50 Ways To Rewire Your Anxious Brain – by Dr. Catherine Pittman & Dr. Maha Zayed-Hoffman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book is divided into sections:
- Calming the amygdala
- Rewiring the amygdala
- Calming the cortex
- Resisting cortex traps
…each with a dozen or so ways to do exactly what it says in the title: rewire your anxious brain.
The authors take the stance that since our brain is changing all the time, we might as well choose the direction we prefer. They then set out to provide the tools for the lay reader to do that, and (in that fourth section we mentioned) how to avoid accidentally doing the opposite, no matter how tempting doing the opposite may be.
For a book written by two PhD scientists where a large portion of it is about neuroscience, the style is very light pop science (just a few in-line citations every few pages, where they couldn’t resist the urge), and the focus is on being useful to the reader throughout. This all makes for reassuringly science-based but accessibly readable book.
The fact that the main material comes in the form of 50 very short chapters also makes it a lot more readable for those for whom sitting down to read a lot at a time can be off-putting.
Bottom line: if you experience anxiety and would like to experience it less, this book will guide you through how to get there.
Click here to check out 50 Ways To Rewire Your Anxious Brain, and rewire your anxious brain!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
10almonds Tells The Tea…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Let’s Bust Some Myths!
It’s too late after puberty, hormones won’t change xyz
While yes, many adult trans people dearly wish they’d been able to medically transition before going through the “wrong” puberty, the truth is that a lot of changes will still occur later… even to “unchangeable” things like the skeleton.
The body is remaking itself throughout life, and hormones tell it how to do that. Some parts are just quicker or slower than others. Also: the skeleton is pulled-on constantly by our muscles, and in a battle of muscle vs bone, muscle will always win over time.
Examples of this include:
- trans men building bigger bones to support their bigger muscles
- trans women getting smaller, with wider hips and a pelvic tilt
Trans people have sporting advantages
Assuming at least a year’s cross-sex hormonal treatment, there is no useful advantage to being trans when engaging in a sport. There are small advantages and disadvantages (which goes for any person’s body, really). For example:
- Trans women will tend to be taller than cis women on average…
- …but that larger frame is now being powered by smaller muscles, because they shrink much quicker than the skeleton.
- Trans men taking T are the only athletes allowed to take testosterone…
- …but they will still often be smaller than their fellow male competitors, for example.
Read: Do Trans Women Athletes Have Advantages? (A rather balanced expert overview, which does also cover trans men)
There’s a trans population explosion; it’s a social contagion epidemic!
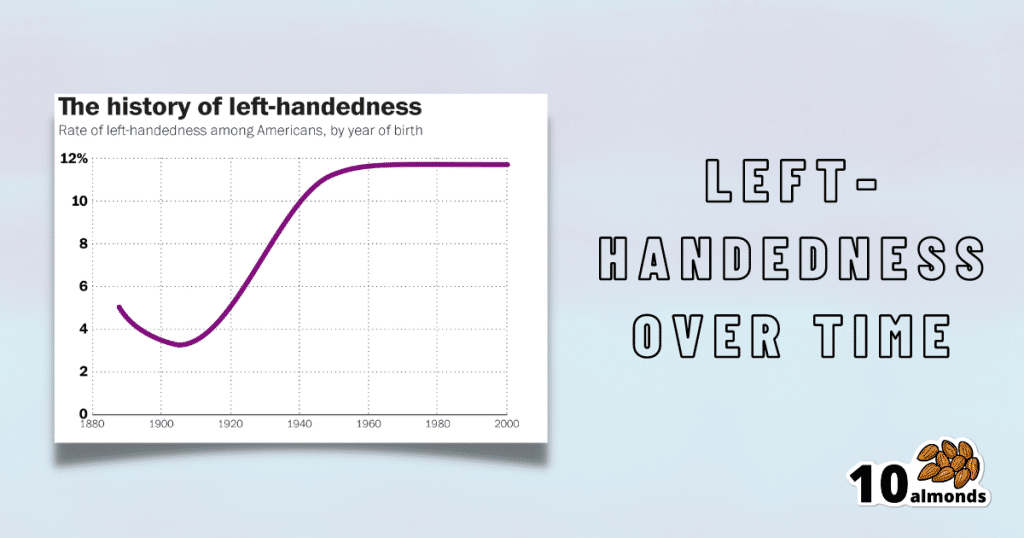
Source for figures: The Overall Rate Of Left-Handedness (Researchgate)
Left-handed people used to make up around 3% of the population… Until the 1920s, when that figure jumped sharply upwards, before plateauing at around 12% in around 1960, where it’s stayed since. What happened?! Simple, schools stopped forcing children to use their right hand.
Today, people ask for trans healthcare because they know it exists! Decades ago, it wasn’t such common knowledge.
The same explanation can be applied to other “population explosions” such as for autism and ADHD.
Fun fact: Mt. Everest was “discovered” in 1852, but scientists suspect it probably existed long before then! People whose ancestors were living on it long before 1852 also agree. Sometimes something exists for a long time, and only comes to wider public awareness later.
Transgender healthcare is too readily available, especially to children!
To believe some press outlets, you’d think:
- HRT is available from school vending machines,
- kids can get a walk-in top surgery at recess,
- and there’s an after-school sterilization club.
In reality, while availability varies from place to place, trans healthcare is heavily gatekept. Even adults have trouble getting it, often having to wait years and/or pay large sums of money… and get permission from a flock of doctors, psychologists, and the like. For those under the age of 18, it’s almost impossible in many places, even with parental support.
Puberty-blockers shouldn’t be given to teenagers, as the effects are irreversible
Quick question: who do you think should be given puberty-blockers? For whom do you think they were developed? Not adults, for sure! They were not developed for trans teens either, but for cis pre-teens with precocious puberty, to keep puberty at bay, to do it correctly later. Nobody argues they’re unsafe for much younger cis children, and only object when it’s trans teens.
They’re not only safe and reversible, but also self-reversing. Stop taking them, and the normally scheduled puberty promptly ensues by itself. For trans kids, the desired effect is to buy the kid time to make an informed and well-considered decision. After all, the effects of the wrong puberty are really difficult to undo!
A lot of people rush medical transition and regret it!
Trans people wish it could be rushed! It’s a lot harder to get gender-affirming care as a trans person, than it is to get the same (or comparable) care as a cis person. Yes, cis people get gender-affirming care, from hormones to surgeries, and have done for a long time.
As for regret… Medical transition has around a 1% regret rate. For comparison, hip replacement has a 4.8% regret rate and knee replacement has a 17.1% regret rate.
A medical procedure with a 99% success rate would generally be considered a miracle cure!
Share This Post
-
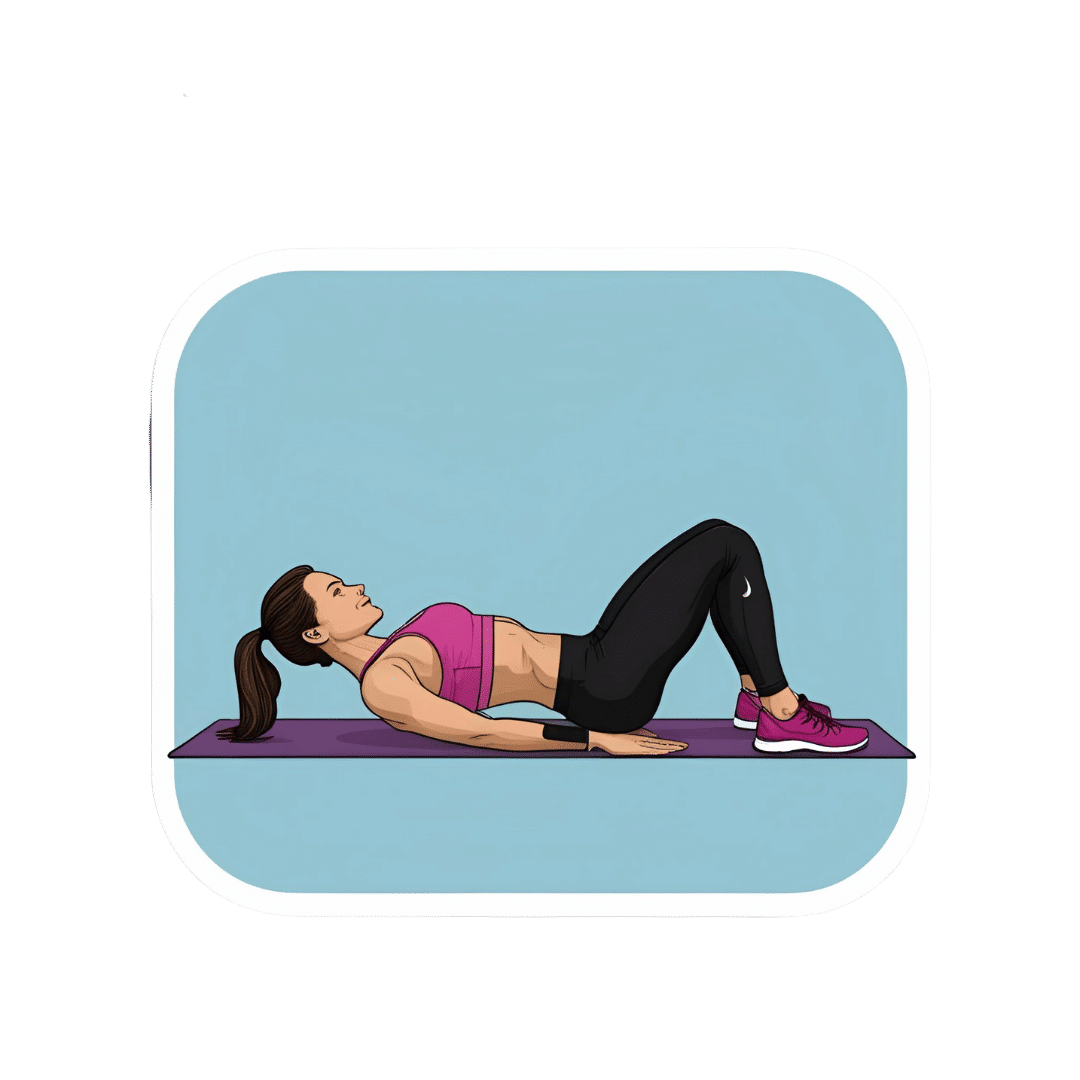
What Happens To Your Body When You Do 100 Glute Bridges Every Day
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Not just for a sculpted butt:
Benefits
With consistent daily glute bridge practice, you may expect:
- Rounder, toned butt: targets the gluteus maximus, toning and lifting the butt for a rounder appearance.
- Improved posture: strengthens glutes to support the spine and pelvis, alleviating lower back and hip pain. Stretches tight hip flexors from prolonged sitting.
- Stronger lower back: glutes support the lower back and spine, reducing pain and making it easier to lift heavy objects. Activating the glutes transfers force from legs to core, preventing injuries.
- Stronger knees: stabilizes the knee joint and promotes alignment by engaging glutes, hamstrings, and quadriceps, reducing knee pain.
- Sculpted hamstrings: contracts hamstrings during lifts for strength, while stretching them on the way down increases flexibility.
- Increased hip flexibility: strengthens muscles around the hip joint, improving mobility and counteracting tight hips from sedentary habits.
- Reduced back pain: strengthens glutes to correct pelvic tilt and reduce strain on the lower back.
- Faster running speed: improves hip extension, strengthens hamstrings, and activates the gluteus medius for better running power and balance.
- Enhanced strength training performance: strengthens glutes, back, and knees, improving performance in exercises like squats and deadlifts.
As for how to get going, the video offers the following very sound advice: begin with 25–30 reps per session and gradually increase to sets of 100 daily. It should take about 5 minutes (that’s 3 seconds per repetition). Results can be seen in as little as 2 weeks, with significant changes after a month of consistent practice.
For more on all of this plus visual demonstrations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Strong Curves: A Woman’s Guide to Building a Better Butt and Body – by Bret Contreras & Kellie Davis
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Food For Life Cookbook – by Dr. Tim Spector
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve previously reviewed Dr. Spector’s “Food For Life”, and while that was more of an “explanatory science” book, this one takes that science (reiterating it more briefly this time, by way of introduction) and makes a cookbook of it.
The nutritional emphasis in these recipes is on two things: maximizing fiber, and maximizing plant diversity. The recipes are not all vegan or even vegetarian, but they are plant-centric, and if the reader is vegetarian/vegan, then substitutions are easy to make.
The recipes themselves are simple without being boring, and are easy to follow, with full-page photos to accompany them. The science parts are very clear, accessible, and pop-science in style.
Bottom line: if you’d like to incorporate more fiber and more plants into your diet without it being a burden, this book is great for that.
Click here to check out the Food For Life Cookbook, and get cooking for life!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Who Initiates Sex & Why It Matters
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In an ideal world, it wouldn’t matter any more than who first says “let’s get something to eat” when hungry. But in reality, it can cause serious problems on both sides:
Fear and loathing?
The person who initiates gets the special prize of an n% chance of experiencing rejection, and then what? Try again, and again, and risk seeming pushy? Or leave the ball in the other person’s court, where it may then go untouched for the next few months, because (in the most positive scenario) they were waiting for you to initiate at a better time for them?
The person who does not initiate, and/but does not want sex at that time, gets the special prize of either making their partner feel unwanted, insecure, and perhaps unloved, or else grudgingly consenting to sex that’s going to be no fun while your heart’s not in it, and thus create the same end result plus you had an extra bad experience?
So, that sucks all around:
- Initiating touch (sex or cuddling) can feel like a test of being wanted, whereupon a lack of initiation or response may be misinterpreted as a lack of love or appreciation.
- Meanwhile, non-reciprocation might stem from exhaustion or unrelated issues. For many, it’s a physiological lottery.
10almonds note: not discussed in this video, but for many couples, problems can also arise because one partner or another just isn’t showing up with the expected physical signs of physiological arousal, so even if they say (and mean!) an enthusiastic “yes”, their body’s signs get misread as a “not really, though”, resulting in one partner feeling rejected, and both feeling inadequate—on account of something that was completely unrelated to how the person actually felt about the prospect of sex*.
*Sometimes, physiological arousal will simply not accompany psychological arousal, no matter how sincere the latter. And on the flipside, sometimes the signs of physiological arousal will just show up without psychological arousal. The human body is just like that sometimes. We all must listen to our partners’ words, not their genitals!
The solution to this problem is thus the same as the solution to the rest of the problem that is discussed in the video, and it’s: good communication.
That can be easier said than done, of course—not everyone is at their most eloquent in such situations! Which is why it can be important to have those conversations first outside of the bedroom when the stakes are low/non-existent.
Even with the best communication, a more general, overarching non-reciprocity (real or perceived) of sexual desire can cause bitterness, resentment, and can ultimately be relationship-ending if a resolution that’s acceptable to everyone involved is not found.
Ultimately, the work as a couple must begin from within as individuals—addressing self-worth issues to better navigate love and intimacy.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Relationships: When To Stick It Out & When To Call It Quits
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Mammography AI Can Cost Patients Extra. Is It Worth It?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
As I checked in at a Manhattan radiology clinic for my annual mammogram in November, the front desk staffer reviewing my paperwork asked an unexpected question: Would I like to spend $40 for an artificial intelligence analysis of my mammogram? It’s not covered by insurance, she added.
I had no idea how to evaluate that offer. Feeling upsold, I said no. But it got me thinking: Is this something I should add to my regular screening routine? Is my regular mammogram not accurate enough? If this AI analysis is so great, why doesn’t insurance cover it?
I’m not the only person posing such questions. The mother of a colleague had a similar experience when she went for a mammogram recently at a suburban Baltimore clinic. She was given a pink pamphlet that said: “You Deserve More. More Accuracy. More Confidence. More power with artificial intelligence behind your mammogram.” The price tag was the same: $40. She also declined.
In recent years, AI software that helps radiologists detect problems or diagnose cancer using mammography has been moving into clinical use. The software can store and evaluate large datasets of images and identify patterns and abnormalities that human radiologists might miss. It typically highlights potential problem areas in an image and assesses any likely malignancies. This extra review has enormous potential to improve the detection of suspicious breast masses and lead to earlier diagnoses of breast cancer.
While studies showing better detection rates are extremely encouraging, some radiologists say, more research and evaluation are needed before drawing conclusions about the value of the routine use of these tools in regular clinical practice.
“I see the promise and I hope it will help us,” said Etta Pisano, a radiologist who is chief research officer at the American College of Radiology, a professional group for radiologists. However, “it really is ambiguous at this point whether it will benefit an individual woman,” she said. “We do need more information.”
The radiology clinics that my colleague’s mother and I visited are both part of RadNet, a company with a network of more than 350 imaging centers around the country. RadNet introduced its AI product for mammography in New York and New Jersey last February and has since rolled it out in several other states, according to Gregory Sorensen, the company’s chief science officer.
Sorensen pointed to research the company conducted with 18 radiologists, some of whom were specialists in breast mammography and some of whom were generalists who spent less than 75% of their time reading mammograms. The doctors were asked to find the cancers in 240 images, with and without AI. Every doctor’s performance improved using AI, Sorensen said.
Among all radiologists, “not every doctor is equally good,” Sorensen said. With RadNet’s AI tool, “it’s as if all patients get the benefit of our very top performer.”
But is the tech analysis worth the extra cost to patients? There’s no easy answer.
“Some people are always going to be more anxious about their mammograms, and using AI may give them more reassurance,” said Laura Heacock, a breast imaging specialist at NYU Langone Health’s Perlmutter Cancer Center in New York. The health system has developed AI models and is testing the technology with mammograms but doesn’t yet offer it to patients, she said.
Still, Heacock said, women shouldn’t worry that they need to get an additional AI analysis if it’s offered.
“At the end of the day, you still have an expert breast imager interpreting your mammogram, and that is the standard of care,” she said.
About 1 in 8 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during their lifetime, and regular screening mammograms are recommended to help identify cancerous tumors early. But mammograms are hardly foolproof: They miss about 20% of breast cancers, according to the National Cancer Institute.
The FDA has authorized roughly two dozen AI products to help detect and diagnose cancer from mammograms. However, there are currently no billing codes radiologists can use to charge health plans for the use of AI to interpret mammograms. Typically, the federal Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services would introduce new billing codes and private health plans would follow their lead for payment. But that hasn’t happened in this field yet and it’s unclear when or if it will.
CMS didn’t respond to requests for comment.
Thirty-five percent of women who visit a RadNet facility for mammograms pay for the additional AI review, Sorensen said.
Radiology practices don’t handle payment for AI mammography all in the same way.
The practices affiliated with Boston-based Massachusetts General Hospital don’t charge patients for the AI analysis, said Constance Lehman, a professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School who is co-director of the Breast Imaging Research Center at Mass General.
Asking patients to pay “isn’t a model that will support equity,” Lehman said, since only patients who can afford the extra charge will get the enhanced analysis. She said she believes many radiologists would never agree to post a sign listing a charge for AI analysis because it would be off-putting to low-income patients.
Sorensen said RadNet’s goal is to stop charging patients once health plans realize the value of the screening and start paying for it.
Some large trials are underway in the United States, though much of the published research on AI and mammography to date has been done in Europe. There, the standard practice is for two radiologists to read a mammogram, whereas in the States only one radiologist typically evaluates a screening test.
Interim results from the highly regarded MASAI randomized controlled trial of 80,000 women in Sweden found that cancer detection rates were 20% higher in women whose mammograms were read by a radiologist using AI compared with women whose mammograms were read by two radiologists without any AI intervention, which is the standard of care there.
“The MASAI trial was great, but will that generalize to the U.S.? We can’t say,” Lehman said.
In addition, there is a need for “more diverse training and testing sets for AI algorithm development and refinement” across different races and ethnicities, said Christoph Lee, director of the Northwest Screening and Cancer Outcomes Research Enterprise at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The long shadow of an earlier and largely unsuccessful type of computer-assisted mammography hangs over the adoption of newer AI tools. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, “computer-assisted detection” software promised to improve breast cancer detection. Then the studies started coming in, and the results were often far from encouraging. Using CAD at best provided no benefit, and at worst reduced the accuracy of radiologists’ interpretations, resulting in higher rates of recalls and biopsies.
“CAD was not that sophisticated,” said Robert Smith, senior vice president of early cancer detection science at the American Cancer Society. Artificial intelligence tools today are a whole different ballgame, he said. “You can train the algorithm to pick up things, or it learns on its own.”
Smith said he found it “troubling” that radiologists would charge for the AI analysis.
“There are too many women who can’t afford any out-of-pocket cost” for a mammogram, Smith said. “If we’re not going to increase the number of radiologists we use for mammograms, then these new AI tools are going to be very useful, and I don’t think we can defend charging women extra for them.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
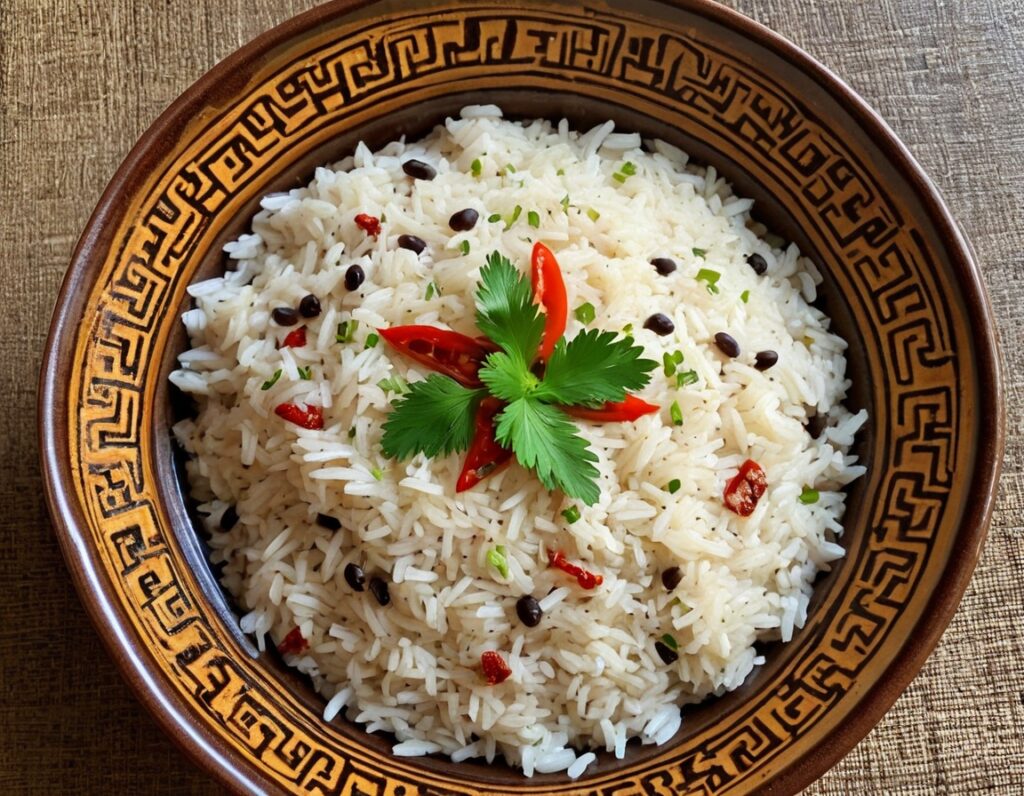
Jamaican Coconut Rice
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a great dish that can be enjoyed hot or cold, as a main or as a side. It has carbs, proteins, healthy fats, fiber, as well as an array of healthy phytochemicals. Not to mention, a great taste!
You will need
- 1 cup wholegrain basmati rice (it may also be called “brown basmati rice“; this is the same) (traditional recipe calls for pudding rice, but we’re going with the healthier option here)
- 2 cans (each 12 z / 400g) coconut milk
- 2 cups (or 2 cans, of which the drained weight is comparable to a cup each) cooked black beans. If you cook them yourself, this is better, as you will be able to cook them more al dente than you can get from a can, and this firmness is desirable. But canned is fine if that’s what’s available.
- 1 large red onion, finely chopped
- ½ cup low-sodium vegetable stock (ideally you made this yourself from vegetable offcuts you saved in the freezer for this purpose, but failing that, low-sodium stock cubes can be bought at any large supermarket)
- 2 serrano chilis, finely chopped
- 1 Scotch bonnet chili, without doing anything to it
- 1 tbsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tbsp chia seeds
- 1 tbsp coconut oil
- Garnish: parsley, chopped
Note: we have erred on the side of low-heat when it comes to the chilis. If you know that you and (if applicable) everyone else eating would enjoy more heat, add more heat. If not, let extra heat be added at the table via your hot sauce of choice. Sounds heretical, but it ensures everyone gets the right amount! It’s easy to add heat than to take it out, after all.
However: if you do end up with too much heat in this or any other dish, adding acid will usually help to neutralize that. In the case of this dish, we’d recommend lime juice as a complementary flavor.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) In a big sauté pan, add the coconut oil, melt it if not already melted, and add the chopped onion and the chopped chilis, at a temperature sufficient to sizzle. Keep them all moving. Once the coconut oil is absorbed into the onion (this will happen before the onion is fully cooked), add the vegetable stock, followed by the coconut milk; mix it all gently to create a smooth consistency.
2) Add the rice, chia seeds, and black pepper; mix it all gently but thoroughly; turn the temperature to a simmer, and add the Scotch bonnet chili, without cutting it at all.
3) Cover and keep on low for about 20–30 minutes until the rice is looking done. Check on it periodically to make sure it’s not running out of liquid, but resist the urge to stir it; it shouldn’t be burning but paradoxically, once you start stirring you can’t stop or it will definitely burn.
4) Take out the Scotch bonnet chili, and discard*. Add the black beans.
*its job was to add flavor without adding the high-level heat of that particular chili. If you’re a regular heat-fiend, feel free to experiment with using sliced Scotch bonnet chilis instead of serrano chilis; just be aware that there’s a big difference in heat. Only do this if you really like heat. Using it the way we described in the main recipe is what’s traditional in the Caribbean, by the way.
5) Now you can (and in fact must) stir, to mix in the black beans and bring them back to temperature within the dish. Be aware that once you start stirring, you need to keep stirring until you’re ready to take it off the heat.
6) Serve, adding the parsley garnish.
(this example went light on the beans; our recipe includes more for a heartier dish)
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Should You Go Light Or Heavy On Carbs?
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Burn! How To Boost Your Metabolism
- Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: