Celeriac vs Celery – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celeriac to celery, we picked the celeriac.
Why?
Yes, these are essentially the same plant, but there are important nutritional differences:
In terms of macros, celeriac has more than 2x the protein, and slightly more carbs and fiber. Both are very low glycemic index, so the higher protein and fiber makes celeriac the winner in this category.
In the category of vitamins, celeriac has more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, C, E, K, and choline, while celery has more of vitamins A and B9. An easy win for celeriac.
When it comes to minerals, celeriac has more copper, calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while celery is not higher in any minerals. Another obvious win for celeriac.
Adding these sections up makes for a clear overall win for celeriac, but by all means enjoy either or both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Cherries vs Blueberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cherries to blueberries, we picked the blueberries.
Why?
It was close! And blueberries only won by virtue of taking an average value for cherries; we could have (if you’ll pardon the phrase) cherry-picked tart cherries for extra benefits that’d put them ahead of blueberries. That’s how close it is.
In terms of macros, they are almost identical, so nothing to set them apart there.
In the category of vitamins, they are mostly comparable except that blueberries have a lot more vitamin K, and cherries have a lot more vitamin A. Since vitamin K is the vitamin that’s scarcer in general, we’ll call blueberries’ vitamin K content a win.
Blueberries do also have about 6x more vitamin E, with a cup of blueberries containing about 10% of the daily requirement (and cherries containing almost none). Another small win for blueberries.
When it comes to minerals, they are mostly comparable; the largest point of difference is that blueberries contain more manganese while cherries contain more copper; nothing to decide between them here.
We’re down to counting amino acids and antioxidants now, so blueberries have a lot more cystine and tyrosine. They also have slightly more of amino acids that they both only have trace amounts of. And as for antioxidants? Blueberries contain notably more quercetin.
So, blueberries win the day—but if we had specified tart cherries rather than taking an average, they could have come out on top. Enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Eggs: Nutritional Powerhouse or Heart-Health Timebomb?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Eggs: All Things In Moderation?
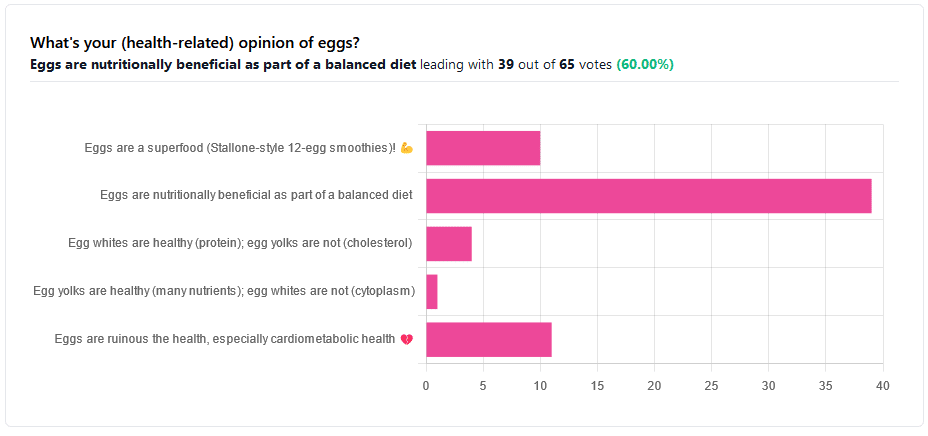
We asked you for your (health-related) opinion on eggs. We specified that, for the sake of simplicity, let’s say that they are from happy healthy backyard hens who enjoy a good diet.
Apparently this one wasn’t as controversial as it might have been! We (for myth-busting purposes) try to pick something polarizing and sometimes even contentious for our Friday editions, and pick apart what science lies underneath public perceptions.
However, more than half (in fact, 60%) of the subscribers who voted in the poll voted for “Eggs are nutritionally beneficial as part of a balanced diet”, which very moderate statement is indeed pretty much the global scientific consensus.
Still, we’ve a main feature to write, so let’s look at the science, and what the other 40% had in mind:
Eggs are ruinous to health, especially cardiometabolic health: True or False?
False, per best current science, anyway!
Scientific consensus has changed over the years. We learned about cholesterol, then we learned about different types of cholesterol, and now we’ve even learned about in some instances even elevated levels of “bad” cholesterol aren’t necessarily a cause of cardiometabolic disorders so much as a symptom—especially in women.
Not to derail this main feature about eggs (rather than just cholesterol), but for those who missed it, this is actually really interesting: basically, research (pertaining to the use of statins) has found that in women, higher LDL levels aren’t anywhere near the same kind of risk factor as they are for men, and thus may mean that statins (whose main job is reducing LDL) may be much less helpful for women than for men, and more likely to cause unwanted serious side effects in women.
Check out our previous main feature about this: Statins: His & Hers?
But, for back on topic, several large studies (totalling 177,000 people in long-term studies in 50 countries) found:
❝Results from the three cohorts and from the updated meta-analysis show that moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) is not associated with cardiovascular disease risk overall, and is associated with potentially lower cardiovascular disease risk in Asian populations.❞
Egg whites are healthy (protein); egg yolks are not (cholesterol): True or False?
True and False, respectively. That is to say, egg whites are healthy (protein), and egg yolks are also healthy (many nutrients).
We talked a bit already about cholesterol, so we’ll not rehash that here. As to the rest:
Eggs are one of the most nutritionally dense foods around. After all, they have everything required to allow a cluster of cells to become a whole baby chick. That’s a lot of body-building!
They’re even more nutritionally heavy-hitters if you get omega-3 enriched eggs, which means the hens were fed extra omega-3, usually in the form of flax seeds.
Also, free-range is better healthwise than others. Do bear in mind that unless they really are from your backyard, or a neighbor’s, chances are that the reality is not what the advertising depicts, though. There are industry minimum standards to be able to advertise as “free-range”, and those standards are a) quite low b) often ignored, because an occasional fine is cheaper than maintaining good conditions.
So if you can look after your own hens, or get them from somewhere that you can see for yourself how they are looked after, so much the better!
Check out the differences side-by-side, though:
Pastured vs Omega-3 vs “Conventional” Eggs: What’s the Difference?
Stallone-style 12-egg smoothies are healthy: True or False?
False, at least if taken with any regularity. One can indeed have too much of a good thing.
So, what’s the “right amount” to eat?
It may vary depending on individual factors (including age and ethnicity), but a good average, according to science, is to keep it to 3 eggs or fewer per day. There are a lot of studies, but we only have so much room here, so we’ll pick one. Its findings are representative of (and in keeping with) the many other studies we looked at, so this seems uncontroversial scientifically:
❝Intake of 1 egg/d was sufficient to increase HDL function and large-LDL particle concentration; however, intake of 2-3 eggs/d supported greater improvements in HDL function as well as increased plasma carotenoids. Overall, intake of ≤3 eggs/d favored a less atherogenic LDL particle profile, improved HDL function, and increased plasma antioxidants in young, healthy adults.❞
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
7 Principles of Becoming a Leader – by Riku Vuorenmaa
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We urge you to overlook the cliché cover art (we don’t know what they were thinking, going for the headless suited torso) because…
This one could be the best investment you make in your career this year! You may be wondering what the titular 7 principles are. We won’t keep you guessing; they are:
- Professional development: personal excellence, productivity, and time management
- Leadership development: mindset and essential leadership skills
- Personal development: your motivation, character, and confidence as a leader
- Career management: plan your career, get promoted and paid well
- Social skills & networking: work and connect with the right people
- Business- & company-understanding: the big picture
- Commitment: make the decision and commit to becoming a great leader
A lot of leadership books repeat the same old fluff that we’ve all read many times before… padded with a lot of lengthy personal anecdotes and generally editorializing fluff. Not so here!
While yes, this book does also cover some foundational things first, it’d be remiss not to. It also covers a whole (much deeper) range of related skills, with down-to-earth, brass tacks advice on putting them into practice.
This is the kind of book you will want to set as a recurring reminder in your phone, to re-read once a year, or whatever schedule seems sensible to you.
There aren’t many books we’d put in that category!
Pick Up Your Copy of the “7 Principles of Becoming a Leader” on Amazon Today!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How can I stop overthinking everything? A clinical psychologist offers solutions
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As a clinical psychologist, I often have clients say they are having trouble with thoughts “on a loop” in their head, which they find difficult to manage.
While rumination and overthinking are often considered the same thing, they are slightly different (though linked). Rumination is having thoughts on repeat in our minds. This can lead to overthinking – analysing those thoughts without finding solutions or solving the problem.
It’s like a vinyl record playing the same part of the song over and over. With a record, this is usually because of a scratch. Why we overthink is a little more complicated.
We’re on the lookout for threats
Our brains are hardwired to look for threats, to make a plan to address those threats and keep us safe. Those perceived threats may be based on past experiences, or may be the “what ifs” we imagine could happen in the future.
Our “what ifs” are usually negative outcomes. These are what we call “hot thoughts” – they bring up a lot of emotion (particularly sadness, worry or anger), which means we can easily get stuck on those thoughts and keep going over them.
However, because they are about things that have either already happened or might happen in the future (but are not happening now), we cannot fix the problem, so we keep going over the same thoughts.
Who overthinks?
Most people find themselves in situations at one time or another when they overthink.
Some people are more likely to ruminate. People who have had prior challenges or experienced trauma may have come to expect threats and look for them more than people who have not had adversities.
Deep thinkers, people who are prone to anxiety or low mood, and those who are sensitive or feel emotions deeply are also more likely to ruminate and overthink.
We all overthink from time to time, but some people are more prone to rumination.
BĀBI/UnsplashAlso, when we are stressed, our emotions tend to be stronger and last longer, and our thoughts can be less accurate, which means we can get stuck on thoughts more than we would usually.
Being run down or physically unwell can also mean our thoughts are harder to tackle and manage.
Acknowledge your feelings
When thoughts go on repeat, it is helpful to use both emotion-focused and problem-focused strategies.
Being emotion-focused means figuring out how we feel about something and addressing those feelings. For example, we might feel regret, anger or sadness about something that has happened, or worry about something that might happen.
Acknowledging those emotions, using self-care techniques and accessing social support to talk about and manage your feelings will be helpful.
The second part is being problem-focused. Looking at what you would do differently (if the thoughts are about something from your past) and making a plan for dealing with future possibilities your thoughts are raising.
But it is difficult to plan for all eventualities, so this strategy has limited usefulness.
What is more helpful is to make a plan for one or two of the more likely possibilities and accept there may be things that happen you haven’t thought of.
Think about why these thoughts are showing up
Our feelings and experiences are information; it is important to ask what this information is telling you and why these thoughts are showing up now.
For example, university has just started again. Parents of high school leavers might be lying awake at night (which is when rumination and overthinking is common) worrying about their young person.
Think of what the information is telling you.
TheVisualsYouNeed/ShutterstockKnowing how you would respond to some more likely possibilities (such as they will need money, they might be lonely or homesick) might be helpful.
But overthinking is also a sign of a new stage in both your lives, and needing to accept less control over your child’s choices and lives, while wanting the best for them. Recognising this means you can also talk about those feelings with others.
Let the thoughts go
A useful way to manage rumination or overthinking is “change, accept, and let go”.
Challenge and change aspects of your thoughts where you can. For example, the chance that your young person will run out of money and have no food and starve (overthinking tends to lead to your brain coming up with catastrophic outcomes!) is not likely.
You could plan to check in with your child regularly about how they are coping financially and encourage them to access budgeting support from university services.
Your thoughts are just ideas. They are not necessarily true or accurate, but when we overthink and have them on repeat, they can start to feel true because they become familiar. Coming up with a more realistic thought can help stop the loop of the unhelpful thought.
Accepting your emotions and finding ways to manage those (good self-care, social support, communication with those close to you) will also be helpful. As will accepting that life inevitably involves a lack of complete control over outcomes and possibilities life may throw at us. What we do have control over is our reactions and behaviours.
Remember, you have a 100% success rate of getting through challenges up until this point. You might have wanted to do things differently (and can plan to do that) but nevertheless, you coped and got through.
So, the last part is letting go of the need to know exactly how things will turn out, and believing in your ability (and sometimes others’) to cope.
What else can you do?
A stressed out and tired brain will be more likely to overthink, leading to more stress and creating a cycle that can affect your wellbeing.
So it’s important to manage your stress levels by eating and sleeping well, moving your body, doing things you enjoy, seeing people you care about, and doing things that fuel your soul and spirit.
Find ways to manage your stress levels.
antoniodiaz/ShutterstockDistraction – with pleasurable activities and people who bring you joy – can also get your thoughts off repeat.
If you do find overthinking is affecting your life, and your levels of anxiety are rising or your mood is dropping (your sleep, appetite and enjoyment of life and people is being negatively affected), it might be time to talk to someone and get some strategies to manage.
When things become too difficult to manage yourself (or with the help of those close to you), a therapist can provide tools that have been proven to be helpful. Some helpful tools to manage worry and your thoughts can also be found here.
When you find yourself overthinking, think about why you are having “hot thoughts”, acknowledge your feelings and do some future-focused problem solving. But also accept life can be unpredictable and focus on having faith in your ability to cope.
Kirsty Ross, Associate Professor and Senior Clinical Psychologist, Massey University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why STIs Are On The Rise In Older Adults
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Three Little Words
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are often thought of as something that predominantly plagues younger people… The truth, however, is different:
❝Rising divorce rates, forgoing condoms as there is no risk of pregnancy, the availability of drugs for sexual dysfunction, the large number of older adults living together in retirement communities, and the increased use of dating apps are likely to have contributed to the growing incidence of STIs in the over-50s.
These data likely underestimate the true extent of the problem as limited access to sexual health services for the over 50s, and trying to avoid the stigma and embarrassment both on the part of older people and healthcare professionals, is leading to this age group not seeking help for STIs.❞
Read more: Managing The Rise In STIs Among Older Adults
That said, there is a gender gap when it comes to the increased risk, for example:
❝A retrospective study from the USA involving 420,790 couples aged 67 to 99 years, found that widowhood was associated with an increased risk of STIs in older men, but not women❞
~ US Dept of Health & Human Services
Source: CDC: | Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance
Is abstinence the best preventative, then?
It is inarguably the most effective, but not necessarily the best for everyone.
This is because for most adults, a healthy sex life is an important part of overall wellbeing.
See also: Mythbusting The Big O
Even in this case there is a gender gap in:
- the level of importance placed on frequency of sexual interactions
- what act(s) of sexuality are held to be most important:
❝Among sexually active men, frequent (≥2 times a month) sexual intercourse (P < .001) and frequent kissing, petting, or fondling (P < .001) were associated with greater enjoyment of life.
Among sexually active women, frequent kissing, petting, or fondling was also associated with greater enjoyment of life (P < .001), but there was no significant association with frequent intercourse (P = .101).
Concerns about one’s sex life and problems with sexual function were strongly associated with lower levels of enjoyment of life in men and to a lesser extent in women.❞
Source: Sexual Activity is Associated with Greater Enjoyment of Life in Older Adults
If you have the time to go into it much more deeply, this paper from the Journal of Gerontology is much more comprehensive, looking also at related lifestyle factors, religious/political backgrounds, views on monogamy or non-monogamy (of various kinds), hormonal considerations, the impact of dementia or other long-term disabilities that may affect things, widowhood, and many other elements:
The National Social Life, Health, and Aging Project: An Introduction
What’s the best preventative, then?
Regular health screening for yourself and your partner(s) is an important key to preventative health when it comes to STIs.
You can Google search for a local STI clinic, and worry not, they are invariably discreet and are well-used to everybody coming in. They’re just glad you’re being responsible about things. It’s also not their job to judge your sexual activities, even if it’s something you might have reason to wish to be secretive about, try to be honest there.
Secondly, most of the usual advice about safe sex still goes, even when there’s no risk of pregnancy. For example, if there’s at least one penis involved, then condoms remain the #1 barrier to all manner of potential infections (we know, almost nobody likes condoms, but sometimes the truth isn’t what we want to hear).
Lastly, if there’s at least one vagina involved, then please for the love of all that is holey, do not put anything there that could cause a yeast infection.
What can cause a yeast infection? Pretty much anything with sugar, which includes but is not limited to:
- Most kinds of food that Cosmo-style “liven things up in the bedroom” advice columns might suggest using (including fruit, honey, chocolate sauce, whipped cream, etc)
- Hands that are not clean (watch out for bacteria too)
- A mouth that has recently been eating or drinking anything with sugar in it, and that includes many kinds of alcohol, as well as milk or hot drinks that had milk in
Yeast infections are not nearly so serious as the STIs the other measures are there to avoid, but they’re not fun either, so some sensible policies in that regard are always good!
On a related note, see also: How To Avoid UTIs
Recap on the single most important part of this article:
At all ages, it remains a good health practice—unless one is absolutely celibate—to regularly get oneself and one’s partner(s) checked for STIs.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sleep wrinkles are real. Here’s how they leave their mark
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You wake up, stagger to the bathroom and gaze into the mirror. No, you’re not imagining it. You’ve developed face wrinkles overnight. They’re sleep wrinkles.
Sleep wrinkles are temporary. But as your skin loses its elasticity as you age, they can set in.
Here’s what you can do to minimise the chance of them forming in the first place.
How side-sleeping affects your face
Your skin wrinkles for a number of reasons, including ageing, sun damage, smoking, poor hydration, habitual facial expressions (such as grinning, pouting, frowning, squinting) and sleeping positions.
When you sleep on your side or stomach, your face skin is squeezed and crushed a lot more than if you sleep on your back. When you sleep on your side or stomach, gravity presses your face against the pillow. Your face skin is distorted as your skin is stretched, compressed and pulled in all directions as you move about in your sleep.
You can reduce these external forces acting on the face by sleeping on your back or changing positions frequently.
Doctors can tell which side you sleep on by looking at your face
In a young face, sleep wrinkles are transient and disappear after waking.
Temporary sleep wrinkles can become persistent with time and repetition. As we age, our skin loses elasticity (recoil) and extensibility (stretch), creating ideal conditions for sleep wrinkles or lines to set in and last longer.
The time spent in each sleeping position, the magnitude of external forces applied to each area of the face, as well as the surface area of contact with the pillow surface, also affects the pattern and rate of sleep wrinkle formation.
Skin specialists can often recognise this. People who favour sleeping on one side of their body tend to have a flatter face on their sleeping side and more visible sleep lines.
Can a night skincare routine avoid sleep wrinkles?
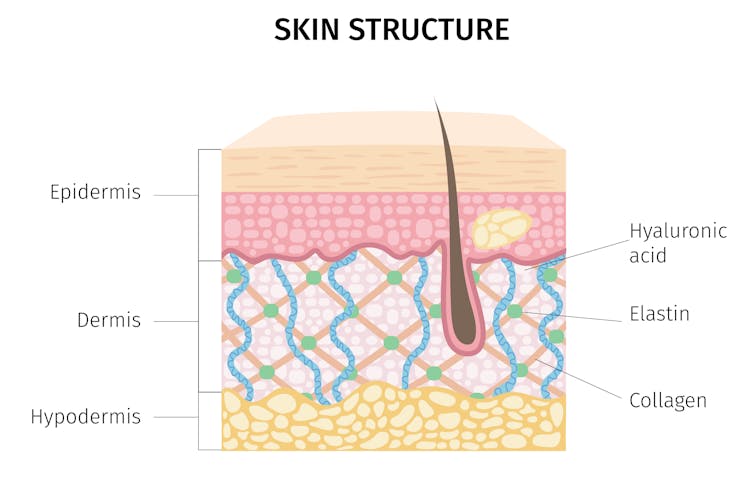
Collagen and elastin are two primary components of the dermis (inner layer) of skin. They form the skin structure and maintain the elasticity of skin.
The dermis is the inner layer of skin. mermaid3/Shutterstock Supplementing collagen through skincare routines to enhance skin elasticity can help reduce wrinkle formation.
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring molecule in human bodies. It holds our skin’s collagen and elastin in a proper configuration, stimulates the production of collagen and adds hydration, which can help slow down wrinkle formation. Hyaluronic acid is one of the most common active ingredients in skincare creams, gels and lotions.
Moisturisers can hydrate the skin in different ways. “Occlusive” substances produce a thin layer of oil on the skin that prevents water loss due to evaporation. “Humectants” attract and hold water in the skin, and they can differ in their capacity to bind with water, which influences the degree of skin hydration.
Do silk pillowcases actually make a difference?
Can they help? New Africa/Shutterstock Silk pillowcases can make a difference in wrinkle formation, if they let your skin glide and move, rather than adding friction and pressure on a single spot. If you can, use silk sheets and silk pillows.
Studies have also shown pillows designed to reduce mechanical stress during sleep can prevent skin deformations. Such a pillow could be useful in slowing down and preventing the formation of certain facial wrinkles.
Sleeping on your back can reduce the risk of sleep lines, as can a nighttime routine of moisturising before sleep.
Otherwise, lifestyle choices and habits, such quitting smoking, drinking plenty of water, a healthy diet (eating enough vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, healthy fats, yogurt and other fermented foods) and regular use of sunscreens can help improve the appearance of the skin on our face.
Yousuf Mohammed, Dermatology researcher, The University of Queensland; Khanh Phan, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Frazer Institute, The University of Queensland, and Vania Rodrigues Leite E. Silva, Honorary Associate Professor, Frazer Institute, The University of Queensland
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: