Chili Hot-Bedded Salmon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This one can be made in less time than it takes to order and receive a Chinese take-out! The principle is simple: it’s a bed of greens giving pride of place to a salmon fillet in a deliciously spicy marinade. So healthwise, we have greens-and-beans, healthy protein and fats, and tasty polyphenols. Experientially, we have food that tastes a lot more decadent than it is!
You will need
- 4 salmon fillets (if vegan, substitute firm tofu; see also how to make this no-salmon salmon)
- 2 bok choy, washed and stems trimmed
- 7 oz green beans, trimmed
- 4 oz sugar snap peas
- 4 spring onions, sliced
- 2 tbsp chili oil*
- 1 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tsp garlic paste
- 1 tsp ginger paste
- 1 tsp black pepper
*this can be purchased as-is, but if you want to make your own in advance, simply take extra virgin olive oil and infuse it with [finely chopped, red] chili. This is a really good thing to do for commonly-used flavored oils, by the way—chili oil and garlic oil are must-haves in this writer’s opinion; basil oil, sage oil, and rosemary oil, are all excellent things to make and have in, too. Just know, infusing is not quick, so it’s good to do these in batch and make plenty well before you need it. For now, if you don’t have any homemade already, then store-bought is fine 🙂
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 360℉/180℃/gas mark 6
2) Lay out 4 large squares of foil, and put the bok choy, green beans, and sugar snap peas in a little pile in the middle of each one. Put a salmon fillet on top of each (if it has skin, score the skin first, so that juices will be able to penetrate, and put it skin-side down), and then top with the spring onions.
3) Mix the rest of the ingredients in a small bowl, and then spoon this marinade evenly over each of the fillets (alternatively, if you have occasion to marinade the fillets in advance and let them sit in the marinade in the fridge for some hours before, do so, in which case this step will already be done now, because past-you did it. Yay for past-you!)
4) Fold up the edges of the foil, making each one an enclosed parcel, gently sealed at the top by folding it over. Put them on a baking tray and bake for about 20 minutes.
5) Serve! If you’d like some carbs with it, we recommend our tasty versatile rice recipe.
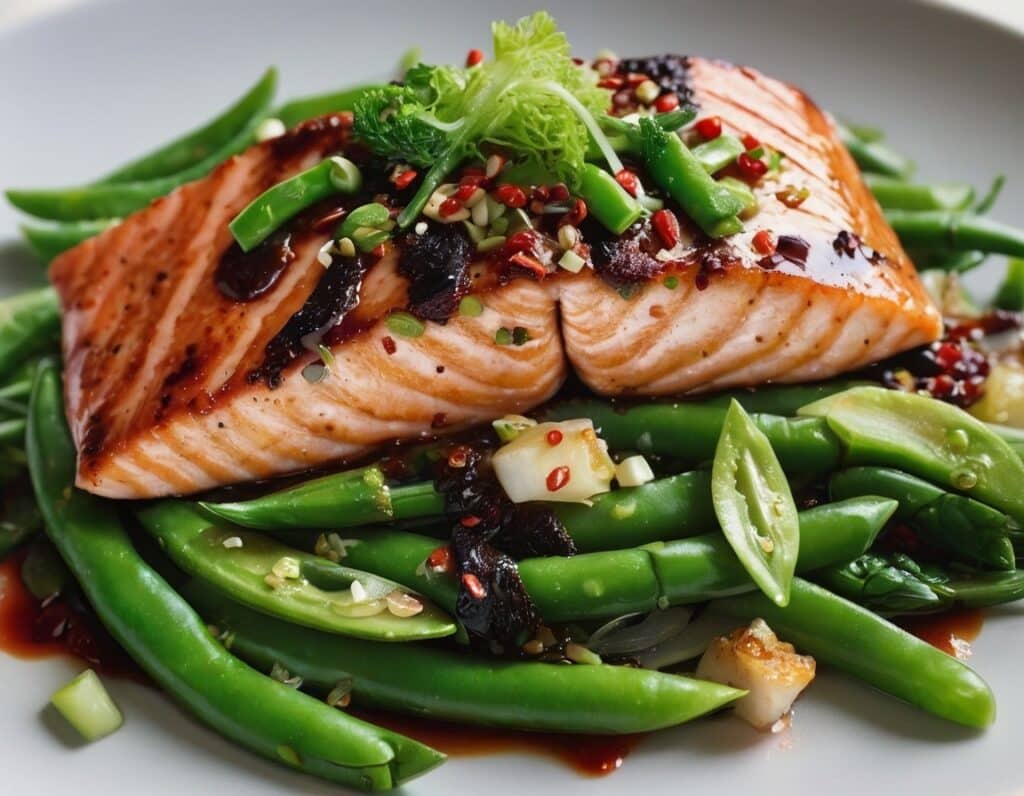

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Farmed Fish vs Wild-Caught ← don’t underestimate the difference this makes!
- Tasty Polyphenols For Your Heart And Brain
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
100 Hikes of a Lifetime – by Kate Siber
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is published by National Geographic, so you can imagine the quality of the photos throughout.
Inside, and after a general introduction and guide to gear and packing appropriately, it’s divided into continents, with a diverse array of “trips of a lifetime” for anyone who enjoys hiking.
It’s not a narrative book, rather, it is a guide, a little in the style of “Lonely Planet”, with many “know before you go” tips, information about the best time to go, difficult level, alternative routes if you want to get most of the enjoyment while having an easier time of it (or, conversely, if you want to see some extra sights along the way), and what to expect at all points.
Where the book really excels is in balancing inspiration with information. There are some books that make you imagine being in a place, but you’ll never actually go there. There are other books that are technical manuals but not very encouraging. This one does both; it provides the motivation and the “yes, you really can, here’s how” information that, between them, can actually get you packing and on your way.
Bottom line: if you yearn for breathtaking views and time in the great outdoors, but aren’t sure where to start, this will give you an incredible menu to choose from, and give you the tools to go about doing it.
Click here to check out 100 Hikes Of A Lifetime, and live it!
Share This Post
-
The Paleo Diet
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s The Real Deal With The Paleo Diet?
The Paleo diet is popular, and has some compelling arguments for it.
Detractors, meanwhile, have derided Paleo’s inclusion of modern innovations, and have also claimed it’s bad for the heart.
But where does the science stand?
First: what is it?
The Paleo diet looks to recreate the diet of the Paleolithic era—in terms of nutrients, anyway. So for example, you’re perfectly welcome to use modern cooking techniques and enjoy foods that aren’t from your immediate locale. Just, not foods that weren’t a thing yet. To give a general idea:
Paleo includes:
- Meat and animal fats
- Eggs
- Fruits and vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- Herbs and spices
Paleo excludes:
- Processed foods
- Dairy products
- Refined sugar
- Grains of any kind
- Legumes, including any beans or peas
Enjoyers of the Mediterranean Diet or the DASH heart-healthy diet, or those with a keen interest in nutritional science in general, may notice they went off a bit with those last couple of items at the end there, by excluding things that scientific consensus holds should be making up a substantial portion of our daily diet.
But let’s break it down…
First thing: is it accurate?
Well, aside from the modern cooking techniques, the global market of goods, and the fact it does include food that didn’t exist yet (most fruits and vegetables in their modern form are the result of agricultural engineering a mere few thousand years ago, especially in the Americas)…
…no, no it isn’t. Best current scientific consensus is that in the Paleolithic we ate mostly plants, with about 3% of our diet coming from animal-based foods. Much like most modern apes.
Ok, so it’s not historically accurate. No biggie, we’re pragmatists. Is it healthy, though?
Well, health involves a lot of factors, so that depends on what you have in mind. But for example, it can be good for weight loss, almost certainly because of cutting out refined sugar and, by virtue of cutting out all grains, that means having cut out refined flour products, too:
Diet Review: Paleo Diet for Weight Loss
Measured head-to-head with the Mediterranean diet for all-cause mortality and specific mortality, it performed better than the control (Standard American Diet, or “SAD”), probably for the same reasons we just mentioned. However, it was outperformed by the Mediterranean Diet:
So in lay terms: the Paleo is definitely better than just eating lots of refined foods and sugar and stuff, but it’s still not as good as the Mediterranean Diet.
What about some of the health risk claims? Are they true or false?
A common knee-jerk criticism of the paleo-diet is that it’s heart-unhealthy. So much red meat, saturated fat, and no grains and legumes.
The science agrees.
For example, a recent study on long-term adherence to the Paleo diet concluded:
❝Results indicate long-term adherence is associated with different gut microbiota and increased serum trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), a gut-derived metabolite associated with cardiovascular disease. A variety of fiber components, including whole grain sources may be required to maintain gut and cardiovascular health.❞
Bottom line:
The Paleo Diet is an interesting concept, and certainly can be good for short-term weight loss. In the long-term, however (and: especially for our heart health) we need less meat and more grains and legumes.
Share This Post
-
What Your Hands Can Tell You About Your Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Siobhan Deshauer tells us what our hands say about our health—she’s not practicing palmistry though; she’s a rheumatologist, and everything here is about clinical signs of health/disease.
The signs include…
“Spider fingers” (which your writer here has; I always look like I’m ready to cast a spell of some kind), and that’s really the medical name, or arachnodactyly for those who like to get Greek about it. It’s about elongated digits. Elongated other bones too, typically, but the hands are where it’s most noticeable.
The tests:
- Make a fist with your thumb inside (the way you were told never to punch); does your thumb poke out the side notably past the edge of your hand, unassisted (i.e., don’t poke it, just let it rest where it goes to naturally)?
- Take hold of one of your wrists with the fingers of the other hand, wrapping them around. If they reach, that’s normal; if there’s a notable overlap, we’re in Spidey-territory now.
If both of those are positive results for you, Dr. Deshauer recommends getting a genetic test to see if you have Marfan syndrome, because…
Arachnodactyly often comes from a genetic condition called Marfan syndrome, and as well as the elongated digits of arachnodactyly, Marfan syndrome affects the elastic fibers of the body, and comes with the trade-off of an increased risk of assorted kinds of sudden death (if something goes “ping” where it shouldn’t, like the heart or lungs).
But it can also come from Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome!
EDS is characterized by hypermobility of joints, meaning that they are easily flexed past the normal human limit, and/but also easily dislocated.
The tests:
- Put your hand flat on a surface, and using your other hand, see how far back your fingers will bend (without discomfort, please); do they go further than 90°?
- Can you touch your thumb to your wrist* (on the same side?)
*She says “wrist”; for this arachnodactylic writer here it’s halfway down my forearm, but you get the idea
For many people this is a mere quirk and inconvenience, for others it can be more serious and a cause of eventual chronic pain, and for a few, it can be very serious and come with cardiovascular problems (similar to the Marfan syndrome issues above). This latter is usually diagnosed early in life, though, such as when a child comes in with an aneurysm, or there’s a family history of it. Another thing to watch out for!
Check out the video for more information on these, as well as what our fingerprints can mean, indicators of diabetes (specifically, a test for diabetic cheiroarthropathy that you can do at home, like the tests above), carpal tunnel syndrome, Raynaud phenomenon, and more!
She covers 10 main medical conditions in total:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to read more?
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of ← because collagen comes up a lot in the video
- How To Really Look After Your Joints
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
9 Reasons To Avoid Mobility Training
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Why might someone not want to do mobility training? Here are some important reasons:
Make an informed choice
Here’s Liv’s hit-list of reasons to skip mobility training:
- Poor Circulation: Avoid mobility training if you don’t want to improve or maintain good blood circulation, which aids muscle recovery and reduces soreness.
- Low Energy Levels: Mobility training increases oxygen flow to the brain and muscles, boosting energy. Skip it if you prefer feeling sluggish!
- Digestive Health: Stretches that rotate the torso aid digestion and relieve bloating. Definitely best to avoid it if you’re uninterested in improving digestive health.
- Joint Health: Mobility work stimulates synovial fluid production, reducing joint friction and promoting longevity. You can skip it if you don’t care about comfortable movement.
- Sleep Quality: Gentle stretching triggers relaxation, aiding restful sleep. Avoid it if you enjoy restless nights!
- Pain Tolerance: Stretching trains the nervous system to handle discomfort better. Skip it if you prefer suffering 🙂
- Headache Reduction: Mobility work relieves tension in the neck and shoulders, reducing the occurrence and severity of headaches. No need to do it if you’re fine with frequent headaches.
- Immune System Support: Mobility training boosts lymphatic circulation, aiding the immune system. Avoid it if you prefer your immune system to get exciting in a bad way.
- Stress Reduction: Mobility exercises release endorphins and lower cortisol levels, reducing stress. So, it is certainly best to skip it if you prefer feeling stressed and enjoy the many harmful symptoms of high cortisol levels!
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Mobility As Though A Sporting Pursuit: Train For The Event Of Your Life!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
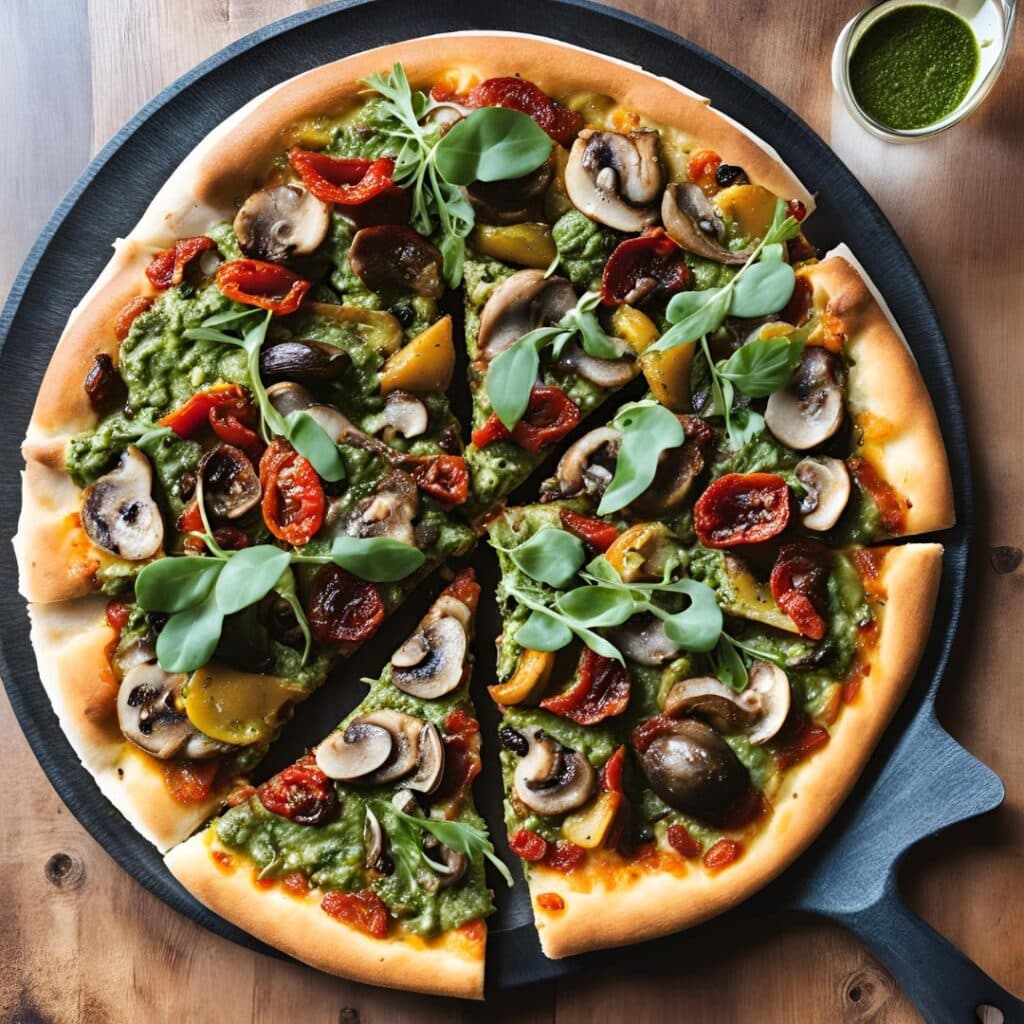
Superfood Pesto Pizza
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not only is this pizza full of foods that punch above their weight healthwise, there’s no kneading and no waiting when it comes to the base, either. Homemade pizzas made easy!
You will need
For the topping:
- 1 zucchini, sliced
- 1 red bell pepper, cut into strips
- 3 oz mushrooms, sliced
- 3 shallots, cut into quarters
- 6 sun-dried tomatoes, roughly chopped
- ½ bulb garlic (paperwork done, but cloves left intact, unless they are very large, in which case halve them)
- 1 oz pitted black olives, halved
- 1 handful arugula
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
For the base:
- ½ cup chickpea flour (also called besan or gram flour)
- 2 tsp extra virgin olive oil
- ½ tsp baking powder
- ⅛ tsp MSG or ¼ tsp low-sodium salt
For the pesto sauce:
- 1 large bunch basil, chopped
- ½ avocado, pitted and peeled
- 1 oz pine nuts
- ¼ bulb garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper
- Juice of ½ lemon
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Toss the zucchini, bell pepper, mushrooms, shallots, and garlic cloves in 1 tbsp olive oil, ensuring an even coating. Season with the black pepper and MSG/salt, and put on a baking tray lined with baking paper, to roast for about 20 minutes, until they are slightly charred.
3) When the vegetables are in the oven, make the pizza base by combining the dry ingredients in a bowl, making a pit in the middle of it, adding the olive oil and whisking it in, and then slowly (i.e., a little bit at a time) whisking in 1 cup cold water. This should take under 5 minutes.
4) Don’t panic when this doesn’t become a dough; it is supposed to be a thick batter, so that’s fine. Pour it into a 9″ pizza pan, and bake for about 15 minutes, until firm. Rotate it if necessary partway through; whether it needs this or not will depend on your oven.
5) While the pizza base is in the oven, make the pesto sauce by blending all the pesto sauce ingredients in a high-speed blender until smooth.
6) When the base and vegetables are ready (these should be finished around the same time), spread the pesto sauce on the base, scatter the arugula over it followed by the vegetables and then the olives and sun-dried tomatoes.
7) Serve, adding any garnish or other final touches that take your fancy.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Which Bell Peppers To Pick? A Spectrum Of Specialties
- Ergothioneine In Mushrooms: “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
- Black Olives vs Green Olives – Which is Healthier
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
- Herbs for Evidence-Based Health & Healing
- Spermidine For Longevity
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Metformin For Weight-Loss & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Metformin Without Diabetes?
Metformin is a diabetes drug; it works by:
- decreasing glucose absorption from the gut
- decreasing glucose production in the liver
- increasing glucose sensitivity
It doesn’t change how much insulin is secreted, and is unlikely to cause hypoglycemia, making it relatively safe as diabetes drugs go.
It’s a biguanide drug, and/but so far as science knows (so far), its mechanism of action is unique (i.e. no other drug works the same way that metformin does).
Today we’ll examine its off-label uses and see what the science says!
A note on terms: “off-label” = when a drug is prescribed to treat something other than the main purpose(s) for which the drug was approved.
Other examples include modafinil against depression, and beta-blockers against anxiety.
Why take it if not diabetic?
There are many reasons people take it, including just general health and life extension:
However, its use was originally expanded (still “off-label”, but widely prescribed) past “just for diabetes” when it showed efficacy in treating pre-diabetes. Here for example is a longitudinal study that found metformin use performed similarly to lifestyle interventions (e.g. diet, exercise, etc). In their words:
❝ Lifestyle intervention or metformin significantly reduced diabetes development over 15 years. There were no overall differences in the aggregate microvascular outcome between treatment groups❞
But, it seems it does more, as this more recent review found:
❝Long-term weight loss was also seen in both [metformin and intensive lifestyle intervention] groups, with better maintenance under metformin.
Subgroup analyses from the DPP/DPPOS have shed important light on the actions of metformin, including a greater effect in women with prior gestational diabetes, and a reduction in coronary artery calcium in men that might suggest a cardioprotective effect.
Long-term diabetes prevention with metformin is feasible and is supported in influential guidelines for selected groups of subjects.❞
Source: Metformin for diabetes prevention: update of the evidence base
We were wondering about that cardioprotective effect, so…
Cardioprotective effect
In short, another review (published a few months after the above one) confirmed the previous findings, and also added:
❝Patients with BMI > 35 showed an association between metformin use and lower incidence of CVD, including African Americans older than age 65. The data suggest that morbidly obese patients with prediabetes may benefit from the use of metformin as recommended by the ADA.❞
We wondered about the weight loss implications of this, and…
For weight loss
The short version is, it works:
- Effectiveness of metformin on weight loss in non-diabetic individuals with obesity
- Metformin for weight reduction in non-diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Metformin induces weight loss associated with gut microbiota alteration in non-diabetic obese women
…and many many more where those came from. As a point of interest, it has also been compared and contrasted to GLP-1 agonists.
Compared/contrasted with GLP-1 agonists
It’s not quite as effective for weight loss, and/but it’s a lot cheaper, is tablets rather than injections, has fewer side effects (for most people), and doesn’t result in dramatic yoyo-ing if there’s an interruption to taking it:
Or if you prefer a reader-friendly pop-science version:
Ozempic vs Metformin: Comparing The Two Diabetes Medications
Is it safe?
For most people yes, but there are a stack of contraindications, so it’s best to speak with your doctor. However, particular things to be aware of include:
- Usually contraindicated if you have kidney problems of any kind
- Usually contraindicated if you have liver problems of any kind
- May be contraindicated if you have issues with B12 levels
See also: Metformin: Is it a drug for all reasons and diseases?
Where can I get it?
As it’s a prescription-controlled drug, we can’t give you a handy Amazon link for this one.
However, many physicians are willing to prescribe it for off-label use (i.e., for reasons other than diabetes), so speak with yours (telehealth options may also be available).
If you do plan to speak with your doctor and you’re not sure they’ll be agreeable, you might want to get this paper and print it to take it with you:
Off-label indications of Metformin – Review of Literature
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: