Lacking Motivation? Science Has The Answer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Science Of Motivation (And How To Use It To Your Advantage)
When we do something rewarding, our brain gets a little (or big!) spike of dopamine. Dopamine is popularly associated with pleasure—which is fair— but there’s more to it than this.
Dopamine is also responsible for motivation itself, as a prime mover before we do the thing that we find rewarding. If we eat a banana, and enjoy it, perhaps because our body needed the nutrients from it, our brain gets a hit of dopamine.
(and not because bananas contain dopamine; that dopamine is useful for the body, but can’t pass the blood-brain barrier to have an effect on the brain)
So where does the dopamine in our brain come from? That dopamine is made in the brain itself.
Key Important Fact: the brain produces dopamine when it expects an activity to be rewarding.
If you take nothing else away from today’s newsletter, let it be this!
It makes no difference if the activity is then not rewarding. And, it will keep on motivating you to do something it anticipated being rewarding, no matter how many times the activity disappoints, because it’ll remember the very dopamine that it created, as having been the reward.
To put this into an example:
- How often have you spent time aimlessly scrolling social media, flitting between the same three apps, or sifting through TV channels when “there’s nothing good on to watch”?
- And how often did you think afterwards “that was a good and rewarding use of my time; I’m glad I did that”?
In reality, whatever you felt like you were in search of, you were really in search of dopamine. And you didn’t find it, but your brain did make some, just enough to keep you going.
Don’t try to “dopamine detox”, though.
While taking a break from social media / doomscrolling the news / mindless TV-watching can be a great and healthful idea, you can’t actually “detox” from a substance your body makes inside itself.
Which is fortunate, because if you could, you’d die, horribly and miserably.
If you could “detox” completely from dopamine, you’d lose all motivation, and also other things that dopamine is responsible for, including motor control, language faculties, and critical task analysis (i.e. planning).
This doesn’t just mean that you’d not be able to plan a wedding; it also means:
- you wouldn’t be able to plan how to get a drink of water
- you wouldn’t have any motivation to get water even if you were literally dying of thirst
- you wouldn’t have the motor control to be able to physically drink it anyway
Read: Dopamine and Reward: The Anhedonia Hypothesis 30 years on
(this article is deep and covers a lot of ground, but is a fascinating read if you have time)
Note: if you’re wondering why that article mentions schizophrenia so much, it’s because schizophrenia is in large part a disease of having too much dopamine.
Consequently, antipsychotic drugs (and similar) used in the treatment of schizophrenia are generally dopamine antagonists, and scientists have been working on how to treat schizophrenia without also crippling the patient’s ability to function.
Do be clever about how you get your dopamine fix
Since we are hardwired to crave dopamine, and the only way to outright quash that craving is by inducing anhedonic depression, we have to leverage what we can’t change.
The trick is: question how much your motivation aligns with your goals (or doesn’t).
So if you feel like checking Facebook for the eleventieth time today, ask yourself: “am I really looking for new exciting events that surely happened in the past 60 seconds since I last checked, or am I just looking for dopamine?”
You might then realize: “Hmm, I’m actually just looking for dopamine, and I’m not going to find it there”
Then, pick something else to do that will actually be more rewarding. It helps if you make a sort of dopa-menu in advance, of things to pick from. You can keep this as a list on your phone, or printed and pinned up near your computer.
Examples might be: Working on that passion project of yours, or engaging in your preferred hobby. Or spending quality time with a loved one. Or doing housework (surprisingly not something we’re commonly motivated-by-default to do, but actually is rewarding when done). Or exercising (same deal). Or learning that language on Duolingo (all those bells and whistles the app has are very much intentional dopamine-triggers to make it addictive, but it’s not a terrible outcome to be addicted to learning!).
Basically… Let your brain’s tendency to get led astray work in your favor, by putting things in front of it that will lead you in good directions.
Things for your health and/or education are almost always great things to allow yourself the “ooh, shiny” reaction and pick them up, try something new, etc.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Arterial plaque is a big deal, and statistically it’s more of a risk as we get older, often coming to a head around age 72 for women and 65 for men—these are the median ages at which people who are going to get heart attacks, get them. Or get it, because sometimes one is all it takes.
The Ankle-Brachial Index Test
Dr. Brewer recommends a home test for detecting arterial plaque called the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI), which uses a blood pressure monitor. The test involves measuring blood pressure in both the arms and ankles, then calculating the ratio of these measurements:
- A healthy ABI score is between 1.0 and 1.4; anything outside this range may indicate arterial problems.
- Low ABI scores (below 0.8) suggest plaque is likely obstructing blood flow
- High ABI scores (above 1.4) may indicate artery hardening
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), associated with poor ABI results (be they high or low), can cause a whole lot of problems that are definitely better tackled sooner rather than later—remember that atherosclerosis is a self-worsening thing once it gets going, because narrower walls means it’s even easier for more stuff to get stuck in there (and thus, the new stuff that got stuck also becomes part of the walls, and the problem gets worse).
If you need a blood pressure monitor, by the way, here’s an example product on Amazon.
Do note also that yes, if you have plaque obstructing blood flow and hardened arteries, your scores may cancel out and give you a “healthy” score, despite your arteries being very much not healthy. For this reason, this test can be used to raise the alarm, but not to give the “all clear”.
For more on all of the above, plus a demonstration and more in-depth explanation of the test, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
We’re only using a fraction of health workers’ skills. This needs to change
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Roles of health professionals are still unfortunately often stuck in the past. That is, before the shift of education of nurses and other health professionals into universities in the 1980s. So many are still not working to their full scope of practice.
There has been some expansion of roles in recent years – including pharmacists prescribing (under limited circumstances) and administering a wider range of vaccinations.
But the recently released paper from an independent Commonwealth review on health workers’ “scope of practice” identifies the myriad of barriers preventing Australians from fully benefiting from health professionals’ skills.
These include workforce design (who does what, where and how roles interact), legislation and regulation (which often differs according to jurisdiction), and how health workers are funded and paid.
There is no simple quick fix for this type of reform. But we now have a sensible pathway to improve access to care, using all health professionals appropriately.
A new vision for general practice
I recently had a COVID booster. To do this, I logged onto my general practice’s website, answered the question about what I wanted, booked an appointment with the practice nurse that afternoon, got jabbed, was bulk-billed, sat down for a while, and then went home. Nothing remarkable at all about that.
But that interaction required a host of facilitating factors. The Victorian government regulates whether nurses can provide vaccinations, and what additional training the nurse requires. The Commonwealth government has allowed the practice to be paid by Medicare for the nurse’s work. The venture capitalist practice owner has done the sums and decided allocating a room to a practice nurse is economically rational.
The future of primary care is one involving more use of the range of health professionals, in addition to GPs.
It would be good if my general practice also had a physiotherapist, who I could see if I had back pain without seeing the GP, but there is no Medicare rebate for this. This arrangement would need both health professionals to have access to my health record. There also needs to be trust and good communication between the two when the physio might think the GP needs to be alerted to any issues.
This vision is one of integrated primary care, with health professionals working in a team. The nurse should be able to do more than vaccination and checking vital signs. Do I really need to see the GP every time I need a prescription renewed for my regular medication? This is the nub of the “scope of practice” issue.
How about pharmacists?
An integrated future is not the only future on the table. Pharmacy owners especially have argued that pharmacists should be able to practise independently of GPs, prescribing a limited range of medications and dispensing them.
This will inevitably reduce continuity of care and potentially create risks if the GP is not aware of what other medications a patient is using.
But a greater role for pharmacists has benefits for patients. It is often easier and cheaper for the patient to see a pharmacist, especially as bulk billing rates fall, and this is one of the reasons why independent pharmacist prescribing is gaining traction.
It’s often easier for a patient to see a pharmacist than a GP. PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock Every five years or so the government negotiates an agreement with the Pharmacy Guild, the organisation of pharmacy owners, about how much pharmacies will be paid for dispensing medications and other services. These agreements are called “Community Pharmacy Agreements”. Paying pharmacists independent prescribing may be part of the next agreement, the details of which are currently being negotiated.
GPs don’t like competition from this new source, even though there will be plenty of work around for GPs into the foreseeable future. So their organisations highlight the risks of these changes, reopening centuries old turf wars dressed up as concerns about safety and risk.
Who pays for all this?
Funding is at the heart of disputes about scope of practice. As with many policy debates, there is merit on both sides.
Clearly the government must increase its support for comprehensive general practice. Existing funding of fee-for-service medical benefits payments must be redesigned and supplemented by payments that allow practices to engage a range of other health professionals to create health-care teams.
This should be the principal direction of primary care reform, and the final report of the scope of practice review should make that clear. It must focus on the overall goal of better primary care, rather than simply the aspirations of individual health professionals, and working to a professional’s full scope of practice in a team, not a professional silo.
In parallel, governments – state and federal – must ensure all health professionals are used to their best of their abilities. It is a waste to have highly educated professionals not using their skills fully. New funding arrangements should facilitate better access to care from all appropriately qualified health professionals.
In the case of prescribing, it is possible to reconcile the aspirations of pharmacists and the concerns of GPs. New arrangements could be that pharmacists can only renew medications if they have agreements with the GP and there is good communication between them. This may be easier in rural and suburban areas, where the pharmacists are better known to the GPs.
The second issues paper points to the complexity of achieving scope of practice reforms. However, it also sets out a sensible path to improve access to care using all health professionals appropriately.
Stephen Duckett, Honorary Enterprise Professor, School of Population and Global Health, and Department of General Practice and Primary Care, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Should You Shower Daily?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝I read an article that daily showering is “performative” and doesn’t really give any health benefits, what do you say?❞
We looked to find the article you might be referring to, and this seems to be about a BBC article that was then picked up, rehashed in fewer (but more sensational) words, and widely popularized by the New York Post (not the most scholarly of publications, but it seems to have “done numbers”).
Here’s the BBC article:
BBC | There’s no need to shower every day—here’s why
Looking for the science behind the “Experts say…” claims, none of the articles we found linked to any new research. One of them did link to some old (2005) research:
We also see (in the dearth of scholarly research to cite), a Harvard Health article being cited quite a bit, and this is more helpful and informative than the flashy news articles, without requiring to read through a lot of hard science.
To summarize, Harvard’s Dr. Shmerling says daily showering can:
- Cause/worsen dry skin
- Make skin more permeable to pathogens
- Upset our natural balance of bacteria that are supposed to be there
- Weaken our immune system
Read in full: Harvard Health | Showering daily—is it necessary?
But what if I like showering?
Well, don’t let us stop you. But you might consider using less in the way of shower products. We wrote about this previously, in answer to a different-but-related subscriber question:
10almonds | Body Scrubs: Benefits, Risks, and Guidance
PS…
Handwashing, though? Most people could reasonably do that more often:
Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
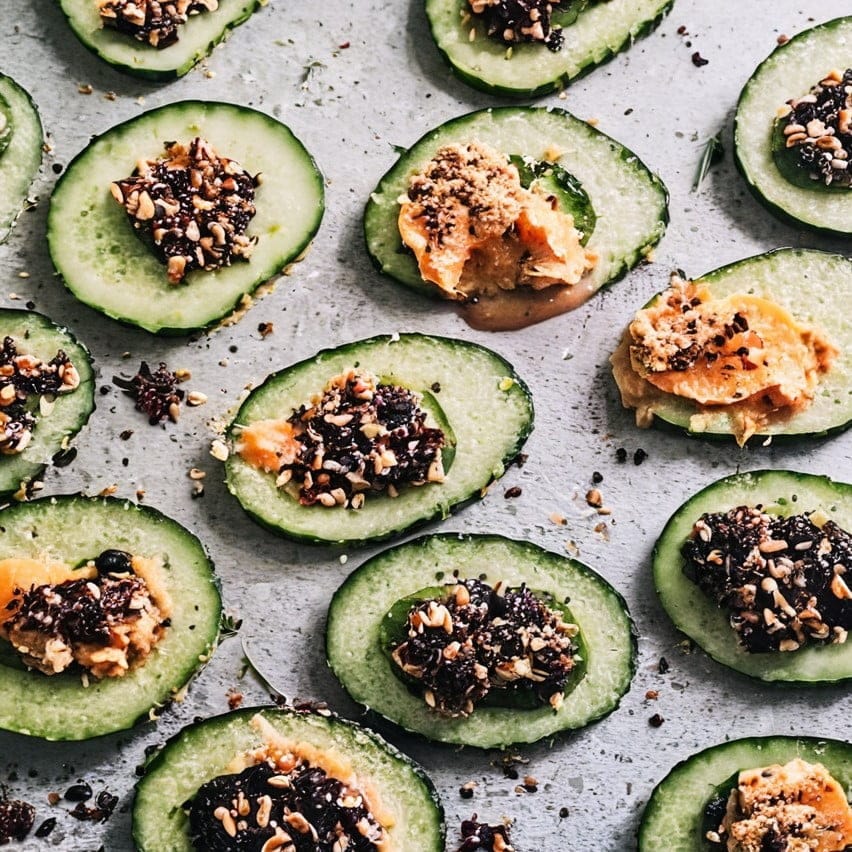
Cucumber Canapés-Crudités
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s time to party with these delicious snacks, which are great as an hors d’œuvre, amuse-bouche, or part of a buffet. And like all our offerings, they’re very healthy too—in this case, especially for the gut and heart!
You will need
- 1 cucumber, sliced
- 1 cup pitted Kalamata olives (or other black olives)
- 1 cup sun-dried tomatoes
- 2 oz feta cheese (or vegan equivalent, or pine nuts)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp fresh basil, chopped
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Make the first topping by combining the olives, half the olive oil, and half the black pepper, into a food processor and blending until it is a coarse pâté.
2) Make the second topping by doing the same with the tomatoes, basil, feta cheese (or substitution), and the other half of the olive oil and black pepper, again until it is a coarse pâté.
3) Assemble the canapés-crudités by topping the cucumber slices alternately with the two toppings, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?! ← yes, you can get this benefit by eating cucumber
- Black Olives vs Green Olives – Which is Healthier? ← have a guess!
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More ← tomatoes are very rich in lycopene
- Herbs for Evidence-Based Health & Healing ←Basil features here
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Kettlebell Sport & Fitness Basics – by Audrey Burgio
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Professional athlete & coach Audrey Burgio covers how to get a full-body workout that will make you stronger and more flexible (there are stretches here too, and many exercises are about strength and suppleness), as well as building stability and balance. In short, more robust and with better mobility.
Which is one of the best things about kettlebell training—unlike dumbbells and barbells, a kettlebell requires the kind of strength that one has to use when doing many routine tasks, from carrying the groceries to moving a big pan in the kitchen.
Because it is otherwise absolutely possible to look like Arnold Schwarzenegger in the gym, and then still pull a muscle moving something at home because the angle was awkward or somesuch!
However, making one’s body so robust does require training safely, and the clear instructions in this book will help the reader avoid injuries that might otherwise be incurred by just picking up some kettlebells and guessing.
Bottom line: if you’d like to get strong and supple from the comfort of your own home, this book can definitely lead the way!
Click here to check out Kettlebell Sport & Fitness Basics, and see the difference in your body!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Peaches vs Plums – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peaches to plums, we picked the peaches.
Why?
Both are great! But there is a clear winner out of these two botanically-similar fruits:
In terms of macronutrients they are very similar. Peaches have slightly more protein and plums have slightly more carbs, but the numbers are close enough to make no meaningful difference; they’re both mostly water.
They’re also not too far from each other in the category of vitamins; peaches have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, E, and choline, while plums have more of vitamins B1, B6, B9, C, and K. They’re equal on vitamin A, by the way, and the vitamins they do differ in, differ by around the same margins, so this category is a clear tie.
When it comes to minerals, however, peaches win easily with more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. The two fruits are equal on calcium, and plum is not higher in any minerals.
While they already won easily because of the mineral situation, it should be noted that peaches also have the lower glycemic index. But honestly, plums are fine too; peaches are just even lower.
So: enjoy both, but if you’re going to pick one, peaches boast the most!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Dried Apricots vs Dried Prunes – Which is Healthier? (prunes are dried plums, usually partially rehydrated)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: