Are You Stuck Playing These Three Roles in Love?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The psychology of Transactional Analysis holds that our interpersonal dynamics can be modelled in the following fashion:
The roles
- Child: vulnerable, trusting, weak, and support-seeking
- Parent: strong, dominant, responsible—but also often exhausted and critical
- Adult: balanced, thoughtful, creative, and kind
Ideally we’d be able to spend most of our time in “Adult” mode, and occasionally go into “Child” or “Parent” mode when required, e.g. child when circumstances have rendered us vulnerable and we need help; parent when we need to go “above and beyond” in the pursuit of looking after others. That’s all well and good and healthy.
However, in relationships, often it happens that partners polarize themselves and/or each other, with one shouldering all of the responsibility, and the other willfully losing their own agency.
The problem lies in that either role can be seductive—on the one hand, it’s nice to be admired and powerful and it’s a good feeling to look after one’s partner; on the other hand, it’s nice to have someone who will meet your every need. What love and trust!
Only, it becomes toxic when these roles stagnate, and each forgets how to step out of them. Each can become resentful of the other (for not pulling their weight, on one side, and for not being able to effortlessly solve all life problems unilaterally and provide endlessly in both time and substance, on the other), digging in to their own side and exacerbating the less healthy qualities.
As to the way out? It’s about self-exploration and mutual honesty—and mutual support:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Further reading
While we haven’t (before today) written about TA per se, we have previously written about AT (Attachment Theory), and on this matter, the two can overlap, where certain attachment styles can result in recreating parent/child/adult dynamics:
How To Leverage Attachment Theory In Your Relationship ← this is about understanding and recognizing attachment styles, and then making sure that both you and your partner(s) are armed with the necessary knowledge and understanding to meet each other’s needs.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
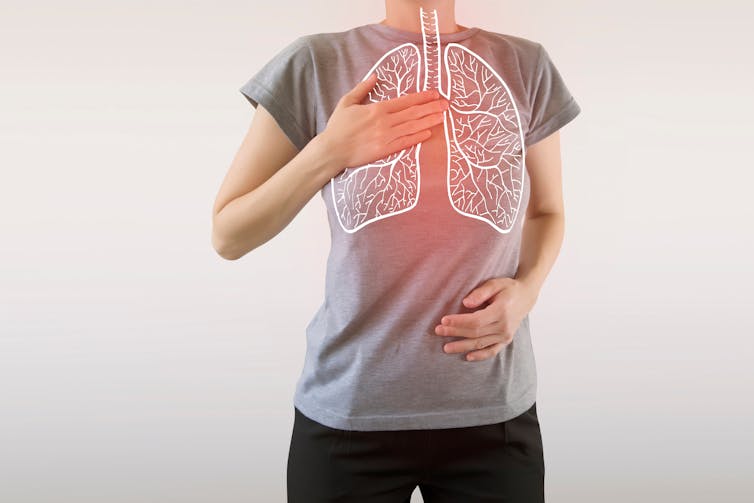
What is ‘breathwork’? And do I need to do it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From “breathwork recipes” to breathing techniques, many social media and health websites are recommending breathwork to reduce stress.
But breathwork is not new. Rather it is the latest in a long history of breathing techniques such as Pranayama from India and qigong from China. Such practices have been used for thousands of years to promote a healthy mind and body.
The benefits can be immediate and obvious. Try taking a deep breath in through your nose and exhaling slowly. Do you feel a little calmer?
So, what’s the difference between the breathing we do to keep us alive and breathwork?
Taras Grebinets/Shutterstock Breathwork is about control
Breathwork is not the same as other mindfulness practices. While the latter focus on observing the breath, breathwork is about controlling inhalation and exhalation.
Normally, breathing happens automatically via messages from the brain, outside our conscious control. But we can control our breath, by directing the movement of our diaphragm and mouth.
The diaphragm is a large muscle that separates our thoracic (chest) and abdominal (belly) cavities. When the diaphragm contracts, it expands the thoracic cavity and pulls air into the lungs.
Controlling how deep, how often, how fast and through what (nose or mouth) we inhale is the crux of breathwork, from fire breathing to the humming bee breath.
Breathwork can calm or excite
Even small bits of breathwork can have physical and mental health benefits and complete the stress cycle to avoid burnout.
Calming breathwork includes diaphragmatic (belly) breathing, slow breathing, pausing between breaths, and specifically slowing down the exhale.
In diaphragmatic breathing, you consciously contract your diaphragm down into your abdomen to inhale. This pushes your belly outwards and makes your breathing deeper and slower.
You can also slow the breath by doing:
- box breathing (count to four for each of four steps: breathe in, hold, breathe out, hold), or
- coherent breathing (controlled slow breathing of five or six breaths per minute), or
- alternate nostril breathing (close the left nostril and breathe in slowly through the right nostril, then close the right nostril and breathe out slowly through the left nostril, then repeat the opposite way).
You can slow down the exhalation specifically by counting, humming or pursing your lips as you breathe out.
In contrast to these calming breathing practices, energising fast-paced breathwork increases arousal. For example, fire breathing (breathe in and out quickly, but not deeply, through your nose in a consistent rhythm) and Lion’s breath (breathe out through your mouth, stick your tongue out and make a strong “haa” sound).
What is happening in the body?
Deep and slow breathing, especially with a long exhale, is the best way to stimulate the vagus nerves. The vagus nerves pass through the diaphragm and are the main nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Simulating the vagus nerves calms our sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) stress response. This improves mood, lowers the stress hormone cortisol and helps to regulate emotions and responses. It also promotes more coordinated brain activity, improves immune function and reduces inflammation.
Taking deep, diaphragmatic breaths also has physical benefits. This improves blood flow, lung function and exercise performance, increases oxygen in the body, and strengthens the diaphragm.
Slow breathing reduces heart rate and blood pressure and increases heart rate variability (normal variation in time between heart beats). These are linked to better heart health.
Taking shallow, quick, rhythmic breaths in and out through your nose stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. Short-term, controlled activation of the stress response is healthy and develops resilience to stress.
Breathing in through the nose
We are designed to inhale through our nose, not our mouth. Inside our nose are lots of blood vessels, mucous glands and tiny hairs called cilia. These warm and humidify the air we breathe and filter out germs and toxins.
We want the air that reaches our airways and lungs to be clean and moist. Cold and dry air is irritating to our nose and throat, and we don’t want germs to get into the body.
Nasal breathing increases parasympathetic activity and releases nitric oxide, which improves airway dilation and lowers blood pressure.
Consistently breathing through our mouth is not healthy. It can lead to pollutants and infections reaching the lungs, snoring, sleep apnoea, and dental issues including cavities and jaw joint problems.
Breathing can be high and shallow when we are stressed. mi_viri/Shutterstock A free workout
Slow breathing – even short sessions at home – can reduce stress, anxiety and depression in the general population and among those with clinical depression or anxiety. Research on breathwork in helping post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is also promising.
Diaphragmatic breathing to improve lung function and strengthen the diaphragm can improve breathing and exercise intolerance in chronic heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. It can also improve exercise performance and reduce oxidative stress (an imbalance of more free radicals and/or less antioxidants, which can damage cells) after exercise.
Waiting at the lights? This could be your signal to do some breathwork. doublelee/Shutterstock A mind-body connection you can access any time
If you feel stressed or anxious, you might subconsciously take shallow, quick breaths, but this can make you feel more anxious. Deep diaphragmatic breaths through your nose and focusing on strong exhalations can help break this cycle and bring calm and mental clarity.
Just a few minutes a day of breathwork can improve your physical and mental health and wellbeing. Daily deep breathing exercises in the workplace reduce blood pressure and stress, which is important since burnout rates are high.
Bottom line: any conscious control of your breath throughout the day is positive.
So, next time you are waiting in a line, at traffic lights or for the kettle to boil, take a moment to focus on your breath. Breathe deeply into your belly through your nose, exhale slowly, and enjoy the benefits.
Theresa Larkin, Associate professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong and Judy Pickard, Senior Lecturer, Clinical Psychology, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Get Rid Of Female Facial Hair Easily
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Sam Ellis, dermatologist, explains:
Hair today; gone tomorrow
While a little peach fuzz is pretty ubiquitous, coarser hairs are less common in women especially earlier in life. However, even before menopause, such hair can be caused by main things, ranging from PCOS to genetics and more. In most cases, the underlying issue is excess androgen production, for one reason or another (i.e. there are many possible reasons, beyond the scope of this article).
Options for dealing with this include…
- Topical, such as eflornithine (e.g. Vaniqa) thins terminal hairs (those are the coarse kind); a course of 6–8 weeks continued use is needed.
- Hormonal, such as estrogen (opposes testosterone and suppresses it), progesterone (downregulates 5α-reductase, which means less serum testosterone is converted to the more powerful dihydrogen testosterone (DHT) form), and spironolactone or other testosterone-blockers; not hormones themselves, but they do what it says on the tin (block testosterone).
- Non-medical, such as electrolysis, laser, and IPL. Electrolysis works on all hair colors but takes longer; laser needs to be darker hair against paler skin* (because it works by superheating the pigment of the hair while not doing the same to the skin) but takes more treatments, and IPL is a less-effective more-convenient at-home option, that works on the same principles as laser (and so has the same color-based requirements), and simply takes even longer than laser.
*so for example:
- Black hair on white skin? Yes
- Red hair on white skin? Potentially; it depends on the level of pigmentation. But it’s probably not the best option.
- Gray/blonde hair on white skin? No
- Black hair on mid-tone skin? Yes, but a slower pace may be needed for safety
- Anything else on mid-tone skin? No
- Anything on dark skin? No
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Too Much Or Too Little Testosterone?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Mental Health First-Aid That You’ll Hopefully Never Need
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Take Your Mental Health As Seriously As General Health!
Sometimes, health and productivity means excelling—sometimes, it means avoiding illness and unproductivity. Both are essential, and today we’re going to tackle some ground-up stuff. If you don’t need it right now, great; we suggest to read it for when and if you do. But how likely is it that you will?
- One in four of us are affected by serious mental health issues in any given year.
- One in five of us have suicidal thoughts at some point in our lifetime.
- One in six of us are affected to at least some extent by the most commonly-reported mental health issues, anxiety and depression, in any given week.
…and that’s just what’s reported, of course. These stats are from a UK-based source but can be considered indicative generally. Jokes aside, the UK is not a special case and is not measurably worse for people’s mental health than, say, the US or Canada.
While this is not an inherently cheery topic, we think it’s an important one.
Depression, which we’re going to focus on today, is very very much a killer to both health and productivity, after all.
One of the most commonly-used measures of depression is known by the snappy name of “PHQ9”. It stands for “Patient Health Questionnaire Nine”, and you can take it anonymously online for free (without signing up for anything; it’s right there on the page already):
Take The PHQ9 Test Here! (under 2 minutes, immediate results)
There’s a chance you took that test and your score was, well, depressing. There’s also a chance you’re doing just peachy, or maybe somewhere in between. PHQ9 scores can fluctuate over time (because they focus on the past two weeks, and also rely on self-reports in the moment), so you might want to bookmark it to test again periodically. It can be interesting to track over time.
In the event that you’re struggling (or: in case one day you find yourself struggling, or want to be able to support a loved one who is struggling), some top tips that are useful:
Accept that it’s a medical condition like any other
Which means some important things:
- You/they are not lazy or otherwise being a bad person by being depressed
- You/they will probably get better at some point, especially if help is available
- You/they cannot, however, “just snap out of it”; illness doesn’t work that way
- Medication might help (it also might not)
Do what you can, how you can, when you can
Everyone knows the advice to exercise as a remedy for depression, and indeed, exercise helps many. Unfortunately, it’s not always that easy.
Did you ever see the 80s kids’ movie “The Neverending Story”? There’s a scene in which the young hero Atreyu must traverse the “Swamp of Sadness”, and while he has a magical talisman that protects him, his beloved horse Artax is not so lucky; he slows down, and eventually stops still, sinking slowly into the swamp. Atreyu pulls at him and begs him to keep going, but—despite being many times bigger and stronger than Atreyu, the horse just sinks into the swamp, literally drowning in despair.
See the scene: The Neverending Story movie clip – Artax and the Swamp of Sadness (1984)
Wow, they really don’t make kids’ movies like they used to, do they?
But, depression is very much like that, and advice “exercise to feel less depressed!” falls short of actually being helpful, when one is too depressed to do it.
If you’re in the position of supporting someone who’s depressed, the best tool in your toolbox will be not “here’s why you should do this” (they don’t care; not because they’re an uncaring person by nature, but because they are physiologically impeded from caring about themself at this time), but rather:
“please do this with me”
The reason this has a better chance of working is because the depressed person will in all likelihood be unable to care enough to raise and/or maintain an objection, and while they can’t remember why they should care about themself, they’re more likely to remember that they should care about you, and so will go with your want/need more easily than with their own. It’s not a magic bullet, but it’s worth a shot.
What if I’m the depressed person, though?
Honestly, the same, if there’s someone around you that you do care about; do what you can to look after you, for them, if that means you can find some extra motivation.
But I’m all alone… what now?
Firstly, you don’t have to be alone. There are free services that you can access, for example:
- US: https://nami.org/help
- Canada: https://www.wellnesstogether.ca/en-CA
- UK: https://www.samaritans.org/
…which varyingly offer advice, free phone services, webchats, and the like.
But also, there are ways you can look after yourself a little bit; do the things you’d advise someone else to do, even if you’re sure they won’t work:
- Take a little walk around the block
- Put the lights on when you’re not sleeping
- For that matter, get out of bed when you’re not sleeping. Literally lie on the floor if necessary, but change your location.
- Change your bedding, or at least your clothes
- If changing the bedding is too much, change just the pillowcase
- If changing your clothes is too much, change just one item of clothing
- Drink some water; it won’t magically cure you, but you’ll be in slightly better order
- On the topic of water, splash some on your face, if showering/bathing is too much right now
- Do something creative (that’s not self-harm). You may scoff at the notion of “art therapy” helping, but this is a way to get at least some of the lights on in areas of your brain that are a little dark right now. Worst case scenario is it’ll be a distraction from your problems, so give it a try.
- Find a connection to community—whatever that means to you—even if you don’t feel you can join it right now. Discover that there are people out there who would welcome you if you were able to go join them. Maybe one day you will!
- Hiding from the world? That’s probably not healthy, but while you’re hiding, take the time to read those books (write those books, if you’re so inclined), learn that new language, take up chess, take up baking, whatever. If you can find something that means anything to you, go with that for now, ride that wave. Motivation’s hard to come by during depression and you might let many things slide; you might as well get something out of this period if you can.
If you’re not depressed right now but you know you’re predisposed to such / can slip that way?
Write yourself instructions now. Copy the above list if you like.
Most of all: have a “things to do when I don’t feel like doing anything” list.
If you only take one piece of advice from today’s newsletter, let that one be it!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy – by Dr. Anne Argur & Dr. Arthur Dalley
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Imagine, if you will, Grey’s Anatomy but beautifully illustrated in color and formatted in a way that’s easy to read—both in terms of layout and searchability, and also in terms of how this book presents anatomy described in a practical, functional context, with summary boxes for each area, so that the primary concepts don’t get lost in the very many details.
(In contrast, if you have a copy of the famous Grey’s Anatomy, you’ll know it’s full of many pages of nothing but tiny dense text, a large amount of which is Latin, with occasional etchings by way of illustration)
Another way in which this does a lot better than the aforementioned seminal work is that it also describes and discusses very many common variations and abnormalities, both congenital and acquired, so that it’s not just a text of “what a theoretical person looks like inside”, but rather also reflects the diverse reality of the human form (we weren’t made identically in a production line, and so we can vary quite a bit).
The book is, of course, intended for students and practitioners of medicine and related fields, so what good is it to the lay person? Well, if you ask the average person where the gallbladder is and why we have one, they will gesture in the general direction of the abdomen, and sort of shrug sheepishly. You don’t have to be that person 🙂
Bottom line: if you’d like to know your acetabulum from your zygomatic arch, this is the best anatomy book this reviewer has yet seen.
Click here to check out Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy, and prepare to be amazed!
PS: this one is expensive, but consider it a fair investment in your personal education, if you’re serious about it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Real Benefit Of Genetic Testing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Genetic Testing: Health Benefits & Methods
Genetic testing is an oft-derided American pastime, but there’s a lot more to it than finding out about your ancestry!
Note: because there are relatively few companies offering health-related genetic testing services, and we are talking about the benefits of those services, some of this main feature may seem like an advert.
It’s not; none of those companies are sponsoring us, and if any of them become a sponsor at some point, we’ll make it clear and put it in the clearly-marked sponsor segment.
As ever, our only goal here is to provide science-backed information, to enable you to make your own, well-informed, decisions.
Health genomics & genetic testing
The basic goal of health genomics and genetic testing is to learn:
- What genetic conditions you have
- Clearcut genetic conditions, such as Fragile X syndrome, or Huntington’s disease
- What genetic predispositions you have
- Such as an increased/decreased risk for various kinds of cancer, diabetes, heart conditions, and so forth
- What genetic traits you have
- These may range from “blue eyes” to “superathlete muscle type”
- More specifically, pharmacogenomic information
- For example, “fast caffeine metabolizer” or “clopidogrel (Plavix) non-responder” (i.e., that drug simply will not work for you)
Wait, what’s the difference between health genomics and genetic testing?
- Health genomics is the science of how our genes affect our health.
- Genetic testing can be broadly defined as the means of finding out which genes we have.
A quick snippet…
More specifically, a lot of these services look at which single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs, pronounced “snips”) we have. While we share almost all of our DNA with each other (and indeed, with most vertebrates), our polymorphisms are the bits that differ, and are the bits that, genetically speaking, make us different.
So, by looking just at the SNPs, it means we “only” need to look at about 3,000,000 DNA positions, and not our entire genome. For perspective, those 3,000,000 DNA positions make up about 0.1% of our whole genome, so without focusing on SNPs, the task would be 1000x harder.
For example, the kind of information that this sort of testing may give you, includes (to look at some “popular” SNPs):
- rs53576 in the oxytocin receptor influences social behavior and personality
- rs7412 and rs429358 can raise the risk of Alzheimer’s disease by more than 10x
- rs6152 can influence baldness
- rs333 resistance to HIV
- rs1800497 in a dopamine receptor may influence the sense of pleasure
- rs1805007 determines red hair and sensitivity to anesthetics
- rs9939609 triggers obesity and type-2 diabetes
- rs662799 prevents weight gain from high fat diets
- rs12255372 linked to type-2 diabetes and breast cancer
- rs1799971 makes alcohol cravings stronger
- rs17822931 determines earwax, sweating and body odor
- rs1333049 coronary heart disease
- rs1051730 and rs3750344 nicotine dependence
- rs4988235 lactose intolerance
(You can learn about these and more than 100,000 other SNPs at SNPedia.com)
I don’t know what SNPs I have, and am disinclined to look them up one by one!
The first step to knowing, is to get your DNA out of your body and into a genetic testing service. This is usually done by saliva or blood sample. This writer got hers done many years ago by 23andMe and was very happy with that service, but there are plenty of other options.
Healthline did an independent review of the most popular companies, so you might like to check out:
Healthline: Best DNA Testing Kits of 2023
Those companies will give you some basic information, such as “6x higher breast cancer risk” or “3x lower age-related macular degeneration risk” etc.
However, to really get bang-for-buck, what you want to do next is:
- Get your raw genetic data (the companies above should provide it); this will probably look like a big text file full of As, Cs, Gs, and Ts, but it make take another form.
- Upload it to Promethease. When this writer got hers done , the cost was $2; that price has now gone up to a whopping $12.
- You will then get a report that will cross-reference your data with everything known about SNPs, and give a supremely comprehensive, readable-to-the-human-eye, explanation of what it all means for you—from much more specific health risk prognostics, to more trivial things like whether you can roll your tongue or smell decomposed asparagus metabolites in urine.
A note on privacy: anything you upload to Promethease will be anonymized, and/but in doing so, you consent to it going into the grand scientific open-source bank of “things we know about the human genome”, and thus contribute to the overall sample size of genetic data.
In our opinion, it means you’re doing your bit for science, without personal risk. But your opinion may differ, and that’s your decision to make.
Lastly, on the pros and cons of pharmacogenetic testing specifically:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
- What genetic conditions you have
-
The End of Heart Disease – by Dr. Joel Fuhrman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed another of Dr. Fuhrman’s books, “Eat To Live”, and this time, he’s focusing specifically on preventing/reversing heart disease.
Dr. Fuhrman takes the stance that our food can either kill or heal us, and we get to choose which. As such, nutrition is central to his heart-healthy plan; he mostly leaves matters of exercise, sleep, etc to other sources.
His dietary approach is mostly uncontroversial: for example, advices include: enjoy nutritionally dense foods, skip processed foods, eat at least mostly plants, skip the added salt. A slightly more controversial aspect is that he advocates for avoiding cooking oils, including the healthiest oils, including olive and avocado, which are by current scientific consensus considered heart-healthy in moderation. As in, not even just heart-neutral, but rather, they actively improve triglycerides.
He compares different cardioprotective diets, and while he’s not unbiased, he does provide 40 pages of scholarly references, so we may understand that at the very least, his approach is sound.
There are also recipes—94 pages of them—for any who might wonder “how do I cook without…?” and some ingredient he would rather you omit.
The style is information-dense (and this is a 448-page book) but still very readable.
Bottom line: if you’re serious about improving your heart health, this book can help a lot with that.
Click here to check out The End Of Heart Disease, and end heart disease for yourself!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: