Mung Beans vs Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing mung beans to black beans, we picked the black beans.
Why?
Both are great! But…
In terms of macros, black beans have more protein, carbs, and fiber, as well as the lower glycemic index (although both are already low). So, a clear win for black beans here.
In the category of vitamins, mung beans have more of vitamins A, B5, B9, and C, while black beans have more of vitamins B1, B6, E, K, and choline. Thus, a slight win for black beans this time.
When it comes to minerals, mung beans have more selenium and zinc, while black beans have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and potassium. An easy win for black beans.
Of course, enjoy either or both—but if you’re going to pick one, we say black beans win the day.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Plant vs Animal Protein: Head-to-Head
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Are The “Bright Lines” Of Bright Line Eating?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is Dr. Susan Thompson. She’s a cognitive neuroscientist who has turned her hand to helping people to lose weight and maintain it at a lower level, using psychology to combat overeating. She is the founder of “Bright Line Eating”.
We’ll say up front: it’s not without some controversy, and we’ll address that as we go, but we do believe the ideas are worth examining, and then we can apply them or not as befits our personal lives.
What does she want us to know?
Bright Line Eating’s general goal
Dr. Thompson’s mission statement is to help people be “happy, thin, and free”.
You will note that this presupposes thinness as desirable, and presumes it to be healthy, which frankly, it’s not for everyone. Indeed, for people over a certain age, having a BMI that’s slightly into the “overweight” category is a protective factor against mortality (which is partly a flaw of the BMI system, but is an interesting observation nonetheless):
When BMI Doesn’t Quite Measure Up
Nevertheless, Dr. Thompson makes the case for the three items (happy, thin, free) coming together, which means that any miserable or unhealthy thinness is not what the approach is valuing, since it is important for “thin” to be bookended by “happy” and “free”.
What are these “bright lines”?
Bright Line Eating comes with 4 rules:
- No flour (no, not even wholegrain flour; enjoy whole grains themselves yes, but flour, no)
- No sugar (and as a tag-along to this, no alcohol) (sugars naturally found in whole foods, e.g. the sugar in an apple if eating an apple, is ok, but other kinds are not, e.g. foods with apple juice concentrate as a sweetener; no “natural raw cane sugar” etc is not allowed either; despite the name, it certainly doesn’t grow on the plant like that)
- No snacking, just three meals per day(not even eating the ingredients while cooking—which also means no taste-testing while cooking)
- Weigh all your food (have fun in restaurants—but more seriously, the idea here is to plan each day’s 3 meals to deliver a healthy macronutrient balance and a capped calorie total).
You may be thinking: “that sounds dismal, and not at all bright and cheerful, and certainly not happy and free”
The name comes from the idea that these rules are lines that one does not cross. They are “bright” lines because they should be observed with a bright and cheery demeanour, for they are the rules that, Dr. Thompson says, will make you “happy, thin, and free”.
You will note that this is completely in opposition to the expert opinion we hosted last week:
What Flexible Dieting Really Means
Dr. Thompson’s position on “freedom” is that Bright Line Eating is “very structured and takes a liberating stand against moderation”
Which may sound a bit of an oxymoron—is she really saying that we are going to be made free from freedom?
But there is some logic to it, and it’s about the freedom from having to make many food-related decisions at times when we’re likely to make bad ones:
Where does the psychology come in?
Dr. Thompson’s position is that willpower is a finite, expendable resource, and therefore we should use it judiciously.
So, much like Steve Jobs famously wore the same clothes every day because he had enough decisions to make later in the day that he didn’t want unnecessary extra decisions to make… Bright Line Eating proposes that we make certain clear decisions up front about our eating, so then we don’t have to make so many decisions (and potentially the wrong decisions) later when hungry.
You may be wondering: ”doesn’t sticking to what we decided still require willpower?”
And… Potentially. But the key here is shutting down self-negotiation.
Without clear lines drawn in advance, one must decide, “shall I have this cake or not?”, perhaps reflecting on the pros and cons, the context of the situation, the kind of day we’re having, how hungry we are, what else there is available to eat, what else we have eaten already, etc etc.
In short, there are lots of opportunities to rationalize the decision to eat the cake.
With clear lines drawn in advance, one must decide, “shall I have this cake or not?” and the answer is “no”.
So while sticking to that pre-decided “no” still may require some willpower, it no longer comes with a slew of tempting opportunities to rationalize a “yes”.
Which means a much greater success rate, both in adherence and outcomes. Here’s an 8-week interventional study and 2-year follow-up:
Bright Line Eating | Research Publications
Counterpoint: pick your own “bright lines”
Dr. Thompson is very keen on her 4 rules that have worked for her and many people, but she recognizes that they may not be a perfect fit for everyone.
So, it is possible to pick and choose our own “bright lines”; it is after all a dietary approach, not a religion. Here’s her response to someone who adopted the first 3 rules, but not the 4th:
Bright Lines as Guidelines for Weight Loss
The most important thing for Bright Line Eating, therefore, is perhaps the action of making clear decisions in advance and sticking to them, rather than seat-of-the-pantsing our diet, and with it, our health.
Want to know more from Dr. Thompson?
You might like her book, which we reviewed a while ago:
Bright Line Eating – by Dr. Susan Peirce Thompson
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Celeriac vs Celery – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing celeriac to celery, we picked the celeriac.
Why?
Yes, these are essentially the same plant, but there are important nutritional differences:
In terms of macros, celeriac has more than 2x the protein, and slightly more carbs and fiber. Both are very low glycemic index, so the higher protein and fiber makes celeriac the winner in this category.
In the category of vitamins, celeriac has more of vitamins B1, B3, B5, B6, C, E, K, and choline, while celery has more of vitamins A and B9. An easy win for celeriac.
When it comes to minerals, celeriac has more copper, calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while celery is not higher in any minerals. Another obvious win for celeriac.
Adding these sections up makes for a clear overall win for celeriac, but by all means enjoy either or both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
What’s Your Plant Diversity Score?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Is ADHD Being Over-Diagnosed For Cash?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is ADHD Being Systematically Overdiagnosed?
The BBC’s investigative “Panorama” program all so recently did a documentary in which one of their journalists—who does not have ADHD—went to three private clinics and got an ADHD diagnosis from each of them:
- The BBC documentary: Private ADHD Clinics Exposed (28 mins)
- Their “5 Minutes” version: ADHD Undercover: How I Was Misdiagnosed (6 mins)
So… Is it really a case of show up, pay up, and get a shiny new diagnosis?
The BBC Panorama producers cherry-picked 3 private providers, and during those clinical assessments, their journalist provided answers that would certainly lead to a diagnosis.
This was contrasted against a three-hour assessment with an NHS psychiatrist—something that rarely happens in the NHS. Which prompts the question…
How did he walk into a 3-hour psychiatrist assessment, when most people have to wait in long waiting lists for a much more cursory appointment first with assorted gatekeepers, before going on another long waiting list, for an also-much-shorter appointment with a psychiatrist?
That would be because the NHS psychiatrist was given advance notification that this was part of an investigation and would be filmed (the private clinics were not gifted the same transparency)
So, maybe just a tad unequal treatment!
In case you’re wondering, here’s what that very NHS psychiatrist had to say on the topic:
Is it really too easy to be diagnosed with ADHD?
(we’ll give you a hint—remember Betteridge’s Law!)
❝Since the documentary aired, I have heard from people concerned that GPs could now be more likely to question legitimate diagnoses.
But as an NHS psychiatrist it is clear to me that the root of this issue is not overdiagnosis.
Instead, we are facing the combined challenges of remedying decades of underdiagnosis and NHS services that were set up when there was little awareness of ADHD.❞
~ Dr. Mike Smith, Psychiatrist
The ADHD foundation, meanwhile, has issued its own response, saying:
❝We are disappointed that BBC Panorama has opted to broadcast a poorly researched, sensationalist piece of television journalism.❞
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
You can train your nose – and 4 other surprising facts about your sense of smell
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Would you give up your sense of smell to keep your hair? What about your phone?
A 2022 US study compared smell to other senses (sight and hearing) and personally prized commodities (including money, a pet or hair) to see what people valued more.
The researchers found smell was viewed as much less important than sight and hearing, and valued less than many commodities. For example, half the women surveyed said they’d choose to keep their hair over sense of smell.
Smell often goes under the radar as one of the least valued senses. But it is one of the first sensory systems vertebrates developed and is linked to your mental health, memory and more.
Here are five fascinating facts about your olfactory system.
DimaBerlin/Shutterstock 1. Smell is linked to memory and emotion
Why can the waft of fresh baking trigger joyful childhood memories? And why might a certain perfume jolt you back to a painful breakup?
Smell is directly linked to both your memory and emotions. This connection was first established by American psychologist Donald Laird in 1935 (although French novelist Marcel Proust had already made it famous in his reverie about the scent of madeleines baking.)
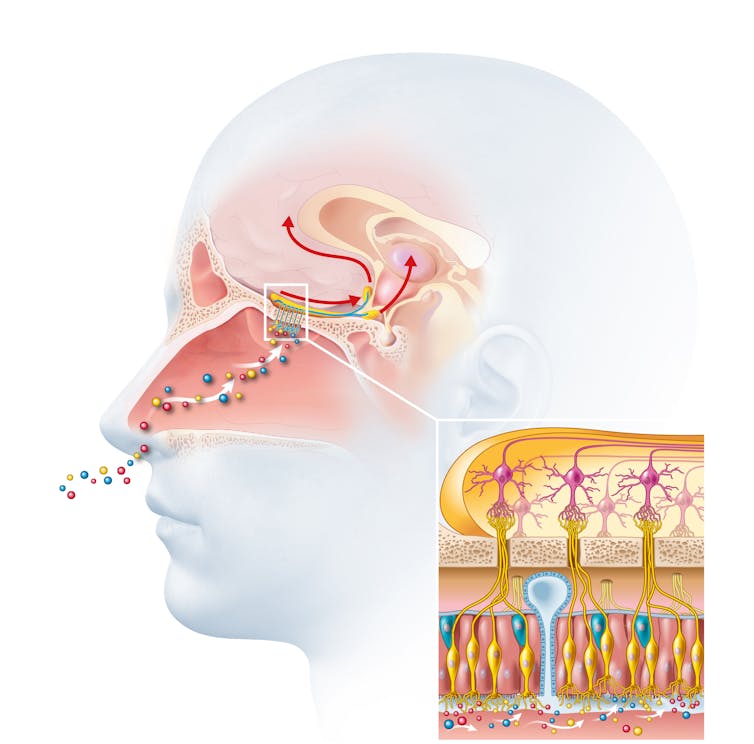
Odours are first captured by special olfactory nerve cells inside your nose. These cells extend upwards from the roof of your nose towards the smell-processing centre of your brain, called the olfactory bulb.
Smells are first detected by nerve cells in the nose. Axel_Kock/Shutterstock From the olfactory bulb they form direct connection with the brain’s limbic system. This includes the amygdala, where emotions are generated, and the hippocampus, where memories are created.
Other senses – such as sight and hearing – aren’t directly connected to the lymbic system.
One 2004 study used functional magnetic resonance imaging to demonstrate odours trigger a much stronger emotional and memory response in the brain than a visual cue.
2. Your sense of smell constantly regenerates
You can lose your ability to smell due to injury or infection – for example during and after a COVID infection. This is known as olfactory dysfunction. In most cases it’s temporary, returning to normal within a few weeks.
This is because every few months your olfactory nerve cells die and are replaced by new cells.
We’re not entirely sure how this occurs, but it likely involves your nose’s stem cells, the olfactory bulb and other cells in the olfactory nerves.
Other areas of your nervous system – including your brain and spinal cord – cannot regenerate and repair after an injury.
Constant regeneration may be a protective mechanism, as the olfactory nerves are vulnerable to damage caused by the external environment, including toxins (such as cigarette smoke), chemicals and pathogens (such as the flu virus).
But following a COVID infection some people might continue to experience a loss of smell. Studies suggest the virus and a long-term immune response damages the cells that allow the olfactory system to regenerate.
3. Smell is linked to mental health
Around 5% of the global population suffer from anosmia – total loss of smell. An estimated 15-20% suffer partial loss, known as hyposmia.
Given smell loss is often a primary and long-term symptom of COVID, these numbers are likely to be higher since the pandemic.
Yet in Australia, the prevalence of olfactory dysfunction remains surprisingly understudied.
Losing your sense of smell is shown to impact your personal and social relationships. For example, it can mean you miss out on shared eating experiences, or cause changes in sexual desire and behaviour.
In older people, declining ability to smell is associated with a higher risk of depression and even death, although we still don’t know why.
Losing your sense of smell can have a major impact on mental health. Halfpoint/Shutterstock 4. Loss of smell can help identify neurodegenerative diseases
Partial or full loss of smell is often an early indicator for a range of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Patients frequently report losing their sense of smell years before any symptoms show in body or brain function. However many people are not aware they are losing their sense of smell.
There are ways you can determine if you have smell loss and to what extent. You may be able to visit a formal smell testing centre or do a self-test at home, which assesses your ability to identify household items like coffee, wine or soap.
5. You can train your nose back into smelling
“Smell training” is emerging as a promising experimental treatment option for olfactory dysfunction. For people experiencing smell loss after COVID, it’s been show to improve the ability to detect and differentiate odours.
Smell training (or “olfactory training”) was first tested in 2009 in a German psychology study. It involves sniffing robust odours — such as floral, citrus, aromatic or fruity scents — at least twice a day for 10—20 seconds at a time, usually over a 3—6 month period.
Participants are asked to focus on the memory of the smell while sniffing and recall information about the odour and its intensity. This is believed to help reorganise the nerve connections in the brain, although the exact mechanism behind it is unclear.
Some studies recommend using a single set of scents, while others recommend switching to a new set of odours after a certain amount of time. However both methods show significant improvement in smelling.
This training has also been shown to alleviate depressive symptoms and improve cognitive decline both in older adults and those suffering from dementia.
Just like physiotherapy after a physical injury, olfactory training is thought to act like rehabilitation for your sense of smell. It retrains the nerves in your nose and the connections it forms within the brain, allowing you to correctly detect, process and interpret odours.
Lynn Nazareth, Research Scientist in Olfactory Biology, CSIRO
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Seasonal Affective Disorder (Beyond Sunlight!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those of us in the Northern Hemisphere, the time of increasing darkness is upon us again. Depending on our latitude, the sun barely rises before it skitters off again. And depending on other factors of our geography, we might not get much sun during that time (writer’s example: the ancient bog from which I write has been surrounded by fog for two weeks now).
So, what to do about it?
Firstly, we can make the most of whatever sun we do get (especially in the morning, if possible), and we can of course make some use of artificial sunlight. To save doubling up, we’ll link to what we previously wrote about optimizing both of those things:
‘Tis To Season To Be SAD-Savvy
More ways to get serotonin
Sunlight, of course, triggers our bodies to make serotonin, and hence we often make less of it during winter. But, there are other ways to get serotonin too, and one of the best ways is spending time in nature. Yes, even if the weather is gloomy, provided there are still visible green things and you are seeing them, it will promote serotonin production.
Of course, it may not be the season for picnics, but a morning walk through a local park or other green space is ideal.
On which note, gardening remains a good activity. Not a lot of people do so much gardening after a certain point in the year, but in one way, it’s more important than ever to get some soil under your fingernails:
There are bacteria in soil (specifically: Mycobacterium vaccae) that work similarly to antidepressants.
When something is described as having an effect similar to antidepressants, it’s usually hyperbole. In this case, it’s medicine, and literally works directly on the serotonergic system (as do many, but not all, antidepressants).
See also: Antidepressants: Personalization Is Key!
While many antidepressants are selective serotonin uptake inhibitors (i.e., they slow the rate at which your brain loses serotonin), Mycobacterium vaccae increases the rate at which you produce serotonin. So, you feel happier, more relaxed, while also feeling more energized.
^this one’s a mouse study, but we’re including it because it covers exactly how it works in the brain, which is something that the ethics board wouldn’t let them do on humans, due to the need for slicing the brains up for examination.
As to how to benefit: touching soil will get you “infected” by the bacteria, yes, even if you wash your hands later. Growing food in the soil and eating the good (including if you wash and cook it) is even better.
Boost the other “happiness chemicals”
Serotonin is just one “happiness hormone”, other feel-good neurotransmitters that are just as important include dopamine and oxytocin.
Dopamine is most associated with being the “reward chemical”, so it pays to do things that you find rewarding. If you’re stuck for ideas, engaging in small acts of kindness is a sure-fire way to get dopamine flowing and lift your own mood as well as theirs.
See also: 10 Ways To Naturally Boost Dopamine
Oxytocin, meanwhile is the “cuddle chemical”, and can be triggered even if you have nobody to cuddle*. If you do, by the way, make it at least 20–30 seconds, as that’s generally how long it takes to get oxytocin flowing.
*Vividly imagining it has much the same effect, since the brain can’t tell the difference. Alternatively, looking at pictures/videos (your choice) of small cute animals tends to work for most people also.
For more on these things, check out: Neurotransmitter Cheatsheet
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The BAT-pause!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When Cold Weather & The Menopause Battle It Out
You may know that (moderate, safe) exposure to the cold allows our body to convert our white and yellow fat into the much healthier brown fat—also called brown adipose tissue, or “BAT” to its friends.
If you didn’t already know that, then well, neither did scientists until about 15 years ago:
The Changed Metabolic World with Human Brown Adipose Tissue: Therapeutic Visions
You can read more about it here:
Cool Temperature Alters Human Fat and Metabolism
This is important, especially because the white fat that gets converted is the kind that makes up most visceral fat—the kind most associated with all-cause mortality:
Visceral Belly Fat & How To Lose It ← this is not the same as your subcutaneous fat, the kind that sits directly under your skin and keeps you warm; this is the fat that goes between your organs and of which we should only have a small amount!
The BAT-pause
It’s been known (since before the above discovery) that BAT production slows considerably as we get older. Not too shocking—after all, many metabolic functions slow as we get older, so why should fat regulation be any different?
But! Rodent studies found that this was tied less to age, but to ovarian function: rats who underwent ovariectomies suffered reduced BAT production, regardless of their age.
Naturally, it’s been difficult to recreate such studies in humans, because it’s difficult to find a large sample of young adults willing to have their ovaries whipped out (or even suppressed chemically) to see how badly their metabolism suffers as a result.
Nor can an observational study (for example, of people who incidentally have ovaries removed due to ovarian cancer) usefully be undertaken, because then the cancer itself and any additional cancer treatments would be confounding factors.
Perimenopausal study to the rescue!
A recent (published last month, at time of writing!) study looked at women around the age of menopause, but specifically in cohorts before and after, measuring BAT metabolism.
By dividing the participants into groups based on age and menopausal status, and dividing the post-menopausal group into “takes HRT” and “no HRT” groups, and dividing the pre-menopausal group into “normal ovarian function” and “ovarian production of estrogen suppressed to mimic slightly early menopause” groups (there’s a drug for that), and then having groups exposed to warm and cold temperatures, and measuring BAT metabolism in all cases, they were able to find…
It is about estrogen, not age!
You can read more about the study here:
“Good” fat metabolism changes tied to estrogen loss, not necessarily to aging, shows study
…and the study itself, here:
Brown adipose tissue metabolism in women is dependent on ovarian status
What does this mean for men?
This means nothing directly for (cis) men, sorry.
But to satisfy your likely curiosity: yes, testosterone does at least moderately suppress BAT metabolism—based on rodent studies, anyway, because again it’s difficult to find enough human volunteers willing to have their testicles removed for science (without there being other confounding variables in play, anyway):
Testosterone reduces metabolic brown fat activity in male mice
So, that’s bad per se, but there isn’t much to be done about it, since the rest of your (addressing our male readers here) metabolism runs on testosterone, as do many of your bodily functions, and you would suffer many unwanted effects without it.
However, as men do typically have notably less body fat in general than women (this is regulated by hormones), the effects of changes in BAT metabolism are rather less pronounced in men (per testosterone level changes) than in women (per estrogen level changes), because there’s less overall fat to convert.
In summary…
While menopausal HRT is not necessarily a silver bullet to all metabolic problems, its BAT-maintaining ability is certainly one more thing in its favor.
See also:
Dr. Jen Gunter | What You Should Have Been Told About The Menopause Beforehand
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: