoming a professional carer, or even just by being a parent.
Oftentimes we didn’t. Sometimes because our own parents now need care from us, or because a partner becomes disabled.
Philosophical note: an argument could be made for that latter also having been a pre-emptive choice; we probably at some point said words to the effect of “in sickness and in health”, hopefully with free will, and hopefully meant it. And of course, sometimes we enter into a relationship with someone who is already disabled.
But, we are not a philosophy publication, and will henceforth keep to the practicalities.
First: are you the right person?
Sometimes, a caregiving role might fall upon you unasked-for, and it’s worth considering whether you are really up for it. Are you in a position to be that caregiver? Do you want to be that caregiver?
It may be that you do, and would actively fight off anyone or anything that tried to stop you. If so, great, now you only need to make sure that you are actually in a position to provide the care in question.
It may be that you do want to, but your circumstances don’t allow you to do as good a job of it as you’d like, or it means you have to drop other responsibilities, or you need extra help. We’ll cover these things later.
It may be that you don’t want to, but you feel obliged, or “have to”. If that’s the case, it will be better for everyone if you acknowledge that, and find someone else to do it. Nobody wants to feel a burden, and nobody wants someone providing care to be resentful of that. The result of such is two people being miserable; that’s not good for anyone. Better to give the job to someone who actually wants to (a professional, if necessary).
So, be honest (first with yourself, then with whoever may be necessary) about your own preferences and situation, and take steps to ensure you’re only in a caregiving role that you have the means and the will to provide.
Second: are you out of your depth?
Some people have had a life that’s prepared them for being a carer. Maybe they worked in the caring profession, maybe they have always been the family caregiver for one reason or another.
Yet, even if that describes you… Sometimes someone’s care needs may be beyond your abilities. After all, not all care needs are equal, and someone’s condition can (and more often than not, will) deteriorate.
So, learn. Learn about the person’s condition(s), medications, medical equipment, etc. If you can, take courses and such. The more you invest in your own development in this regard, the more easily you will handle the care, and the less it will take out of you.
And, don’t be afraid to ask for help. Maybe the person knows their condition better than you, and certainly there’s a good chance they know their care needs best. And certainly, there are always professionals that can be contacted to ask for advice.
Sometimes, a team effort may be required, and there’s no shame in that either. Whether it means enlisting help from family/friends or professionals, sometimes “many hands make light work”.
Check out: Caregiver Action Network: Organizations Near Me
A very good resource-hub for help, advice, & community
Third: put your own oxygen mask on first
Like the advice to put on one’s own oxygen mask first before helping others (in the event of a cabin depressurization in an airplane), the rationale is the same here. You can’t help others if you are running on empty yourself.
As a carer, sometimes you may have to put someone else’s needs above yours, both in general and in the moment. But, you do have needs too, and cannot neglect them (for long).
One sleepless night looking after someone else is… a small sacrifice for a loved one, perhaps. But several in a row starts to become unsustainable.
Sometimes it will be necessary to do the best you can, and accept that you cannot do everything all the time.
There’s a saying amongst engineers that applies here too: “if you don’t schedule time for maintenance, your equipment will schedule it for you”.
In other words: if you don’t give your body rest, your body will break down and oblige you to rest. Please be aware this goes for mental effort too; your brain is just another organ.
So, plan ahead, schedule breaks, find someone to take over, set up your cared-for-person with the resources to care for themself as well as possible (do this anyway, of course—independence is generally good so far as it’s possible), and make the time/effort to get you what you need for you. Sleep, distraction, a change of scenery, whatever it may be.
Lastly: what if it’s you?
If you’re reading this and you’re the person who has the higher care needs, then firstly:all strength to you. You have the hardest job here; let’s not forget that.
About that independence: well-intentioned people may forget that, so don’t be afraid to remind them when “I would prefer to do that myself”. Maintaining independence is generally good for the health, even if sometimes it is more work for all concerned than someone else doing it for you. The goal, after all, is your wellbeing, so this shouldn’t be cast aside lightly.
On the flipside: you don’t have to be strong all the time; nobody should.
Being disabled can also be quite isolating (this is probably not a revelation to you), so if you can find community with other people with the same or similar condition(s), even if it’s just online, that can go a very, very long way to making things easier. Both practically, in terms of sharing tips, and psychologically, in terms of just not feeling alone.
See also: How To Beat Loneliness & Isolation
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Stop Pain Spreading
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Put Your Back Into It (Or Don’t)!
We’ve written before about Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!), and today we’re going to tackle a particular aspect of chronic pain management.
- It’s a thing where the advice is going to be “don’t do this”
- And if you have chronic pain, you will probably respond “yep, I do that”
However, it’s definitely a case of “when knowing isn’t the problem”, or at the very least, it’s not the whole problem.
Stop overcompensating and address the thing directly
We all do it, whether in chronic pain, or just a transient injury. But we all need to do less of it, because it causes a lot of harm.
Example: you have pain in your right knee, so you sit, stand, walk slightly differently to try to ease that pain. It works, albeit marginally, at least for a while, but now you also have pain in your left hip and your lumbar vertebrae, because of how you leaned a certain way. You adjust how you sit, stand, walk, to try to ease both sets of pain, and before you know it, now your neck also hurts, you have a headache, and you’re sure your digestion isn’t doing what it should and you feel dizzy when you stand. The process continues, and before long, what started off as a pain in one knee has now turned your whole body into a twisted aching wreck.
What has happened: the overcompensation due to the original pain has unduly stressed a connected part of the body, which we then overcompensate for somewhere else, bringing down the whole body like a set of dominoes.
For more on this: Understanding How Pain Can Spread
“Ok, but how? I can’t walk normally on that knee!”
We’re keeping the knee as an example here, but please bear in mind it could be any chronic pain and resultant disability.
Note: if you found the word “disability” offputting, please remember: if it adversely affects your abilities, it is a disability. Disabilities are not something that only happen to other people! They will happen to most of us at some point!
Ask yourself: what can you do, and what can’t you do?
For example:
- maybe you can walk, but not normally
- maybe you can walk normally, but not without great pain
- maybe you can walk normally, but not at your usual walking pace
First challenge: accept your limitations. If you can’t walk at your usual walking pace without great pain and/or throwing your posture to the dogs, then walk more slowly. To Hell with societal expectations that it shouldn’t take so long to walk from A to B. Take the time you need.
Second challenge: accept help. It doesn’t have to be help from another person (although it could be). It might be accepting the help of a cane, or maybe even a wheelchair for “flare-up” days. Society, especially American society which is built on ideas of self-sufficiency, has framed a lot of such options as “giving up”, but if they help you get about your day while minimizing doing further harm to your body, then they can be good and even health-preserving things. Same goes for painkillers if they help you from doing more harm to your body by balling up tension in a part of your body in a way that ends up spreading out and laying ruin to your whole body.
Speaking of which:
How Much Does It Hurt? Get The Right Help For Your Pain
After which, you might want to check out:
The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
and
Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief
Third challenge: deserves its own section, so…
Do what you can
If you have chronic pain (or any chronic illness, really), you are probably fed up of hearing how this latest diet will fix you, or yoga will fix you, and so on. But, while these things may not be miracle cures…
- A generally better diet really will lessen symptoms and avoid flare-ups (a low-inflammation diet is a great start for lessening the symptoms of a lot of chronic illnesses)
- Doing what exercise you can, being mindful of your limitations yes but still keeping moving as much as possible, will also prevent (or at least slow) deterioration. Consider consulting a physiotherapist for guidance (a doctor will more likely just say “rest, take it easy”, whereas a physiotherapist will be able to give more practical advice).
- Getting good sleep may be a nightmare in the case of chronic pain (or other chronic illnesses! Here’s to those late night hyperglycemia incidents for Type 1 Diabetics that then need monitoring for the next few hours while taking insulin and hoping it goes back down) but whatever you can do to prioritize it, do it.
Want to read more?
We reviewed a little while ago a great book about this; the title sounds like a lot of woo, but we promise the content is extremely well-referenced science:
…and if your issue is back pain specifically, we highly recommend:
Healing Back Pain: The Mind-Body Connection – by Dr. John Sarno
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cannabis Myths vs Reality
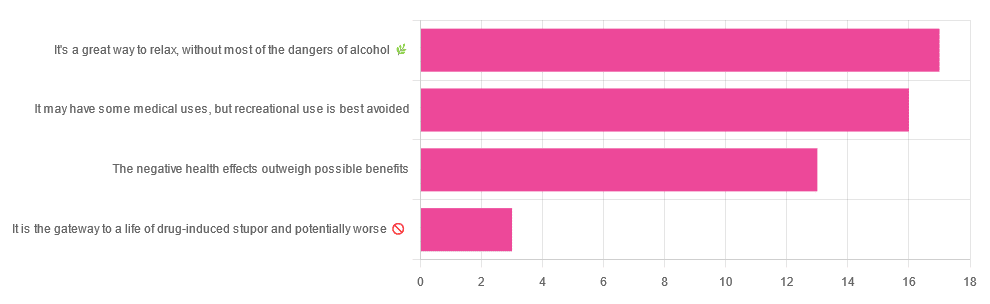
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on cannabis use—specifically, the kind with psychoactive THC, not just CBD. We got the above-pictured, below-described, spread of responses:
- A little over a third of you voted for “It’s a great way to relax, without most of the dangers of alcohol”.
- A little under a third of you voted for “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”.
- About a quarter of you voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits”
- Three of you voted for “It is the gateway to a life of drug-induced stupor and potentially worse”
So, what does the science say?
A quick legal note first: we’re a health science publication, and are writing from that perspective. We do not know your location, much less your local laws and regulations, and so cannot comment on such. Please check your own local laws and regulations in that regard.
Cannabis use can cause serious health problems: True or False?
True. Whether the risks outweigh the benefits is a personal and subjective matter (for example, a person using it to mitigate the pain of late stage cancer is probably unconcerned with many other potential risks), but what’s objectively true is that it can cause serious health problems.
One subscriber who voted for “The negative health effects outweigh the possible benefits” wrote:
❝At a bare minimum, you are ingesting SMOKE into your lungs!! Everyone SEEMS TO BE against smoking cigarettes, but cannabis smoking is OK?? Lung cancer comes in many forms.❞
Of course, that is assuming smoking cannabis, and not consuming it as an edible. But, what does the science say on smoking it, and lung cancer?
There’s a lot less research about this when it comes to cannabis, compared to tobacco. But, there is some:
❝Results from our pooled analyses provide little evidence for an increased risk of lung cancer among habitual or long-term cannabis smokers, although the possibility of potential adverse effect for heavy consumption cannot be excluded.❞
Read: Cannabis smoking and lung cancer risk: Pooled analysis in the International Lung Cancer Consortium
Another study agreed there appears to be no association with lung cancer, but that there are other lung diseases to consider, such as bronchitis and COPD:
❝Smoking cannabis is associated with symptoms of chronic bronchitis, and there may be a modest association with the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Current evidence does not suggest an association with lung cancer.❞
Read: Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues
Cannabis edibles are much safer than smoking cannabis: True or False?
Broadly True, with an important caveat.
One subscriber who selected “It may have some medical uses, but recreational use is best avoided”, wrote:
❝I’ve been taking cannabis gummies for fibromyalgia. I don’t know if they’re helping but they’re not doing any harm. You cannot overdose you don’t become addicted.❞
Firstly, of course consuming edibles (rather than inhaling cannabis) eliminates the smoke-related risk factors we discussed above. However, other risks remain, including the much greater ease of accidentally overdosing.
❝Visits attributable to inhaled cannabis are more frequent than those attributable to edible cannabis, although the latter is associated with more acute psychiatric visits and more ED visits than expected.❞
Note: that “more frequent” for inhaled cannabis, is because more people inhale it than eat it. If we adjust the numbers to control for how much less often people eat it, suddenly we see that the numbers of hospital admissions are disproportionately high for edibles, compared to inhaled cannabis.
Or, as the study author put it:
❝There are more adverse drug events associated on a milligram per milligram basis of THC when it comes in form of edibles versus an inhaled cannabis. If 1,000 people smoked pot and 1,000 people at the same dose in an edible, then more people would have more adverse drug events from edible cannabis.❞
See the numbers: Acute Illness Associated With Cannabis Use, by Route of Exposure
Why does this happen?
- It’s often because edibles take longer to take effect, so someone thinks “this isn’t very strong” and has more.
- It’s also sometimes because someone errantly eats someone else’s edibles, not realising what they are.
- It’s sometimes a combination of the above problems: a person who is now high, may simply forget and/or make a bad decision when it comes to eating more.
On the other hand, that doesn’t mean inhaling it is necessarily safer. As well as the pulmonary issues we discussed previously, inhaling cannabis has a higher risk of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (and the resultant cyclic vomiting that’s difficult to treat).
You can read about this fascinating condition that’s sometimes informally called “scromiting”, a portmanteau of screaming and vomiting:
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome
You can’t get addicted to cannabis: True or False?
False. However, it is fair to say that the likelihood of developing a substance abuse disorder is lower than for alcohol, and much lower than for nicotine.
See: Prevalence of Marijuana Use Disorders in the United States Between 2001–2002 and 2012–2013
If you prefer just the stats without the science, here’s the CDC’s rendering of that:
Addiction (Marijuana or Cannabis Use Disorder)
However, there is an interesting complicating factor, which is age. One is 4–7 times more likely to develop a substance abuse disorder, if one starts use as an adolescent, rather than later in life:
Cannabis is the gateway to use of more dangerous drugs: True or False?
False, generally speaking. Of course, for any population there will be some outliers, but there appears to be no meaningful causal relation between cannabis use and other substance use:
Interestingly, the strongest association (where any existed at all) was between cannabis use and opioid use. However, rather than this being a matter of cannabis use being a gateway to opioid use, it seems more likely that this is a matter of people looking to both for the same purpose: pain relief.
As a result, growing accessibility of cannabis may actually reduce opioid problems:
- Cannabis as a Gateway Drug for Opioid Use Disorder
- Association between medical cannabis laws and opioid overdose mortality has reversed over time
Some final words…
Cannabis is a complex drug with complex mechanisms and complex health considerations, and research is mostly quite young, due to its historic illegality seriously cramping science by reducing sample sizes to negligible. Simply put, there’s a lot we still don’t know.
Also, we covered some important topics today, but there were others we didn’t have time to cover, such as the other potential psychological benefits—and risks. Likely we’ll revisit those another day.
Lastly, while we’ve covered a bunch of risks today, those of you who said it has fewer and lesser risks than alcohol are quite right—the only reason we couldn’t focus on that more, is because to talk about all the risks of alcohol would make this feature many times longer!
Meanwhile, whether you partake or not, stay safe and stay well.
Share This Post
-
Exercise and Fat Loss (5 Things You Need To Know)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s easy to think “I’ll eat whatever; I can always burn it off later”, and if it’s an odd occasion, then that’s fine; indeed, a fit and healthy body can usually weather small infrequent dietary indiscretions easily. But…
You can’t outrun a bad diet
Exercise can create a calorie deficit, but over time, the body balances this out by adjusting one’s metabolism, leading to a plateau in fat loss—and as you might know, you can’t out-exercise a bad diet. On the contrary, dietary adjustments are crucial for fat loss and body recomposition.
About that calorie deficit in the first place, by the way: extreme calorie deficits through exercise alone can lead to muscle loss, reduced energy, and thus sabotage long-term fat loss because having muscle mass increases one’s base metabolic rate (while having fat does not).
Another thing to bear in mind about exercise is that longer workouts without adequate rests in between can cause burnout, injury, or weight gain due to the body doing its best to conserve energy.
So, a good diet is a necessary condition for both muscle maintenance and fat loss.
Five Key Diet Tips:
- Include foods you love: don’t feel obliged cut out favorite foods that are a little unhealthy; incorporate them in moderation for sustainability.
- Keep adjustments small: avoid making drastic dietary changes all at once; make gradual tweaks to prevent feeling deprived.
- Prioritize protein: focus on including a protein source in every meal to increase satiety and aid in muscle building.
- Avoid low-calorie diets: drastically cutting calories can lead to muscle loss, metabolic adaptation, and overeating.
- Embrace diet evolution: changes may not feel sustainable at first, but adjustments over time help achieve long-term balance. You can always “adjust course” as you go.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Are You A Calorie-Burning Machine?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
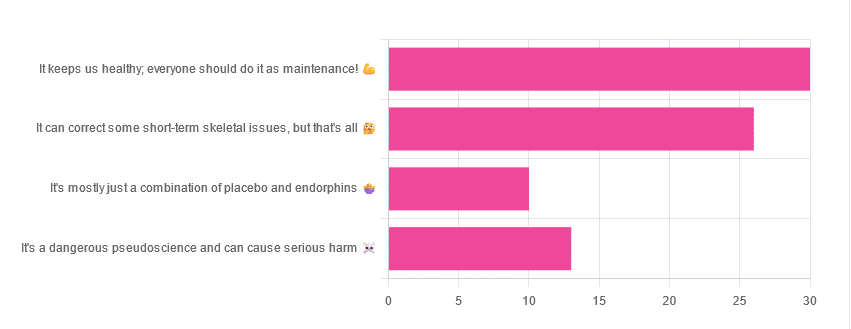
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on chiropractic medicine, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- 38% of respondents said it keeps us healthy, and everyone should do it as maintenance
- 33% of respondents said it can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all
- 16% of respondents said that it’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause serious harm
- 13% of respondents said that it’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins
Respondents also shared personal horror stories of harm done, personal success stories of things cured, and personal “it didn’t seem to do anything for me” stories.
What does the science say?
It’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause harm: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
That is to say, chiropractic in its simplest form that makes the fewest claims, is not a pseudoscience. If somebody physically moves your bones around, your bones will be physically moved. If your bones were indeed misaligned, and the chiropractor is knowledgeable and competent, this will be for the better.
However, like any form of medicine, it can also cause harm; in chiropractic’s case, because it more often than not involves manipulation of the spine, this can be very serious:
❝Twenty six fatalities were published in the medical literature and many more might have remained unpublished.
The reported pathology usually was a vascular accident involving the dissection of a vertebral artery.
Conclusion: Numerous deaths have occurred after chiropractic manipulations. The risks of this treatment by far outweigh its benefit.❞
Source: Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases
From this, we might note two things:
- The abstract doesn’t note the initial sample size; we would rather have seen this information expressed as a percentage. Unfortunately, the full paper is not accessible, and nor are many of the papers it cites.
- Having a vertebral artery fatally dissected is nevertheless not an inviting prospect, and is certainly a very reasonable cause for concern.
It’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins: True or False?
True or False, depending on what you went in for:
- If you went in for a regular maintenance clunk-and-click, then yes, you will get your clunk-and-click and feel better for it because you had a ritualized* experience and endorphins were released.
- If you went in for something that was actually wrong with your skeletal alignment, to get it corrected, and this correction was within your chiropractor’s competence, then yes, you will feel better because a genuine fault was corrected.
*this is not implying any mysticism, by the way. Rather it means simply that placebo effect is strongest when there is a ritual associated with it. In this case it means going to the place, sitting in a pleasant waiting room, being called in, removing your shoes and perhaps some other clothes, getting the full attention of a confident and assured person for a while, this sort of thing.
With regard to its use to combat specifically spinal pain (i.e., perhaps the most obvious thing to treat by chiropractic spinal manipulation), evidence is slightly in favor, but remains unclear:
❝Due to the low quality of evidence, the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulation compared with a placebo or no treatment remains uncertain. ❞
Source: Clinical Effectiveness and Efficacy of Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation for Spine Pain
It can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all: True or False?
Probably True.
Why “probably”? The effectiveness of chiropractic treatment for things other than short-term skeletal issues has barely been studied. From this, we may wish to keep an open mind, while also noting that it can hardly claim to be evidence-based—and it’s had hundreds of years to accumulate evidence. In all likelihood, publication bias has meant that studies that were conducted and found inconclusive or negative results were simply not published—but that’s just a hypothesis on our part.
In the case of using chiropractic to treat migraines, a very-related-but-not-skeletal issue, researchers found:
❝Pre-specified feasibility criteria were not met, but deficits were remediable. Preliminary data support a definitive trial of MCC+ for migraine.❞
Translating this: “it didn’t score as well as we hoped, but we can do better. We got some positive results, and would like to do another, bigger, better trial; please fund it”
Source: Multimodal chiropractic care for migraine: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Meanwhile, chiropractors’ claims for very unrelated things have been harshly criticized by the scientific community, for example:
Misinformation, chiropractic, and the COVID-19 pandemic
About that “short-term” aspect, one of our subscribers put it quite succinctly:
❝Often a skeletal correction is required for initial alignment but the surrounding fascia and muscles also need to be treated to mobilize the joint and release deep tissue damage surrounding the area. In combination with other therapies chiropractic support is beneficial.❞
This is, by the way, very consistent with what was said in the very clinically-dense book we reviewed yesterday, which has a chapter on the short-term benefits and limitations of chiropractic.
A truism that holds for many musculoskeletal healthcare matters, holds true here too:
❝In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win❞
In other words…
Chiropractic can definitely help put misaligned bones back where they should be. However, once they’re there, if the cause of their misalignment is not treated, they will just re-misalign themselves shortly after you walking out of your session.
This is great for chiropractors, if it keeps you coming back for endless appointments, but it does little for your body beyond give you a brief respite.
So, by all means go to a chiropractor if you feel so inclined (and you do not fear accidental arterial dissection etc), but please also consider going to a physiotherapist, and potentially other medical professions depending on what seems to be wrong, to see about addressing the underlying cause.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Chromium Picolinate For Blood Sugar Control & Weight Loss
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, a quick disambiguation:
- chromium found in food, trivalent chromium of various kinds, is safe (in the quantities usually consumed) and is sometimes considered an essential mineral, sometimes considered unnecessary but beneficial. It’s hard to know for sure, since it’s in a lot of foods (naturally, like many trace elements)
- chromium found in pollution, hexavalent chromium (so: twice as many cationic bonds, if this writer’s chemistry serves her correctly) is poisonous.
We’re going to be writing about the food kind, which is also possible to take as a supplement.
In this case, supplementing vs getting from food is quite a big difference, by the way, since (unlike for a lot of things, which are often the other way around) the bioavailability of chromium from food is very low (around 2.5%), whereas chromium picolinate, one of the most commonly-used supplement forms, boasts higher bioavailability.
Does it work for blood sugars?
Yes, it does! At least, it does in the case of people with type 2 diabetes. Rather than bombard you with many individual studies, here’s a systematic review and meta-analysis of 22 criteria-meeting randomized clinical trials that found:
❝The available evidence suggests favourable effects of chromium supplementation on glycaemic control in patients with diabetes.
Chromium monosupplement may additionally improve triglycerides and HDL-C levels.❞
Type 1 diabetes does not have anything like the same weight of evidence, and indeed,
we couldn’t find a single human study. It was beneficial for mice with artificially-induced T1D, thoughwait no, we have an update! We found literally a single human study:Chromium picolinate supplementation for diabetes mellitus
Literally, as in: it’s a case study of one person, and the results were a modest reduction in Hb A1c levels after 3 months of 600μg daily; the researchers concluded that ❝chromium picolinate continues to fall squarely within the scope of “alternative medicine,” with both unproven benefits and unknown risks❞.
As for people without diabetes, it may reduce the risk of diabetes:
Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Is Lower in US Adults Taking Chromium-Containing Supplements
However! This was an observational study, and correlation ≠ causation.
Furthermore, they said:
❝Over one-half the adult US population consumes nutritional supplements, and over one-quarter consumes supplemental chromium. The odds of having T2D were lower in those who, in the previous 30 d, had consumed supplements containing chromium❞
That “over one-quarter consumes supplemental chromium” brought our attention to the fact that this is not talking about specifically chromium “monosupplements” (definitely not quarter of the adult population take those), but rather, “multivitamin and mineral” supplements that also contain a tiny amount (often under 50μg) of chromium.
In other words, this ruins the data and honestly the benefit could have been from anything in the “multivitamin and mineral” supplement, or indeed, could just be “the kind of person who takes supplements is the kind of person who lives a lifestyle that is less conducive to becoming diabetic”.
Does it work for weight loss?
We’re running out of space here, so we’ll be brief:
No.
There are many papers that have concluded this, but here are two:
Chromium picolinate supplementation for overweight or obese adults
and
Is it safe?
Science’s current best answer is “we don’t know; it hasn’t been tested enough; we haven’t even established the tolerable upper limit, which is usually step 1 of establishing safety”.
Nor is there an estimated average requirement (if indeed there even is a requirement, which question is also not as yet answered conclusively by science), and science falls back to “here’s an average of what people consume in their diet, so that’s probably safe, we guess”.
(that average was reckoned as 25μg/day for young women and 25μg/day for young men, by the way; older ages not as yet reckoned)
You can read about this sorry state of affairs here.
Want to try some?
Notwithstanding the above lack of data for safety, it does have benefits for blood sugars, so if that’s a gamble you’re willing to make, then here’s an example product on Amazon.
Note: the dosage per capsule there (800μg) is half of the low end of the dose that was implicated in the serious kidney condition caused in this case study (1200–2400μg), so if you are going to try it, we strongly recommend not taking more than one per day.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Could ADHD drugs reduce the risk of early death? Unpacking the findings from a new Swedish study
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) can have a considerable impact on the day-to-day functioning and overall wellbeing of people affected. It causes a variety of symptoms including difficulty focusing, impulsivity and hyperactivity.
For many, a diagnosis of ADHD, whether in childhood or adulthood, is life changing. It means finally having an explanation for these challenges, and opens up the opportunity for treatment, including medication.
Although ADHD medications can cause side effects, they generally improve symptoms for people with the disorder, and thereby can significantly boost quality of life.
Now a new study has found being treated for ADHD with medication reduces the risk of early death for people with the disorder. But what can we make of these findings?
A large study from Sweden
The study, published this week in JAMA (the prestigious journal of the American Medical Association), was a large cohort study of 148,578 people diagnosed with ADHD in Sweden. It included both adults and children.
In a cohort study, a group of people who share a common characteristic (in this case a diagnosis of ADHD) are followed over time to see how many develop a particular health outcome of interest (in this case the outcome was death).
For this study the researchers calculated the mortality rate over a two-year follow up period for those whose ADHD was treated with medication (a group of around 84,000 people) alongside those whose ADHD was not treated with medication (around 64,000 people). The team then determined if there were any differences between the two groups.
What did the results show?
The study found people who were diagnosed and treated for ADHD had a 19% reduced risk of death from any cause over the two years they were tracked, compared with those who were diagnosed but not treated.
In understanding this result, it’s important – and interesting – to look at the causes of death. The authors separately analysed deaths due to natural causes (physical medical conditions) and deaths due to unnatural causes (for example, unintentional injuries, suicide, or accidental poisonings).
The key result is that while no significant difference was seen between the two groups when examining natural causes of death, the authors found a significant difference for deaths due to unnatural causes.
So what’s going on?
Previous studies have suggested ADHD is associated with an increased risk of premature death from unnatural causes, such as injury and poisoning.
On a related note, earlier studies have also suggested taking ADHD medicines may reduce premature deaths. So while this is not the first study to suggest this association, the authors note previous studies addressing this link have generated mixed results and have had significant limitations.
In this new study, the authors suggest the reduction in deaths from unnatural causes could be because taking medication alleviates some of the ADHD symptoms responsible for poor outcomes – for example, improving impulse control and decision-making. They note this could reduce fatal accidents.
The authors cite a number of studies that support this hypothesis, including research showing ADHD medications may prevent the onset of mood, anxiety and substance use disorders, and lower the risk of accidents and criminality. All this could reasonably be expected to lower the rate of unnatural deaths.
Strengths and limitations
Scandinavian countries have well-maintained national registries that collect information on various aspects of citizens’ lives, including their health. This allows researchers to conduct excellent population-based studies.
Along with its robust study design and high-quality data, another strength of this study is its size. The large number of participants – almost 150,000 – gives us confidence the findings were not due to chance.
The fact this study examined both children and adults is another strength. Previous research relating to ADHD has often focused primarily on children.
One of the important limitations of this study acknowledged by the authors is that it was observational. Observational studies are where the researchers observe and analyse naturally occurring phenomena without intervening in the lives of the study participants (unlike randomised controlled trials).
The limitation in all observational research is the issue of confounding. This means we cannot be completely sure the differences between the two groups observed were not either partially or entirely due to some other factor apart from taking medication.
Specifically, it’s possible lifestyle factors or other ADHD treatments such as psychological counselling or social support may have influenced the mortality rates in the groups studied.
Another possible limitation is the relatively short follow-up period. What the results would show if participants were followed up for longer is an interesting question, and could be addressed in future research.
What are the implications?
Despite some limitations, this study adds to the evidence that diagnosis and treatment for ADHD can make a profound difference to people’s lives. As well as alleviating symptoms of the disorder, this study supports the idea ADHD medication reduces the risk of premature death.
Ultimately, this highlights the importance of diagnosing ADHD early so the appropriate treatment can be given. It also contributes to the body of evidence indicating the need to improve access to mental health care and support more broadly.
Hassan Vally, Associate Professor, Epidemiology, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: