To Pee Or Not To Pee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is it “strengthening” to hold, or are we doing ourselves harm if we do? Dr. Heba Shaheed explains in this short video:
A flood of reasons not to hold
Humans should urinate 4–6 times daily, but for many people, the demands of modern life often lead to delaying urination, raising questions about its effects on the body.
So first, let’s look at how it all works: the bladder is part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, urethra, and sphincters. Urine is produced by the kidneys and transported via the ureters into the bladder, a hollow organ with a muscular wall. This muscle (called the detrusor) allows the bladder to inflate as it fills with urine (bearing in mind, the main job of any muscle is to be able to stretch and contract).
As the bladder fills, stretch receptors in that muscle signal fullness to the spinal cord. This triggers the micturition reflex, causing the detrusor to contract and the internal urethral sphincter to open involuntarily. Voluntary control over the external urethral sphincter allows a person to delay or release urine as needed.
So, at what point is it best to go forth and pee?
For most people, bladder fullness is first noticeable at around 150-200ml, with discomfort occurring at 400-500ml (that’s about two cups*). Although the bladder can stretch to hold up to a liter, exceeding this capacity can cause it to rupture, a rare but serious condition requiring surgical intervention.
*note, however, that this doesn’t necessarily mean that drinking two cups will result in two cups being in your bladder; that’s not how hydration works. Unless you are already perfectly hydrated, most if not all of the water will be absorbed into the rest of your body where it is needed. Your bladder gets filled when your body has waste products to dispose of that way, and/or is overhydrated (though overhydration is not very common).
Habitually holding urine and/or urinating too quickly (note: not “too soon”, but literally, “too quickly”, we’re talking about the velocity at which it exits the body) can weaken pelvic floor muscles over time. This can lead to bladder pain, urgency, incontinence, and/or a damaged pelvic floor.
In short: while the body’s systems are equipped to handle occasional delays, holding it regularly is not advisable. For the good of your long-term urinary health, it’s best to avoid straining the system and go whenever you feel the urge.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Keeping your kidneys happy: it’s more than just hydration!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
NADᐩ Against Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or “NAD” to its friends, is a coenzyme produced in the human body (amongst other places), and it is critical for cellular energy metabolism, but there’s more to it than that.
Today we’ll be looking mostly at NAD+, of which the + indicates the positive formal charge of one of its nitrogen atoms. We won’t get too much into the chemistry of this, but we will mention that it’s a cofactor with NADH—the former accepting electrons and the latter donating electrons.
Both NAD+ and NADH are critical to good health, but we’re going to focus on NAD+ for the simple reason that it gets depleted with aging.
Note: it gets depleted with aging.
Chronological age is not so important here, but there is a direct relationship between biological aging and NAD+ depletion.
For example, healthy centenarians tend not to have depleted NAD+ levels. Further, its depletion (in those in whom it is depleted) is then a causal factor for many age-related diseases:
❝Remarkably, ageing is accompanied by a gradual decline in tissue and cellular NAD+ levels in multiple model organisms, including rodents and humans.
This decline in NAD+ levels is linked causally to numerous ageing-associated diseases, including cognitive decline, cancer, metabolic disease, sarcopenia and frailty.
Many of these ageing-associated diseases can be slowed down and even reversed by restoring NAD+ levels.❞
~ Dr. Rosalba Perrone et al.
Read in full: NAD+ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing
As for restoring those NADᐩ levels, that does help in interventional trials, whether by supplementing directly, or with NAD precursors*:
❝NAD+ levels steadily decline with age, resulting in altered metabolism and increased disease susceptibility.
Restoration of NAD+ levels in old or diseased animals can promote health and extend lifespan, prompting a search for safe and efficacious NAD-boosting molecules that hold the promise of increasing the body’s resilience, not just to one disease, but to many, thereby extending healthy human lifespan.❞
~ Dr. David Sinclair et al.
Read more: Therapeutic Potential of NAD-Boosting Molecules: The In Vivo Evidence
*There are actually also other NAD-boosting molecules besides NAD itself and its precursors. For example, the liver will not produce NADᐩ unless it has aminocarboxymuconate-semialdehyde decarboxylase (or “ACMSD”, to its friends), which limits the production of NADᐩ. Why, you ask? The theory is that it is a kind of evolutionary conservativism, much like not lighting a fire without the ability to put it out. In any case, taking ACMSD-blockers will thus result in an increased endogenous production of NADᐩ.
You can read about this here:
De novo NAD+ synthesis enhances mitochondrial function and improves health
Nor is taking supplements or drugs the only way to get more of it; there’s an enzyme nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (“NAMPT”, to its friends) involved in the synthesis of NADᐩ, and exercise boosts levels by 127% (i.e., it more than doubles the levels), based on a modest three-week exercise bike regimen:
Skeletal muscle NAMPT is induced by exercise in humans
And to underline that point, another study found that resistance training (so, a different kind of exercise from that of the previous study) boosts levels of NADᐩ itself by the same 127%:
One way to get more out of NADᐩ
We’ll get straight to the point: it works very well paired with a senolytic agent, i.e. something that kills aging cells so that they get recycled sooner:
NAD+, Senolytics, or Pyruvate for Healthy Aging?
To read more about senolytics, check out:
Fisetin: The Anti-Aging Assassin
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
I’m feeling run down. Why am I more likely to get sick? And how can I boost my immune system?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It has been a long winter, filled with many viruses and cost-of-living pressures, on top of the usual mix of work, study, life admin and caring responsibilities.
Stress is an inevitable part of life. In short bursts, our stress response has evolved as a survival mechanism to help us be more alert in fight or flight situations.
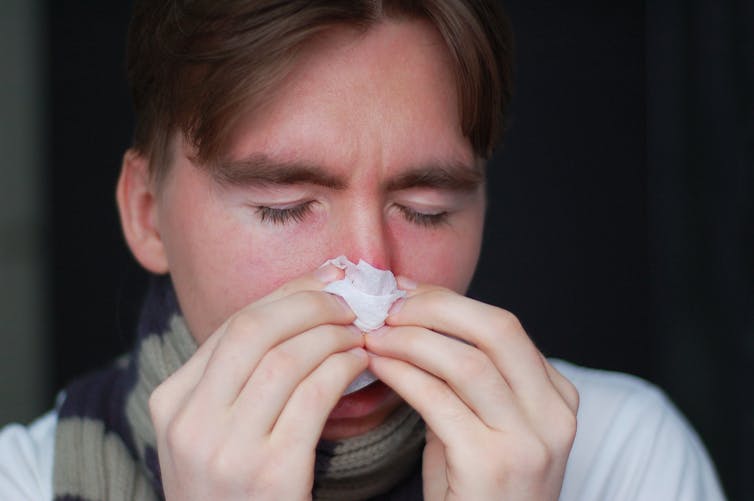
But when stress is chronic, it weakens the immune system and makes us more vulnerable to illnesses such as the common cold, flu and COVID.
Pexels/Ketut Subiyanto Stress makes it harder to fight off viruses
When the immune system starts to break down, a virus that would normally have been under control starts to flourish.
Once you begin to feel sick, the stress response rises, making it harder for the immune system to fight off the disease. You may be sick more often and for longer periods of time, without enough immune cells primed and ready to fight.
In the 1990s, American psychology professor Sheldon Cohen and his colleagues conducted a number of studies where healthy people were exposed to an upper respiratory infection, through drops of virus placed directly into their nose.
These participants were then quarantined in a hotel and monitored closely to determine who became ill.
One of the most important factors predicting who got sick was prolonged psychological stress.
Cortisol suppresses immunity
“Short-term stress” is stress that lasts for a period of minutes to hours, while “chronic stress” persists for several hours per day for weeks or months.
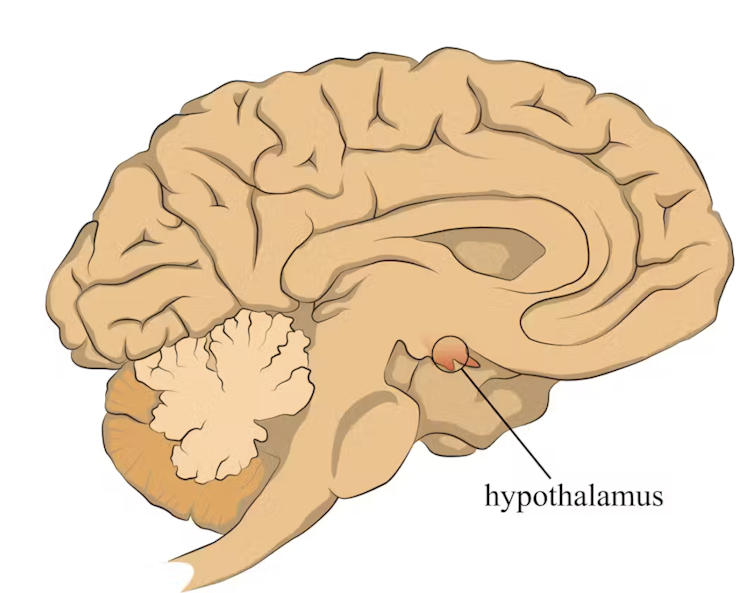
When faced with a perceived threat, psychological or physical, the hypothalamus region of the brain sets off an alarm system. This signals the release of a surge of hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol.
The hypothalamus sets off an alarm system in response to a real or perceived threat. stefan3andrei/Shutterstock In a typical stress response, cortisol levels quickly increase when stress occurs, and then rapidly drop back to normal once the stress has subsided. In the short term, cortisol suppresses inflammation, to ensure the body has enough energy available to respond to an immediate threat.
But in the longer term, chronic stress can be harmful. A Harvard University study from 2022 showed that people suffering from psychological distress in the lead up to their COVID infection had a greater chance of experiencing long COVID. They classified this distress as depression, probable anxiety, perceived stress, worry about COVID and loneliness.
Those suffering distress had close to a 50% greater risk of long COVID compared to other participants. Cortisol has been shown to be high in the most severe cases of COVID.
Stress causes inflammation
Inflammation is a short-term reaction to an injury or infection. It is responsible for trafficking immune cells in your body so the right cells are present in the right locations at the right times and at the right levels.
The immune cells also store a memory of that threat to respond faster and more effectively the next time.
Initially, circulating immune cells detect and flock to the site of infection. Messenger proteins, known as pro-inflammatory cytokines, are released by immune cells, to signal the danger and recruit help, and our immune system responds to neutralise the threat.
During this response to the infection, if the immune system produces too much of these inflammatory chemicals, it can trigger symptoms such as nasal congestion and runny nose.
Our immune response can trigger symptoms such as a runny nose. Alyona Mandrik/Shutterstock What about chronic stress?
Chronic stress causes persistently high cortisol secretion, which remains high even in the absence of an immediate stressor.
The immune system becomes desensitised and unresponsive to this cortisol suppression, increasing low-grade “silent” inflammation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (the messenger proteins).
Immune cells become exhausted and start to malfunction. The body loses the ability to turn down the inflammatory response.
Over time, the immune system changes the way it responds by reprogramming to a “low surveillance mode”. The immune system misses early opportunities to destroy threats, and the process of recovery can take longer.
So how can you manage your stress?
We can actively strengthen our immunity and natural defences by managing our stress levels. Rather than letting stress build up, try to address it early and frequently by:
1) Getting enough sleep
Getting enough sleep reduces cortisol levels and inflammation. During sleep, the immune system releases cytokines, which help fight infections and inflammation.
2) Taking regular exercise
Exercising helps the lymphatic system (which balances bodily fluids as part of the immune system) circulate and allows immune cells to monitor for threats, while sweating flushes toxins. Physical activity also lowers stress hormone levels through the release of positive brain signals.
3) Eating a healthy diet
Ensuring your diet contains enough nutrients – such as the B vitamins, and the full breadth of minerals like magnesium, iron and zinc – during times of stress has a positive impact on overall stress levels. Staying hydrated helps the body to flush out toxins.
4) Socialising and practising meditation or mindfulness
These activities increase endorphins and serotonin, which improve mood and have anti-inflammatory effects. Breathing exercises and meditation stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which calms down our stress responses so we can “reset” and reduce cortisol levels.
Sathana Dushyanthen, Academic Specialist & Lecturer in Cancer Sciences & Digital Health| Superstar of STEM| Science Communicator, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Coconut Milk vs Soy Milk – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing coconut milk to soy milk, we picked the soy.
Why?
First, because there are many kinds of both, let’s be clear which ones we’re comparing. For both, we picked the healthiest options commonly available, which were:
- Soy milk, unsweetened, fortified
- Coconut milk, raw (liquid expressed from grated meat and water)
Macronutrients are our first consideration; coconut milk has about 3x the carbs and about 14x the fat. Now, the fats are famously healthy medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), but still, one cup of coconut milk contains about 2.5x the recommended daily amount of saturated fat, so it’s wise to go easy on that. Coconut milk also has about 4x the fiber, but still, because the saturated fat difference, we’re calling this one a win for soy milk.
In the category of vitamins, the fortified soy milk wins. In case you’re curious: milk in general (animal or plant) is generally fortified with vitamin D (in N. America, anyway; other places may vary), and vitamin B12. In this case, the soy milk has those, plus some natural vitamins, meaning it has more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, and D, while coconut milk has more of vitamins B3, B5, and C. A fair win for soy milk.
When it comes to minerals, the only fortification for the soy milk is calcium, of which it has more than 7x what coconut milk has. The coconut milk, however, has more copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium. An easy win for coconut milk.
Adding up the sections gives us a win for soy milk—but if consumed in moderation as part of a diet otherwise low in saturated fat, a case could be made for the coconut.
The real take-away here today is not this specific head-to-head but rather: milks (animal or plant) vary a lot, have a lot of different fortifications and/or additives, and yes that goes even for brands (cow milk brands do this a lot) who don’t advertise their additives because their branding is going for a “natural” look. So, read labels, and make informed decisions about which additives you do or don’t want.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Sugar, Hazelnuts, Books & Brains
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day!
Each Thursday, we respond to subscriber questions and requests! If it’s something small, we’ll answer it directly; if it’s something bigger, we’ll do a main feature in a follow-up day instead!
So, no question/request to big or small; they’ll just get sorted accordingly
Remember, you can always hit reply to any of our emails, or use the handy feedback widget at the bottom. We always look forward to hearing from you!
Q: Interesting info, however, I drink hazelnut milk LOL so would have liked a review of that. But now I want to give hemp and pea milks a try. Thanks
Aww! Here then just for you, is a quick rundown…
- Pros: high in protein¹, vitamin B, and vitamin E
- Cons: high in fat², low in calcium
¹Compared head-to-head with almond milk for example, it has double the protein (but also double the calories)
²However, is also has been found to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol (and incidentally, also reduce inflammation), and in a later systematic review, it was found to not correlate to weight gain, despite its high calorie-content.
If you don’t already, and would like to try making your own…
Click here for step-by-step instructions to make your own hazelnut milk! (very simple)
Q: Wondering if you can evaluate CLA and using it to assist with weight loss. Thanks
Will do! (Watch this space)
Q: What’s the process behind the books you recommend? You seem to have a limitless stream of recommendations
We do our best!
The books we recommend are books that…
- are on Amazon—it makes things tidy, consistent, and accessible. And if you end up buying one of the books, we get a small affiliate commission*.
- we have read—we would say “obviously”, but you might be surprised how many people write about books without having read them.
- pertain in at least large part to health and/or productivity.
- are written by humans—bookish people (and especially Kindle Unlimited users) may have noticed lately that there are a lot of low quality AI-written books flooding the market, sometimes with paid 5-star reviews to bolster them. It’s frustrating, but we can tell the difference and screen those out.
- are of a certain level of quality. They don’t have to be “top 5 desert-island books”, because well, there’s one every day and the days keep coming. But they do have to genuinely deliver the value that we describe, and merit a sincere recommendation.
- are varied—we try to not give a run of “samey” books one after another. We will sometimes review a book that covers a topic another previously-reviewed book did, but it must have something about it that makes it different. It may be a different angle or a different writing style, but it needs something to set it apart.
*this is from Amazon and isn’t product-specific, so this is not affecting our choice of what books to review at all—just that they will be books that are available on Amazon.
Q: Great video on dopamine. Thumbs up on the book recommendation. Would you please consider doing a piece or two on inflammation? I live with Lupus and it is a constant struggle. Thanks for the awesome work you do. Have an excellent day.
Great suggestion! We will do that, and thank you for the kind words!
Q: Why is your newsletter called 10almonds? Maybe I missed it in the intro email, but my curiosity wants to know the significance. Thanks!”
It’s a reference to a viral Facebook hoax! There was a post going around that claimed:
❝HEADACHE REMEDY. Eat 10–12 almonds, the equivalent of two aspirins, next time you have a headache❞ ← not true!
It made us think about how much health-related disinformation there was online… So, calling ourselves 10almonds was a bit of a tongue-in-cheek reference to that story… but also a reminder to ourselves:
We must always publish information with good scientific evidence behind it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
It’s Not Hysteria – by Dr. Karen Tan
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Firstly, who this book is aimed at: in case it wasn’t clear, this book assumes you have, or at least have had, a uterus. If that’s not you, then well, it’ll still be an interesting read but it won’t be about your reproductive health.
Secondly, about that “reproductive health”: it’s mostly not actually about reproductive health literally, but rather, the health of one’s reproductive organs and the things that they affect—which is a lot more than the ability to reproduce!
Dr. Tang takes us on a (respectably in-depth) tour of the relevant anatomy, before moving on to physiology, before continuing to pathology (i.e. things that can go wrong, and often do), and finally various treatment options, including elective procedures, and the pros and cons thereof.
She also talks the reader through talking about things with gynecologists and other healthcare providers, and making sure concerns are not dismissed out-of-hand (something that happens a lot, of course).
The style throughout is quite detailed prose, but without being difficult at all to read, and (assuming one is interested in the topic) it’s very engaging.
Bottom line: if you would like to know more about uteri and everything that is (or commonly/unfortunately) can be attached to them, the effects they have on the rest of the body and health, and what can be done about things not being quite right, then this is a good book for that.
Click here to check out It’s Not Hysteria, and understand more of what’s going on down there!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Marrakesh Sorghum Salad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As the name suggests, it’s a Maghreb dish today! Using sorghum, a naturally gluten-free whole grain with a stack of vitamins and minerals. This salad also comes with fruit and nuts (apricots and almonds; a heavenly combination for both taste and nutrients) as well as greens, herbs, and spices.
Note: to keep things simple today, we’ve listed ras el-hanout as one ingredient. If you’re unfamiliar, it’s a spice blend; you can probably buy a version locally, but you might as well know how to make it yourself—so here’s our recipe for that!
You will need
- 1½ cups sorghum, soaked overnight in water (if you can’t find it locally, you can order it online (here’s an example product on Amazon), or substitute quinoa) and if you have time, soaked overnight and then kept in a jar with just a little moisture for a few days until they begin to sprout—this will be best of all. But if you don’t have time, don’t worry about it; overnight soaking is sufficient already.
- 1 carrot, grated
- ½ cup chopped parsley
- 1 tbsp apple cider vinegar
- ½ tbsp chopped chives
- 2 tbsp ras el-hanout
- 3 cloves garlic, crushed
- 2 tbsp almond butter
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- 1 tsp white miso paste
- ½ cup sliced almonds
- 4 fresh apricots, pitted and cut into wedges
- 1 cup mint leaves, chopped
- To serve: your choice of salad greens; we suggest chopped romaine lettuce and rocket
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Cook the sorghum, which means boiling it for about 45 minutes, or 30 in a pressure cooker. If unsure, err on the side of cooking longer—even up to an hour will be totally fine. You have a lot of wiggle room, and will soon get used to how long it takes with your device/setup. Drain the cooked sorghum, and set it aside to cool. If you’re entertaining, we recommend doing this part the day before and keeping it in the fridge.
2) When it’s cool, add the carrot, the parsley, the chives, the vinegar, and 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout. Toss gently but thoroughly to combine.
3) Make the dressing, which means putting ¼ cup water into a blender with the other 1 tbsp of the ras el-hanout, the garlic, the almond butter, the lemon juice, and the miso paste. Blend until smooth.
4) Assemble the salad, which means adding the dressing to sorghum-and-ingredients bowl, along with the almonds, apricots, and mint leaves. Toss gently, but sufficiently that everything is coated.
5) Serve on a bed of salad greens.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean Diet ← including an anti-inflammatory version, which is functionally what we’re doing today. As an aside when people hear “Mediterranean” they often think “Italy and Greece”. Which, sure, but N. Africa (and thus Maghreb cuisine) is also very much Mediterranean, and it shows!
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Brain Food? The Eyes Have It!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: