Don’t Do *This* If You’re Over 50 (And Want Better Sleep)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Michael Breus, sleep specialist, explains:
Don’t make these mistakes
Dr. Breus recommends avoiding…
- Misusing magnesium: magnesium is a helpful sleep aid but must be carefully monitored. Recommended doses are 250mg for women and 300–350 mg for men, with slight adjustments for hot climates or active lifestyles. Overdosing can cause stomach issues, diarrhea, and dehydration, disrupting sleep. He recommends starting with magnesium glycinate for fewer stomach issues, and later mix with magnesium citrate. Always check supplements to avoid excessive magnesium intake.
- Misusing melatonin: melatonin production declines after age 55–60, making low-dose supplementation (0.5–1 mg) beneficial. He recommends, however, avoiding high doses (3–10mg), and he recommends to take it 90 minutes before bedtime. Melatonin interacts with some medications (including some meds for blood pressure or depression), so consult a pharmacist before use to avoid risks like serotonin syndrome.
- Going to bed too early: going to bed too early disrupts circadian rhythms and reduces sleep drive, causing earlier waking. Now, being an “early bird” is a generally healthy thing, but if you’re already getting up at 5am, say, you probably want your schedule to not continue to creep further forwards until you become nocturnal. Set a consistent wake-up time and count 7.5 hours backward (plus a set time to fall asleep, e.g. 20 minutes, but you’ll know what it is for you) to determine bedtime.
- Excessive caffeine consumption: from the heading, it may seem like a no-brainer, but older adults metabolize caffeine 33% slower on average, prolonging its effects. Dr. Breus recommends to reduce intake with “caffeine fading,” switching to half-caffeinated coffee for a while and then considering transitioning to decaf. He also suggests enjoying increasingly lower-caffeine teas, like black tea in the morning, matcha in the afternoon, and herbal tea at night to reduce caffeine’s impact on sleep.
- Falling foul of serotonin: avoid taking 5-HTP supplements with SSRI antidepressants like Prozac or Zoloft due to the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- Consider checking for physical problems: if you regularly wake up tired and/or groggy (despite having ostensibly had enough sleep, and there not being a pharmaceutical explanation for your grogginess), consider screening for sleep apnea. Home sleep tests are a convenient way to identify and treat this common but often undiagnosed condition.
For more on each of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
How to Fall Asleep Faster: CBT-Insomnia Treatment
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
90% Of People Skip This Essential Exercise—Are You One Of Them?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Single-leg strengthening is essential for joint health at any age (unless you want to bunny-hop up and down the stairs with both feet at once, for example), yet many people overlook it. This neglect often leads to pain, stiffness, and a higher risk of injury.
Dr. Alyssa Kuhn, arthritis specialist, explains how to do it:
On the rise
In this video, different exercise variations—beginner, intermediate, and advanced—are presented to help you build strength at your own pace:
Beginner: start by using a chair, adding a cushion for support if needed. Sit at the edge and position one foot slightly in front of the other in a staggered stance. Stand up and sit down in a controlled manner, allowing the back leg to bear more weight and work harder than the front leg. Do 8–10 repetitions per side and pay attention to whether one side feels weaker. To build strength, incorporate this movement into daily activities, such as standing up from the couch. Master this variation before progressing, to avoid knee injury.
Intermediate: to make the exercise more challenging, you can either use a lower chair, or extend your front foot further out, shifting more weight to your back leg. Only modify one variable at a time to maintain control. Do 8–10 repetitions per side, ensuring proper form. A common mistake is allowing the back knee to move inward, which can cause knee stress. To prevent this, use a mirror to check your form and keep the knee and ankle aligned during movement.
Advanced: when you’re ready, extend your front leg completely with the heel on the ground and toes up, removing its stability and forcing the back leg to work even harder. Maintain controlled movement while keeping your knee and ankle aligned. Repeat the exercise on both sides, focusing extra effort on the weaker leg to build balanced strength.
For more on each of these, plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
The Secret To Better Squats: Foot, Knee, & Ankle Mobility
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Hitting the beach? Here are some dangers to watch out for – plus 10 essentials for your first aid kit
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Summer is here and for many that means going to the beach. You grab your swimmers, beach towel and sunscreen then maybe check the weather forecast. Did you think to grab a first aid kit?
The vast majority of trips to the beach will be uneventful. However, if trouble strikes, being prepared can make a huge difference to you, a loved one or a stranger.
So, what exactly should you be prepared for?
FTiare/Shutterstock Knowing the dangers
The first step in being prepared for the beach is to learn about where you are going and associated levels of risk.
In Broome, you are more likely to be bitten by a dog at the beach than stung by an Irukandji jellyfish.
In Byron Bay, you are more likely to come across a brown snake than a shark.
In the summer of 2023–24, Surf Life Saving Australia reported more than 14 million Australian adults visited beaches. Surf lifesavers, lifeguards and lifesaving services performed 49,331 first aid treatments across 117 local government areas around Australia. Surveys of beach goers found perceptions of common beach hazards include rips, tropical stingers, sun exposure, crocodiles, sharks, rocky platforms and waves.
Sun and heat exposure are likely the most common beach hazard. The Cancer Council has reported that almost 1.5 million Australians surveyed during summer had experienced sunburn during the previous week. Without adequate fluid intake, heat stroke can also occur.
Lacerations and abrasions are a further common hazard. While surfboards, rocks, shells and litter might seem more dangerous, the humble beach umbrella has been implicated in thousands of injuries.
Sprains and fractures are also associated with beach activities. A 2022 study linked data from hospital, ambulance and Surf Life Saving cases on the Sunshine Coast over six years and found 79 of 574 (13.8%) cervical spine injuries occurred at the beach. Surfing, smaller wave heights and shallow water diving were the main risks.
Rips and rough waves present a higher risk at areas of unpatrolled beach, including away from surf lifesaving flags. Out of 150 coastal drowning deaths around Australia in 2023–24, nearly half were during summer. Of those deaths:
- 56% occurred at the beach
- 31% were rip-related
- 86% were male, and
- 100% occurred away from patrolled areas.
People who had lived in Australia for less than two years were more worried about the dangers, but also more likely to be caught in a rip.
Safety Beach on Victoria’s Mornington Peninsula. Still bring your first aid essentials though. Julia Kuleshova/Shutterstock Knowing your DR ABCs
So, beach accidents can vary by type, severity and impact. How you respond will depend on your level of first aid knowledge, ability and what’s in your first aid kit.
A first aid training company survey of just over 1,000 Australians indicated 80% of people agree cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the most important skill to learn, but nearly half reported feeling intimidated by the prospect.
CPR training covers an established checklist for emergency situations. Using the acronym “DR ABC” means checking for:
- Danger
- Response
- Airway
- Breathing
- Circulation
A complete first aid course will provide a range of skills to build confidence and be accredited by the national regulator, the Australian Skills Quality Authority.
What to bring – 10 first aid essentials
Whether you buy a first aid kit or put together you own, it should include ten essential items in a watertight, sealable container:
- Band-Aids for small cuts and abrasions
- sterile gauze pads
- bandages (one small one for children, one medium crepe to hold on a dressing or support strains or sprains, and one large compression bandage for a limb)
- large fabric for sling
- a tourniquet bandage or belt to restrict blood flow
- non-latex disposable gloves
- scissors and tweezers
- medical tape
- thermal or foil blanket
- CPR shield or breathing mask.
Before you leave for the beach, check the expiry dates of any sunscreen, solutions or potions you choose to add.
If you’re further from help
If you are travelling to a remote or unpatrolled beach, your kit should also contain:
- sterile saline solution to flush wounds or rinse eyes
- hydrogel or sunburn gel
- an instant cool pack
- paracetamol and antihistamine medication
- insect repellent.
Make sure you carry any “as-required” medications, such as a Ventolin puffer for asthma or an EpiPen for severe allergy.
Vinegar is no longer recommended for most jellyfish stings, including Blue Bottles. Hot water is advised instead.
In remote areas, also look out for Emergency Response Beacons. Located in high-risk spots, these allow bystanders to instantly activate the surf emergency response system.
If you have your mobile phone or a smart watch with GPS function, make sure it is charged and switched on and that you know how to use it to make emergency calls.
First aid kits suitable for the beach range in price from $35 to over $120. Buy these from certified first aid organisations such as Surf Lifesaving Australia, Australian Red Cross, St John Ambulance or Royal Life Saving. Kits that come with a waterproof sealable bag are recommended.
Be prepared this summer for your trip to the beach and pack your first aid kit. Take care and have fun in the sun.
Andrew Woods, Lecturer, Nursing, Faculty of Health, Southern Cross University and Willa Maguire, Associate Lecturer in Nursing, Southern Cross University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Cross That Bridge – by Samuel J. Lucas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Books of this genre usually have several chapters of fluff before getting to the point. You know the sort:
- Let me tell you about some cherry-picked celebrity stories that overlook survivorship bias
- Let me tell you my life story, the bad parts
- My life story continued, the good parts now
- What this book can do for you, an imaginative pep talk that keeps circling back to me
…then there will be two or three chapters of the actual advertised content, and then a closing chapter that’s another pep talk.
This book, in contrast, throws that out of the window. Instead, Lucas provides a ground-up structure… within which, he makes a point of giving value in each section:
- exercises
- summaries
- actionable advice
For those who like outlines, lists, and overviews (as we do!), this is perfect. There are also plenty of exercises to do, so for those who like exercises, this book will be great too!
Caveat: occasionally, the book’s actionable advices are direct but unclear, for example:
- Use the potential and power of tea, to solve problems
Context: there was no context. This was a bullet-pointed item, with no explanation. It was not a callback to anything earlier; this is the first (and only) reference to tea.
However! The book as a whole is a treasure trove of genuine tips, tools, and voice-of-experience wisdom. Occasional comments may leave you scratching your head, but if you take value from the rest, then the book was already more than worth its while.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Parents are increasingly saying their child is ‘dysregulated’. What does that actually mean?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Welcome aboard the roller coaster of parenthood, where emotions run wild, tantrums reign supreme and love flows deep.
As children reach toddlerhood and beyond, parents adapt to manage their child’s big emotions and meltdowns. Parenting terminology has adapted too, with more parents describing their child as “dysregulated”.
But what does this actually mean?
ShUStudio/Shutterstock More than an emotion
Emotional dysregulation refers to challenges a child faces in recognising and expressing emotions, and managing emotional reactions in social settings.
This may involve either suppressing emotions or displaying exaggerated and intense emotional responses that get in the way of the child doing what they want or need to do.
“Dysregulation” is more than just feeling an emotion. An emotion is a signal, or cue, that can give us important insights to ourselves and our preferences, desires and goals.
An emotionally dysregulated brain is overwhelmed and overloaded (often, with distressing emotions like frustration, disappointment and fear) and is ready to fight, flight or freeze.
Developing emotional regulation
Emotion regulation is a skill that develops across childhood and is influenced by factors such as the child’s temperament and the emotional environment in which they are raised.
In the stage of emotional development where emotion regulation is a primary goal (around 3–5 years old), children begin exploring their surroundings and asserting their desires more actively.
A child’s temperament and upbringing affect how they regulate emotions. bluedog studio/Shutterstock It’s typical for them to experience emotional dysregulation when their initiatives are thwarted or criticised, leading to occasional tantrums or outbursts.
A typically developing child will see these types of outbursts reduce as their cognitive abilities become more sophisticated, usually around the age they start school.
Express, don’t suppress
Expressing emotions in childhood is crucial for social and emotional development. It involves the ability to convey feelings verbally and through facial expressions and body language.
When children struggle with emotional expression, it can manifest in various ways, such as difficulty in being understood, flat facial expressions even in emotionally charged situations, challenges in forming close relationships, and indecisiveness.
Several factors, including anxiety, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, giftedness, rigidity and both mild and significant trauma experiences, can contribute to these issues.
Common mistakes parents can make is dismissing emotions, or distracting children away from how they feel.
These strategies don’t work and increase feelings of overwhelm. In the long term, they fail to equip children with the skills to identify, express and communicate their emotions, making them vulnerable to future emotional difficulties.
We need to help children move compassionately towards their difficulties, rather than away from them. Parents need to do this for themselves too.
Caregiving and skill modelling
Parents are responsible for creating an emotional climate that facilitates the development of emotion regulation skills.
Parents’ own modelling of emotion regulation when they feel distressed. The way they respond to the expression of emotions in their children, contributes to how children understand and regulate their own emotions.
Children are hardwired to be attuned to their caregivers’ emotions, moods, and coping as this is integral to their survival. In fact, their biggest threat to a child is their caregiver not being OK.
Unsafe, unpredictable, or chaotic home environments rarely give children exposure to healthy emotion expression and regulation. Children who go through maltreatment have a harder time controlling their emotions, needing more brainpower for tasks that involve managing feelings. This struggle could lead to more problems with emotions later on, like feeling anxious and hypervigilant to potential threats.
Recognising and addressing these challenges early on is essential for supporting children’s emotional wellbeing and development.
A dysregulated brain and body
When kids enter “fight or flight” mode, they often struggle to cope or listen to reason. When children experience acute stress, they may respond instinctively without pausing to consider strategies or logic.
If your child is in fight mode, you might observe behaviours such as crying , clenching fists or jaw, kicking, punching, biting, swearing, spitting or screaming.
In flight mode, they may appear restless, have darting eyes, exhibit excessive fidgeting, breathe rapidly, or try to run away.
A shut-down response may look like fainting or a panic attack.
When a child feels threatened, their brain’s frontal lobe, responsible for rational thinking and problem-solving, essentially goes offline.
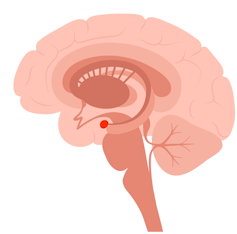
The amygdala, shown here in red, triggers survival mode. pikovit/Shutterstock This happens when the amygdala, the brain’s alarm system, sends out a false alarm, triggering the survival instinct.
In this state, a child may not be able to access higher functions like reasoning or decision-making.
While our instinct might be to immediately fix the problem, staying present with our child during these moments is more effective. It’s about providing support and understanding until they feel safe enough to engage their higher brain functions again.
Reframe your thinking so you see your child as having a problem – not being the problem.
Tips for parents
Take turns discussing the highs and lows of the day at meal times. This is a chance for you to be curious, acknowledge and label feelings, and model that you, too, experience a range of emotions that require you to put into practice skills to cope and has shown evidence in numerous physical, social-emotional, academic and behavioural benefits.
Talk about your day over dinner. Monkey Business Images/Shutterstock Spending even small amounts (five minutes a day!) of quality one-on-one time with your child is an investment in your child’s emotional wellbeing. Let them pick the activity, do your best to follow their lead, and try to notice and comment on the things they do well, like creative ideas, persevering when things are difficult, and being gentle or kind.
Take a tip from parents of children with neurodiversity: learn about your unique child. Approaching your child’s emotions, temperament, and behaviours with curiosity can help you to help them develop emotion regulation skills.
When to get help
If emotion dysregulation is a persistent issue that is getting in the way of your child feeling happy, calm, or confident – or interfering with learning or important relationships with family members or peers – talk to their GP about engaging with a mental health professional.
Many families have found parenting programs helpful in creating a climate where emotions can be safely expressed and shared.
Remember, you can’t pour from an empty cup. Parenting requires you to be your best self and tend to your needs first to see your child flourish.
Cher McGillivray, Assistant Professor Psychology Department, Bond University and Shawna Mastro Campbell, Assistant Professor Psychology, Bond University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
New News From The Centenarian Blue Zones
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From Blue To Green…
We sometimes write about supercentenarians, which word is usually used in academia to refer to people who are not merely over 100 years of age, but over 110 years. These people can be found in many countries, but places where they have been found to be most populous (as a percentage of the local population) have earned the moniker “Blue Zones”—of which Okinawa and Sardinia are probably the most famous, but there are others too.
This is in contrast to, for example “Red Zones”, a term often used for areas where a particular disease is endemic, or areas where a disease is “merely” epidemic, but particularly rife at present.
In any case, back to the Blue Zones, where people live the longest and healthiest—because the latter part is important too! See also:
- Lifespan: how long we live
- Healthspan: how long we stay healthy (portmanteau of “healthy lifespan”)
Most of our readers don’t live in a Blue Zone (in fact, many live in the US, which is a COVID Red Zone, a diabetes Red Zone, and a heart disease Red Zone), but that doesn’t mean we can’t all take tips from the Blue Zones and apply them, for example:
- The basics: The Blue Zones’ Five Pillars Of Longevity
- Going beyond: The Five Key Traits Of Healthy Aging
You may be wondering… How much good will this do me? And, we do have an answer for that:
When All’s Said And Done, How Likely Are You To Live To 100?
Now that we’re all caught-up…
The news from the Blues
A team of researchers did a big review of observational studies of centenarians and near-centenarians (aged 95+). Why include the near-centenarians, you ask? Well, most of the studies are also longitudinal, and if we’re doing an observational study of the impact of lifestyle factors on a 100-year-old, it’s helpful to know what they’ve been doing recently. Hence nudging the younger-end cutoff a little lower, so as to not begin each study with fresh-faced 100-year-olds whom we know nothing about.
Looking at thousands of centenarians (and near-centenarians, but also including some supercentenarians, up the age of 118), the researchers got a lot of very valuable data, far more than we have room to go into here (do check out the paper at the bottom of this article, if you have time; it’s a treasure trove of data), but one of the key summary findings was a short list of four factors they found contributed the most to extreme longevity:
- A diverse diet with low salt intake: in particular, a wide variety of plant diversity, including protein-rich legumes, though fish featured prominently also. On average they got 57% and 65% of their energy intake from carbohydrates, 12% to 32% from protein, and 27% to 31% from fat. As for salt, they averaged 1.6g of sodium per day, which is well within the WHO’s recommendation of averaging under 2g of sodium per day. As a matter of interest, centenarians in Okinawa itself averaged 1.1g of sodium per day.
- Low medication use: obviously there may be a degree of non-causal association here, i.e. the same people who just happened to be healthier and therefore lived longer, correspondingly took fewer medications—they took fewer medications because they were healthier; they weren’t necessarily healthier because they took fewer medications. That said, overmedication can be a big problem, especially in places with a profit motive like the US, and can increase the risk of harmful drug interactions, and side effects that then need more medications to treat the side effects, as well as direct iatrogenic damage (i.e. this drug treats your condition, but as the cost of harming you in some other way). Naturally, sometimes we really do need meds, but it’s a good reminder to do a meds review with one’s doctor once in a while, and see if everything’s still of benefit.
- Getting good sleep: not shocking, and this one’s not exactly news. But what may be shocking is that 68% of centenarians reported consistently getting enough good-quality sleep. To put that into perspective, only 35% of 10almonds readers reported regularly getting sleep in the 7–9 hours range.
- Rural living environment: more than 75% of the centenarians and near-centenarians lived in rural areas. This is not usually something touted as a Blue Zones thing on lists of Blue zones things, but this review strongly highlighted it as very relevant. In the category of things that are more obvious once it’s pointed out, though, this isn’t necessarily such a difference between “country folk” and “city folk”, so much as the ability to regularly be in green spaces has well-established health benefits physically, mentally, and both combined (such as: neurologically).
And showing that yes, even parks in cities make a significant difference:
Want to know more?
You can read the study in full here:
A systematic review of diet and medication use among centenarians and near-centenarians worldwide
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How Ibogaine Can Beat Buprenorphine For Beating Addictions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Questions?❞
It seems that this week, everyone was so satisfied with our information, that we received no questions! (If you sent one and we somehow missed it, please accept our apologies and do bring our attention to it)
However, we did receive some expert feedback that we wanted to share because it’s so informative:
❝I work at a detox rehab in Mexico, where we can use methods not legal in the United States. Therefore, while much of the linked articles had useful information, I’m in the “trenches” every day, and there’s some information I’d like to share that you may wish to share, with additional information:
- Buprenorphine is widely used and ineffective for addiction because it’s synthetic and has many adverse side effects. For heavy drug users it isn’t enough and they still hit the streets for more opioid, resulting in fentanyl deaths. Depending on length of usage and dose, it can take WEEKS to get off of, and it’s extremely difficult.
- Ibogaine is the medicine we use to detox people off opiates, alcohol, meth as well as my own specialty, bulimia. It’s psychoactive and it temporarily “resets” the brain to a pre-addictive state. Supplemented by behavior and lifestyle changes, as well as addressing the traumas that led to the addiction is extremely effective.
Our results are about 50%, meaning the client is free of the substance or behavior 1 year later. Ibogaine isn’t a “magic pill” or cure, it’s an opening tool that makes the difficult work of reclaiming one’s life easier.
Ibogaine is not something that should be done outside a medical setting. It requires an EKG to ensure the heart is healthy and doesn’t have prolonged QT intervals; also blood testing to ensure organs are functioning (especially the liver) and mineral levels such as magnetic and potassium are where they should be. It is important that this treatment be conducted by experienced doctors or practitioners, and monitoring vital signs constantly is imperative.
I’m taking time to compose this information because it needs to be shared that there is an option available most people have not heard about.❞
~ 10almonds reader (slightly edited for formatting and privacy)
Thank you for that! Definitely valuable information for people to know, and (if applicable for oneself or perhaps a loved one) ask about when it comes to local options.
We see it’s also being studied for its potential against other neurological conditions, too:
❝The combination of ibogaine and antidepressants produces a synergistic effect in reducing symptoms of psychiatric disorders such as bipolar disorder, depression, schizophrenia, paranoia, anxiety, panic disorder, mania, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and obsessive–compulsive disorder. Though ibogaine and the antidepressant act in different pathways, together they provide highly efficient therapeutic responses compared to when each of the active agents is used alone.❞
Read more: Ibogaine and Their Analogs as Therapeutics for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders
For those who missed it, today’s information about ibogaine was in response to our article:
Let’s Get Letting Go (Of These Three Things)
…which in turn referenced our previous main feature:
Which Addiction-Quitting Methods Work Best?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: