What does lion’s mane mushroom actually do, anyway?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You may know it as an ingredient in nootropic supplements. You may have heard of lion’s mane mushroom coffee. You may know it as the big shaggy white mushroom that grows in nature and can look very impressive.
What’s special about it?
The lion’s mane mushroom, or Hericium erinaceus (we mention, as studies we’ll cite often use the botanical name) is an adaptogenic agent that has an established ability to promote nerve regeneration through nerve growth factor neurotrophic activity. In other words, it helps (re)grow neurons.
In a 2023 study, researchers wondered if its abilities (well-established in the peripheral nervous system) would work in the central nervous system too, namely the brain, specifically the hippocampus (responsible for memory).
To boil what they found down to a single line, they concluded:
❝[Lion’s mane extract] therefore acts through a novel pan-neurotrophic signaling pathway, leading to improved cognitive performance.❞
You can read the full study for yourself (with pictures!) here:
Limitations of the study
It’s worth noting that the above study was performed on mice brains, not those of humans. As there is a shortage of human volunteers willing to have their brains sliced and examined under microscopes, we do not expect this study to be repeated with humans any time soon.
So, are there human studies that have been done?
There are! Particularly promising was this 2020 study of people with Alzheimer’s disease, wherein supplementation with 1g of lion’s mane mushroom daily for 49 weeks significantly increased cognitive test scores compared with a placebo; you can read about it here:
Additionally, this 2019 study showed that taking 1.2g daily for eight weeks helped relieve depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders in overweight or obese patiences:
Are there other health benefits?
It seems so! Unfortunately, most of its other health claims are only supported by animal studies so far, aside from one small study funded by a supplement company for their supplement that contained mostly Agaricus blazei (a different mushroom) with 14% lion’s mane.
However, in animal studies, lion’s mane has also shown promise:
- For digestion
- Against inflammation
- For cardiovascular health
- For diabetes management
- Against cancer
- Against aging
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it (or anything else, for that matter) but if you’d like to try it, here’s an example product for your convenience:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Who Initiates Sex & Why It Matters
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In an ideal world, it wouldn’t matter any more than who first says “let’s get something to eat” when hungry. But in reality, it can cause serious problems on both sides:
Fear and loathing?
The person who initiates gets the special prize of an n% chance of experiencing rejection, and then what? Try again, and again, and risk seeming pushy? Or leave the ball in the other person’s court, where it may then go untouched for the next few months, because (in the most positive scenario) they were waiting for you to initiate at a better time for them?
The person who does not initiate, and/but does not want sex at that time, gets the special prize of either making their partner feel unwanted, insecure, and perhaps unloved, or else grudgingly consenting to sex that’s going to be no fun while your heart’s not in it, and thus create the same end result plus you had an extra bad experience?
So, that sucks all around:
- Initiating touch (sex or cuddling) can feel like a test of being wanted, whereupon a lack of initiation or response may be misinterpreted as a lack of love or appreciation.
- Meanwhile, non-reciprocation might stem from exhaustion or unrelated issues. For many, it’s a physiological lottery.
10almonds note: not discussed in this video, but for many couples, problems can also arise because one partner or another just isn’t showing up with the expected physical signs of physiological arousal, so even if they say (and mean!) an enthusiastic “yes”, their body’s signs get misread as a “not really, though”, resulting in one partner feeling rejected, and both feeling inadequate—on account of something that was completely unrelated to how the person actually felt about the prospect of sex*.
*Sometimes, physiological arousal will simply not accompany psychological arousal, no matter how sincere the latter. And on the flipside, sometimes the signs of physiological arousal will just show up without psychological arousal. The human body is just like that sometimes. We all must listen to our partners’ words, not their genitals!
The solution to this problem is thus the same as the solution to the rest of the problem that is discussed in the video, and it’s: good communication.
That can be easier said than done, of course—not everyone is at their most eloquent in such situations! Which is why it can be important to have those conversations first outside of the bedroom when the stakes are low/non-existent.
Even with the best communication, a more general, overarching non-reciprocity (real or perceived) of sexual desire can cause bitterness, resentment, and can ultimately be relationship-ending if a resolution that’s acceptable to everyone involved is not found.
Ultimately, the work as a couple must begin from within as individuals—addressing self-worth issues to better navigate love and intimacy.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Relationships: When To Stick It Out & When To Call It Quits
Take care!
Share This Post
-
‘Free birthing’ and planned home births might sound similar but the risks are very different
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The death of premature twins in Byron Bay in an apparent “wild birth”, or free birth, last week has prompted fresh concerns about giving birth without a midwife or medical assistance.
This follows another case from Victoria this year, where a baby was born in a critical condition following a reported free birth.
It’s unclear how common free birthing is, as data is not collected, but there is some evidence free births increased during the COVID pandemic.
Planned home births also became more popular during the pandemic, as women preferred to stay away from hospitals and wanted their support people with them.
But while free births and home births might sound similar, they are a very different practice, with free births much riskier. So what’s the difference, and why might people opt for a free birth?
What are home births?
Planned home births involve care from midwives, who are registered experts in childbirth, in a woman’s home.
These registered midwives work privately, or are part of around 20 publicly funded home birth programs nationally that are attached to hospitals.
They provide care during the pregnancy, labour and birth, and in the first six weeks following the birth.
The research shows that for women with low risk pregnancies, planned home births attended by competent midwives (with links to a responsive mainstream maternity system) are safe.
Home births result in less intervention than hospital births and women perceive their experience more positively.
What are free births?
A free birth is when a woman chooses to have a baby, usually at home, without a registered health professional such as a midwife or doctor in attendance.
Different terms such as unassisted birth or wild pregnancy or birth are also used to refer to free birth.
The parents may hire an unregulated birth worker or doula to be a support at the birth but they do not have the training or medical equipment needed to manage emergencies.
Women may have limited or no health care antenatally, meaning risk factors such as twins and breech presentations (the baby coming bottom first) are not detected beforehand and given the right kind of specialist care.
Why do some people choose to free birth?
We have been studying the reasons women and their partners choose to free birth for more than a decade. We found a previous traumatic birth and/or feeling coerced into choices that are not what the woman wants were the main drivers for avoiding mainstream maternity care.
Australia’s childbirth intervention rates – for induction or augmentation of labour, episiotomy (cutting the tissue between the vaginal opening and the anus) and caesarean section – are comparatively high.
One in ten women report disrespectful or abusive care in childbirth and some decide to make different choices for future births.
Lack of options for a natural birth and birth choices such as home birth or birth centre birth also played a major role in women’s decision to free birth.
Publicly funded home birth programs have very strict criteria around who can be accepted into the program, excluding many women.
In other countries such as the United Kingdom, Netherlands and New Zealand, publicly funded home births are easier to access.
It can be difficult to access home birth services in Australia.
Ink Drop/ShutterstockOnly around 200 midwives provide private midwifery services for home births nationally. Private midwives are yet to obtain insurance for home births, which means they are risking their livelihoods if something goes wrong and they are sued.
The cost of a home birth with a private midwife is not covered by Medicare and only some health funds rebate some of the cost. This means women can be out of pocket A$6-8,000.
Access to home birth is an even greater issue in rural and remote Australia.
How to make mainstream care more inclusive
Many women feel constrained by their birth choices in Australia. After years of research and listening to thousands of women, it’s clear more can be done to reduce the desire to free birth.
As my co-authors and I outline in our book, Birthing Outside the System: The Canary in the Coal Mine, this can be achieved by:
- making respectful care a reality so women aren’t traumatised and alienated by maternity care and want to engage with it
- supporting midwifery care. Women are seeking more physiological and social ways of birthing, minimising birth interventions, and midwives are the experts in this space
- supporting women’s access to their chosen place of birth and model of care and not limiting choice with high out-of-pocket expenses
- providing more flexible, acceptable options for women experiencing risk factors during pregnancy and/or birth, such as having a previous caesarean birth, having twins or having a baby in breech position. Women experiencing these complications experience pressure to have a caesarean section
- getting the framework right with policies, guidelines, education, research, regulation and professional leadership.
Ensuring women’s rights and choices are informed and respected means they’re less likely to feel they’re left with no other option.
Hannah Dahlen, Professor of Midwifery, Associate Dean Research and HDR, Midwifery Discipline Leader, Western Sydney University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
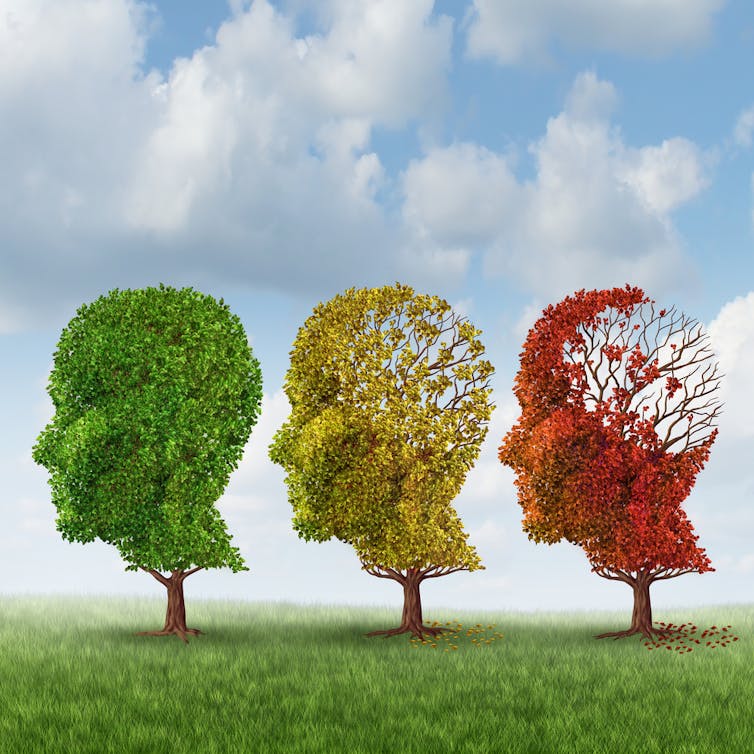
What’s the difference between Alzheimer’s and dementia?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
Changes in thinking and memory as we age can occur for a variety of reasons. These changes are not always cause for concern. But when they begin to disrupt daily life, it could indicate the first signs of dementia.
Another term that can crop up when we’re talking about dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, or Alzheimer’s for short.
So what’s the difference?
Lightspring/Shutterstock What is dementia?
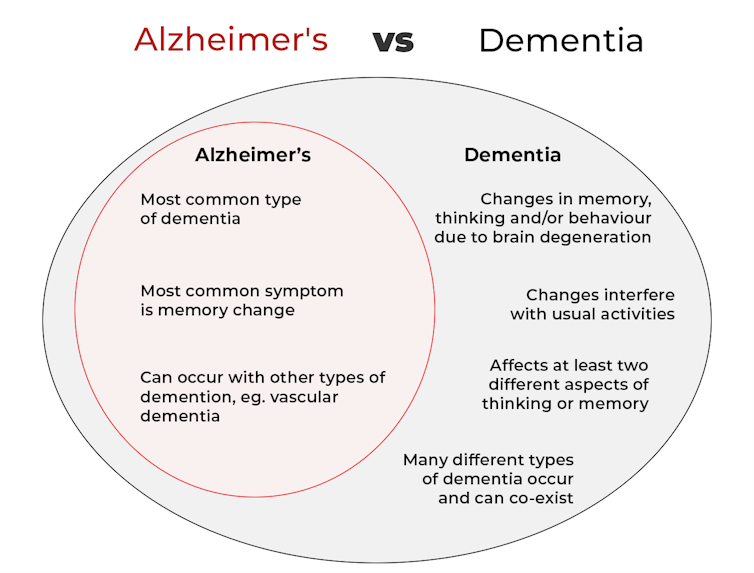
Dementia is an umbrella term used to describe a range of syndromes that result in changes in memory, thinking and/or behaviour due to degeneration in the brain.
To meet the criteria for dementia these changes must be sufficiently pronounced to interfere with usual activities and are present in at least two different aspects of thinking or memory.
For example, someone might have trouble remembering to pay bills and become lost in previously familiar areas.
It’s less-well known that dementia can also occur in children. This is due to progressive brain damage associated with more than 100 rare genetic disorders. This can result in similar cognitive changes as we see in adults.
So what’s Alzheimer’s then?
Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia, accounting for about 60-80% of cases.
So it’s not surprising many people use the terms dementia and Alzheimer’s interchangeably.
Changes in memory are the most common sign of Alzheimer’s and it’s what the public most often associates with it. For instance, someone with Alzheimer’s may have trouble recalling recent events or keeping track of what day or month it is.
People with dementia may have trouble keeping track of dates. Daisy Daisy/Shutterstock We still don’t know exactly what causes Alzheimer’s. However, we do know it is associated with a build-up in the brain of two types of protein called amyloid-β and tau.
While we all have some amyloid-β, when too much builds up in the brain it clumps together, forming plaques in the spaces between cells. These plaques cause damage (inflammation) to surrounding brain cells and leads to disruption in tau. Tau forms part of the structure of brain cells but in Alzheimer’s tau proteins become “tangled”. This is toxic to the cells, causing them to die. A feedback loop is then thought to occur, triggering production of more amyloid-β and more abnormal tau, perpetuating damage to brain cells.
Alzheimer’s can also occur with other forms of dementia, such as vascular dementia. This combination is the most common example of a mixed dementia.
Vascular dementia
The second most common type of dementia is vascular dementia. This results from disrupted blood flow to the brain.
Because the changes in blood flow can occur throughout the brain, signs of vascular dementia can be more varied than the memory changes typically seen in Alzheimer’s.
For example, vascular dementia may present as general confusion, slowed thinking, or difficulty organising thoughts and actions.
Your risk of vascular dementia is greater if you have heart disease or high blood pressure.
Frontotemporal dementia
Some people may not realise that dementia can also affect behaviour and/or language. We see this in different forms of frontotemporal dementia.
The behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia is the second most common form (after Alzheimer’s disease) of younger onset dementia (dementia in people under 65).
People living with this may have difficulties in interpreting and appropriately responding to social situations. For example, they may make uncharacteristically rude or offensive comments or invade people’s personal space.
Semantic dementia is also a type of frontotemporal dementia and results in difficulty with understanding the meaning of words and naming everyday objects.
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Dementia with Lewy bodies results from dysregulation of a different type of protein known as α-synuclein. We often see this in people with Parkinson’s disease.
So people with this type of dementia may have altered movement, such as a stooped posture, shuffling walk, and changes in handwriting. Other symptoms include changes in alertness, visual hallucinations and significant disruption to sleep.
Do I have dementia and if so, which type?
If you or someone close to you is concerned, the first thing to do is to speak to your GP. They will likely ask you some questions about your medical history and what changes you have noticed.
Sometimes it might not be clear if you have dementia when you first speak to your doctor. They may suggest you watch for changes or they may refer you to a specialist for further tests.
There is no single test to clearly show if you have dementia, or the type of dementia. A diagnosis comes after multiple tests, including brain scans, tests of memory and thinking, and consideration of how these changes impact your daily life.
Not knowing what is happening can be a challenging time so it is important to speak to someone about how you are feeling or to reach out to support services.
Dementia is diverse
As well as the different forms of dementia, everyone experiences dementia in different ways. For example, the speed dementia progresses varies a lot from person to person. Some people will continue to live well with dementia for some time while others may decline more quickly.
There is still significant stigma surrounding dementia. So by learning more about the various types of dementia and understanding differences in how dementia progresses we can all do our part to create a more dementia-friendly community.
The National Dementia Helpline (1800 100 500) provides information and support for people living with dementia and their carers. To learn more about dementia, you can take this free online course.
Nikki-Anne Wilson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA), UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Chia Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing chia seeds to pumpkin seeds, we picked the chia.
Why?
Both are great! But chia is best.
Note: we’re going to abbreviate them both to “chia” and “pumpkin”, respectively, but we’ll still be referring to the seeds throughout.
In terms of macros, pumpkin has a little more protein and notably higher carbs, whereas chia has nearly 2x the fiber, as well as more fat, and/but they are famously healthy fats. We’ll call this category a subjective win for chia, though you might disagree if you want to prioritize an extra 2g of protein per 100g (for pumpkin) over an extra 16g of fiber per 100g (for chia). Chia is also vastly preferable for omega-3.
When it comes to vitamins, pumpkin is marginally higher in vitamin A, while chia is a lot higher in vitamins B1, B2, B3, B9, C, and E. An easy win for chia.
In the category of minerals, for which pumpkin seeds are so famously a good source, chia has a lot more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and selenium. On the other hand, pumpkin has more potassium and zinc. Still, that’s a 7:2 win for chia.
Adding up the categories makes for a very compelling win for the humble chia seed.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
PlantYou: Scrappy Cooking – by Carleigh Bodrug
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a book that took “whole foods plant-based diet” and ran with it.
“Whole foods”, you say? Carleigh Bodrug has you covered in this guide to using pretty much everything.
One of the greatest strengths of the book is its “Got this? Make that” section, for using up those odds and ends that you’d normally toss.
You may be thinking: “ok, but if to use this unusual ingredient I have to buy four other ingredients to make this recipe, generating waste from those other ingredients, then this was a bad idea”, but fear not.
Bodrug covers that too, and in many cases leftover “would get wasted” ingredients can get turned into stuff that can go into longer-term storage one way or another, to use at leisure.
Which also means that on the day “there’s nothing in the house to eat” and you don’t want to go grocery-shopping, or if some global disaster causes the supply lines to fail and the stores become empty (that could never happen though, right?), you will have the mystical ability to conjure a good meal out of assorted odds and ends that you stored because of this book.
Bottom line: if you love food and hate food waste, this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out Scrappy Cooking, and do domestic magic!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Pistachios vs Brazil Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to Brazil nuts, we picked the pistachios.
Why?
In terms of macros, pistachios have more protein, carbs, and fiber, while Brazil nuts have more fat. The fats are mostly healthy, although it is worth noting that Brazil nuts have not only more total saturated fat, but also more saturated fat proportionally to total fats. All in all, Brazil nuts’ macro balance isn’t bad, but we say pistachios have it better.
When it comes to vitamins, pistachios have a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and C, while Brazil nuts have more vitamin E. An easy win for pistachios here.
In the category of minerals, it gets interesting: pistachios have more iron and potassium, while Brazil nuts have more calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc. Sounds great, but… About that selenium:
- A cup of cashews contains 38% of the RDA of selenium. This will go towards helping your hair be luscious and shiny (also important for energy conversion).
- A cup of Brazil nuts contains 10,456% of the RDA of selenium. This is way past the point of selenium toxicity, and your (luscious, shiny) hair will fall out.
For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
We consider that a point against Brazil nuts.
Adding up the sections gives us an overall win for pistachios. Of course, enjoy Brazil nuts too if you will, but in careful moderation please!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: