Can You Gain Muscle & Lose Fat At The Same Time?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small 😎
❝Is it possible to lose fat and gain muscle at the same time, or do we need to focus on one and then the other, and if so, which order is best?❞
Contrary to popular belief, you can do both simultaneously! However, it’s not as easy as doing just one or the other, which is why most bodybuilders, for example, have a “building phase” and a “cutting phase”.
The reason it’s difficult is because of the diet. Growing muscle doesn’t just take protein and micronutrients; it takes energy as well, which must come from carbohydrates and/or fats. Therefore, it is tricky to eat enough to build muscle and to fuel the workouts that are required to build the muscle (you can’t hit the gym in a state of rabbit starvation* and expect to perform well at your workout), while at the same time not eating enough carbs/fats to have any excess to store as fat.
*So-called because rabbit-meat is very lean, such that when during times of famine, European peasants tried to subsist off mostly rabbits, their health quickly plummeted for lack of energy. It’s also been called “salmon starvation”, apparently, for the same reason:
In French it’s called “Mal de caribou” (caribou sickness), by the way. But you get the idea: eat too much lean protein without enough carbs/fats, and woe shall befall.
So, if you want to do both at once, you need to be incredibly on top of your macros, and the bad news is, only you (or a coach working directly with you) can work out what precise macros requirements your body has, because it depends on your body and your activities.
The easier “half-way house”
We will get to the “building phase” and “cutting phase” of bodybuilders, but first, here’s an option that’s very worthy of consideration, and it is: forget about your weight and just focus on health while incidentally doing regular resistance exercises and HIIT.
What will happen if you do this (assuming a healthy balanced diet, nothing special and without counting anything, but we’re talking at least mostly whole-foods, and at least mostly plants; the Mediterranean diet is great for this, as it is for most things) is:
- The dietary approach described will gradually improve your metabolic health if it wasn’t already good. If it was already good, it’ll likely just maintain it, rather than improve it.
- The resistance exercises will, if engaged with seriously (it has to be difficult to do, or your muscles won’t have any reason to grow), gradually build muscle. This will be very gradual, because you’re not eating for bodybuilding, nor optimizing your general lifestyle for same. Historically many women have feared lifting weights because they don’t want to “look like a weightlifter”, but the kinds of bodies that word brings to mind are not the kind that happen by accident (especially for women, with our different hormones guiding our bodies to a different composition); it takes a lot of single-minded dedication to specifically optimize size gains, for a long time.
- The high-intensity interval training (HIIT) will more rapidly improve your metabolic health, and unlike most forms of exercise, it will actually result in a gradual reduction of fat, if you have superfluous fat to lose. This is because whereas most forms of cardio exercise increase the heartrate for a while but then have a corresponding metabolic slump afterwards to make up for it, HIIT confuses the heart (in a good way) which results in it having to grow stronger, and not doing any compensatory metabolic slump:
How To Do HIIT (Without Wrecking Your Body) ← as well as the “how to”, this also gives some of the science behind it, too
This will, thus, result in gradual gain of muscle and loss of fat—or if you take it easier with the exercise, then you can easily settle into just maintaining your body composition as it is, but that wasn’t the question today.
So, there you have it, that’s how to do both at once! Now, if you want more dramatic results, then more dramatic methods are called for:
What bodybuilders (mostly) do
Matters of genetic predisposition and commonplace use of steroids aside, here’s how bodybuilders get that “lots of muscle, no fat” figure:
- First, get into “moderate” shape if not already there.
- Bulk up: eat amounts of food that will seem unreasonable to a non-bodybuilder; eating 2x or even 3x the “recommended” daily calorie amount is common; focus is typically on getting adequate (for bodybuilding purposes) protein while also carb-loading for workouts and getting at least enough fats for fat-soluble vitamins to work. In the gym, focus on doing sets of very few reps with the heaviest weights one can safely lift, while doing minimal cardio, and also sleeping a lot (9–12hrs per day), which is essential because this is putting a huge strain on the body and it needs a chance to recover and rebuild.
- Cut down: maintain protein intake (to at least mostly maintain muscles) while keeping carbs and fats low, doing cardio work (HIIT is still ideal) and running a calorie deficit for a short while (there is no use in trying to maintain a long-term calorie deficit; your body will try to save you from starvation by storing any fat it can and slowing your metabolism).
Phases 2 and 3 are then cycled, alternating every month, or every 6 weeks, or every 2 months or so, depending on personal preferences and scheduling considerations (bodybuilders will often have competitions they are working towards, so they need to time things to be at the end of a cutting phase to look their “best” by bodybuilder standards).
Disclaimer: bodybuilding is complex, and can be ruinous to the health if practised inexpertly, because of its extreme nature. We don’t recommend serious bodybuilding per se in general, but if you are going to do it, please consult with a professional bodybuilding coach, and do not rely on a few paragraphs from us that are intended only to give the most basic overview of how bodybuilders can approach the “gain muscle, lose fat” problem.
Want to know more?
We’ve written on some related topics previously; here’s a three-part series:
- How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
- How To Build Muscle (Healthily!)
- How To Gain Weight (Healthily!) ← this one’s specifically about gaining healthy levels of fat, for any who want/need that
And also:
Can We Do Fat Redistribution? ← yes we can, but there are caveats
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
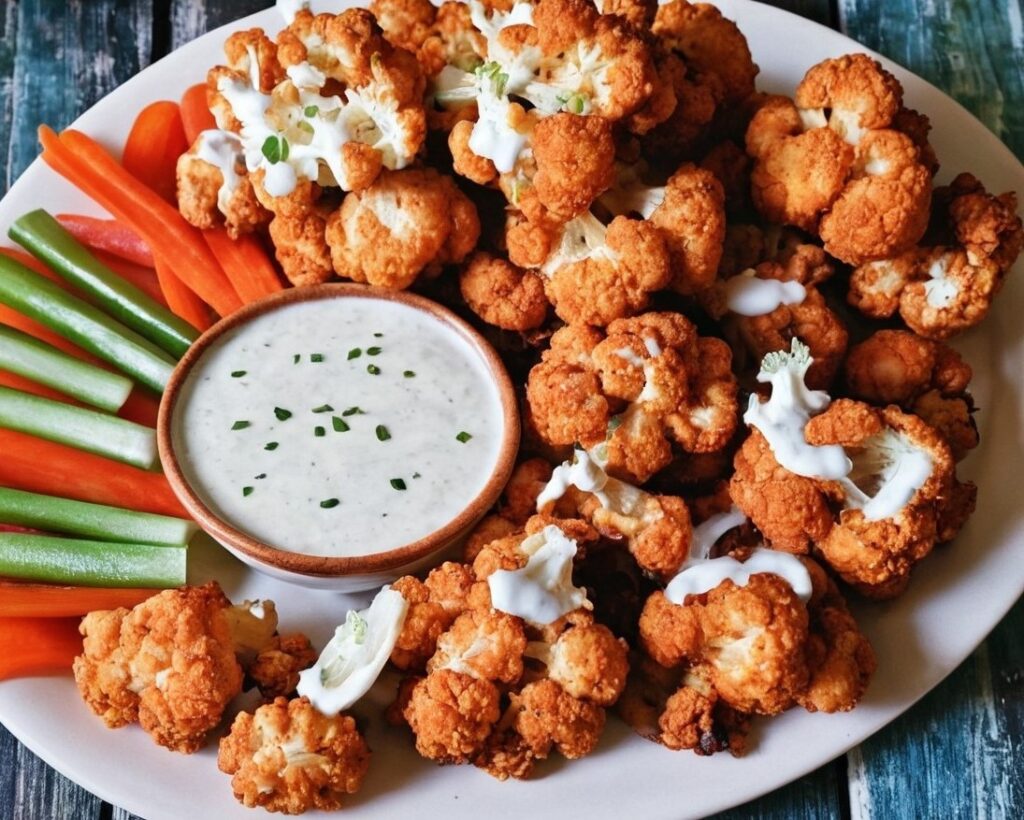
Buffed-Up Buffalo Cauliflower
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a tasty snack that also more protein than you’d think, because of the garbanzo bean flour. It also has plenty of health-giving spices, as well as blood-sugar-balancing vinegar, no added sugar, and very little salt.
You will need
- 1 medium head of cauliflower, cut into florets
- ½ cup garbanzo bean flour
- ½ cup water
- ⅓ cup hot sauce (we recommend a low-sugar kind; Nando’s hot sauce is good for this if available where you are, as it has no added sugar and its main ingredient by volume is vinegar, which is good for balancing blood sugars)
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for the pan
- 2 tsp garlic powder
- 2 tsp nutritional yeast
- 2 tsp black pepper, freshly ground
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low sodium salt
For the ranch sauce:
- ½ cup raw sunflower seeds
- ⅓ cup water
- ⅓ cup milk (plant milk being healthiest if you choose one that’s unsweetened)
- 2 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tsp onion powder
- 1 tsp dried thyme
- 1 tsp dried oregano
- 1 tsp dried dill
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉/200℃.
2) Blend the ranch sauce ingredients until smooth, and set aside.
3) Mix the buffalo cauliflower ingredients except for the cauliflower, in a big bowl.
4) Add the cauliflower to the big bowl, mixing well to coat evenly.
5) Bake the buffalo cauliflower florets on a baking tray lined with baking paper, for about 25 minutes, turning gently if it seems they are at risk of cooking unevenly.
6) Serve hot, with the sunflower ranch on the side!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Imposter Syndrome (and why almost everyone has it)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Imposter Syndrome (and why almost everyone has it)
Imposter syndrome is the pervasive idea that we’re not actually good enough, people think we are better than we are, and at any moment we’re going to get found out and disappoint everyone.
Beyond the workplace
Imposter syndrome is most associated with professionals. It can range from a medical professional who feels like they’ve been projecting an image of confidence too much, to a writer or musician who is sure that their next piece will never live up to the acclaim of previous pieces and everyone will suddenly realize they don’t know what they’re doing, to a middle-manager who feels like nobody above or below them realizes how little they know how to do.
But! Less talked-about (but no less prevalent) is imposter syndrome in other areas of life. New parents tend to feel this strongly, as can the “elders” of a family that everyone looks to for advice and strength and support. Perhaps worst is when the person most responsible for the finances of a household feels like everyone just trusts them to keep everything running smoothly, and maybe they shouldn’t because it could all come crashing down at any moment and everyone will see them for the hopeless shambles of a human being that they really are.
Feelings are not facts
And yet (while everyone makes mistakes sometimes) the reality is that we’re all doing our best. Given that imposter syndrome affects up to 82% of people, let’s remember to have some perspective. Everyone feels like they’re winging it sometimes. Everyone feels the pressure.
Well, perhaps not everyone. There’s that other 18%. Some people are sure they’re the best thing ever. Then again, there’s probably some in that 18% that actually feel worse than the 82%—they just couldn’t admit it, even in an anonymized study.
But one thing’s for sure: it’s very, very common. Especially in high-performing women, by the way, and people of color. In other words, people who typically “have to do twice as much to get recognized as half as good”.
That said, the flipside of this is that people who are not in any of those categories may feel “everything is in my favor, so I really have no excuse to not achieve the most”, and can sometimes take very extreme actions to try to avoid perceived failure, and it can be their family that pays the price.
Things to remember
If you find imposter syndrome nagging at you, remember these things:
- There are people far less competent than you, doing the same thing
- Nobody knows how to do everything themselves, especially at first
- If you don’t know how to do something, you can usually find out
- There is always someone to ask for help, or at least advice, or at least support
At the end of the day, we evolved to eat fruit and enjoy the sun. None of us are fully equipped for all the challenges of the modern world, but if we do our reasonable best, and look after each other (and that means that you too, dear reader, deserve looking after as well), we can all do ok.
Share This Post
-
Goji Berries vs Blueberries – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing goji berries to blueberries, we picked the goji berries.
Why?
As you might have guessed, both are very good options:
- Both have plenty of vitamins and minerals, and/but goji berries have more. How much more? It varies, but for example about 5x more vitamin C, about 25x more iron, about 30x more calcium, about 50x more vitamin A.
- Blueberries beat goji berries with some vitamins (B, E, K), but only in quite small amounts.
- Both are great sources of antioxidants, and/but goji berries have 2–4 times the antioxidants that blueberries do.
- Goji berries do have more sugar, but since they have about 4x more sugar and 5x more fiber, we’re still calling this a win for goji berries on the glycemic index front (and indeed, the GI of goji berries is lower).
In short: blueberries are great, but goji berries beat them in most metrics.
Want to read more?
Check out our previous main features, detailing some of the science, and also where to get them:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Reduce Chronic Stress
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sunday Stress-Buster
First, an important distinction:
- Acute stress (for example, when stepping out of your comfort zone, engaging in competition, or otherwise focusing on something that requires your full attention for best performance) is generally a good thing. It helps you do you your best. It’s sometimes been called “eustress”, “good stress”.
- Chronic stress (for example, when snowed under at work and you do not love it, when dealing with a serious illness, and/or faced with financial problems) is unequivocally a bad thing. Our body is simply not made to handle that much cortisol (the stress hormone) all the time.
Know the dangers of too much cortisol
We covered this as a main feature last month: Lower Your Cortisol! (Here’s Why & How)
…but it bears mentioning again and for those who’ve joined us since then:
A little spike of cortisol now and again can be helpful. Having it spiking all the time, or even a perpetual background low-to-moderate level, can be ruinous to the health in so many ways.
The good news is, the physiological impact of stress on the body (which ranges from face-and-stomach fat deposits, to rapid aging), can be reversed—even the biological aging!
Read: Biological age is increased by stress and restored upon recovery ← this study is so hot-of-the-press that it was published literally two days ago
Focus on what you can control
A lot of things that cause you stress may be outside of your control. Focus on what is within your control. Oftentimes, we are so preoccupied with the stress, that we employ coping strategies that don’t actually deal with the problem.
That’s a maladaptive response to an evolutionary quirk—our bodies haven’t caught up with modern life, and on an evolutionary scale, are still priming us to deal with sabre-toothed tigers, not financial disputes, for example.
But, how to deal with the body’s “wrong” response?
First, deal with the tiger. There isn’t one, but your body doesn’t know that. Do some vigorous exercise, or if that’s not your thing, tense up your muscles strongly for a few seconds and then relax them, doing each part of your body. This is called progressive relaxation, and how it works is basically tricking your body into thinking you successfully fled the tiger, or fought the tiger and won.
Next, examine what the actual problem is, that’s causing you stress. You’re probably heavily emotionally attached to the problem, or else it wouldn’t be stressing you. So, imagine what advice you would give to help a friend deal with the same problem, and then do that.
Better yet: enlist an actual friend (or partner, family member, etc) to help you. We are evolved to live in a community, engaged in mutual support. That’s how we do well; that’s how we thrive best.
By dealing with the problem—or sometimes even just having support and/or something like a plan—your stress will evaporate soon enough.
The power of “…and then what?”
Sometimes, things are entirely out of your control. Sometimes, bad things are entirely possible; perhaps even probable. Sometimes, they’re so bad, that it’s difficult to avoid stressing about the possible outcomes.
If something seems entirely out of your control and/or inevitable, ask yourself:
“…and then what?”
Writer’s storytime: when I was a teenager, sometimes I would go out without a coat, and my mother would ask, pointedly, “But what will you do if it rains?!”
I’d reply “I’ll get wet, of course”
This attitude can go just the same for much more serious outcomes, up to and including death.
So when you find yourself stressing about some possible bad outcome, ask yourself, “…and then what?”.
- What if this is cancer? Well, it might be. And then what? You might seek cancer treatment.
- What if I can’t get treatment, or it doesn’t work? Well, you might die. And then what?
In Dialectic Behavior Therapy (DBT), this is called “radical acceptance” and acknowledges bad possible/probable/known outcomes, allows one to explore the feelings, and come up with a plan for managing the situation, or even just coming to terms with the fact that sometimes, suffering is inevitable and is part of the human condition.
It’ll still be bad—but you won’t have added extra suffering in the form of stress.
Breathe.
Don’t underestimate the power of relaxed deep breathing to calm the rest of your body, including your brain.
Also: we’ve shared this before, a few months ago, but this 8 minute soundscape was developed by sound technicians working with a team of psychologists and neurologists. It’s been clinically tested, and found to have a much more relaxing effect(in objective measures of lowering heart rate and lowering cortisol levels, as well as in subjective self-reports) than merely “relaxing music”.
Try it and see for yourself:
! Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Are The “Bright Lines” Of Bright Line Eating?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Susan Thompson. She’s a cognitive neuroscientist who has turned her hand to helping people to lose weight and maintain it at a lower level, using psychology to combat overeating. She is the founder of “Bright Line Eating”.
We’ll say up front: it’s not without some controversy, and we’ll address that as we go, but we do believe the ideas are worth examining, and then we can apply them or not as befits our personal lives.
What does she want us to know?
Bright Line Eating’s general goal
Dr. Thompson’s mission statement is to help people be “happy, thin, and free”.
You will note that this presupposes thinness as desirable, and presumes it to be healthy, which frankly, it’s not for everyone. Indeed, for people over a certain age, having a BMI that’s slightly into the “overweight” category is a protective factor against mortality (which is partly a flaw of the BMI system, but is an interesting observation nonetheless):
When BMI Doesn’t Quite Measure Up
Nevertheless, Dr. Thompson makes the case for the three items (happy, thin, free) coming together, which means that any miserable or unhealthy thinness is not what the approach is valuing, since it is important for “thin” to be bookended by “happy” and “free”.
What are these “bright lines”?
Bright Line Eating comes with 4 rules:
- No flour (no, not even wholegrain flour; enjoy whole grains themselves yes, but flour, no)
- No sugar (and as a tag-along to this, no alcohol) (sugars naturally found in whole foods, e.g. the sugar in an apple if eating an apple, is ok, but other kinds are not, e.g. foods with apple juice concentrate as a sweetener; no “natural raw cane sugar” etc is not allowed either; despite the name, it certainly doesn’t grow on the plant like that)
- No snacking, just three meals per day(not even eating the ingredients while cooking—which also means no taste-testing while cooking)
- Weigh all your food (have fun in restaurants—but more seriously, the idea here is to plan each day’s 3 meals to deliver a healthy macronutrient balance and a capped calorie total).
You may be thinking: “that sounds dismal, and not at all bright and cheerful, and certainly not happy and free”
The name comes from the idea that these rules are lines that one does not cross. They are “bright” lines because they should be observed with a bright and cheery demeanour, for they are the rules that, Dr. Thompson says, will make you “happy, thin, and free”.
You will note that this is completely in opposition to the expert opinion we hosted last week:
What Flexible Dieting Really Means
Dr. Thompson’s position on “freedom” is that Bright Line Eating is “very structured and takes a liberating stand against moderation”
Which may sound a bit of an oxymoron—is she really saying that we are going to be made free from freedom?
But there is some logic to it, and it’s about the freedom from having to make many food-related decisions at times when we’re likely to make bad ones:
Where does the psychology come in?
Dr. Thompson’s position is that willpower is a finite, expendable resource, and therefore we should use it judiciously.
So, much like Steve Jobs famously wore the same clothes every day because he had enough decisions to make later in the day that he didn’t want unnecessary extra decisions to make… Bright Line Eating proposes that we make certain clear decisions up front about our eating, so then we don’t have to make so many decisions (and potentially the wrong decisions) later when hungry.
You may be wondering: ”doesn’t sticking to what we decided still require willpower?”
And… Potentially. But the key here is shutting down self-negotiation.
Without clear lines drawn in advance, one must decide, “shall I have this cake or not?”, perhaps reflecting on the pros and cons, the context of the situation, the kind of day we’re having, how hungry we are, what else there is available to eat, what else we have eaten already, etc etc.
In short, there are lots of opportunities to rationalize the decision to eat the cake.
With clear lines drawn in advance, one must decide, “shall I have this cake or not?” and the answer is “no”.
So while sticking to that pre-decided “no” still may require some willpower, it no longer comes with a slew of tempting opportunities to rationalize a “yes”.
Which means a much greater success rate, both in adherence and outcomes. Here’s an 8-week interventional study and 2-year follow-up:
Bright Line Eating | Research Publications
Counterpoint: pick your own “bright lines”
Dr. Thompson is very keen on her 4 rules that have worked for her and many people, but she recognizes that they may not be a perfect fit for everyone.
So, it is possible to pick and choose our own “bright lines”; it is after all a dietary approach, not a religion. Here’s her response to someone who adopted the first 3 rules, but not the 4th:
Bright Lines as Guidelines for Weight Loss
The most important thing for Bright Line Eating, therefore, is perhaps the action of making clear decisions in advance and sticking to them, rather than seat-of-the-pantsing our diet, and with it, our health.
Want to know more from Dr. Thompson?
You might like her book, which we reviewed a while ago:
Bright Line Eating – by Dr. Susan Peirce Thompson
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Chiropractic All It’s Cracked Up To Be?
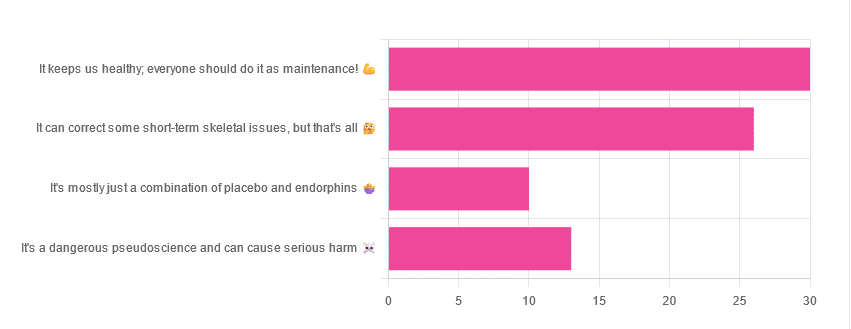
Yesterday, we asked you for your opinions on chiropractic medicine, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of results:
- 38% of respondents said it keeps us healthy, and everyone should do it as maintenance
- 33% of respondents said it can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all
- 16% of respondents said that it’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause serious harm
- 13% of respondents said that it’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins
Respondents also shared personal horror stories of harm done, personal success stories of things cured, and personal “it didn’t seem to do anything for me” stories.
What does the science say?
It’s a dangerous pseudoscience and can cause harm: True or False?
False and True, respectively.
That is to say, chiropractic in its simplest form that makes the fewest claims, is not a pseudoscience. If somebody physically moves your bones around, your bones will be physically moved. If your bones were indeed misaligned, and the chiropractor is knowledgeable and competent, this will be for the better.
However, like any form of medicine, it can also cause harm; in chiropractic’s case, because it more often than not involves manipulation of the spine, this can be very serious:
❝Twenty six fatalities were published in the medical literature and many more might have remained unpublished.
The reported pathology usually was a vascular accident involving the dissection of a vertebral artery.
Conclusion: Numerous deaths have occurred after chiropractic manipulations. The risks of this treatment by far outweigh its benefit.❞
Source: Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases
From this, we might note two things:
- The abstract doesn’t note the initial sample size; we would rather have seen this information expressed as a percentage. Unfortunately, the full paper is not accessible, and nor are many of the papers it cites.
- Having a vertebral artery fatally dissected is nevertheless not an inviting prospect, and is certainly a very reasonable cause for concern.
It’s mostly just a combination of placebo and endorphins: True or False?
True or False, depending on what you went in for:
- If you went in for a regular maintenance clunk-and-click, then yes, you will get your clunk-and-click and feel better for it because you had a ritualized* experience and endorphins were released.
- If you went in for something that was actually wrong with your skeletal alignment, to get it corrected, and this correction was within your chiropractor’s competence, then yes, you will feel better because a genuine fault was corrected.
*this is not implying any mysticism, by the way. Rather it means simply that placebo effect is strongest when there is a ritual associated with it. In this case it means going to the place, sitting in a pleasant waiting room, being called in, removing your shoes and perhaps some other clothes, getting the full attention of a confident and assured person for a while, this sort of thing.
With regard to its use to combat specifically spinal pain (i.e., perhaps the most obvious thing to treat by chiropractic spinal manipulation), evidence is slightly in favor, but remains unclear:
❝Due to the low quality of evidence, the efficacy of chiropractic spinal manipulation compared with a placebo or no treatment remains uncertain. ❞
Source: Clinical Effectiveness and Efficacy of Chiropractic Spinal Manipulation for Spine Pain
It can correct some short-term skeletal issues, but that’s all: True or False?
Probably True.
Why “probably”? The effectiveness of chiropractic treatment for things other than short-term skeletal issues has barely been studied. From this, we may wish to keep an open mind, while also noting that it can hardly claim to be evidence-based—and it’s had hundreds of years to accumulate evidence. In all likelihood, publication bias has meant that studies that were conducted and found inconclusive or negative results were simply not published—but that’s just a hypothesis on our part.
In the case of using chiropractic to treat migraines, a very-related-but-not-skeletal issue, researchers found:
❝Pre-specified feasibility criteria were not met, but deficits were remediable. Preliminary data support a definitive trial of MCC+ for migraine.❞
Translating this: “it didn’t score as well as we hoped, but we can do better. We got some positive results, and would like to do another, bigger, better trial; please fund it”
Source: Multimodal chiropractic care for migraine: A pilot randomized controlled trial
Meanwhile, chiropractors’ claims for very unrelated things have been harshly criticized by the scientific community, for example:
Misinformation, chiropractic, and the COVID-19 pandemic
About that “short-term” aspect, one of our subscribers put it quite succinctly:
❝Often a skeletal correction is required for initial alignment but the surrounding fascia and muscles also need to be treated to mobilize the joint and release deep tissue damage surrounding the area. In combination with other therapies chiropractic support is beneficial.❞
This is, by the way, very consistent with what was said in the very clinically-dense book we reviewed yesterday, which has a chapter on the short-term benefits and limitations of chiropractic.
A truism that holds for many musculoskeletal healthcare matters, holds true here too:
❝In a battle between muscle and bone, muscle will always win❞
In other words…
Chiropractic can definitely help put misaligned bones back where they should be. However, once they’re there, if the cause of their misalignment is not treated, they will just re-misalign themselves shortly after you walking out of your session.
This is great for chiropractors, if it keeps you coming back for endless appointments, but it does little for your body beyond give you a brief respite.
So, by all means go to a chiropractor if you feel so inclined (and you do not fear accidental arterial dissection etc), but please also consider going to a physiotherapist, and potentially other medical professions depending on what seems to be wrong, to see about addressing the underlying cause.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: