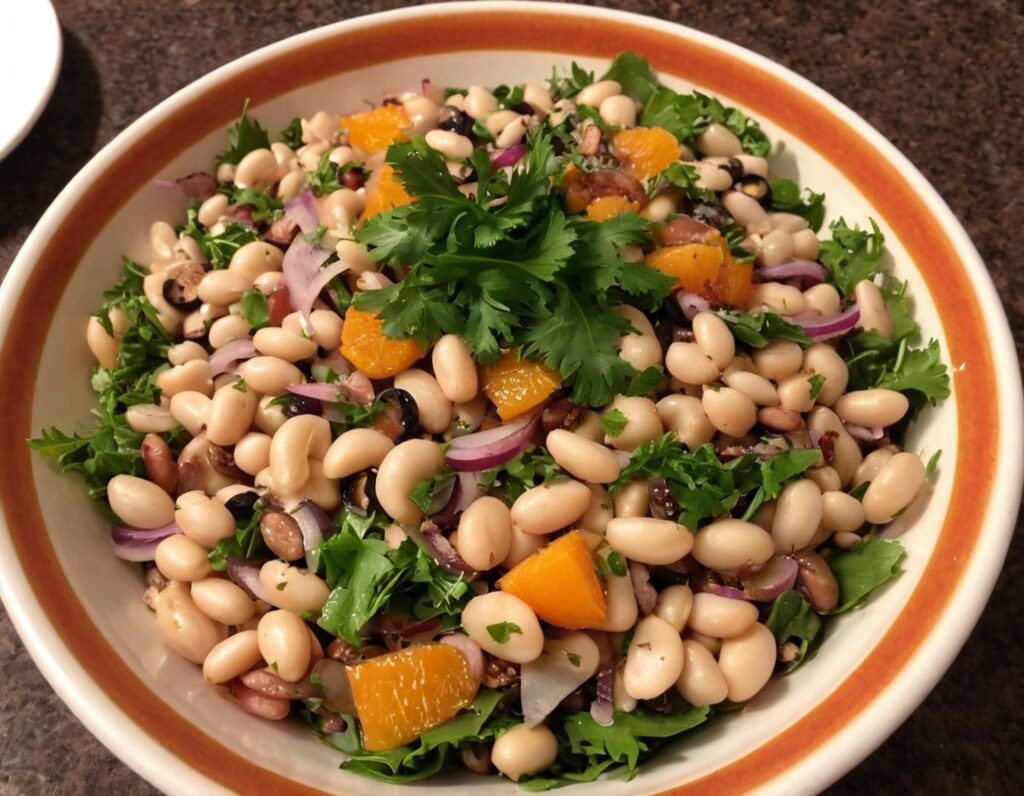
Which B Vitamins? It Makes A Difference
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Everyone knows “B vitamins are for energy!” and that is definitely a theme, but there’s a lot more to it than that, and in some cases, there are big mistakes that people make when it comes to supplementing their diet.
First, let’s do a quick overview of what each of the B vitamins do, by number, and putting names to them:
B1 (Thiamine)
- Function: helps convert carbohydrates into energy, supports nerve function
- Forms: thiamine hydrochloride, thiamine mononitrate, benfotiamine (fat-soluble form)
- Example foods: lentils, sunflower seeds
B2 (Riboflavin)
- Function: supports energy production, skin health, and eye function, turns your pee fluorescent yellow (the latter is really only if you consume exciting amounts of it; this will usually occur from supplementation, not from normal diet)
- Forms: riboflavin, riboflavin-5’-phosphate
- Example foods: almonds, mushrooms
B3 (Niacin)
- Function: aids metabolism, supports skin, nerves, and cholesterol levels
- Forms: niacin (nicotinic acid), niacinamide (nicotinamide), inositol hexanicotinate (flush-free niacin)
- Example foods: whole grains, peanuts (literally the best nut for this)
B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Function: essential for fatty acid metabolism and hormone production
- Forms: pantothenic acid, calcium pantothenate, panthenol (alcohol form!)
- Example foods: it’s in pretty much everything (hence the name); it’s almost impossible to be deficient in this vitamin unless you are literally starving
B6 (Pyridoxine)
- Function: needed for red blood cell production, supports brain function, as well as specifically being a part of neurotransmitter production (including dopamine and serotonin, despite them being made in different places—the brain and the gut, respectively),
- Forms: pyridoxine hydrochloride, pyridoxal-5’-phosphate (active form)
- Example foods: bananas, potatoes
B7 (Biotin)
- Function: helps with fatty acid synthesis, skin, hair, and nail health
- Forms: d-biotin, biotinylated compounds of various kinds
- Example foods: fava beans, walnuts
B9 (Folate/Folic Acid)
- Function: crucial for DNA synthesis, cell division, and fetal development
- Forms: folic acid, folinic acid, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF, active form)
- Example foods: chickpeas, spinach ← we only mentioned one leafy green here for fairness, but leafy greens in general are great sources of vitamin B9, hence the name, from the Latin “folium”, meaning leaf.
B12 (Cobalamin)
- Function: supports red blood cell formation, nerve function, and DNA synthesis
- Forms: cyanocobalamin, methylcobalamin (active), hydroxocobalamin (active), adenosylcobalamin (active)
- Example foods: nutritional yeast, nori
You may be wondering: what about vitamins B4, B8, B10, and B11? Those are now vacant spots, that once contained things that are no longer considered vitamins.
Three Critical Vitamin B Mistakes That May Be Sabotaging Your Health
Some mistakes that people make include:
Not supplementing when necessary
This occurs most often after midlife, especially in women, and the most common deficiencies are B1, B9, and B12.
See also: These Signs Often Mean These Nutrient Deficiencies (Do You Have Any?)
While it’s tempting to think “if I have a good balanced diet, I won’t need…” but the fact is sometimes our diet isn’t as nutrient dense as we hope—often through no fault of our own! But many modern farming methods prioritize yield over nutritional value, and that can result in plants and animals that do not have the nutritional qualities they “should”.
We wrote about this a while back, weighing up the “supplementation vs diet alone” dilemma:
Does Our Diet Need A Little Help? ← this also has a very useful chart of which vitamins people usually get too little or too much of. Note however that the statement of marginally excessive folate is slightly misleading, as the data pool contains men and women aged 18–65, while B9 is mostly needed more by women, and especially around childbirth or menopause, so B9 is actually a very common deficiency, but here it’s being balanced out lots of men getting too much (because every multivitamin has it).
Supplementing to excess
Most B vitamins have a very high maximum tolerable dose, because (with the exception of where we marked otherwise) they are water-soluble, which means that if you take more than you need, you’ll just pee it out later. Hence the famous fluorescence, for example.
However, the fat soluble form of vitamin B1 is harder to get in and harder to get out.
As for the others, problems usually only occur if you take enough to cause toxicity, faster than you pee it out. In other words, go easy on those Berocca drinks!
Nevertheless, there are other problems that can arise:
Vitamin B6 is essential—but too much can be toxic. Here’s what to know to stay safe ← tl;dr: there are issues with it causing peripheral neuropathy at doses over 10mg (the safe dose is disputed, so we’re mentioning the lowest safe dose here, but you can read about the others in the article)
Getting forms that don’t work so well
Those different forms we listed? They are not all created equal! For example:
- Folic acid is cheap; unfortunately, it’s not absorbed or used well
- Cyanocobalamin is cheap; unfortunately, it’s not absorbed or used well
Let us quote a recent book review of ours:
❝Rather, the most common forms of vitamins B9 and B12 provided in supplements are folic acid and cyanocobalamin, respectively, which as he demonstrates with extensive research to back up his claims, cannot be easily absorbed or used especially well.
About those vitamers: a vitamer is simply a form of a vitamin—most vitamins we need can arrive in a variety of forms. In the case of vitamins B9 and B12, he advocates for ditching vitamers folic acid and cyanocobalamin, cheap as they are, and springing for bioactive vitamers L-methylfolate, methylcobalamin, and adenosylcobalamin.
He also discusses (again, just as well-evidenced as the above things) why we might struggle to get enough from our diet after a certain age. For example, if trying to get these vitamins from meat, 50% of people over 50 cannot manufacture enough stomach acid to break down that protein to release the vitamins.
And as for methyl-B12 vitamers, you might expect you can get those from meat, and technically you can, but they don’t occur in all animals, just in one kind of animal. Specifically, the kind that has the largest brain-to-body ratio. However, eating the meat of this animal can result in protein folding errors in general and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease in particular, so the author does not recommend eating humans, however nutritionally convenient that would be.
All this means that supplementation after a certain age really can be a sensible way to do it—but do it wisely, and pick the right vitamers.❞
You can read that review in full here: Your Vitamins are Obsolete: The Vitamer Revolution – by Dr. Sheldon Zablow
Want to try those latter two?
We don’t sell them, but here for your convenience are example products on Amazon:
L-methylfolate (active form of vitamin B9)
Methylcobalamin, adenosylcobalamin, & hydroxocobalamin (active forms of vitamin B12)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The “Yes I Can” Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Sometimes, we are given to ask ourselves: “Can I produce a healthy and tasty salad out of what I have in?” and today we show how, with a well-stocked pantry, the answer is “yes I can”, regardless of what is (or isn’t) in the fridge.
You will need
- 1 can cannellini beans, drained
- 1 can sardines (if vegetarian/vegan, substitute ½ can chickpeas, drained)
- 1 can mandarin segments
- 1 handful pitted black olives, from a jar (or from a can, if you want to keep the “yes I can” theme going)
- ½ red onion, thinly sliced (this can be from frozen, defrosted—sliced/chopped onion is always a good thing to have in your freezer, by the way; your writer here always has 1–6 lbs of chopped onions in hers, divided into 1lb bags)
- 1 oz lemon juice
- 1 tbsp chopped parsley (this can be freeze-dried, but fresh is good if you have it)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tsp miso paste
- 1 tsp honey (omit if you don’t care for sweetness; substitute with agave nectar if you do like sweetness but don’t want to use honey specifically)
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine the onion and the lemon juice in a small bowl, massaging gently
2) Mix (in another bowl) the miso paste with the chili flakes, chia seeds, honey, olive oil, and the spare juice from the can of mandarin segments, and whisk it to make a dressing.
3) Add the cannellini beans, sardines (break them into bite-size chunks), mandarin segments, olives, and parsley, tossing them thoroughly (but gently) in the dressing.
4) Top with the sliced onion, discarding the excess lemon juice, and serve:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Three Daily Servings of Beans?
- We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
- Chia: The Tiniest Seeds With The Most Value
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Wandering Mind – by Dr. Michael Corballis
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our mind’s tendency to wander can be a disability, but could it also be a superpower? Dr. Corballis makes the case for such.
While many authors focus on, well, how to focus, Dr. Corballis argues in this book that our wandering imagination can be more effective at problem-solving and creative tasks, than a focused, blinkered mind.
The book’s a quick read (184 pages of quite light reading), and yet still quite dense with content. He takes us on a tour of the brain, theory of mind, the Default Mode Network (where a lot of the brain’s general ongoing organization occurs), learning, memory, forgetting, and creativity.
Furthermore, he cites (and explains) studies showing what kinds of “breaks” from mental work allow the wandering mind to do its thing at peak efficiency, and what kinds of breaks are counterproductive. Certainly this has practical applications for all of us!
Bottom line: if you’d like to be less frustrated by your mind’s tendency to wander, this is a fine book to show how to leverage that trait to your benefit.
Click here to check out The Wandering Mind, and set yours onto more useful tracks!
Share This Post
-
Clams vs Oysters – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing clams to oysters, we picked the clams.
Why?
Considering the macros first, clams have more than 2x the protein, while oysters have nearly 2x the fat, of which, a little over 5x the saturated fat. So, in all accounts, clam is the winner here.
In terms of vitamins, clams have more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, and C, while oysters are not higher in any vitamins. Another win for clams.
The category of minerals is more balanced; clams are higher in manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while oysters are higher in copper, iron, magnesium, and zinc. This makes for a 4:4 tie, though it’s worth noting that the margin of difference for zinc is very large, so that can be an argument for oysters.
Nevertheless, adding up the sections makes for a clear win for clams.
A quick aside on “are oysters an aphrodisiac?”:
That zinc content is probably largely responsible for oysters’ reputation as an aphrodisiac, and zinc is important in the synthesis of both estrogen and testosterone. However, as the synthesis is not instant, and those sex hormones rise most in the morning (around 8am to 9am), to enjoy aphrodisiac benefits it’d be more sensible, on a biochemical level, to eat oysters one day, and then have morning sex the next day when those hormones are peaking. That said, while testosterone is the main driver of male libido, progesterone is usually more relevant for women’s, and unlike estrogen, progesterone usually peaks around 10pm to 2am, and is uninfluenced by having just eaten oysters.
So, in what way, if any, could oysters be responsible for libido in women? Well, the zinc is still important in energy metabolism, so that’s a factor, and also, we might hypothesize that oysters’ high saturated fat and cholesterol content may increase blood pressure which, while not fabulous for the health in general, may be considered desirable in the bedroom since the clitoris is anatomically analogous to the penis, and—while estrogen vs testosterone makes differences to the nervous system down there that are beyond the scope of today’s article—also enjoys localized increased blood pressure (and thus, a flushing response and resultant engorgement) during arousal.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Does Eating Shellfish Really Contribute To Gout? ← short answer is: it can if consumed frequently over a long period of time, but that risk factor is greatly overstated, compared to some other risk factors
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Immunostimulant Superfood –
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book is not: a “detox cleanse” book of the kind that claims you can flush out the autism if you just eat enough celery.
What it rather is: an overview brain chemistry, gut microbiota, and the very many other bodily systems that interact with these “two brains”.
She also does some mythbusting of popular misconceptions (for example with regard to tryptophan), and explains with good science just what exactly such substances as gluten and casein can and can’t do.
The format is less of a textbook and more a multipart (i.e., chapter-by-chapter) lecture, in pop-science style though, making it very readable. There are a lot of practical advices too, and options to look up foods by effect, and what to eat for/against assorted mental states.
Bottom line: anyone who eats food is, effectively, drugging themselves in one fashion or another—so you might as well make a conscious choice about how to do so.
Click here to check out This Is Your Brain On Food, and choose what kind of day you have!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Art of Being Unflappable (Tricks For Daily Life)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Art of Being Unflappable
From Stoicism to CBT, thinkers through the ages have sought the unflappable life.
Today, in true 10almonds fashion, we’re going to distil it down to some concentrated essentials that we can all apply in our daily lives:
Most Common/Impactful Cognitive Distortions To Catch (And Thus Avoid)
These are like the rhetorical fallacies with which you might be familiar (ad hominem, no true Scotsman, begging the question, tu quoque, straw man, etc), but are about what goes on between your own ears, pertaining to your own life.
If we learn about them and how to recognize them, however, we can catch them before they sabotage us, and remain “unflappable” in situations that could otherwise turn disastrous.
Let’s take a look at a few:
Catastrophizing / Crystal Ball
- Distortion: not just blowing something out of proportion, but taking an idea and running with it to its worst possible conclusion. For example, we cook one meal that’s a “miss” and conclude we are a terrible cook, and in fact for this reason a terrible housewife/mother/friend/etc, and for this reason everyone will probably abandon us and would be right to do so
- Reality: by tomorrow, you’ll probably be the only one who even remembers it happened
Mind Reading
- Distortion: attributing motivations that may or may not be there, and making assumptions about other people’s thoughts/feelings. An example is the joke about two partners’ diary entries; one is long and full of feelings about how the other is surely dissatisfied in their marriage, has been acting “off” with them all day, is closed and distant, probably wants to divorce, may be having an affair and is wondering which way to jump, and/or is just wondering how to break the news—the other partner’s diary entry is short, and reads “motorcycle won’t start; can’t figure out why”
- Reality: sometimes, asking open questions is better than guessing, and much better than assuming!
All-or-Nothing Thinking / Disqualifying the Positive / Magnifying the Negative
- Distortion: having a negative bias that not only finds a cloud in every silver lining, but stretches it out so that it’s all that we can see. In a relationship, this might mean that one argument makes us feel like our relationship is nothing but strife. In life in general, it may lead us to feel like we are “naturally unlucky”.
- Reality: those negative things wouldn’t even register as negative to us if there weren’t a commensurate positive we’ve experienced to hold them in contrast against. So, find and remember that positive too.
For brevity, we put a spotlight on (and in some cases, clumped together) the ones we think have the most bang-for-buck to know about, but there are many more.
So for the curious, here’s some further reading:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Prostate Health: What You Should Know
We’re aware that very many of our readers are women, who do not have a prostate.
However, dear reader: if you do have one, and/or love someone who has one, this is a good thing to know about.
The prostate gland is a (hopefully) walnut-sized gland (it actually looks a bit like a walnut too), that usually sits just under the bladder.
See also: How to Locate Your Prostate*
*The scale is not great in these diagrams, but they’ll get the job done. Besides, everyone is different on the inside, anyway. Not in a “special unique snowflake” way, but in a “you’d be surprised how much people’s insides move around” way.
Fun fact: did you ever feel like your intestines are squirming? That’s because they are.
You can’t feel it most of the time due to the paucity of that kind of nervous sensation down there, but the peristaltic motion that they use to move food along them on the inside, also causes them push against the rest of your guts, on the outside of them. This is the exact same way that many snakes move about.
If someone has to perform an operation in that region, sometimes it will be necessary to hang the intestines on a special rack, to keep them in one place for the surgery.
What can go wrong?
There are two very common things that can go wrong with the prostate:
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH), otherwise known as an enlarged prostate
- Prostate cancer
For most men, the prostate gland continues to grow with age, which is how the former comes about so frequently.
For everyone, due to the nature of the mathematics involved in cellular mutation and replication, we will eventually get cancer if something else doesn’t kill us first.
- Prostate cancer affects 12% of men overall, and 60% of men aged 60+, with that percentage climbing each year thereafter.
- Prostate cancer can look like BPH in the early stages (and/or, an enlarged prostate can turn cancerous) so it’s important to not shrug off the symptoms of BPH.
How can BPH be avoided/managed?
There are prescription medications that can help reduce the size of the prostate, including testosterone blockers (such as spironolactone and bicalutamide) and 5α-reductase inhibitors, such as finasteride. Each have their pros and cons:
- Testosterone-blockers are the heavy-hitters, and work very well… but have more potential adverse side effects (your body is used to running on testosterone, after all)
- 5α-reductase inhibitors aren’t as powerful, but they block the conversion of free testosterone to dihydrogen testosterone (DHT), and it’s primarily DHT that causes the problems. By blocking the conversion of T to DHT, you may actually end up with higher serum testosterone levels, but fewer ill-effects. Exact results will vary depending on your personal physiology, and what else you are taking, though.
There are also supplements that can help, including saw palmetto and pumpkin seed oil. Here’s a good paper that covers both:
We have recommended saw palmetto before for a variety of uses, including against BPH:
Too much or too little testosterone? This one supplement may fix that
You might want to avoid certain medications that can worsen BPH symptoms (but not actually the size of the prostate itself). They include:
- Antihistamines
- Decongestants
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (most modern antidepressants aren’t this kind; ask your pharmacist/doctor if unsure)
You also might want to reduce/skip:
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
In all the above cases, it’s because of how they affect the bladder, not the prostate, but given their neighborliness, each thing affects the other.
What if it’s cancer? How do I know and what do I do?
The creator of the Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) test has since decried it as “a profit-driven health disaster” that is “no better than a coin toss”, but it remains the first go-to of many medical services.
However, there’s a newer, much more accurate test, called the Prostate Screening Episwitch (PSE) test, which is 94% accurate, so you might consider asking your healthcare provider whether that’s an option:
The new prostate cancer blood test with 94 per cent accuracy
As for where to go from there, we’re out of space for today, but we previously reviewed a very good book about this, Dr. Patrick Walsh’s Guide to Surviving Prostate Cancer, and we highly recommend it—it could easily be a literal lifesaver.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: