Breakfasting For Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Breakfast Time!
In yesterday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions on the timings of meals.
But what does the science say?
Quick recap on intermittent fasting first:
Today’s article will rely somewhat on at least a basic knowledge of intermittent fasting, what it is, and how and why it works.
Armed with that knowledge, we can look at when it is good to break the fast (i.e. breakfast) and when it is good to begin the fast (i.e. eat the last meal of the day).
So, if you’d like a quick refresher on intermittent fasting, here it is:
Intermittent Fasting: We Sort The Science From The Hype
And now, onwards!
One should eat breakfast first thing: True or False?
True! Give or take one’s definition of “first thing”. We did a main feature about this previously, and you can read a lot about the science of it, and see links to studies:
The Circadian Rhythm: Far More Than Most People Know
In case you don’t have time to read that now, we’ll summarize the most relevant-to-today’s-article conclusion:
The optimal time to breakfast is around 10am (this is based on getting sunlight around 8:30am, so adjust if this is different for you)
It doesn’t matter when we eat; calories are calories & nutrients are nutrients: True or False?
Broadly False, for practical purposes. Because, indeed calories are calories and nutrients are nutrients at any hour, but the body will do different things with them depending on where we are in the circadian cycle.
For example, this study in the Journal of Nutrition found…
❝Our results suggest that in relatively healthy adults, eating less frequently, no snacking, consuming breakfast, and eating the largest meal in the morning may be effective methods for preventing long-term weight gain.
Eating breakfast and lunch 5-6 h apart and making the overnight fast last 18-19 h may be a useful practical strategy.❞
Read in full: Meal Frequency and Timing Are Associated with Changes in Body Mass Index
We should avoid eating too late at night: True or False?
False per se, True in the context of the above. Allow us to clarify:
There is nothing inherently bad about eating late at night; there is no “bonus calorie happy hour” before bed.
However…
If we are eating late at night, that makes it difficult to breakfast in the morning (as is ideal) and still maintain a >16hr fasting window as is optimal, per:
❝the effects of the main forms of fasting, activating the metabolic switch from glucose to fat and ketones (G-to-K), starting 12-16 h after cessation or strong reduction of food intake❞
~ Dr. Françoise Wilhelmi de Toledo et al.
So in other words: since the benefits of intermittent fasting start at 12 hours into the fast, you’re not going to get them if you’re breakfasting at 10am and also eating in the evening.
Summary:
- It is best to eat breakfast around 10am, generally (ideally after some sunlight and exercise)
- While there’s nothing wrong with eating in the evening per se, doing so means that a 10am breakfast will eliminate any fasting benefits you might otherwise get
- If a “one meal a day, and that meal is breakfast” lifestyle doesn’t suit you, then one possible good compromise is to have a large breakfast, and then a smaller meal in the late afternoon / early evening.
One last tip: the above is good, science-based information. Use it (or don’t), as you see fit. We’re not the boss of you:
- Maybe you care most about getting the best circadian rhythm benefits, in which case, prioritizing breakfast being a) in the morning and b) the largest meal of the day, is key
- Maybe you care most about getting the best intermittent fasting benefits, in which case, for many people’s lifestyle, a fine option is skipping eating in the morning, and having one meal in the late afternoon / early evening.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Wholewheat Bread vs Seeded White – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing wholewheat bread to seeded bread, we picked the wholewheat.
Why?
First, we will acknowledge that this is a false dichotomy; it is possible to have seeded wholewheat bread. However, it is very common to have wholewheat bread that isn’t seeded, and white bread that is seeded. So, it’s important to be able to decide which is the healthier option, since very often, this false dichotomy is what’s on offer.
We will also advise checking labels (or the baker, if getting from a bakery) to ensure that visibly brown bread is actually wholewheat, and not just dyed brown with caramel coloring or such (yes, that is a thing that some companies do).
Now, as for why we chose the wholewheat over the seeded white…
In terms of macronutrients, wholewheat bread has (on average; individual breads may vary of course) has 2x the protein and a lot more fiber.
Those seeds in seeded bread? They just aren’t enough to make a big impact on the overall nutritional value of the bread in those regards. Per slice, you are getting, what, 10 seeds maybe? This is not a meaningful dietary source of much.
Seeded bread does have proportionally more healthy fats, but the doses are still so low as to make it not worth the while; it just looks like a lot of expressed as a percentage of comparison, because of the wholewheat bread has trace amounts, and the seeded bread has several times those trace amounts, it’s still a tiny amount. So, we’d recommend looking to other sources for those healthy fats.
Maybe dip your bread, of whatever kind, into extra virgin olive oil, for example.
Wholewheat bread of course also has a lower glycemic index. Those seeds in seeded white bread don’t really slow it down at all, because they’re not digested until later.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Carb-Strong or Carb-Wrong?
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Gluten: What’s The Truth?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
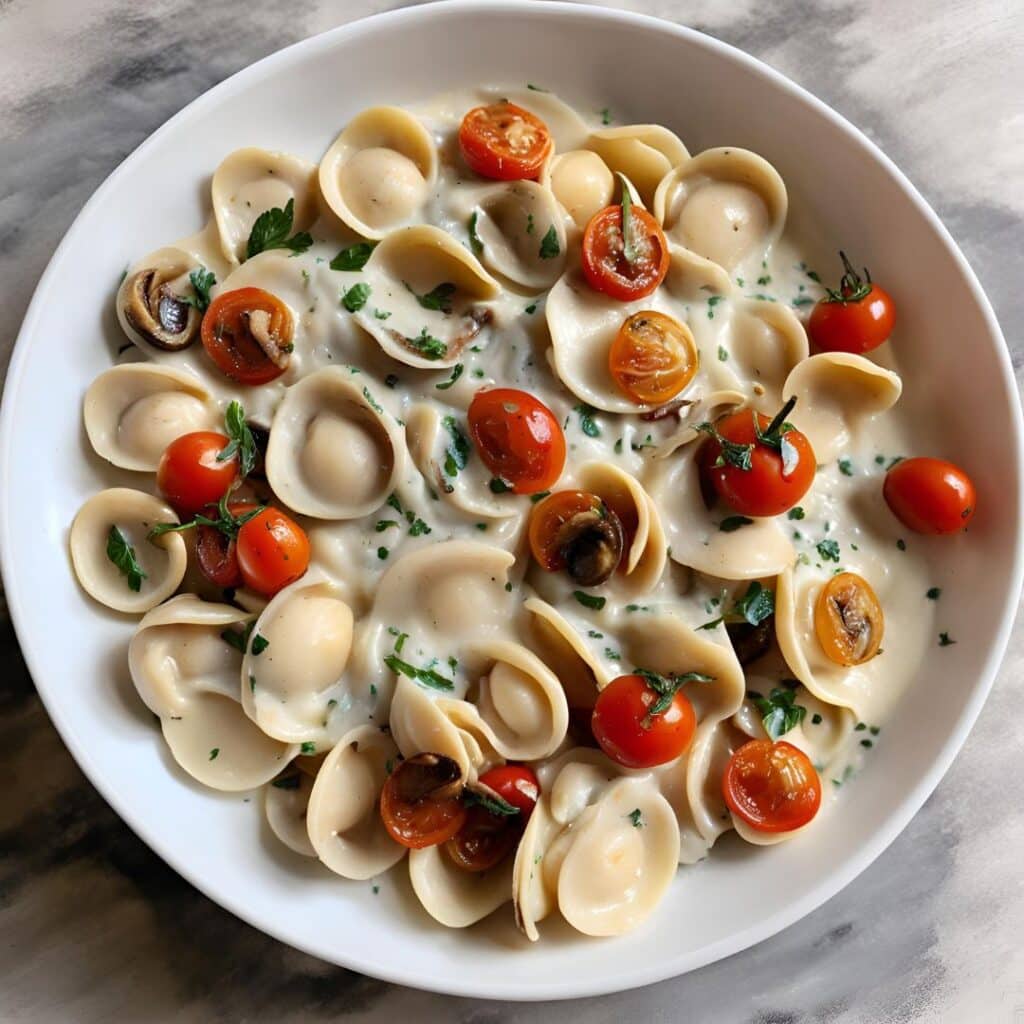
Gut-Healthy Labneh Orecchiette
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Labneh (a sort of yogurt-cheese made from strained yogurt) is a great probiotic, and there’s plenty of resistant starch in this dish too, from how we cook, cool, and reheat the pasta. Add to this the lycopene from the tomatoes, the ergothioneine from the mushrooms, and the healthful properties of the garlic, black pepper, and red chili, and we have a very healthy dish!
You will need
- 10 oz labneh (if you can’t buy it locally, you can make your own by straining Greek yogurt through a muslin cloth, suspended over a bowl to catch the water that drips out, overnight—and yes, plant-based is also fine if you are vegan, and the gut benefits are similar because unlike vegan cheese, vegan yogurt is still fermented)
- 6 oz wholegrain orecchiette (or other pasta, but this shape works well for this sauce)
- ¼ bulb garlic, grated
- Juice of ½ lemon
- Large handful chopped parsley
- Large handful chopped dill
- 9 oz cherry tomatoes, halved
- 9 oz mushrooms (your choice what kind), sliced (unless you went for shiitake or similar, which don’t need it due to already being very thin)
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the pasta as you normally would. Drain, and rinse with cold water. Set aside.
2) Combine the labneh with the garlic, black pepper, dill, parsley, and lemon juice, in a large bowl. Set aside.
3) Heat a little olive oil in a skillet; add the chili flakes, followed by the mushrooms. Cook until soft and browned, then add the tomatoes and fry for a further 1 minute—we want the tomatoes to be blistered, but not broken down. Stir in the MSG/salt, and take off the heat.
4) Refresh the pasta by passing a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander, then add the hot pasta to the bowl of labneh sauce, stirring to coat thoroughly.
5) Serve, spooning the mushrooms and tomatoes over the labneh pasta.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- “The Longevity Vitamin” (That’s Not A Vitamin)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
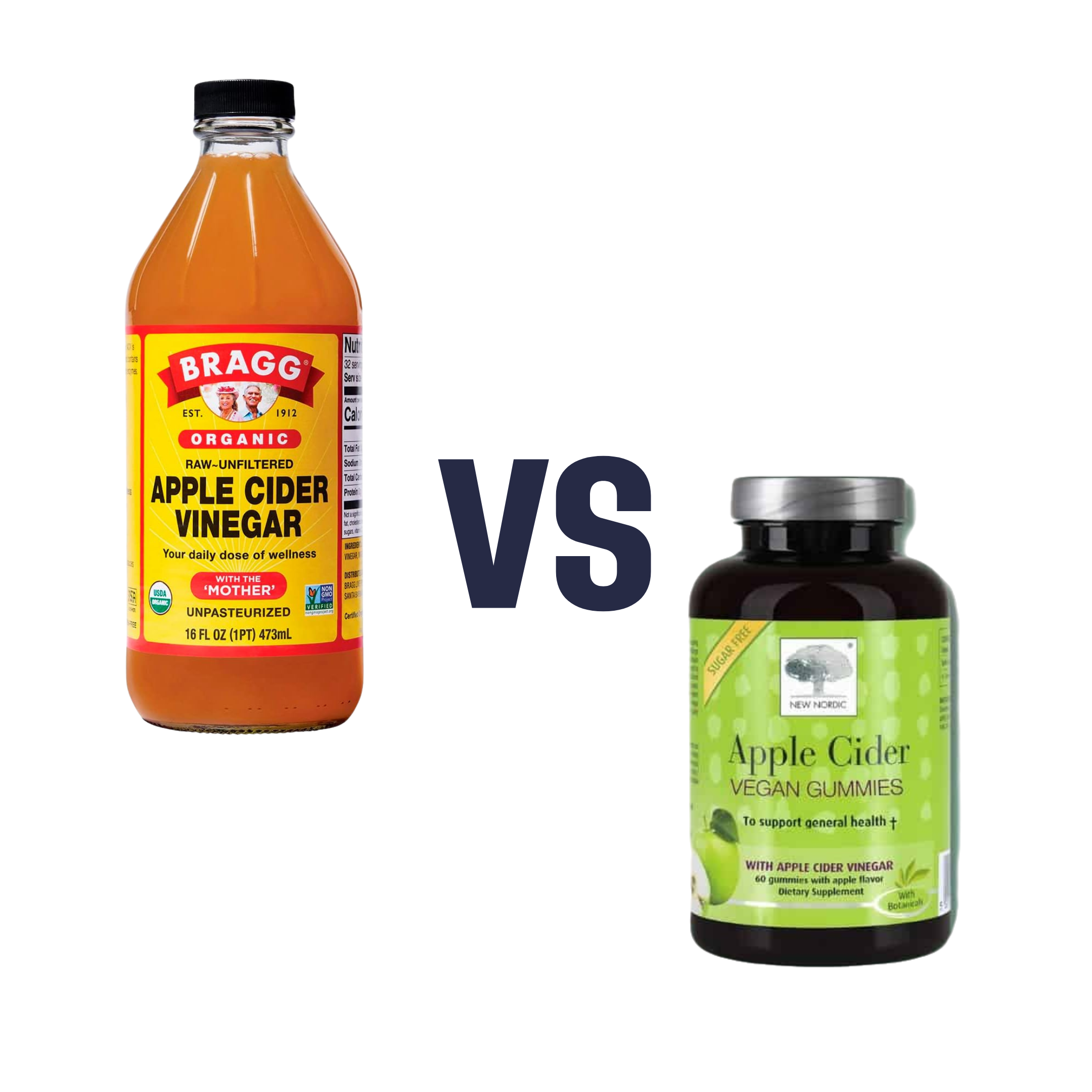
Apple Cider Vinegar vs Apple Cider Vinegar Gummies – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing apple cider vinegar (bottled) to apple cider vinegar (gummies), we picked the bottled.
Why?
There are several reasons!
The first reason is about dosage. For example, the sample we picked for apple cider vinegar gummies, boasts:
❝2 daily chewable gummies deliver 800 mg of Apple Cider Vinegar a day, equivalent to a teaspoon of liquid apple cider vinegar❞
That sounds good until you note that it’s recommended to take 1–2 tablespoons (not teaspoons) of apple vinegar. So this would need more like 4–8 gummies to make the dose. Suddenly, either that bottle of gummies is running out quickly, or you’re just not taking a meaningful dose and your benefits will likely not exceed placebo.
The other is reason about sugar. Most apple cider vinegar gummies are made with some kind of sugar syrup, often even high-fructose corn syrup, which is one of the least healthy foodstuffs (in the loosest sense of the word “foodstuffs”) known to science.
The specific brand we picked today was the best we can find; it used maltitol syrup.
Maltitol syrup, a corn derivative (and technically a sugar alcohol), has a Glycemic Index of 52, so it does raise blood sugars but not as much as sucrose would. However (and somewhat counterproductive to taking apple cider vinegar for gut health) it can cause digestive problems for many people.
And remember, you’re taking 4–8 gummies, so this is amounting to several tablespoons of the syrup by now.
On the flipside, apple cider vinegar itself has two main drawbacks, but they’re much less troublesome issues:
- many people don’t like the taste
- its acidic nature is not good for teeth
To this the common advice for both is to dilute it with water, thus diluting the taste and the acidity.
(this writer shoots hers from a shot glass, thus not bathing the teeth since it passes them “without touching the sides”; as for the taste, well, I find it invigorating—I do chase it with water, though to be sure of not leaving vinegar in my mouth)
Want to check them out for yourself?
Here they are:
Apple cider vinegar | Apple cider vinegar gummies
Want to know more about apple cider vinegar?
Check out:
- An Apple (Cider Vinegar) A Day…
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- How To Recover Quickly From A Stomach Bug
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Natural Alternatives for Depression Treatment
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Questions and Answers at 10almonds
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
This newsletter has been growing a lot lately, and so have the questions/requests, and we love that! In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
Natural alternatives to medication for depression?
Great question! We did a mean feature a while back, but we definitely have much more to say! We’ll do another main feature soon, but in the meantime, here’s what we previously wrote:
See: The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
^This covers not just the obvious, but also why the most common advice is not helpful, and practical tips to actually make manageable steps back to wellness, on days when “literally just survive the day” is one’s default goal.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
52 Small Changes – by Brett Blumenthal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We see a lot of books that exhort us to get a six-pack in a month, change our life in 7 days, learn Japanese in 24 hours. The reality is, things take time!
Brett Blumenthal is more realistic while being just as motivational:
The idea is simple… Make one small change per week for 52 weeks, and at the end of the year, you’ll be healthier and happier.
At 10almonds, we’re big fans of small changes that add up (or rather: compound!) to make big differences, so this one’s absolutely our style!
Best of all, she offers us not just “do this” advice, but also “and here’s the information and resources you’ll need to make this change work the best it can for you”
The advices range in topic from nutrition to exercise to sleep to mental wellness to interpersonal stuff and more. The biggest focus is on personal health, though, with small changes to exercise and nutrition making up the lion’s share of the changes.
Bottom line: this is a book you’ll want to grab once a week. Consider setting a reminder on your phone to check in with it each Sunday, for example!
Take the first step and order “52 Small Changes” from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Your Doctor Wants You to Know to Crush Medical Debt – by Dr. Virgie Ellington
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First things first: this one’s really only of relevance to people living in the US. That’s most of our readership, but if it’s not you, then apologies, this one won’t be of interest.
For the US Americans, though, Dr. Ellington starts strong with “you got a bill—now get the right bill”, and then gives a step-by-step process for finding the mistakes in your medical bills, fixing them, dealing with insurers who do not want to live up to their part of the bargain, and how to minimize what you need to pay, when you actually arrive at your final bill.
The biggest strength of this book is the wealth of insider knowledge (the author has worked as a primary care physician as well as as a health insurance executive), and while this information won’t stay current forever, its relatively recent publication date (2022) means that little has changed since then, and once you’re up to speed with how things are now, it’ll be easy to roll with whatever changes may come in the future.
Bottom line: if you’re living in the US and would like to not be ripped off as badly as possible when it comes to healthcare costs, this book is a very small, very powerful, investment.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: