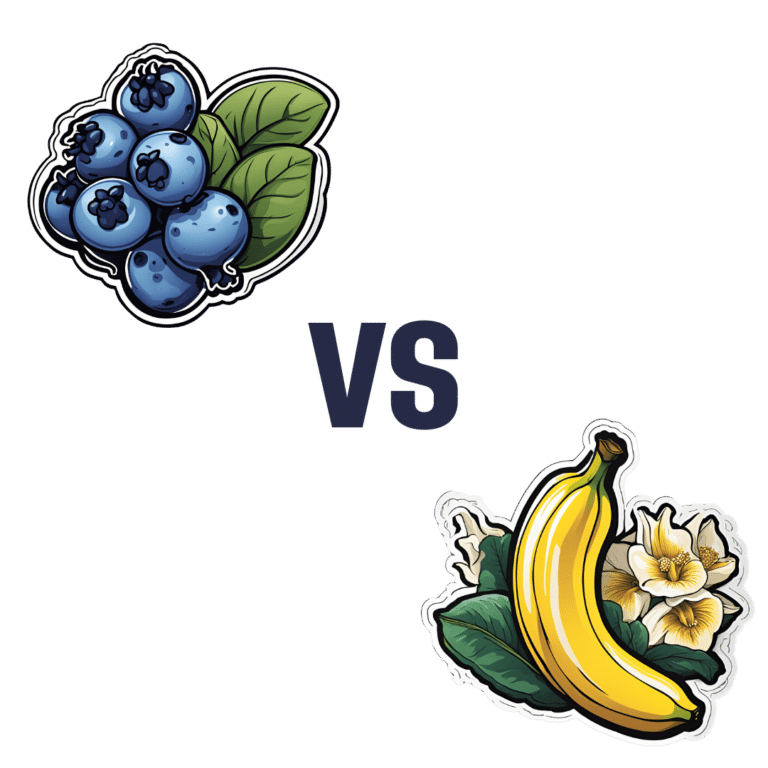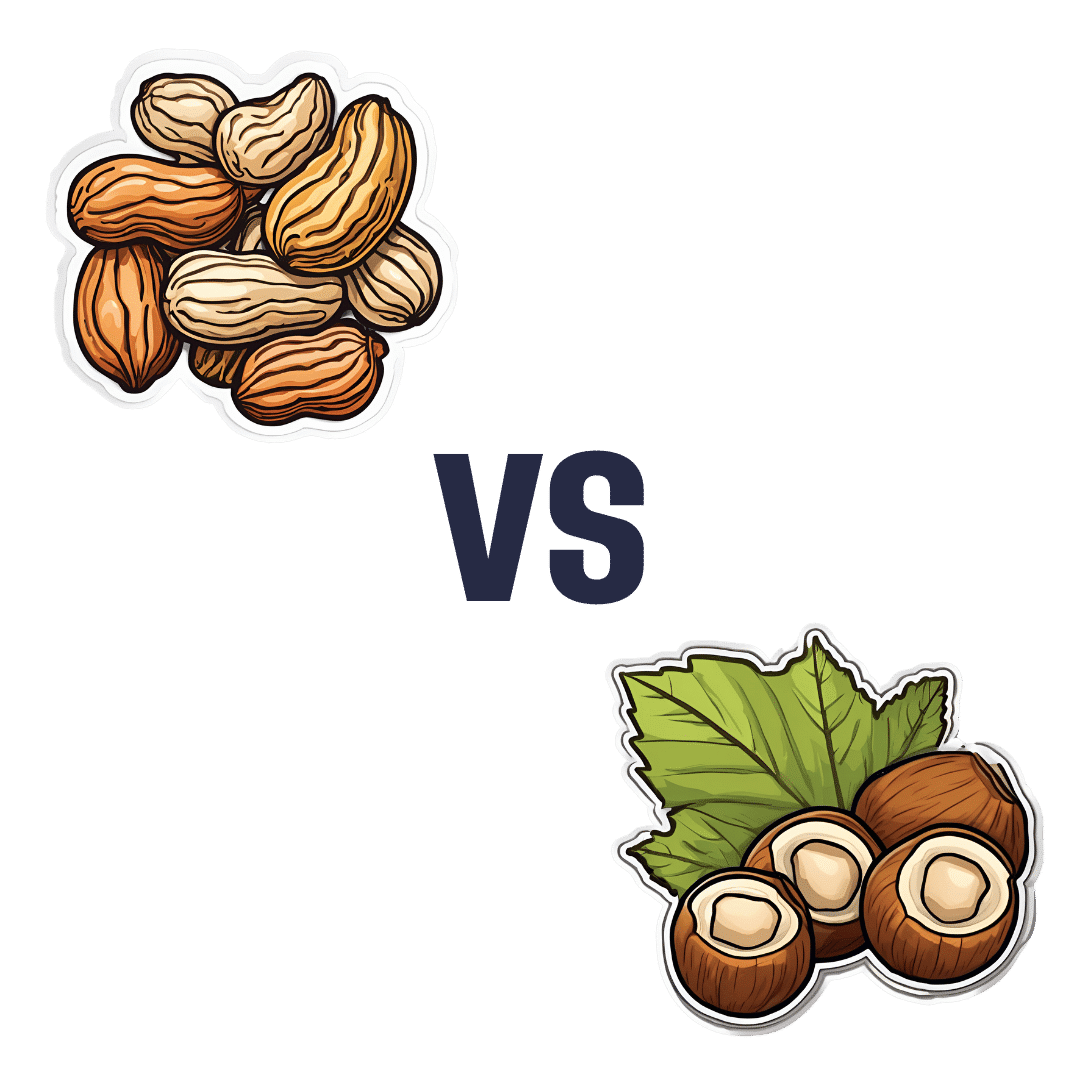
Peanuts vs Hazelnuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peanuts to hazelnuts, we picked the hazelnuts.
Why?
It was close!
In terms of macros, peanuts have more protein while hazelnuts have more fiber and fat; the fat is healthy (mostly monounsaturated, some polyunsaturated, and very little saturated; less saturated fat than peanuts), so all in all, we’ll call this category a modest, subjective win for hazelnuts (since it depends on what we consider most important).
In the category of vitamins, peanuts have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, B9, and choline, while hazelnuts have more of vitamins A, B1, B6, C, E, and K, making this one a marginal win for hazelnuts.
When it comes to minerals, peanuts have more magnesium, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while hazelnuts have more calcium, copper, iron, and manganese, so we’re calling it a tie on minerals.
Adding up the sections makes for a very close win for hazelnuts, but by all means enjoy both (unless you are allergic, of course)!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Burn – by Dr. Herman Pontzer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all have reasons to want to focus on our metabolism. Speed it up to burn more fat; slow it down to live longer. Tweak it for more energy in the day. But what actually is it, and how does it work?
Dr. Herman Pontzer presents a very useful overview of not just what our metabolism is and how it works, but also why.
The style of the book is casual, but doesn’t skimp on the science. Whether we are getting campfire stories of Hadza hunter-gatherers, or an explanation of the use of hydrogen isotopes in metabolic research, Dr. Pontzer keeps things easy-reading.
One of the main premises of the book is that our caloric expenditure is not easy to change—if we exercise more, our bodies will cut back somewhere else. After all, the body uses energy for a lot more than just moving. With this in mind, Dr. Pontzer makes the science-based case for focusing more on diet than exercise if weight management is our goal.
In short, if you’d like your metabolism to be a lot less mysterious, this book can help render a lot of science a lot more comprehensible!
Share This Post
-
How to Permanently Loosen a Tight Psoas
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Is Your Psoas?
Your psoas is a deep muscle in your lower back and hip area that connects your spine to your thigh bone. It helps you bend your hips and spine, making it a hip flexor.
In today’s video, Your Wellness Nerd (the YouTube channel behind the video below) has revealed some great tips on loosening said tight hip flexors!
How to loosen them
First off, the big reveal…your tight psoas is likely stemming from an overlooked cause: your lower back! The video kicks off with a simple technique to loosen up that stiff area in your lower back. All you need is a foam roller.
But, before diving into the exercises, it’s essential to gauge your current flexibility. A basic hip flexor stretch serves as a pre-test.
Note: the goal here isn’t to stretch, but rather to feel how tight you are.
After testing, it’s time to roll…literally. Working through the lower back, use your roller or tennis ball to any find stiff spots and loosen them out; those spots are likely increasing the tension on your psoas.
After some rolling, retest with the hip flexor stretch. Chances are, you’ll feel more mobility and less tightness right away.
Note: this video focuses on chronic psoas issues. If you have sore psoas from a muscular workout, you may want to read our piece on speeding up muscle recovery.
Is That All?
But wait, there’s more! The video also covers two more exercises specifically targeting the psoas. This one’s hard to describe, so we recommend watching the video. However, to provide an overview, you’re doing the “classic couch stretch”, but with a few alterations.
Next, the tennis ball technique zeroes in on specific tight spots in the psoas. By lying on the ball and adjusting its position around the hip area, you can likely release some deeply held tension.
Additionally, some of our readers advocate for acupuncture for psoas relief – we’ve done an acupuncture myth-busting article here for reference.
Other Sources
If you’re looking for some more in-depth guides on stretching your psoas, and your body in general, we’ve made a range of 1-minute summaries of books that specifically target stretching:
- 11 Minutes to Pain-Free Hips (perfect for psoas muscles)
- Stretching Scientifically
- Stretching & Mobility
- Stretching to Stay Young
The final takeaway? If you’re constantly battling tight psoas muscles despite trying different exercises and stretches, it might be time to look at your lower back and your daily habits. This video isn’t just a band-aid fix; it’s about addressing the root cause for long-term relief:
How did you find that video? If you’ve discovered any great videos yourself that you’d like to share with fellow 10almonds readers, then please do email them to us!
Share This Post
-
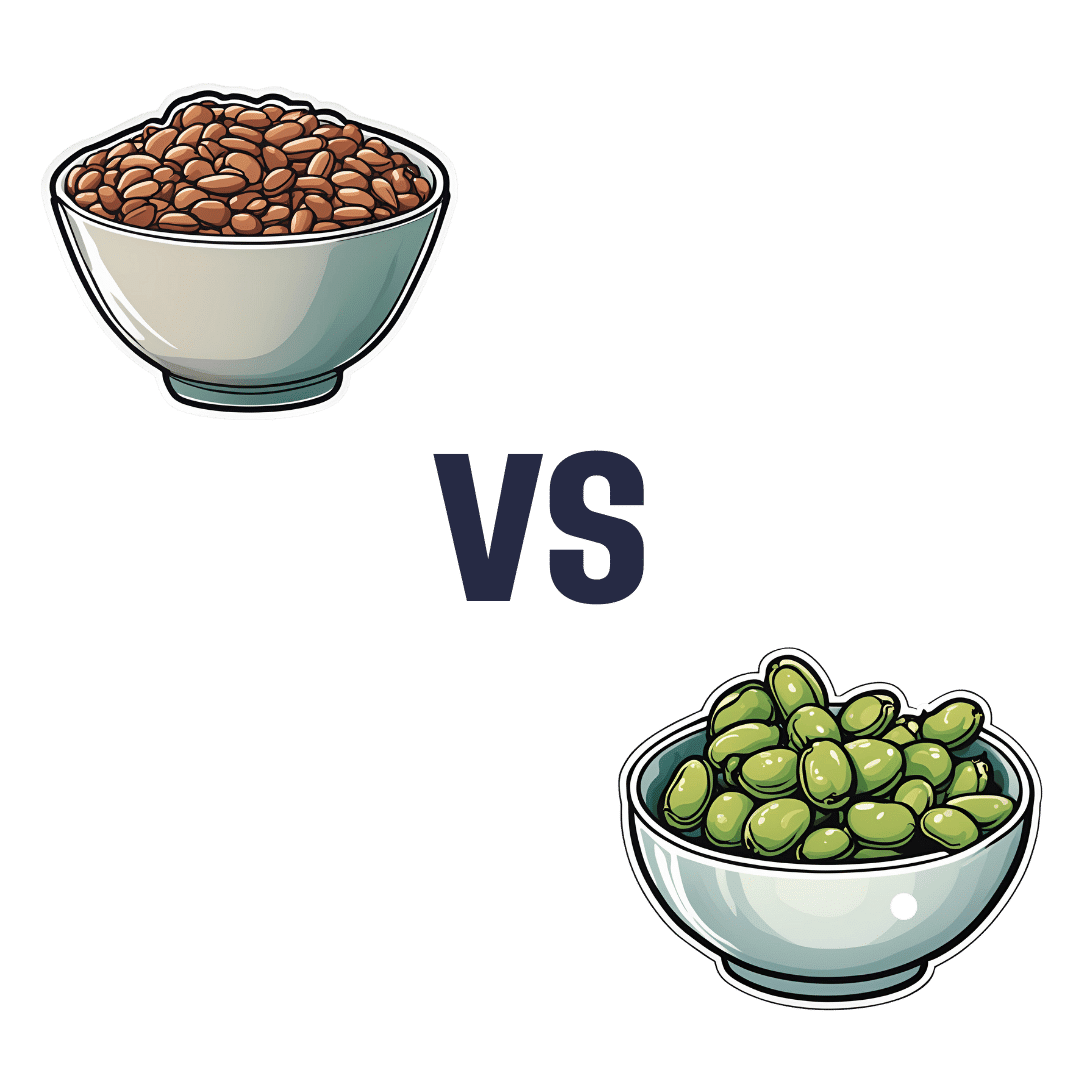
Pinto Beans vs Fava Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pinto beans to fava beans, we picked the pinto beans.
Why?
It wasn’t close!
In terms of macros, pinto beans have more protein and carbs, and much more fiber, resulting in a much lower glycemic index. We mention this, because while often the GI of two similar foods is similar, in this case pinto beans have a GI of 39 (low), while fava beans have a GI of 79 (high). In other words, not at all close, and pinto beans are the clear winner.
When it comes to vitamins, pinto beans have more of vitamins B1, B5, B6, B7, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while fava beans have more of vitamins B2 and B3. Once again, not close, and that’s before we take into account the margins of difference for those vitamins; the margins of difference are much greater on the pinto beans’ side of the scale, for example pinto beans having 47x more vitamin E, while fava beans have only 43% more vitamin B2. So, orders of magnitude less. A clear win for pinto beans in all respects.
In the category of minerals, pinto beans have more calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while fava beans have more copper and zinc. This time, the margins of difference were quite moderate across the board, and/but pinto beans win on clear strength of numbers.
All in all, three clear wins for pinto beans add up to one big clear win for pinto beans.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Healthy Butternut Macaroni Cheese
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A comfort food classic, healthy and plant-based, without skimping on the comfort.
You will need
- ½ butternut squash, peeled and cut into small pieces (if buying ready-chopped, this should be about 1 lb)
- 1 onion, chopped
- ¼ bulb garlic
- 2 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 12 oz (or thereabouts) wholegrain macaroni, or similar pasta shape (even penne works fine—which is good, as it’s often easier to buy wholegrain penne than wholegrain macaroni) (substitute with a gluten-free pasta such as buckwheat pasta, if avoiding gluten)
- 6 oz (or thereabouts) cashews, soaked in hot water for at least 15 minutes (but longer is better)
- ½ cup milk (your preference what kind; we recommend hazelnut for its mellow nutty flavor)
- 3 tbsp nutritional yeast
- Juice of ½ lemon
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- ½ tsp MSG, or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: smoked paprika, to serve
Note: if you are allergic to nuts, please accept our apologies that there’s no substitution available in this one. Simply put, removing the cashews would mean changing most of the rest of the recipe to compensate, so there’s no easy “or substitute with…” that we can mention. We’ll have to find/develop a good healthy plant-based no-nuts recipe for you at a later date.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Combine the butternut squash, onion, and garlic with the olive oil, in a large roasting tin, tossing thoroughly to ensure an even coat of oil. Roast them for about 25 minutes until soft.
3) Cook the macaroni while you wait (this should take about 10 minutes or so in salted water), drain, and rinse thoroughly in cold water, before setting aside. This cooling increases the pasta’s resistant starch content (that’s good, for your gut and for your blood sugars, and thus also for your heart and brain), and it will maintain this benefit even when we reheat it later.
4) Drain the cashews, and tip them into a high-speed blender with the milk, and process until smooth. Add the roasted vegetables and the remaining ingredients apart from the pasta, and continue to process until again smooth. You can add a little more milk if you need to, but go easy with it.
5) Heat the sauce (that you just made in the food processor) gently in a saucepan, and refresh the pasta by pouring a kettle of boiling water through it in a colander.
6) Optional: combine the pasta and sauce in an ovenproof dish or cast iron pan, and give it a few minutes under the hottest grill (or browning iron, if you have such) your oven can muster. Alternatively, use a culinary blowtorch, if you have one.
7) Serve; and if you didn’t do the optional step above, this means combining the pasta and sauce. You can also dust the top with some extra seasonings if you like. Smoked paprika works well for this.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Butternut Squash vs Pumpkin – Which is Healthier?
- Cashew Nuts vs Coconut – Which is Healthier?
- The Many Health Benefits Of Garlic
- Black Pepper’s Impressive Anti-Cancer Arsenal (And More)
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fruit Is Healthy; Juice Isn’t (Here’s Why)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Biochemist and “Glucose Goddess” Jessie Inchauspé wants us to understand the difference:
Stripped!
A glass of orange juice contains 22 grams of sugar (about six sugar cubes), nearly as much as a can of soda (27 grams).
Orange juice is widely perceived as healthy due to vitamin content—but if you add vitamins to soda, it won’t make it healthy, because the main health effect is still the sugar, leading to glucose spikes and many resultant health risks. The positive image of fruit juice is mainly from industry marketing.
In reality, Inchauspé advises, fruit juice should be treated like a dessert—consumed for pleasure, not health benefits.
But why, then, is fruit healthy if fruit juice is unhealthy? Isn’t the sugar there too?
Whole fruit contains plenty of fiber, which slows sugar absorption and prevents glucose spikes. Juicing strips it of its fiber, leaving water and sugar.
The American Heart Association suggests a sugar limit: 25g/day for women, 36g/day for men. One glass of orange juice nearly meets the daily limit for women. If that’s how you want to “spend” your daily sugar allowance, go for it, but do so consciously, by choice, knowing that the allowance is now “spent”.
In contrast, if you eat whole fruit, that basically “doesn’t count” for sugar purposes. The sugar is there, but the fiber more than offsets it, making whole fruit very good for blood sugars.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Best Salt for Neti Pots?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❓ Q&A With 10almonds Subscribers!
Q: What kind of salt is best for neti pots?
A: Non-iodised salt is usually recommended, but really, any human-safe salt is fine. By this we mean for example:
- Sodium chloride (like most kitchen salts),
- Potassium chloride (as found in “reduced sodium” kitchen salts), or
- Magnesium sulfate (also known as epsom salts).
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: