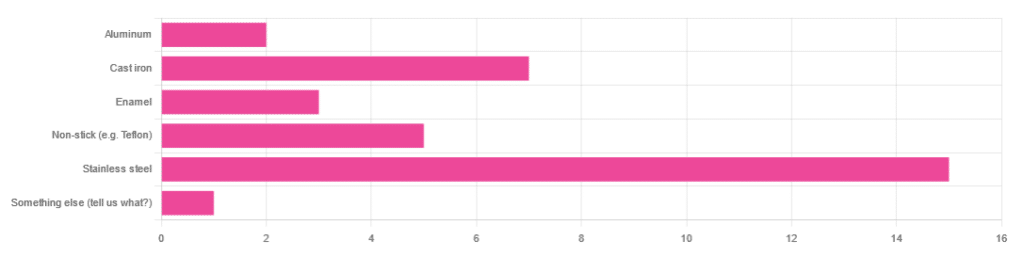Neuropsychologist Explains What She’s Got Out Of 6 Years Taking L-Theanine
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Inka Land, MSc neuropsychology, PgDip(c) Nutrition and Disease, talks about her use of l-theanine and the biochemistry behind it:
So, what’s the tea?
While she’s tested over 60 supplements, she regularly uses only a few. L-theanine made the cut, and has been a staple for over six years due to its noticeable effects on her brain, nervous system in general, and gut. Some notes from the video:
- L-theanine was discovered during university studies as a way to enhance focus and reduce stress. Initially, 50mg doses combined with coffee showed no effect, but increasing to 150mg, paired with 100mg of caffeine, produced significant nootropic benefits.
- L-theanine enhances sustained focus, enabling prolonged attention on repetitive tasks while avoiding distractions. It’s particularly effective for maintaining concentration during monotonous activities.
- L-theanine alleviates gut inflammation by boosting antioxidant activity and supporting glutamine metabolism. Combined with l-glutamine, it is more effective for reducing gut inflammation, and she mentions anecdotally that it seemed to help her personally recover quickly from food poisoning.
- Known for its calming effects, L-theanine reduces anxiety and regulates the nervous system. It is beneficial before stressful or crowded events and has anecdotal support for alleviating social anxiety specifically, though that’s not been formally tested in RCTs (yet). That said, since it has been tested against anxiety in the lab (usually combined with stress tests), it would be strange if it didn’t help alleviate social anxiety too, since what’s required for the nervous system is the same.
- Studies suggest 100–200mg twice daily, but she personally takes 250mg in the morning with coffee or 200–250mg PRN.
Want to try some? Here’s an example product on Amazon 😎
For more on all of this, enjoy (and kindly disregard that she clearly is holding a jar of curcumin in the thumbnail):
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like:
L-Theanine Against Stress, Anxiety, Inflammation, & More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Viruses aren’t always harmful. 6 ways they’re used in health care and pest control
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We tend to just think of viruses in terms of their damaging impacts on human health and lives. The 1918 flu pandemic killed around 50 million people. Smallpox claimed 30% of those who caught it, and survivors were often scarred and blinded. More recently, we’re all too familiar with the health and economic impacts of COVID.
But viruses can also be used to benefit human health, agriculture and the environment.
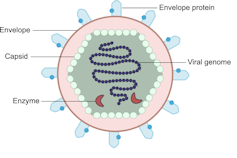
Viruses are comparatively simple in structure, consisting of a piece of genetic material (RNA or DNA) enclosed in a protein coat (the capsid). Some also have an outer envelope.
Viruses get into your cells and use your cell machinery to copy themselves.
Here are six ways we’ve harnessed this for health care and pest control.1. To correct genes
Viruses are used in some gene therapies to correct malfunctioning genes. Genes are DNA sequences that code for a particular protein required for cell function.
If we remove viral genetic material from the capsid (protein coat) we can use the space to transport a “cargo” into cells. These modified viruses are called “viral vectors”.
Viruses consist of a piece of RNA or DNA enclosed in a protein coat called the capsid.
DEXiViral vectors can deliver a functional gene into someone with a genetic disorder whose own gene is not working properly.
Some genetic diseases treated this way include haemophilia, sickle cell disease and beta thalassaemia.
2. Treat cancer
Viral vectors can be used to treat cancer.
Healthy people have p53, a tumour-suppressor gene. About half of cancers are associated with the loss of p53.
Replacing the damaged p53 gene using a viral vector stops the cancerous cell from replicating and tells it to suicide (apoptosis).
Viral vectors can also be used to deliver an inactive drug to a tumour, where it is then activated to kill the tumour cell.
This targeted therapy reduces the side effects otherwise seen with cytotoxic (cell-killing) drugs.
We can also use oncolytic (cancer cell-destroying) viruses to treat some types of cancer.
Tumour cells have often lost their antiviral defences. In the case of melanoma, a modified herpes simplex virus can kill rapidly dividing melanoma cells while largely leaving non-tumour cells alone.
3. Create immune responses
Viral vectors can create a protective immune response to a particular viral antigen.
One COVID vaccine uses a modified chimp adenovirus (adenoviruses cause the common cold in humans) to transport RNA coding for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein into human cells.
The RNA is then used to make spike protein copies, which stimulate our immune cells to replicate and “remember” the spike protein.
Then, when you are exposed to SARS-CoV-2 for real, your immune system can churn out lots of antibodies and virus-killing cells very quickly to prevent or reduce the severity of infection.
4. Act as vaccines
Viruses can be modified to act directly as vaccines themselves in several ways.
We can weaken a virus (for an attenuated virus vaccine) so it doesn’t cause infection in a healthy host but can still replicate to stimulate the immune response. The chickenpox vaccine works like this.
The Salk vaccine for polio uses a whole virus that has been inactivated (so it can’t cause disease).
Others use a small part of the virus such as a capsid protein to stimulate an immune response (subunit vaccines).
An mRNA vaccine packages up viral RNA for a specific protein that will stimulate an immune response.
5. Kill bacteria
Viruses can – in limited situations in Australia – be used to treat antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
Bacteriophages are viruses that kill bacteria. Each type of phage usually infects a particular species of bacteria.
Unlike antibiotics – which often kill “good” bacteria along with the disease-causing ones – phage therapy leaves your normal flora (useful microbes) intact.
Bacteriophages (red) are viruses that kill bacteria (green).
Shutterstock6. Target plant, fungal or animal pests
Viruses can be species-specific (infecting one species only) and even cell-specific (infecting one type of cell only).
This occurs because the proteins viruses use to attach to cells have a shape that binds to a specific type of cell receptor or molecule, like a specific key fits a lock.
The virus can enter the cells of all species with this receptor/molecule. For example, rabies virus can infect all mammals because we share the right receptor, and mammals have other characteristics that allow infection to occur whereas other non-mammal species don’t.
When the receptor is only found on one cell type, then the virus will infect that cell type, which may only be found in one or a limited number of species. Hepatitis B virus successfully infects liver cells primarily in humans and chimps.
We can use that property of specificity to target invasive plant species (reducing the need for chemical herbicides) and pest insects (reducing the need for chemical insecticides). Baculoviruses, for example, are used to control caterpillars.
Similarly, bacteriophages can be used to control bacterial tomato and grapevine diseases.
Other viruses reduce plant damage from fungal pests.
Myxoma virus and calicivirus reduce rabbit populations and their environmental impacts and improve agricultural production.
Just like humans can be protected against by vaccination, plants can be “immunised” against a disease-causing virus by being exposed to a milder version.
Thea van de Mortel, Professor, Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Griffith University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Mythbusting Cookware Materials
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you what kind of cookware you mostly use, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 45% said stainless steel
- About 21% said cast iron
- About 15% said non-stick (e.g. Teflon)
- About 9% said enamel
- About 6% said aluminum
- And 1 person selected “something else”, but then commented to the contrary, writing “I use all of the above”
So, what does the science say about these options?
Stainless steel cookware is safe: True or False?
True! Assuming good quality and normal use, anyway. There really isn’t a lot to say about this, because it’s very unexciting. So long as it is what it is labelled as: there’s nothing coating it, nothing comes out of it unless you go to extremes*, and it’s easy to clean.
*If you cook for long durations at very high temperatures, it can leach nickel and chromium into food. What this means in practical terms: if you are using stainless steel to do deep-frying, then maybe stop that, and also consider going easy on deep-frying in general anyway, because obviously deep-frying is unhealthy for other reasons.
Per normal use, however: pretty much the only way (good quality) stainless steel cookware will harm you is if you touch it while it’s hot, or if it falls off a shelf onto your head.
That said, do watch out for cheap stainless steel cookware that can contain a lot of impurities, including heavy metals. Since you probably don’t have a mass spectrometer and/or chemistry lab at home to check for those impurities, your best guard here is simply to buy from a reputable brand with credible certifications.
Ceramic cookware is safe: True or False?
True… Most of the time! Ceramic pans usually have metal parts and a ceramic cooking surface coated with a very thin layer of silicon. Those metal parts will be as safe as the metals used, so if that’s stainless steel, you’re just as safe as the above. As for the silicon, it is famously inert and body-safe (which is why it’s used in body implants).
However: ceramic cookware that doesn’t have an obvious metal part and is marketed as being pure ceramic, will generally be sealed with some kind of glaze that can leach heavy metals contaminants into the food; here’s an example:
Lead toxicity from glazed ceramic cookware
Copper cookware is safe: True or False?
False! This is one we forgot to mention in the poll, as one doesn’t see a lot of it nowadays. The copper from copper pans can leach into food. Now, of course copper is an important mineral that we must get from our diet, but the amount of copper that that can leach into food from copper pans is far too much, and can induce copper toxicity.
In addition, copper cookware has been found to be, on average, highly contaminated with lead:
Non-stick cookware contaminates the food with microplastics: True or False?
True! If we were to discuss all the common non-stick contaminants here, this email would no longer fit (there’s a size limit before it gets clipped by most email services).
Suffice it to say: the non-stick coating, polytetrafluoroethylene, is itself a PFAS, that is to say, part of the category of chemicals considered environmental pollutants, and associated with a long list of health issues in humans (wherein the level of PFAS in our bloodstream is associated with higher incidence of many illnesses):
You may have noticed, of course, that the “non-stick” coating doesn’t stick very well to the pan, either, and will tend to come off over time, even if used carefully.
Also, any kind of wet cooking (e.g. saucepans, skillets, rice cooker inserts) will leach PFAS into the food. In contrast, a non-stick baking tray lined with baking paper (thus: a barrier between the tray and your food) is really not such an issue.
We wrote about PFAS before, so if you’d like a more readable pop-science article than the scientific paper above, then check out:
PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
Aluminum cookware contaminates the food with aluminum: True or False?
True! But not usually in sufficient quantities to induce aluminum toxicity, unless you are aluminum pans Georg who eats half a gram of aluminum per day, who is a statistical outlier and should not be counted.
That’s a silly example, but an actual number; the dose required for aluminum toxicity in blood is 100mg/L, and you have about 5 liters of blood.
Unless you are on kidney dialysis (because 95% of aluminum is excreted by the kidneys, and kidney dialysis solution can itself contain aluminum), you will excrete aluminum a lot faster than you can possibly absorb it from cookware. On the other hand, you can get too much of it from it being a permitted additive in foods and medications, for example if you are taking antacids they often have a lot of aluminum oxide in them—but that is outside the scope of today’s article.
However, aluminum may not be the real problem in aluminum pans:
❝In addition, aluminum (3.2 ± 0.25 to 4.64 ± 0.20 g/kg) and copper cookware (2.90 ± 0.12 g/kg) were highly contaminated with lead.
The time and pH-dependent study revealed that leaching of metals (Al, Pb, Ni, Cr, Cd, Cu, and Fe, etc.) into food was predominantly from anodized and non-anodized aluminum cookware.
More metal leaching was observed from new aluminum cookware compared to old. Acidic food was found to cause more metals to leach during cooking.❞
~ the same paper we cited when talking about copper
Cast iron cookware contaminates the food with iron: True or False?
True, but unlike with the other metals discussed, this is purely a positive, and indeed, it’s even recommended as a good way to fortify one’s diet with iron:
The only notable counterpoint we could find for this is if you have hemochromatosis, a disorder in which the body is too good at absorbing iron and holding onto it.
Thinking of getting some new cookware?
Here are some example products of high-quality safe materials on Amazon, but of course feel free to shop around:
Stainless Steel | Ceramic* | Cast Iron
*it says “non-stick” in the description, but don’t worry, it’s ceramic, not Teflon etc, and is safe
Bonus: rice cooker with stainless steel inner pot
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Doesn’t Lycopene Do?
Lycopene is an antioxidant carotenoid famously found in tomatoes; it actually appears in even higher levels in watermelon, though. If you are going to get it from tomato, know that cooking improves the lycopene content rather than removing it (watermelon, on the other hand, can be enjoyed as-is and already has the higher lycopene content).
Antioxidant properties
Let’s reiterate the obvious first, for the sake of being methodical and adding a source. Lycopene is a potent antioxidant with multiple health benefits:
Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits
…and as such, it does all the things you might reasonably expect and antioxidant to do. For example…
Anti-inflammatory properties
In particular, it regulates macrophage activity, reducing inflammation while improving immune response:
Lycopene Regulates Macrophage Immune Response through the Autophagy Pathway Mediated by RIPK1
As can be expected of most antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, it also has…
Anticancer properties
Scientific papers tend to be “per cancer type”, so we’re just going to give one example, but there’s pretty much evidence for its utility against most if not all types of cancer. We’re picking prostate cancer though, as it’s one that’s been studied the most in the context of lycopene intake—in this study, for example, it was found that men who enjoyed at least two servings of lycopene-rich tomato sauce per week were 30% less likely to develop prostate cancer than those who didn’t:
Dietary lycopene intake and risk of prostate cancer defined by ERG protein expression
If you’d like to see something more general, however, then check out:
Potential Use of Tomato Peel, a Rich Source of Lycopene, for Cancer Treatment
It also fights Candida albicans
Ok, this is not (usually) so life-and-death as cancer, but reducing our C. albicans content (specifically: in our gut) has a lot of knock-on effects for other aspects of our health, so this isn’t one to overlook:
The title does not make this clear, but yes: this does mean it has an antifungal effect. We mention this because often cellular apoptosis is good for an overall organism, but in this case, it simply kills the Candida.
It’s good for the heart
A lot of studies focus just on triglyceride markers (which lycopene improves), but more tellingly, here’s a 10-year observational study in which diets rich in lycopene were associated to a 17–26% lower risk of heart disease:
Relationship of lycopene intake and consumption of tomato products to incident CVD
…and a 39% overall reduced mortality in, well, we’ll let the study title tell it:
…which means also:
It’s good for the brain
As a general rule of thumb, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain (because the brain needs healthy blood flow to stay healthy, and is especially vulnerable when it doesn’t get that), and in this case that rule of thumb is also borne out by the post hoc evidence, specifically yielding a 31% decreased incidence of stroke:
Dietary and circulating lycopene and stroke risk: a meta-analysis of prospective studies
Is it safe?
As a common food product, it is considered very safe.
If you drink nothing but tomato juice all day for a long time, your skin will take on a reddish hue, which will go away if you stop getting all your daily water intake in tomato juice.
In all likelihood, even if you went to extremes, you would get sick from the excess of vitamin A (generally present in the same foods) sooner than you’d get sick from the excess of lycopene.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, and also we recommend simply enjoying tomatoes, watermelons, etc, but if you do want a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
A Therapeutic Journey – by Alain de Botton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve often featured The School of Life’s videos here on 10almonds, and most of those are written by (and often voiced by) Alain de Botton.
This book lays out the case for mental health being also just health, that no person is perfectly healthy all the time, and sometimes we all need a little help. While he does suggest seeking help from reliable outside sources, he also tells a lot about how we can improve things for ourselves along the way, whether by what we can control in our environment, or just what’s between our ears.
In the category of limitations, the book is written with the assumption that you are in a position to have access to a therapist of your choice, and in a sufficiently safe and stable life situation that there is a limit to how bad things can get.
The style is… Alain de Botton’s usual style. Well-written, clear, decisive, instructive, compassionate, insightful, thought-provoking.
Bottom line: this isn’t a book for absolutely everyone, but if your problems are moderate and your resources are comfortable, then this book has a lot of insights that can make your life more easy-going and joyful, without dropping the seriousness when appropriate.
Click here to check out A Therapeutic Journey, and perhaps begin one of your own!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Oral retinoids can harm unborn babies. But many women taking them for acne may not be using contraception
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Oral retinoids are a type of medicine used to treat severe acne. They’re sold under the brand name Roaccutane, among others.
While oral retinoids are very effective, they can have harmful effects if taken during pregnancy. These medicines can cause miscarriages and major congenital abnormalities (harm to unborn babies) including in the brain, heart and face. At least 30% of children exposed to oral retinoids in pregnancy have severe congenital abnormalities.
Neurodevelopmental problems (in learning, reading, social skills, memory and attention) are also common.
Because of these risks, the Australasian College of Dermatologists advises oral retinoids should not be prescribed a month before or during pregnancy under any circumstances. Dermatologists are instructed to make sure a woman isn’t pregnant before starting this treatment, and discuss the risks with women of childbearing age.
But despite this, and warnings on the medicines’ packaging, pregnancies exposed to oral retinoids continue to be reported in Australia and around the world.
In a study published this month, we wanted to find out what proportion of Australian women of reproductive age were taking oral retinoids, and how many of these women were using contraception.
Our results suggest a high proportion of women are not using effective contraception while on these drugs, indicating Australia needs a strategy to reduce the risk oral retinoids pose to unborn babies.
Contraception options
Using birth control to avoid pregnancy during oral retinoid treatment is essential for women who are sexually active. Some contraception methods, however, are more reliable than others.
Long-acting-reversible contraceptives include intrauterine devices (IUDs) inserted into the womb (such as Mirena, Kyleena, or copper devices) and implants under the skin (such as Implanon). These “set and forget” methods are more than 99% effective.
Oral retinoids taken during pregnancy can cause complications in babies. Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock The effectiveness of oral contraceptive pills among “perfect” users (following the directions, with no missed or late pills) is similarly more than 99%. But in typical users, this can fall as low as 91%.
Condoms, when used as the sole method of contraception, have higher failure rates. Their effectiveness can be as low as 82% in typical users.
Oral retinoid use over time
For our study, we analysed medicine dispensing data among women aged 15–44 from Australia’s Pharmaceutical Benefit Scheme (PBS) between 2013 and 2021.
We found the dispensing rate for oral retinoids doubled from one in every 71 women in 2013, to one in every 36 in 2021. The increase occurred across all ages but was most notable in young women.
Most women were not dispensed contraception at the same time they were using the oral retinoids. To be sure we weren’t missing any contraception that was supplied before the oral retinoids, we looked back in the data. For example, for an IUD that lasts five years, we looked back five years before the oral retinoid prescription.
Our analysis showed only one in four women provided oral retinoids were dispensed contraception simultaneously. This was even lower for 15- to 19-year-olds, where only about one in eight women who filled a prescription for oral retinoids were dispensed contraception.
A recent study found 43% of Australian year 10 and 69% of year 12 students are sexually active, so we can’t assume this younger age group largely had no need for contraception.
One limitation of our study is that it may underestimate contraception coverage, because not all contraceptive options are listed on the PBS. Those options not listed include male and female sterilisation, contraceptive rings, condoms, copper IUDs, and certain oral contraceptive pills.
But even if we presume some of the women in our study were using forms of contraception not listed on the PBS, we’re still left with a significant portion without evidence of contraception.
What are the solutions?
Other countries such as the United States and countries in Europe have pregnancy prevention programs for women taking oral retinoids. These programs include contraception requirements, risk acknowledgement forms and regular pregnancy tests. Despite these programs, unintended pregnancies among women using oral retinoids still occur in these countries.
But Australia has no official strategy for preventing pregnancies exposed to oral retinoids. Currently oral retinoids are prescribed by dermatologists, and most contraception is prescribed by GPs. Women therefore need to see two different doctors, which adds costs and burden.
Preventing pregnancy during oral retinoid treatment is essential. Krakenimages.com/Shutterstock Rather than a single fix, there are likely to be multiple solutions to this problem. Some dermatologists may not feel confident discussing sex or contraception with patients, so educating dermatologists about contraception is important. Education for women is equally important.
A clinical pathway is needed for reproductive-aged women to obtain both oral retinoids and effective contraception. Options may include GPs prescribing both medications, or dermatologists only prescribing oral retinoids when there’s a contraception plan already in place.
Some women may initially not be sexually active, but change their sexual behaviour while taking oral retinoids, so constant reminders and education are likely to be required.
Further, contraception access needs to be improved in Australia. Teenagers and young women in particular face barriers to accessing contraception, including costs, stigma and lack of knowledge.
Many doctors and women are doing the right thing. But every woman should have an effective contraception plan in place well before starting oral retinoids. Only if this happens can we reduce unintended pregnancies among women taking these medicines, and thereby reduce the risk of harm to unborn babies.
Dr Laura Gerhardy from NSW Health contributed to this article.
Antonia Shand, Research Fellow, Obstetrician, University of Sydney and Natasha Nassar, Professor of Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology and Chair in Translational Childhood Medicine, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
No-Exercise Exercise!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Do you love to go to the gym?
If so, today’s article might not be for you so much. Or maybe it will, because let’s face it, exercise is fun!
At least… It can be, and should be 😎
So without further ado, here’s a slew of no-exercise exercise ideas; we’re willing to bet that somewhere in the list there’s at least some you haven’t tried before, and probably some you haven’t done in a while but might enjoy making a reprise!
Walking
No surprises here: walking is great. Hopefully you have some green spaces near you, but if you don’t, [almost] any walking is better than no walking. So unless there’s some sort of environmental disaster going on outside, lace up and get stepping.
If you struggle to “walk for walking’s sake” give yourself a little mission. Walk to the shop to buy one item. Walk to the park and find a flower to photograph. Walk to the library and take out a book. Whatever works for you!
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less, And Move More
Take the stairs
This one doesn’t need many words, just: make it a habit.
Treat the elevators as though they aren’t there!
See also: How To Really Pick Up (And Keep!) Those Habits
Dance
Dance is amazing! Any kind of dance, whatever suits your tastes. This writer loves salsa and tango, but no matter whether for you it’s zouk or zumba, breakdancing or line dancing, whatever gets you moving is going to be great for you.
If you don’t know how, online tutorials abound, and best of all is to attend local classes if you can, because they’re always a fun social experience too.
Make music
Not something often thought of as an exercise, but it is! Most instruments require that we be standing or siting with good posture, focusing intently on our movements, and often as not, breathing very mindfully too. And yes, it’s great for the brain as well!
Check out: This Is Your Brain on Music: The Science of a Human Obsession – by Dr. Daniel Levitin
Take a stand
If you spend a lot of time at a desk, please consider investing in a standing desk; they can be truly life-changing. Not only is it so much better for your back, hips, neck, and internal organs, but also it burns hundreds more calories than sitting, due to the no-exercise exercise that is keeping your body constantly stabilized while on your feet.
(or, if you’re like this writer: on your foot. I do have two feet, I just spend an inordinate amount of time at my desk standing on one leg at a time; I’m a bit of a flamingo like that)
See also: Deskbound: Standing Up to a Sitting World – by Kelly Starrett and Glen Cordoza
Sit, but…
Sit in a sitting squat! Sometimes called a Slav squat, or an Asian squat, or a resting squat, or various other names:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Alternatively, sitting in seiza (the traditional Japanese sitting position) is also excellent, but watch out! While it’s great once your body is accustomed to it, if you haven’t previously sat this way much, you may cut off your own circulation, hurt your knees, and (temporarily) lose feeling in your feet. So if you don’t already sit in seiza often, gradually work up the time period you spend sitting in seiza, so that your vasculature can adapt and improve, which honestly, is a very good thing for your legs and feet to have.
Breathe
Perhaps the absolute most “no-exercise exercise” there is. And yes, of course you are (hopefully) breathing all the time, but how you are breathing matters a lot:
The Inside Job Of Fixing Our Breathing: Exercises That Can Fix Sinus Problems (And More)
Clean
This doesn’t have to mean scrubbing floors like a sailor—even merely giving your house the Marie Kondo treatment counts, because while you’re distracted with all the objects, you’re going to be going back and forth, getting up and down, etc, clocking up lots of exercise that you barely even notice!
PS, check out: The Life-Changing Manga Of Tidying Up – by Marie Kondo
Garden
As with the above, it’s lots of activity that doesn’t necessarily feel like it (assuming you’re doing more pruning and weeding etc, and less digging ditches etc), and as a bonus, there are a stack of mental health benefits to being in a green natural environment and interacting with soil:
Read more: The Antidepressant In Your Garden
Climb
Depending on where you live, this might mean an indoor climbing wall, but give it a go! They have color-coded climbs from beginner to advanced, so don’t worry about being out of your depth.
And the best thing is, the beginner climbs will be as much a workout to a beginner as the advanced climbs will be to an advanced climber, because at the end of the day, you’re still clinging on for dear life, no matter whether it’s a sizeable handhold not far from the ground, or the impression of a fingernail crack in an overhang 100ft in the air.
Video games (but…)
Less in the category of Stardew Valley, and more in the category of Wii Fit.
So, dust off that old controller (or treat yourself to one if you didn’t have one already), and get doing a hundred sports and other physical activities in the comfort of your living room, with a surprisingly addictive gaming system!
Sex!
You probably don’t need instructions here, and if you do, well honestly, we’re running out of space today. But the answer to “does xyz count?” is “did it get your heart racing?” because if so, it counts
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: