Butter vs Margarine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Butter vs Margarine
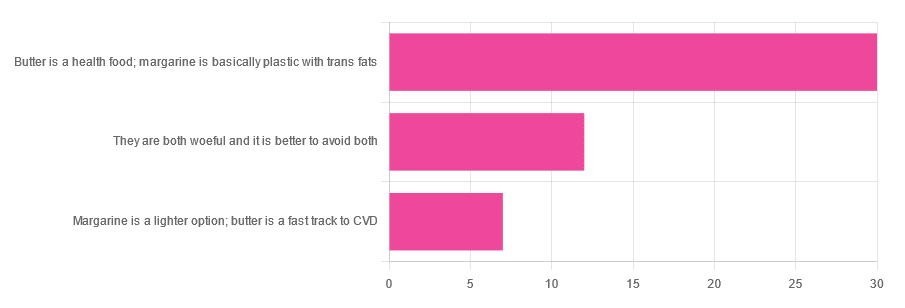
Yesterday, we asked you for your (health-related) opinion on butter vs margarine, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- A little over 60% said butter is a health food and margarine is basically plastic with trans fats
- A little over 20% said that both are woeful and it’s better to avoid both
- A little over 10% said that margarine is a lighter option, and butter is a fast track to cardiovascular disease.
Comments included (we will summarize/paraphrase, for space):
- “…in moderation, though”
- “I’m vegan so I use vegan butter but I know it’s not great, so I use it sparingly”
- “butter is healthy if and only if it’s grass-fed”
- “margarine has unpronounceable ingredients”
To address those quickly:
- “…in moderation” is a stipulation with which one can rarely go too far wrong
- Same! Speaking for myself (your writer here, hi) and not for the company
- Grass-fed is indeed better; alas that so little of it is grass-fed, in the US!
- Butter contains eicosatrienoic acid, linolelaidic acid, and more*. Sometimes big words don’t mean that something is worse for the health, though!
So, what does the science say?
Butter is a health food: True or False?
True or False, depending on amount! Moderation is definitely key, but we’ll return to that (and why not to have more than a small amount of butter) later. But it is a rich source of many nutrients, iff it’s grass-fed, anyway.
The nutritional profile of something isn’t a thing that’s too contentious, so rather than take too much time on it, in this case we’ll point you back up to the scientific paper we linked above, or if you prefer a pop-science rendering, here’s a nice quick rundown:
7 Reasons to Switch to Grass-Fed Butter
Margarine is basically plastic with trans fats: True or False?
False and usually False now, respectively, contingently.
On the first part: chemically, it’s simply not “basically plastic” and everything in it is digestible
On the second part: it depends on the margarine, and here’s where it pays to read labels. Historically, margarines all used to be high in trans fats (which are indeed woeful for the health). Nowadays, since trans fats have such a (well-earned) bad press, there are increasingly many margarines with low (or no) trans fats, and depending on your country, it may be that all margarines no longer have such:
❝It’s a public health success story. Consumers no longer have to worry about reading product nutritional labels to see if they contain hydrogenated oils and trans fats. They can just know that they no longer do❞
Source: Margarines now nutritionally better than butter after hydrogenated oil ban
So this is one where the science is clear (trans fats are unequivocally bad), but the consumer information is not always (it may be necessary to read labels, to know whether a margarine is conforming to the new guidelines).
Butter is a fast track to cardiovascular disease: True or False?
True or False depending on amount. In moderation, predictably it’s not a big deal.
But for example, the World Health Organization recommends that saturated fats (of which butter is a generous source) make up no more than 10% of our calorie intake:
Source: Saturated fatty acid and trans-fatty acid intake for adults and children: WHO guideline
So if you have a 2000 kcal daily intake, that would mean consuming not more than 200 kcal from butter, which is approximately two tablespoons.
If you’d like a deeper look into the complexities of saturated fats (for and against), you might like our previous main feature specifically about such:
Can Saturated Fats Be Healthy?
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lifespan vs Healthspan, And The Spice Of Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Great newsletter. Am taking turmeric for inflammation of hips and feet. Works like magic. Would like to know how it works, and what tumeric is best combined with – also whether there any risks in longterm use.❞
Glad you’re enjoying! As for turmeric, it sure is great, isn’t it? To answer your questions in a brief fashion:
- How it works: it does a lot of things, but perhaps its most key feature is its autoxidative metabolites that mediate its anti-inflammatory effect. This, it slows or inhibits oxidative stress that would otherwise cause inflammation, increase cancer risk, and advance aging.
- Best combined with: black pepper
- Any risks in long-term use: there are no known risks in long-term use ← that’s just one study, but there are lots. Some studies were prompted by reported hepatotoxicity of curcumin supplements, but a) the reports themselves seem to be without evidence b) the reported hepatoxicity was in relation to contaminants in the supplements, not the curcumin itself c) clinical trials were unable to find any hepatotoxicity (or other) risks anyway. Here’s an example of such a study.
You might also like our previous main feature: Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
❝This push for longevity is appealing but watching my mother in her nineties is a life I’m not looking forward to. Healthy longevity, yes, but longevity for the sake of a longer life? No thank you.❞
Yes, you’re quite right, that’s exactly the point! Assuming we live to die of age-related conditions (i.e., we do not suffer a fatal accident or incident in our younger years), those unfun last years are coming whether they come at 75 or 95. Or earlier or later, because that can absolutely happen too!
For example: nearly 10% of Americans over 65 have difficulty with self-care
As a rule, and we’ve covered some of the science of this previously, having at least 4 out of 5 of the “big 5” lifestyle factors (diet, exercise, sleep, low-or-zero alcohol, not smoking) not only extends life, but specifically extends the healthspan, i.e. the count of healthy life-years that precedes final age-related decline.
Share This Post
-
Eat To Beat Hyperthyroidism!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Would love to see more on eating vegan. I am allergic to soy in any form which seems to be in everything❞
There is a lot of it about, isn’t there? Happily, these days, a lot of meat and dairy alternatives are also made from other sources, for example pea protein is getting used a lot more nowadays in meat substitutes, and there are many kinds of alternatives to dairy (e.g. nut milks, oat milk, hemp milk, and—which is a branding nightmare but very healthy—pea milk).
You might like these previous main features of ours:
- Do We Need Animal Products To Be Healthy?
- The Whys and Hows of Cutting Down Meat Consumption
- Plant-Based Milks—What’s Best?
Also, if doing a whole foods plant-based diet, lentils (especially brown lentils) can be used as a great substitute for minced beef/lamb in recipes that call for such.
Boil the lentils (a liter of water to a cup of lentils is great; use a rice cooker if you have one!) along with the seasonings you will use (herbs appropriate to your dish, and then: black pepper is always good; you shouldn’t need to add salt; a teaspoon of low-sodium yeast extract is great though, or to really get the best nutritional benefits, nooch).
When it is done, you shouldn’t have excess water now, so just use as is, or if you want a slightly fatty kick, fry briefly in a little extra virgin olive oil, before using it however you were planning to use it.
Enjoy!
❝What foods should I eat for hyperthyroidism? My doctor tells me what foods to avoid, but not what to eat❞
Great question! We’ll have to do a main feature on hyperthyroidism one of these days, as so far we’ve only done features on hypothyroidism:
As for hyperthyroidism…
Depending on your medications, your doctor might recommend a low iodine diet. If so, then you might want to check out:
American Thyroid Association | Low Iodine Diet Plan
…for recommendations.
But in a way, that’s still a manner of “what to avoid” (iodine) and then the foods to eat to avoid that.
You may be wondering: is there any food that actively helps against hyperthyroidism, as opposed to merely does not cause problems?
And the answer is: yes!
Cruciferous vegetables (e.g. cabbage, sprouts, broccoli, cauliflower, etc) contain goitrin, which in immoderate quantities can cause problems for people with hypothyroidism because it can reduce thyroid hormone synthesis. If you have hyperthyroidism, however, this can work in your favor.
Read more: The role of micronutrients in thyroid dysfunction
The above paper focuses on children, but it was the paper we found that explains it most clearly while showing good science. However, the same holds true for adults:
Notwithstanding that the title comes from the angle of examining hypothyroidism, the mechanism of action makes clear its beneficence in the case of hyperthyroidism.
Selenium is also a great nutrient in the case of autoimmune hyperthyroidism, because it is needed to metabolize thyroid hormone (if you don’t metabolize it, it’ll just build up):
Selenium and Thyroid Disease: From Pathophysiology to Treatment
The absolute top best dietary source of selenium is Brazil nuts, to the point that people without hyperthyroidism have to take care to not eat more than a few per day (because too much selenium could then cause problems):
NIH | Selenium Fact Sheet for Health Professionals
(this contains information on the recommended amount, the upper limit amount, how much is in Brazil nuts and other foods, and what happens if you get too much or too little)
Note: after Brazil nuts (which are about 5 times more rich in selenium than the next highest source), the other “good” sources of selenium—mostly various kinds of fish—are also “good” source of iodine, so you might want to skip those.
Want more ideas?
You might like this from LivHealth:
Hyperthyroidism Diet: 9 Foods To Ease Symptoms
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Chaga Mushrooms’ Immune & Anticancer Potential
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Do Chaga Mushrooms Do?
Chaga mushrooms, which also go by other delightful names including “sterile conk trunk rot” and “black mass”, are a type of fungus that grow on birch trees in cold climates such as Alaska, Northern Canada, Northern Europe, and Siberia.
They’ve enjoyed a long use as a folk remedy in Northern Europe and Siberia, mostly to boost immunity, mostly in the form of a herbal tea.
Let’s see what the science says…
Does it boost the immune system?
It definitely does if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any studies on humans yet. But for example:
- Immunomodulatory Activity of the Water Extract from Medicinal Mushroom Inonotus obliquus
- Inonotus obliquus extracts suppress antigen-specific IgE production through the modulation of Th1/Th2 cytokines in ovalbumin-sensitized mice
(cytokines are special proteins that regulate the immune system, and Chaga tells them to tell the body to produce more white blood cells)
Wait, does that mean it increases inflammation?
Definitely not if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any studies on humans yet. But for example:
- Anti-inflammatory effects of orally administered Inonotus obliquus in ulcerative colitis
- Orally administered aqueous extract of Inonotus obliquus ameliorates acute inflammation
Anti-inflammatory things often fight cancer. Does chaga?
Definitely if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any studies in human cancer patients yet. But for example:
While in vivo human studies are conspicuous by their absence, there have been in vitro human studies, i.e., studies performed on cancerous human cell samples in petri dishes. They are promising:
- Anticancer activities of extracts and compounds from the mushroom Inonotus obliquus
- Extract of Innotus obliquus induces G1 cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer cells
- Anticancer activity of Inonotus obliquus extract in human cancer cells
I heard it fights diabetes; does it?
You’ll never see this coming, but: definitely if you’re a mouse! We couldn’t find any human studies yet. But for example:
- Anti-diabetic effects of Inonotus obliquus in type 2 diabetic mice
- Anti-diabetic effects of Inonotus obliquus in type 2 diabetic mice and potential mechanism
Is it safe?
Honestly, there simply have been no human safety studies to know for sure, or even to establish an appropriate dosage.
Its only-partly-understood effects on blood sugar levels and the immune system may make it more complicated for people with diabetes and/or autoimmune disorders, and such people should definitely seek medical advice before taking chaga.
Additionally, chaga contains a protein that can prevent blood clotting. That might be great by default if you are at risk of blood clots, but not so great if you are already on blood-thinning medication, or otherwise have a bleeding disorder, or are going to have surgery soon.
As with anything, we’re not doctors, let alone your doctors, so please consult yours before trying chaga.
Where can we get it?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience, here’s an example product on Amazon.
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Body by Science – by Dr. Doug McGuff & John Little
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The idea that you’ll get a re-sculpted body at 12 minutes per week is a bold claim, isn’t it? Medical Doctor Doug McGuff and bodybuilder John Little team up to lay out their case. So, how does it stand up to scrutiny?
First, is it “backed by rigorous research” as claimed? Yes… with caveats.
The book uses a large body of scientific literature as its foundation, and that weight of evidence does support this general approach:
- Endurance cardio isn’t very good at burning fat
- Muscle, even just having it without using it much, burns fat to maintain it
- To that end, muscle can be viewed as a fat-burning asset
- Muscle can be grown quickly with short bursts of intense exercise once per week
Why once per week? The most relevant muscle fibers take about that long to recover, so doing it more often will undercut gains.
So, what are the caveats?
The authors argue for slow reps of maximally heavy resistance work sufficient to cause failure in about 90 seconds. However, most of the studies cited for the benefits of “brief intense exercise” are for High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT). HIIT involves “sprints” of exercise. It doesn’t have to be literally running, but for example maxing out on an exercise bike for 30 seconds, slowing for 60, maxing out for 30, etc. Or in the case of resistance work, explosive (fast!) concentric movements and slow eccentric movements, to work fast- and slow-twitch muscle fibers, respectively.
What does this mean for the usefulness of the book?
- Will it sculpt your body as described in the blurb? Yes, this will indeed grow your muscles with a minimal expenditure of time
- Will it improve your body’s fat-burning metabolism? Yes, this will indeed turn your body into a fat-burning machine
- Will it improve your “complete fitness”? No, if you want to be an all-rounder athlete, you will still need HIIT, as otherwise anything taxing your under-worked fast-twitch muscle fibers will exhaust you quickly.
Bottom line: read this book if you want to build muscle efficiently, and make your body more efficient at burning fat. Best supplemented with at least some cardio, though!
Click here to check out Body by Science, and get re-sculpting yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Vodka vs Beer – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing vodka to beer, we picked the vodka.
Why?
As you might have guessed, neither are exactly healthy. But one of them is relatively, and we stress relatively, less bad than the other.
In the category of nutrients, vodka is devoid of nutrients, and beer has small amounts of some vitamins and minerals—but the amounts are so small, that you would need to drink yourself to death before benefiting from them meaningfully. And while beer gets touted as “liquid bread”, it really isn’t. A thousand years ago it will have been a lot less alcoholic and more carby, but even then, it wasn’t a health product aside from that it provided a way of making potentially contaminated water safer to drink.
In the category of carbohydrates, vodka nominally has none, due to the distillation process, and beer has some. Glycemic index websites often advise that the GI of beers, wines, and spirits can’t be measured as their carb content is not sufficient to get a meaningful sample, but diabetes research tells a more useful story:
Any alcoholic drink will generally cause a brief drop in blood sugars, followed by a spike. This happens because the liver prioritises metabolizing alcohol over producing glycogen, so it hits pause on the sugar metabolism and then has a backlog to catch up on. In the case of alcoholic drinks that have alcohol and carbs, this will be more pronounced—so this means that the functional glycemic load of beer is higher.
That’s a point in favor of vodka.
Additionally, in terms of the alcohol content, correctly-distilled vodka’s alcohol is pure ethanol, while beer will contain an amount of methanol that will vary per beer, but an illustrative nominal figure could be about 16mg/L. Methanol is more harmful than ethanol.
So that’s another point in favor of vodka.
Once again, neither drink is healthy; both are distinctly unhealthy. But unit for unit, beer is the least healthy of the two, making vodka the lesser of two evils.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Can We Drink To Good Health? (answer: we cannot, but this was about alcohol’s proposed heart-healthy benefits)
- Guinness Is Good For You* (it isn’t, but this was the long-time slogan and marketing campaign that fooled many)
- How To Reduce Or Quit Alcohol
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Continuous Glucose Monitors Without Diabetes: Pros & Cons
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The “Glucose Goddess”, biochemist Jessie Inchauspé, gives us the low-down:
Knowledge is power (but watch out)
A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device that continually monitors glucose levels, without the need to stab one’s finger every few hours to test blood.
It was designed for diabetics, especially for those with Type 1 Diabetes, where around-the-clock monitoring is necessary for appropriate insulin dosing.
For non-diabetics, they can be a good way of learning what our body’s response to various foods and activities is like, the better to be able to tweak our habits to avoid undue glucose spikes (which are harmful for our pancreas, liver, heart, brain, kidneys, and more).
How it works: there’s a sensor that sits on the arm (or elsewhere, but the arm is a popular placement) with a little probe that goes under the skin. It’s applied using a device that inserts it automatically using a needle (you only need to press a button, you don’t need to guide the needle yourself); the needle then retracts, leaving the soft, flexible probe in place. Having been attached, that sensor can now stay in place for 2 weeks (usually; depends on brand, but for example FreeStyle Libre, the most popular brand, the sensors last 2 weeks), and yes, it’s fine to bathe/shower/etc with it. When you want an update from your CGM, you scan it with your phone (or you can buy a dedicated reader, but that is more expensive and unnecessary), and it uploads the data since your last scan.
Pros: it’s convenient and gives a lot of data, so even if you only use it for a short period of time (for example, a month) you can get a very good idea of what affects your blood sugar levels and how. Also, because of the constant nature of the monitoring, it helps avoid accidental sample bias of the kind that can occur with manual testing, by testing a little too soon or too late, and missing a spike/dip.
Cons: it can be expensive, depending on where you live and what options are available for you locally, so you might not want to do it long-term (since that would require buying two sensors per month). It’s also, for all its wealth of data, slightly less accurate than fingerprick testing—that’s because it takes an interstitial reading instead of directly from the blood. For this reason, if you test both ways, you may find a discrepancy of about 3mg/dL. Given that the healthy range is about 70–140mg/dL, a discrepancy of 3mg/dL is probably not going to be important, but it is a thing to mention can (and probably will) happen.
Patterns to bear in mind (with any kind of blood sugar monitoring):
- Dawn phenomenon: a natural glucose rise upon waking.
- Exercise-induced spikes (normal due to energy demands).
- Fat in meals slowing glucose absorption.
- Different foods can sometimes cause a double-wave after dinner (because glucose from different foods is absorbed differently, and/or different foods affect insulin response independent of glucose)
- Steep, rapid spikes that are more harmful than gradual, sustained increases.
- Vitamin C spikes: temporary chemical interference with the sensor, not actual glucose rises.
- Nighttime glucose dips (often false readings caused by sleeping position).
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: