Does Music Really Benefit The Brain?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is it actually beneficial for the brain to listen to music, or is it just in line with any relaxing activity? And what kind of music is most beneficial❞
The short answer, first of all, is that it is indeed beneficial.
One reason for this without having to get very deep into it, is that a very important thing for general brain health is using it, and that means lighting up all areas of your brain.
Now, we all lead different lives and thus different parts of our brains will get relatively more resources than others depending on what we do with them, and that’s ok.
For example, if you were to scan this writer’s polyglot brain, you’d surely find overdevelopment in areas associated with language use and verbal memory, but if you were to scan a taxi-driver’s brain, then it’d be spatial reasoning and spatial memory that’s overpowered, and for a visual artist, it may be visual processing and creativity that’s enhanced. A musician’s brain? Fine motor skills, auditory processing, auditory memory.
Now, for those of us who aren’t musicians, how then can we light up areas associated with music? By listening to music, of course. It won’t give us the fine motor skills of a concert violinist, but the other areas we mentioned will get a boost.
See also: How To Engage Your Whole Brain ← this covers music too, but it’s about (as the title suggests) the whole brain, so check it out and see if there are any areas you’ve been neglecting!
There are other benefits too, though, including engaging our parasympathetic nervous system, which is good for our heart, gut, brain, and general health—especially if we sing or hum along to the music:
The Science Of Sounds ← this also covers the science (yes, science) of mantra meditation vs music
As for “and what kind of music is most beneficial”, we’d hypothesize that a variety is best, just like with food!
However, there are some considerations to bear in mind, with science to support them. For example…
About tempo:
❝EEG analysis revealed significant changes in brainwave signals across different frequency bands under different tempi.
For instance, slow tempo induced higher Theta and Alpha power in the frontal region, while fast tempo increased Beta and Gamma band power.
Moreover, fast tempo enhanced the average connectivity strength in the frontal, temporal, and occipital regions, and increased phase synchrony value (PLV) between the frontal and parietal regions.❞
Read in full: Music tempo modulates emotional states as revealed through EEG insights
And if you’re wondering about those different brainwave bands, check out:
- How to get many benefits of sleep, while awake! Non-Sleep Deep Rest: A Neurobiologist’s Take ← although it’s not in the title, this does also cover the different brain wave bands
- Alpha, beta, theta: what are brain states and brain waves? And can we control them?
Additionally, if you just want science-backed relaxation, the following 8-minute soundscape was developed by sound technicians working with a team of psychologists and neurologists.
It’s been clinically tested, and found to have a much more relaxing effect (in objective measures of lowering heart rate and lowering cortisol levels, as well as in subjective self-reports) than merely “relaxing music”.
Try it and see for yourself:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
For much deeper dive into the effect of music on the brain, check out this book we reviewed a while back, by an accomplished musician and neuroscientist (that’s one person, who is both things):
This Is Your Brain on Music – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
Enjoy!
And now for a bonus item…
A s a bit of reader feedback prompted some interesting thoughts:
❝You erred on the which is better section. Read this carefully :Looking at minerals, grapes have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while grapes have more potassium and manganese. A clear win for strawberries here.❞
You’re quite right; thank you for pointing it out, and kindly pardon the typo, which has now been corrected!
The reason for the mistake was because when I (writer responsible for it here, hi) was writing this, I had the information for both fruits in front of me, but the information for grapes was on the right in my field of vision, so I errantly put it on the right on the page, too, while also accidentally crediting strawberries’ minerals to grapes, since strawberries’ data was on the left in my field a vision.
The reason for explaining this: it’s a quirky, very human way to err, in an era when a lot of web content is AI-generated with very different kinds of mistakes (usually because AI is very bad at checking sources, so will confidently state something as true despite the fact that the source was The Onion, or Clickhole, or someone’s facetiously joking answer on Quora, for example).
All in all, while we try to not make typos, we’d rather such human errors than doing like an AI and confidently telling you that Amanita phalloides mushrooms are a rich source of magnesium, and also delicious (they are, reportedly, but they are also the most deadly mushroom on the face of the Earth, also known as the Death Cap mushroom).
In any case, here’s the corrected version of the grapes vs strawberries showdown:
Grapes vs Strawberries – Which is Healthier?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Reading At Night: Good Or Bad For Sleep? And Other Questions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would be interested in your views about “reading yourself to sleep”. I find that current affairs magazines and even modern novels do exactly the opposite. But Dickens – ones like David Copperfield and Great Expectations – I find wonderfully effective. It’s like entering a parallel universe where none of your own concerns matter. Any thoughts on the science that may explain this?!❞
Anecdotally: this writer is (like most writers) a prolific reader, and finds reading some fiction last thing at night is a good way to create a buffer between the affairs of the day and the dreams of night—but I could never fall asleep that way, unless I were truly sleep-deprived. The only danger is if I “one more chapter” my way deep into the night! For what it’s worth, bedtime reading for me means a Kindle self-backlit with low, soft lighting.
Scientifically: this hasn’t been a hugely researched area, but there are studies to work from. But there are two questions at hand (at least) here:
- one is about reading, and
- the other is about reading from electronic devices with or without blue light filters.
Here’s a study that didn’t ask the medium of the book, and concluded that reading a book in bed before going to sleep improved sleep quality, compared to not reading a book in bed:
Here’s a study that concluded that reading on an iPad (with no blue light filter) that found no difference in any metrics except EEG (so, there was no difference on time spent in different sleep states or sleep onset latency), but advised against it anyway because of the EEG readings (which showed slow wave activity being delayed by approximately 30 minutes, which is consistent with melatonin production mechanics):
Here’s another study that didn’t take EEG readings, and/but otherwise confirmed no differences being found:
We’re aware this goes against general “sleep hygiene” advice in two different ways:
- General advice is to avoid electronic devices before bedtime
- General advice is to not do activities besides sleep (and sex) in bed
…but, we’re committed to reporting the science as we find it!
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
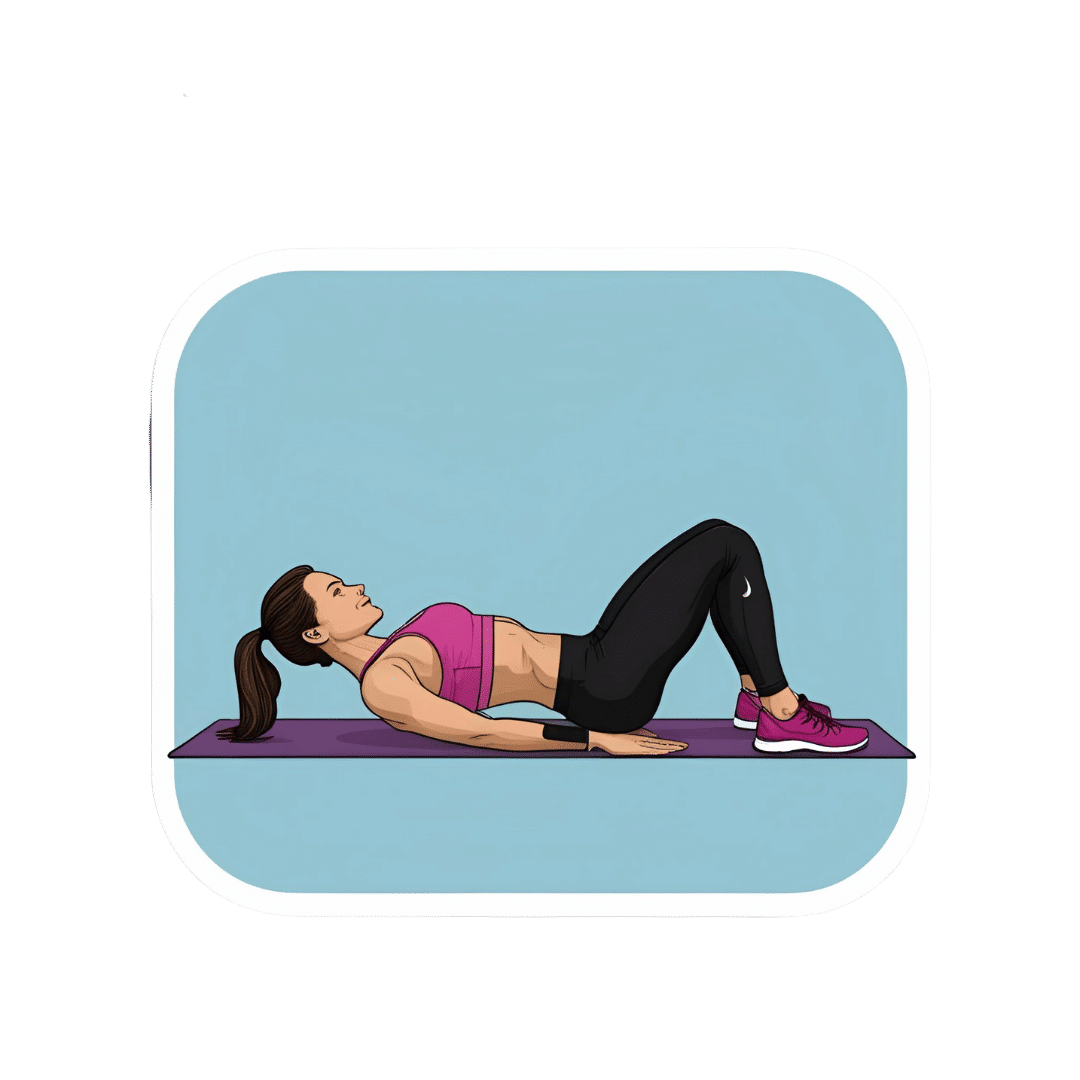
What Happens To Your Body When You Do 100 Glute Bridges Every Day
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not just for a sculpted butt:
Benefits
With consistent daily glute bridge practice, you may expect:
- Rounder, toned butt: targets the gluteus maximus, toning and lifting the butt for a rounder appearance.
- Improved posture: strengthens glutes to support the spine and pelvis, alleviating lower back and hip pain. Stretches tight hip flexors from prolonged sitting.
- Stronger lower back: glutes support the lower back and spine, reducing pain and making it easier to lift heavy objects. Activating the glutes transfers force from legs to core, preventing injuries.
- Stronger knees: stabilizes the knee joint and promotes alignment by engaging glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps, reducing knee pain.
- Sculpted hamstrings: contracts hamstrings during lifts for strength, while stretching them on the way down increases flexibility.
- Increased hip flexibility: strengthens muscles around the hip joint, improving mobility and counteracting tight hips from sedentary habits.
- Reduced back pain: strengthens glutes to correct pelvic tilt and reduce strain on the lower back.
- Faster running speed: improves hip extension, strengthens hamstrings, and activates the gluteus medius for better running power and balance.
- Enhanced strength training performance: strengthens glutes, back, and knees, improving performance in exercises like squats and deadlifts.
As for how to get going, the video offers the following very sound advice: begin with 25–30 reps per session and gradually increase to sets of 100 daily. It should take about 5 minutes (that’s 3 seconds per repetition). Results can be seen in as little as 2 weeks, with significant changes after a month of consistent practice.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Strong Curves: A Woman’s Guide to Building a Better Butt and Body – by Bret Contreras & Kellie Davis
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Do You Have A Personalized Health Plan? (Here’s How)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“Good health” is quite a broad umbrella, and while we all have a general idea of what “healthy” looks like, it’s easy to focus on some areas and overlook others.
Of course, how much one does this will still depend on one’s level of interest in health, which can change over the course of life, and (barring serious midlife health-related curveballs such as a cancer diagnosis or something) often looks like an inverse bell curve:
- As small kids, we probably barely thought about health
- As teenagers, we probably had a narrow view of health (often related to whatever is considered sexually attractive at the time)
- In our 20s, may have a bit of a health kick in which we learn and apply a lot… Which often then gets to later take a bit of a back seat to work responsibilities and so forth
- This is commonly followed by a few decades of just trying to make it to Friday by any means necessary (definite risk factor for substance abuse of various kinds), double if we have kids, triple if we have work, kids, and are also solely responsible for managing the household.
- Then just as suddenly as it is predictably, we are ambushed when approaching retirement age by a cluster of age-related increased health risks that we now get to do our best to mitigate—the focus here is “not dying early”. A lot of health education occurs at this time.
- Finally, upon retirement, we actually get the time to truly focus on our health again, and now it’s easier to learn about all aspects of health, even if now there’s a need to juggle many health issues all at once, most of which affect the others.
See also: How Likely Are You To Live To 100? ← in which we can also see a graph of 10almonds subscribers’ ages, consistent with the above
So, let’s recap, and personalize our health plan
There are often things we wish we could have focused on sooner, so now’s the time to figure out what future-you in your next decade (or later!) is going to thank you for having done now.
So, while 20-year-old us might have been focusing on fat levels or athletic performance, how much does that really help us now? (With apologies to any readers in their 20s, but also, with the bonus for you: now’s the perfect time to plan ahead!)
At 10almonds, while we cover very many health topics, we often especially focus on:
- Brain health
- Heart health
- Gut health
…because they affect everything else so much. We’ve listed them there in the order they appear in the body, but in fact it can be useful to view them upside down, because:
- Gut health is critical for good metabolic health (a happy efficient gut allows us to process nutrients, including energy, efficiently)
- Metabolic health is critical for good heart health (a nicely ticking metabolism will not strain our heart)
- Heart health is critical for good brain health (a strong heart will nourish the brain with well-oxygenated blood and the nutrients it also carries)
So, this isn’t a catch-22 at all! There is a clear starting point:
“How do I do the other bits, though?”
We have you covered here: Your Health Audit, From Head To Toe
“Wait, where’s the personalization?”
This comes once you’ve got those above things in order.
Hopefully you know what particular health risks you have—as in, particular to you.
First, you will have any current diagnoses, and a plan for treating those. Many chronic illnesses can be reversed or at least lessened with lifestyle changes, in particular, if we reduce chronic inflammation, which is implicated in countless chronic illnesses, and exacerbates most of the rest.
So: How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
The same goes for any heightened risks you have as a result of those current diagnoses.
Next, you will have any genetic health risks—so here’s where genetic testing is a good one-shot tool, to get a lot of information all in one go.
Learn more: The Real Benefit Of Genetic Testing
…and then, of course, take appropriate steps to avoid suffering the things of which you are at increased genetic risk.
Finally, you will have any personal concerns or goals—in other words, what do you want to still be able to do, later in life? It’s easy to say “everything”, but what’s most important?
This writer’s example: I want to remain mobile, free from pain, and sharp of mind.
That doesn’t mean I’ll neglect the rest of my health, but it does mean that I will regularly weigh my choices against whether they are consistent with those three things.
As for how to plan for that?
Check out: Train For The Event Of Your Life! ← this one is mostly about the mobility aspect; staying free from pain is in large part a matter of avoiding inflammation which we already discussed, and staying sharp of mind relies on the gut-heart-brain pipeline we also covered.
You can also, of course, personalize your diet per which areas of health are the most important for you:
Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean (most anti-inflammatory, gut-healthiest, heart-healthiest, brain-healthiest)
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Owning Your Weight – by Henri Marcoux
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A lot of diet books—which this isn’t—presuppose that the reader wants to lose weight, and varyingly encourage and shame the reader into trying to do so.
Dr. Henri Marcoux takes a completely different approach.
He starts by assuming we are—whether consciously or not—the weight we want to be, and looks at the various physical and psychological factors that influence us to such. Ranging from food poverty to eating our feelings to social factors and more, he bids us examine our relationship with food and eating—not just in the sense of mindful eating, but from multiple scientific angles too.
From this, Dr. Marcoux gives us questions and suggestions to ensure that our relationship with food and eating is what we want it to be, for us.
Much of the latter part of the book covers not just how to go about the requisite lifestyle changes… But also how to implement things in a way that sticks, and is a genuine pleasure to implement. If this sounds over-the-top, the truth is that it’s just because it honestly is a lower-stress way of living.
Bottom line: if you want to gain or lose weight, there’s a good chance this book will help you. If you want to be happier and healthier at the weight you are, there’s a good chance this book will help you with that, too.
Click here to check out Owning Your Weight, and take control of yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Celery vs Cucumber – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celery to cucumber, we picked the celery.
Why?
They are both great, of course! But celery came out on top:
Their macros are very comparable; they’re both 95% water with just enough other things to hold them together, and those other things are in approximately the same proportions in both celery and cucumber.
In the category of vitamins, however, celery has a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B9, E, and K, as well as slightly more vitamin C. Cucumber, meanwhile, only boasts slightly higher vitamin B1.
An easy win for celery on the vitamin front!
Minerals are closer, but celery still comes out on top with its notably higher calcium and potassium content. Cucumber has more iron and zinc, but the margin is smaller.
As a point in cucumber’s favor, it has been noted for its anti-inflammatory effect in ways that celery hasn’t, but we don’t think this is enough to say it wins over celery sweeping the vitamins category and coming out top for minerals too.
However! They are both great, so enjoy them both, of course.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Cucumber Extract Beats Glucosamine & Chondroitin… At 1/135th Of The Dose?!
- Some Surprising Truths About Hunger And Satiety ← both celery and cucumber are great for this
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to Stay Sane – by Philippa Perry
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book is not: a guide of “how to stay sane” in the popular use of the word “sane”, meaning free from serious mental illness of all and any kinds in general, and especially free from psychotic delusions. Alas, this book will not help with those.
What, then, is it? A guide of “how to stay sane” in the more casual sense of resiliently and adaptively managing stress, anxiety, and suchlike. The “light end” of mental health struggles, that nonetheless may not always feel light when dealing with them.
The author, a psychotherapist, draws from her professional experience and training to lay out psychological tools for our use, as well as giving the reader a broader understanding of the most common ills that may ail us.
The writing style is relaxed and personable; it’s not at all like reading a textbook.
The psychotherapeutic style is not tied to one model, and rather hops from one to another, per what is most likely to help for a given thing. This is, in this reviewer’s opinion at least, far better than the (all-too common) attempt made by a lot of writers to try to present their personal favorite model as the cure for all ills, instead of embracing the whole toolbox as this one does.
Bottom line: if your mental health is anywhere between “mostly good” and “a little frayed around the edges but hanging on by at least a few threads”, then this book likely can help you gain/maintain the surer foundation you’re surely seeking.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: