Reduce Your Stroke Risk
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
❝Each year in the U.S., over half a million people have a first stroke; however, up to 80% of strokes may be preventable.❞
~ American Stroke Association
Source: New guideline: Preventing a first stroke may be possible with screening, lifestyle changes
So, what should we do?
Some of the risk factors are unavoidable or not usefully avoidable, like genetic predispositions and old age, respectively (i.e. it is possible to avoid old age—by dying young, which is not a good approach).
Some of the risk factors are avoidable. Let’s look at the most obvious first:
You cannot drink to your good health
While overall, the World Health Organization has declared that “the only safe amount of alcohol is zero”, when it comes to stroke risk specifically, it seems that low consumption is not associated with stroke, while moderate to high consumption is associated with a commensurately increased risk of stroke:
Alcohol Intake as a Risk Factor for Acute Stroke
Note: there are some studies out there that say that a low to moderate consumption may decrease the risk compared to zero consumption. However, any such study that this writer has seen has had the methodological flaw of not addressing why those who do not drink alcohol, do not drink it. In many cases, someone who drinks no alcohol at all does so because either a) it would cause problems with some medication(s) they are taking, or b) they used to drink heavily, and quit. In either case, their reasons for not drinking alcohol may themselves be reasons for an increased stroke risk—not the lack of alcohol itself.
Smoke now = stroke later
This one is straightforward; smoking is bad for pretty much everything, and that includes stroke risk, as it’s bad for your heart and brain both, increasing stroke risk by 200–400%:
Smoking and stroke: the more you smoke the more you stroke
So, the advice here of course is: don’t smoke
Diet matters
The American Stroke Association’s guidelines recommend, just for a change, the Mediterranean Diet. This does not mean just whatever is eaten in the Mediterranean region though, and there are specifically foods that are included and excluded, and the ratios matter, so here’s a run-down of what the Mediterranean Diet does and doesn’t include:
The Mediterranean Diet: What Is It Good For? ← what isn’t it good for?!
You can outrun stroke
Or out-walk it; that’s fine too. Most important here is frequency of exercise, more than intensity. So basically, getting those 150 minutes moderate exercise per week as a minimum.
See also: The Doctor Who Wants Us To Exercise Less & Move More
Which is good, because it means we can get a lot of exercise in that doesn’t feel like “having to do” exercise, for example:
Do You Love To Go To The Gym? No? Enjoy These “No-Exercise Exercises”!
Your brain needs downtime too
Your brain (and your heart) both need you to get good regular sleep:
Sleep Disorders in Stroke: An Update on Management
We sometimes say that “what’s good for your heart is good for your brain” (because the heart feeds the brain, and also ultimately clears away detritus), and that’s true here too, so we might also want to prioritize sleep regularity over other factors, even over duration:
How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration ← this is about adverse cardiovascular events, including ischemic stroke
Keep on top of your blood pressure
High blood pressure is a very modifiable risk factor for stroke. Taking care of the above things will generally take care of this, especially the DASH variation of the Mediterranean diet:
Hypertension: Factors Far More Relevant Than Salt
However, it’s still important to actually check your blood pressure regularly, because sometimes an unexpected extra factor can pop up for no obvious reason. As a bonus, you can do this improved version of the usual blood pressure test, still using just a blood pressure cuff:
Try This At Home: ABI Test For Clogged Arteries
Consider GLP-1 receptor agonists (or…)
GLP-1 receptor agonists (like Ozempic et al.) seem to have cardioprotective and neuroprotective (thus: anti-stroke) activity independent of their weight loss benefits:
Of course, GLP-1 RAs aren’t everyone’s cup of tea, and they do have their downsides (including availability, cost, and the fact benefits reverse themselves if you stop taking them), so if you want a similar effect from a natural approach, there are some foods that work on the body’s incretin responses in the same way as GLP-1 RAs do:
5 Foods That Naturally Mimic The “Ozempic Effect”
Better to know sooner rather than too late
Rather than waiting until one half of our face is drooping to know that there was a stroke risk, here are things to watch out for to know about it before it’s too late:
6 Signs Of Stroke (One Month In Advance)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The 7 Known Risk Factors For Dementia
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A recent UK-based survey found that…
- while nearly half of adults say dementia is the disease they fear most,
- only a third of those thought you could do anything to avoid it, and
- just 1% could name the 7 known risk factors.
Quick test
Can you name the 7 known risk factors?
Please take a moment to actually try (this kind of mental stimulation is good in any case), and count them out on your fingers (or write them down), and then…
Answer (no peeking if you haven’t listed them yet)
The 7 known risk factors are:
*drumroll please*
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Depression
- Lack of mental stimulation
- Lack of physical activity
How many did you get? If you got them all, well done. If not, then well, now you know, so that’s good.
Did you come here from our “Future-Proof Your Brain” article? If so, you can get back to it here ← and if you didn’t, you should check it out anyway; it’s worth it😉
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Hope Not Nope – by Dr. Dillon Caswell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The author a Doctor of Physical Therapy, writes from both professional expertise and personal experience, when it comes to the treatment of long term injury / disability / chronic illness.
His position here is that while suffering is unavoidable, we don’t have to suffer as much or as long as many might tell us. We can do things to crawl and claw our way to a better position, and we do not have to settle for any outcome we don’t want. That doesn’t mean there’s always a miracle cure—we don’t get to decide that—but we do get to decide whether we keep trying.
Dr. Caswell’s advice is based mostly in psychology—a lot of it in sports psychology, which is no surprise given his long history as an athlete as well as his medical career.
The style is very easy-reading, and a combination of explanation, illustrative (often funny) anecdotes, and a backbone of actual research to keep everything within the realms of science rather than mere wishful thinking—he strikes a good balance.
Bottom line: if your current health outlook is more of an uphill marathon, then this book can give you the tools to carry yourself through the healthcare system that’s been made for numbers, not people.
Share This Post
-
Banana Bread vs Bagel – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing banana bread to bagel, we picked the bagel.
Why?
Unlike most of the items we compare in this section, which are often “single ingredient” or at least highly standardized, today’s choices are rather dependent on recipe. Certainly, your banana bread and your bagels may not be the same as your neighbor’s. Nevertheless, to compare averages, we’ve gone with the FDA’s Food Central Database for reference values, using the most default average recipes available. Likely you could make either or both of them a little healthier, but as it is, this is how we’ve gone about making it a fair comparison. With that in mind…
In terms of macros, bagels have more than 2x the protein and about 4x the fiber, while banana bread has slightly higher carbs and about 7x more fat. You may be wondering: are the fats healthy? And the answer is, it could be better, could be worse. The FDA recipe went with margarine rather than butter, which lowered the saturated fat to being only ¼ of the total fat (it would have been higher, had they used butter) whereas bagels have no saturated fat at all—which characteristic is quite integral to bagels, unless you make egg bagels, which is rather a different beast. All in all, the macros category is a clear win for bagels, especially when we consider the carb to fiber ratio.
In the category of vitamins, bagels have on average more vitamin B1, B3, B5, and B9, while banana bread has on average more of vitamins A and C. A modest win for bagels.
When it comes to minerals, bagels are the more nutrient dense with more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while banana bread is not higher in any minerals. An obvious and easy win for bagels.
Closing thoughts: while the micronutrient profile quite possibly differs wildly from one baker to another, something that will probably stay more or less the same regardless is the carb to fiber ratio, and protein to fat. As a result, we’d weight the macros category as the more universally relevant. Bagels won in all categories today, as it happened, but it’s fairly safe to say that, on average, a baker who makes bagels and banana bread with the same levels of conscientiousness for health (or lack thereof) will tend to make bagels that are healthier than banana bread, based on the carb to fiber ratio, and the protein to fat ratio.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Wholewheat Bread vs Seeded White – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Savor: Mindful Eating, Mindful Life – by Thich Nhat Hanh and Dr. Lilian Cheung
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve talked about mindful eating before at 10almonds, so here’s a book about it. You may wonder how much there is to say!
As it happens, there’s quite a bit. The authors, a Buddhist monk (Hanh) and a Harvard nutritionist (Dr. Cheung) explore the role of mindful eating in our life.
There is an expectation that we the reader want to lose weight. If we don’t, those parts of the book will be a “miss” for us, but still contain plenty of other value.
Most of the same advices can be applied equally to other aspects of health, in any case. A lot of that comes from the book’s Buddhist principles, including the notion that:
- We are experiencing suffering
- Suffering has a cause
- What has a cause can have an end
- The way to this end is mindfulness
As such, the process itself is also mindfulness all the way through:
- To be mindful of our suffering (and not let it become background noise to be ignored)
- To be mindful of the cause of our suffering (rather than dismissing it as just how things are)
- To be mindful of how to address that, and thus end the suffering (rather than despairing in inaction)
- To engage mindfully in the process of doing so (and thus not fall into the trap of thinking “job done”)
And, as for Dr. Cheung? She also has input throughout, with practical advice about the more scientific side of rethinking one’s diet.
Bottom line: this is an atypical book, and/but perhaps an important one. Certainly, at the very least it may be one to try if more conventional approaches have failed!
Click here to check out “Savor” on Amazon today, and get mindful!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Best Kind Of Fiber For Overall Health?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Fiber Of Good Health
We’ve written before about how most people in industrialized nations in general, and N. America in particular, do not get nearly enough fiber:
Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
Fiber’s important for many aspects of health, not least of all the heart:
What Matters Most For Your Heart? Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
As well, of course, as being critical for gut health:
Gut Health 101: Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
But is all fiber “prebiotic fiber”, and/or are some better than others?
Beta-glucan
A recent study (it’s a mouse study, but promising in its applicability for humans) examined the health impacts of 5 different fiber types:
- pectin
- β-glucan
- wheat dextrin
- resistant starch
- cellulose (control)
As for health metrics, they measured:
- body weight
- adiposity
- indirect calorimetry
- glucose tolerance
- gut microbiota
- metabolites thereof
What they found was…
❝Only β-glucan supplementation during HFD-feeding decreased adiposity and body weight gain and improved glucose tolerance compared with HFD-cellulose, whereas all other fibers had no effect. This was associated with increased energy expenditure and locomotor activity in mice compared with HFD-cellulose.
All fibers supplemented into an HFD uniquely shifted the intestinal microbiota and cecal short-chain fatty acids; however, only β-glucan supplementation increased cecal butyrate concentrations. Lastly, all fibers altered the small-intestinal microbiota and portal bile acid composition. ❞
If you’d like to read more, the study itself is here:
If you’d like to read less, the short version is that they are all good but β-glucan scored best in several metrics.
It also acts indirectly as a GLP-1 agonist, by the way:
The right fiber may help you lose weight
You may be wondering: what is β-glucan found in?
It’s found in many (non-animal product) foods, but oats, barley, mushrooms, and yeasts are all good sources.
Is it available as a supplement?
More or less; there are supplements that contain it generously, here’s an example product on Amazon, a cordyceps extract, of which >30% is β-glucan.
As an aside, cordyceps itself has many other healthful properties too:
Cordyceps: Friend Or Foe? ← the answer is, it depends! If you’re human, it’s a friend.
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
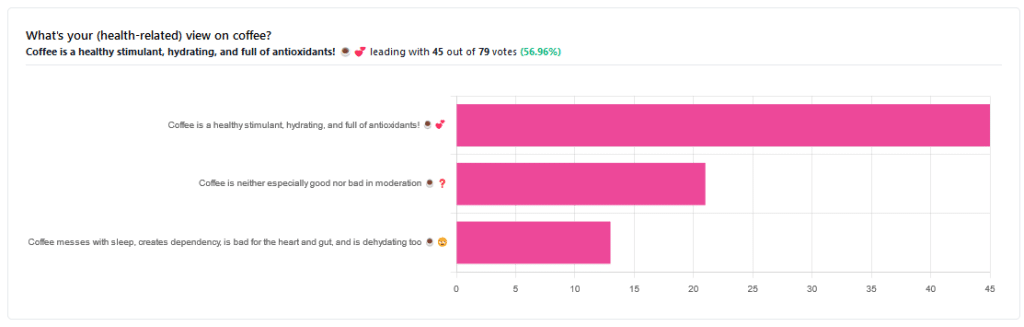
Yesterday, we asked you for your (health-related) views on coffee. The results were clear: if we assume the responses to be representative, we’re a large group of coffee-enthusiasts!
One subscriber who voted for “Coffee is a healthy stimulant, hydrating, and full of antioxidants” wrote:
❝Not so sure about how hydrating it is! Like most food and drink, moderation is key. More than 2 or 3 cups make me buzz! Just too much.❞
And that fine point brings us to our first potential myth:
Coffee is dehydrating: True or False?
False. With caveats…
Coffee, in whatever form we drink it, is wet. This may not come as a startling revelation, but it’s an important starting point. It’s mostly water. Water itself is not dehydrating.
Caffeine, however, is a diuretic—meaning you will tend to pee more. It achieves its diuretic effect by increasing blood flow to your kidneys, which prompts them to release more water through urination.
See: Effect of caffeine on bladder function in patients with overactive bladder symptoms
How much caffeine is required to have a diuretic effect? About 4.5 mg/kg.
What this means in practical terms: if you weigh 70kg (a little over 150lbs), 4.5×70 gives us 315.
315mg is about how much caffeine might be in six shots of espresso. We say “might” because while dosage calculations are an exact science, the actual amount in your shot of espresso can vary depending on many factors, including:
- The kind of coffee bean
- How and when it was roasted
- How and when it was ground
- The water used to make the espresso
- The pressure and temperature of the water
…and that’s all without looking at the most obvious factor: “is the coffee decaffeinated?”
If it doesn’t contain caffeine, it’s not diuretic. Decaffeinated coffee does usually contain tiny amounts of caffeine still, but with nearer 3mg than 300mg, it’s orders of magnitude away from having a diuretic effect.
If it does contain caffeine, then the next question becomes: “and how much water?”
For example, an Americano (espresso, with hot water added to make it a long drink) will be more hydrating than a ristretto (espresso, stopped halfway through pushing, meaning it is shorter and stronger than a normal espresso).
A subscriber who voted for “Coffee messes with sleep, creates dependency, is bad for the heart and gut, and is dehydrating too” wrote:
❝Coffee causes tachycardia for me so staying away is best. People with colon cancer are urged to stay away from coffee completely.❞
These are great points! It brings us to our next potential myth:
Coffee is bad for the heart: True or False?
False… For most people.
Some people, like our subscriber above, have an adverse reaction to caffeine, such as tachycardia. An important reason (beyond basic decency) for anyone providing coffee to honor requests for decaff.
For most people, caffeine is “heart neutral”. It doesn’t provide direct benefits or cause direct harm, provided it is enjoyed in moderation.
See also: Can you overdose on caffeine?
Some quick extra notes…
That’s all we have time for in myth-busting, but it’s worth noting before we close that coffee has a lot of health benefits; we didn’t cover them today because they’re not contentious, but they are interesting nevertheless:
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: