Cherries vs Blueberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing cherries to blueberries, we picked the blueberries.
Why?
It was close! And blueberries only won by virtue of taking an average value for cherries; we could have (if you’ll pardon the phrase) cherry-picked tart cherries for extra benefits that’d put them ahead of blueberries. That’s how close it is.
In terms of macros, they are almost identical, so nothing to set them apart there.
In the category of vitamins, they are mostly comparable except that blueberries have a lot more vitamin K, and cherries have a lot more vitamin A. Since vitamin K is the vitamin that’s scarcer in general, we’ll call blueberries’ vitamin K content a win.
Blueberries do also have about 6x more vitamin E, with a cup of blueberries containing about 10% of the daily requirement (and cherries containing almost none). Another small win for blueberries.
When it comes to minerals, they are mostly comparable; the largest point of difference is that blueberries contain more manganese while cherries contain more copper; nothing to decide between them here.
We’re down to counting amino acids and antioxidants now, so blueberries have a lot more cystine and tyrosine. They also have slightly more of amino acids that they both only have trace amounts of. And as for antioxidants? Blueberries contain notably more quercetin.
So, blueberries win the day—but if we had specified tart cherries rather than taking an average, they could have come out on top. Enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Blind Spots – by Dr. Marty Makary
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From the time the US recommended not giving peanuts to infants for the first three years of life “in order to avoid peanut allergies” (whereupon non-exposure to peanuts early in life led to, instead, an increase in peanut allergies and anaphylactic incidents), to the time the US recommended not taking HRT on the strength of the claim that “HRT causes breast cancer” (whereupon the reduced popularity of HRT led to, instead, an increase in breast cancer incidence and mortality), to many other such incidents of very bad public advice being given on the strength of a single badly-misrepresented study (for each respective thing), Dr. Makary puts the spotlight on what went wrong.
This is important, because this is not just a book of outrage, exclaiming “how could this happen?!”, but rather instead, is a book of inquisition, asking “how did this happen?”, in such a way that we the reader can spot similar patterns going forwards.
Oftentimes, this is a simple matter of having a basic understanding of statistics, and checking sources to see if the dataset really supports what the headlines are claiming—and indeed, whether sometimes it suggests rather the opposite.
The style is a little on the sensationalist side, but it’s well-supported with sound arguments, good science, and clear mathematics.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your scientific literacy, this book is an excellent illustrative guide.
Share This Post
-
Beat The Heat, With Fat
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Surviving Summer
Summer is upon us, for those of us in the Northern Hemisphere anyway, and given that nowadays each year tends to be hotter than the one before, on average, it pays to be prepared.
We’ve talked about dealing with the heat before:
Sun, Sea, And Sudden Killers To Avoid
All the above advice stands this summer too, but today we’re going to speak a little extra on not having a “default body”.
For much of medical literature and common health advice, the default body is that of a slim and/or athletic white cis man aged 25–35 with no disabilities.
When it comes to “women’s health”, this is often confined to “the bikini zone” and everything else is commonly treated based on research conducted with men.
Today we’ll be looking at a particular challenge for a wide variety of people, when it comes to heat…
Beating the heat, with fat
If you are fat, and/or have a bit of a tummy, and/or have breasts, this one’s for you.
Fat acts as an insulator, which naturally does no favors in hot weather. Carrying the weight around is also extra exercise, which also becomes a problem in hot weather. Fat people usually sweat more than thin people do, as a result.
Sweat is great for cooling down the body, because it takes heat with it when it evaporates off. However, that only works if it can evaporate off, and it can’t evaporate off if it’s trapped in a skin fold / fat roll.
If you’re fat, you may have plenty of those; if you have a bit of a tummy (if you’re not fat generally, this might be a leftover from pregnancy, or weight loss, or something else; how it got there doesn’t matter for our purposes today), you’ll have at least one under it, and if you have breasts, unless they’re quite small, you’ll have one under each breast, and potentially your cleavage may become an issue too.
Note: if you are perhaps a man who has fat in the place where breasts go, then medically this goes for you too, except that there’s not a societal expectation that you wear bra. Use today’s information as you see fit.
Sweat-wicking hacks
We don’t want sweat to stay in those folds—both because then it’s not doing its cooling-down job, and also, because it can cause a rash, and even yeast infections and/or bacterial infections.
So, we want there to be some barrier there. You could use something like vaseline or baby powder, as to prevent chafing, but fat better (more effective, and less messy) is to have some kind of cloth there that can wick the sweat away.
There are made-for-purpose curved cotton bands that exist, called “tummy liners”; here’s an example product on Amazon, or you could make your own if you’re so inclined. They’re breathable, absorbent, and reduce friction too, making everything a lot more comfortable.
And for breasts? Same deal, there are made-for-purpose cotton bra-liners that exist; here’s an example product on Amazon, or again, you could make your own if you feel so inclined. The important part is that it makes things so much comfortable, because let’s face it: wearing a bra in the summer is not comfortable.
So with these, it can become more comfortable (and the cotton liners are flat, so they’re not visible if one’s wearing a t-shirt or similar-coverage garment). You could go braless, of course, but then you’re back to having sweaty folds, so if you’re doing something other than swimming or lying on your back, you might want something there.
Different hydration rules
“People should drink this much per day” and guess what, those guidelines were based on, drumroll please, not fat people.
Sweating more means needing to hydrate more, and even without breaking a sweat, having a larger body than average (be it muscle, fat, or both) means having more body to hydrate. That’s simple math.
So instead, a good general guideline is half an ounce of water per your weight in pounds, per day:
How much water do I need each day?
Another good general guideline is to simply drink “little and often”, that is to say, always have a (hydrating!) drink on the go.
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Guava vs Passion Fruit – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing guava to passion fruit, we picked the guava.
Why?
There aren’t many fruits that can beat passion fruit for nutritional density! And even in this case, it wasn’t completely so in every category:
In terms of macros, passion fruit has more carbs and fiber, the ratio of which give it the slightly lower glycemic index. Thus, a modest win for passion fruit in this category.
In the category of vitamins, guava has more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, B9, C, E, and K, while passion fruit has more of vitamins A, B2, and B3. A clear win for guava this time.
When it comes to minerals, it’s a little closer, but: guava has more calcium, copper, manganese, potassium, and zinc, while passion fruit has more iron, magnesium, and phosphorus. So, another win for guava.
Adding up the sections makes for guava winning the day, but by all means enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Fruit Is Healthy; Juice Isn’t (Here’s Why)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
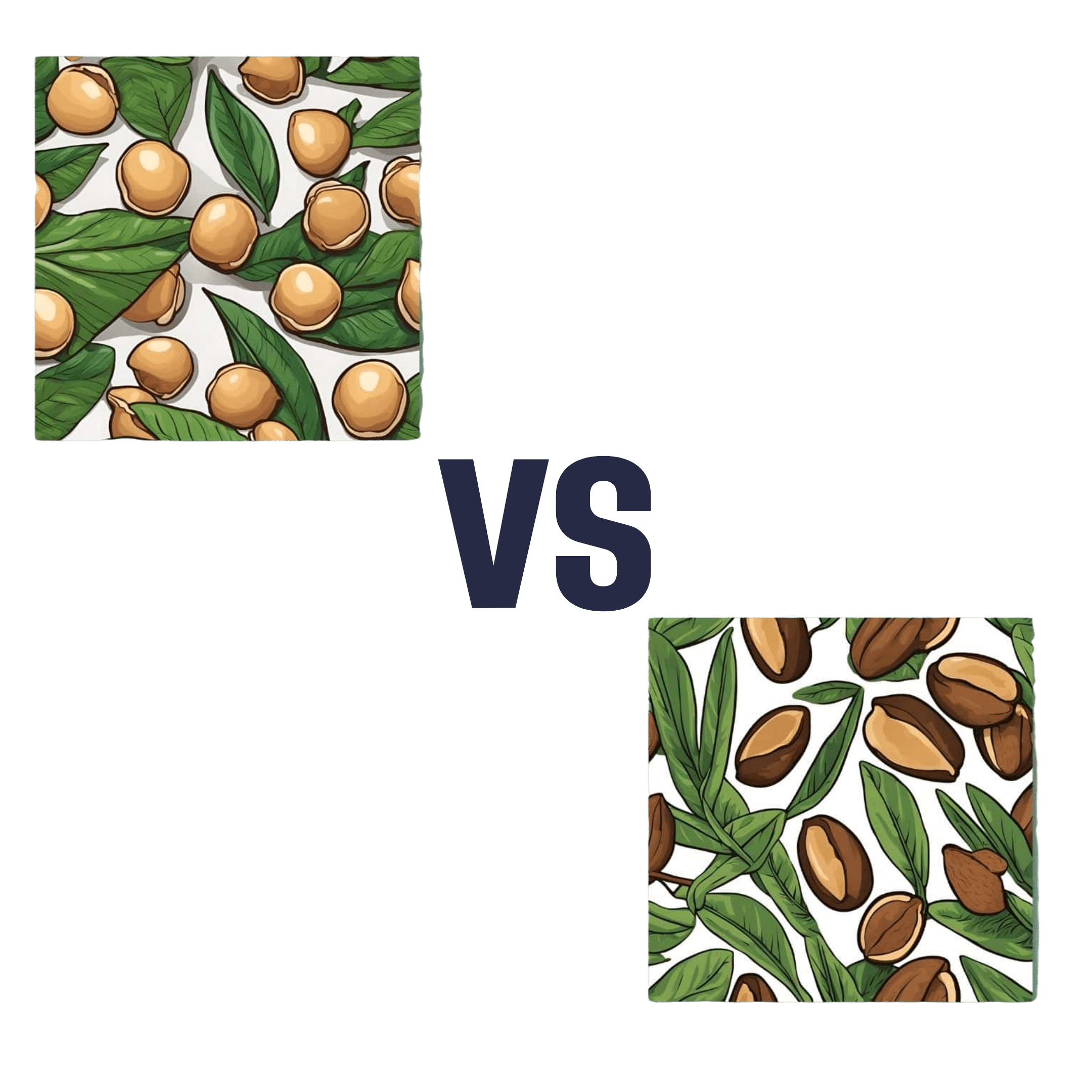
Macadamia Nuts vs Brazil Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing macadamia nuts to Brazil nuts, we picked the Brazil nuts.
Why?
They’re a lot more nutrient dense! But watch out…
First, to do due diligence in terms of macros: Brazil nuts have twice as much protein and less fat, as well as being a little higher in fiber and slightly lower in carbs.
In terms of vitamins, Brazil nuts are about 10x higher in vitamin E, while macadamias are somewhat higher in several B-vitamins.
The category of minerals is where it gets interesting. Macadamia nuts are a little higher in iron and considerably higher in Manganese. But… Brazil nuts are a lot higher in calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc.
About that selenium… Specifically, it’s more than 5,000x higher, and a cup of Brazil nuts would give nearly 10,000x the recommended daily amount of selenium. Now, selenium is an essential mineral (needed for thyroid hormone production, for example), and at the RDA it’s good for good health. Your hair will be luscious and shiny. However, go much above that, and selenium toxicity becomes a thing, you may get sick, and it can cause your (luscious and shiny) hair to fall out. For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
In short… Brazil nuts are much more nutrient dense in general, and thus come out on top here. But, they’re so nutrient dense in the case of selenium, that careful moderation is advised.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Broad Beans vs Green Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing broad beans to green beans, we picked the broad.
Why?
It’s quite a straightforward one today:
In terms of macros, broad beans have 2.5x the protein, and slightly more fiber and carbs, so we pick the broad beans as the more nutrient-dense option here.
In the category of vitamins, broad beans have more of vitamins B1, B3, B9, and C, while green beans have more of vitamins A and B6 (with comparable margins of difference for both beans’ winning vitamins), so another win for broad beans, based on the 4:2 numerical advantage.
When it comes to minerals, broad beans have more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while green beans have more calcium and manganese. Again, comparable mostly margins of difference (except for broad beans bing 5x richer in selenium, which is a bit of an outlier, but it’s not because broad beans are an amazing source of selenium, but rather, that green beans have only a tiny amount), so it’s a clear 7:2 win for broad beans.
Adding up the three wins for broad beans makes an overall win for them, but by all means, enjoy either or both; diversity is good!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Passion Fruit vs Persimmon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing passion fruit to persimmon, we picked the passion fruit.
Why?
You may be wondering: “what is this fruit passionate about?” and the answer is: delivering nutrients of many kinds!
Looking at the macros first, passion fruit has a little more protein and a lot more fiber, while persimmon has more carbs. This means that while persimmon’s glycemic index isn’t bad, passion fruit’s glycemic index is a lot lower.
In terms of vitamins, passion fruit has a lot more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B9, E, K, and choline, while persimmon has more vitamin C. For the record passion fruit is also a good source of vitamin C, with a cup of passion fruit already giving a day’s daily dose of vitamin C, but persimmon gives twice that. Still, that’s a 8:1 win for passion fruit.
When it comes to minerals, passion fruit has more copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while persimmon has more calcium and iron, meaning a 6:2 win for passion fruit.
Adding up the three convincing individual victories shows a clear overall win for passion fruit.
Enjoy (passionately, even)!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Glycemic Index vs Glycemic Load vs Insulin Index
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: