Pomegranate vs Figs – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pomegranate to figs, we picked the pomegranate.
Why?
In terms of macros, pomegranate has a lot more protein* and fiber, while the fig has more carbs. Thus, a win for pomegranate.
*Why such protein in a fruit? In both cases, it’s mostly from the seeds, which in both cases, we’re eating. However, pomegranates have a much greater seed-to-mass ratio than figs, and thus, a correspondingly higher amount of protein. Also some fats from the seeds, again more than figs, but the margin of difference is smaller, and not really enough to be of relevance.
In the category of vitamins, pomegranates lead with more of vitamins B1, B5, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while figs have more of vitamins A, B3, and B6. The largest margins of difference are in vitamins B9, E, and K, so all in pomegranate’s favor.
The minerals scene is closer to even; pomegranate has more copper, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while figs have more calcium, iron, magnesium, and manganese. Thus, a 5:4 lead for pomegranate, and the larger margins of difference are again for pomegranate.
In short, enjoy both, but pomegranates are the more nutritionally dense. Also, don’t throw away the peel! Dry it, and turn it into a powdered supplement—see our linked article below, for why:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Pomegranate’s Health Gifts Are Mostly In Its Peel
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Altered Traits – by Dr. Daniel Goleman & Dr. Richard Davidson
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We know that meditation helps people to relax, but what more than that?This book explores the available science.
We say “explore the available science”, but it’d be remiss of us not to note that the authors have also expanded the available science, conducting research in their own lab.
From stress tests and EEGs to attention tests and fMRIs, this book looks at the hard science of what different kinds of meditation do to the brain. Not just in terms of brain state, either, but gradual cumulative anatomical changes, too. Powerful stuff!
The style is very pop-science in presentation, easily comprehensible to all. Be aware though that this is an “if this, then that” book of science, not a how-to manual. If you want to learn to meditate, this isn’t the book for that.
Bottom line: if you’d like to understand more about how different kinds of meditation affect the brain differently, this is the book for you.
Share This Post
-
How gender-affirming care improves trans mental health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
In recent years, a growing number of states have passed laws restricting or banning gender-affirming care for transgender people, particularly minors. As conversations about gender-affirming care increase, so do false narratives about it, with some opponents falsely suggesting that it’s harmful to mental health.
Despite widespread attacks against gender-affirming care, research clearly shows that it improves mental health outcomes for transgender people.
Read on to learn more about what gender-affirming care is, how it benefits mental well-being, and how you can access it.
What is gender-affirming care?
Gender-affirming care describes a range of medical interventions that help align people’s bodies with their gender identities. While anyone can seek gender-affirming care in the form of laser hair removal, breast augmentation, erectile dysfunction medication, or hormone therapy, among other treatments, most conversations about gender-affirming care center around transgender people, whose gender identity or gender expression does not conform to their sex assigned at birth.
Gender-affirming care for trans people varies based on age. For example, some trans adults seek hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or gender-affirming surgeries that help their bodies match their internal sense of gender.
Trans kids entering adolescence might be prescribed puberty blockers, which temporarily delay the production of hormones that initiate puberty, to give them more time to figure out their gender identities before deciding on next steps. This is the same medication given to cisgender kids—whose gender identities match the sex they were assigned at birth—experiencing early puberty.
What is gender dysphoria?
Gender dysphoria describes a feeling of unease that some trans people experience when their perceived gender doesn’t match their gender identity. This can lead to a range of mental health conditions that affect their quality of life
Some trans people may manage gender dysphoria by wearing gender-affirming clothing, opting for a gender-affirming hairstyle, or asking others to refer to them by a name and pronouns that authentically represent them. Others may need gender-affirming care to feel at home in their bodies.
Trans people who desire gender-affirming care and have not been able to access it experience psychological distress, including depression, anxiety, self-harm, and suicidal ideation. The Trevor Project’s 2023 U.S. National Survey on the Mental Health of LGBTQ Young People found that roughly half of trans youth “seriously considered attempting suicide in the past year.”
How does gender-affirming care improve mental health?
For trans adults, gender-affirming care can alleviate gender dysphoria, which has been shown to improve both short-term and long-term mental health. A 2018 study found that trans adults who do not undergo HRT are four times more likely to experience depression than those who do, although not all trans people desire HRT.
Extensive research has shown that gender-affirming care also alleviates gender dysphoria and improves mental health outcomes in trans kids, teens, and young adults. A 2022 study found that access to HRT and puberty blockers lowered the odds of depression in trans people between the ages of 13 and 20 by 60 percent and reduced the risk of self-harm and suicidal thoughts by 73 percent.
Both the Endocrine Society—which aims to advance hormone research—and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that trans kids and teens have access to developmentally appropriate gender-affirming care.
How can I access gender-affirming care?
If you’re a trans adult seeking gender-affirming care or a guardian of a trans kid or teen who’s seeking gender-affirming care, talk to your health care provider about your options. You can find a trans-affirming provider by searching the World Professional Association for Transgender Health directory or visiting your local LGBTQ+ health center or Planned Parenthood.
Some gender-affirming care may not be covered by insurance. Learn how to make the most of your coverage from the National Center for Transgender Equality. Find insurance plans available through the Marketplace that cover gender-affirming care in some states through Out2Enroll.
Some states restrict or ban gender-affirming care. Learn about the laws in your state by visiting the Trans Legislation Tracker.
Where can trans people and their families find mental health support?
In addition to working with a trans-affirming therapist, trans people and their families can find mental health support through these free services:
- PFLAG offers resources for families and friends of LGBTQ+ people. Find a PFLAG chapter near you.
- The Trevor Project’s hotline has trained counselors who help LGBTQ+ youth in crisis. Call the TrevorLifeline 1-866-488-7386 or text START to 678-678.
- The Trans Lifeline was created by and for the trans community to support trans people in crisis. You can reach the Trans Lifeline hotline at 1-877-565-8860.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
If you or anyone you know is considering suicide or self-harm or is anxious, depressed, upset, or needs to talk, call the Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or text the Crisis Text Line at 741-741. For international resources, here is a good place to begin.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
The Art of Being Unflappable (Tricks For Daily Life)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Art of Being Unflappable
From Stoicism to CBT, thinkers through the ages have sought the unflappable life.
Today, in true 10almonds fashion, we’re going to distil it down to some concentrated essentials that we can all apply in our daily lives:
Most Common/Impactful Cognitive Distortions To Catch (And Thus Avoid)
These are like the rhetorical fallacies with which you might be familiar (ad hominem, no true Scotsman, begging the question, tu quoque, straw man, etc), but are about what goes on between your own ears, pertaining to your own life.
If we learn about them and how to recognize them, however, we can catch them before they sabotage us, and remain “unflappable” in situations that could otherwise turn disastrous.
Let’s take a look at a few:
Catastrophizing / Crystal Ball
- Distortion: not just blowing something out of proportion, but taking an idea and running with it to its worst possible conclusion. For example, we cook one meal that’s a “miss” and conclude we are a terrible cook, and in fact for this reason a terrible housewife/mother/friend/etc, and for this reason everyone will probably abandon us and would be right to do so
- Reality: by tomorrow, you’ll probably be the only one who even remembers it happened
Mind Reading
- Distortion: attributing motivations that may or may not be there, and making assumptions about other people’s thoughts/feelings. An example is the joke about two partners’ diary entries; one is long and full of feelings about how the other is surely dissatisfied in their marriage, has been acting “off” with them all day, is closed and distant, probably wants to divorce, may be having an affair and is wondering which way to jump, and/or is just wondering how to break the news—the other partner’s diary entry is short, and reads “motorcycle won’t start; can’t figure out why”
- Reality: sometimes, asking open questions is better than guessing, and much better than assuming!
All-or-Nothing Thinking / Disqualifying the Positive / Magnifying the Negative
- Distortion: having a negative bias that not only finds a cloud in every silver lining, but stretches it out so that it’s all that we can see. In a relationship, this might mean that one argument makes us feel like our relationship is nothing but strife. In life in general, it may lead us to feel like we are “naturally unlucky”.
- Reality: those negative things wouldn’t even register as negative to us if there weren’t a commensurate positive we’ve experienced to hold them in contrast against. So, find and remember that positive too.
For brevity, we put a spotlight on (and in some cases, clumped together) the ones we think have the most bang-for-buck to know about, but there are many more.
So for the curious, here’s some further reading:
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
For those with a sweet tooth, it can be challenging to indulge one’s desires while also avoiding inflammation. Happily, Dr. Jia-Yia Lui has scientific insights to share!
Dr. Liu’s Top 10
We’ll not keep them a mystery; they are:
- Grapes
- Goji berries
- Barberries
- Persimmons
- Longans
- Lychees
- Raisins¹
- Applesauce²
- Plums³
- Dates
¹Yes, these are technically also grapes, but there are enough differences that Dr. Liu tackles them separately.
²It makes a difference how it’s made, though.
³And dried plums, in other words, prunes.For more details on all of these, plus their extra benefits and relevant considerations, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- How to Prevent (or Reduce) Inflammation
- The Not-So-Sweet Science Of Sugar Addiction
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
I’m feeling run down. Why am I more likely to get sick? And how can I boost my immune system?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It has been a long winter, filled with many viruses and cost-of-living pressures, on top of the usual mix of work, study, life admin and caring responsibilities.
Stress is an inevitable part of life. In short bursts, our stress response has evolved as a survival mechanism to help us be more alert in fight or flight situations.
But when stress is chronic, it weakens the immune system and makes us more vulnerable to illnesses such as the common cold, flu and COVID.
Pexels/Ketut Subiyanto Stress makes it harder to fight off viruses
When the immune system starts to break down, a virus that would normally have been under control starts to flourish.
Once you begin to feel sick, the stress response rises, making it harder for the immune system to fight off the disease. You may be sick more often and for longer periods of time, without enough immune cells primed and ready to fight.
In the 1990s, American psychology professor Sheldon Cohen and his colleagues conducted a number of studies where healthy people were exposed to an upper respiratory infection, through drops of virus placed directly into their nose.
These participants were then quarantined in a hotel and monitored closely to determine who became ill.
One of the most important factors predicting who got sick was prolonged psychological stress.
Cortisol suppresses immunity
“Short-term stress” is stress that lasts for a period of minutes to hours, while “chronic stress” persists for several hours per day for weeks or months.
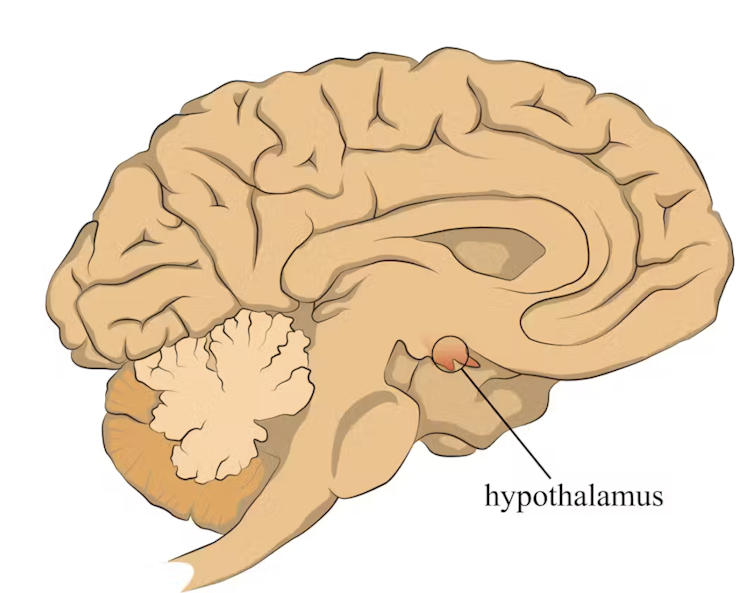
When faced with a perceived threat, psychological or physical, the hypothalamus region of the brain sets off an alarm system. This signals the release of a surge of hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol.
The hypothalamus sets off an alarm system in response to a real or perceived threat. stefan3andrei/Shutterstock In a typical stress response, cortisol levels quickly increase when stress occurs, and then rapidly drop back to normal once the stress has subsided. In the short term, cortisol suppresses inflammation, to ensure the body has enough energy available to respond to an immediate threat.
But in the longer term, chronic stress can be harmful. A Harvard University study from 2022 showed that people suffering from psychological distress in the lead up to their COVID infection had a greater chance of experiencing long COVID. They classified this distress as depression, probable anxiety, perceived stress, worry about COVID and loneliness.
Those suffering distress had close to a 50% greater risk of long COVID compared to other participants. Cortisol has been shown to be high in the most severe cases of COVID.
Stress causes inflammation
Inflammation is a short-term reaction to an injury or infection. It is responsible for trafficking immune cells in your body so the right cells are present in the right locations at the right times and at the right levels.
The immune cells also store a memory of that threat to respond faster and more effectively the next time.
Initially, circulating immune cells detect and flock to the site of infection. Messenger proteins, known as pro-inflammatory cytokines, are released by immune cells, to signal the danger and recruit help, and our immune system responds to neutralise the threat.
During this response to the infection, if the immune system produces too much of these inflammatory chemicals, it can trigger symptoms such as nasal congestion and runny nose.
Our immune response can trigger symptoms such as a runny nose. Alyona Mandrik/Shutterstock What about chronic stress?
Chronic stress causes persistently high cortisol secretion, which remains high even in the absence of an immediate stressor.
The immune system becomes desensitised and unresponsive to this cortisol suppression, increasing low-grade “silent” inflammation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (the messenger proteins).
Immune cells become exhausted and start to malfunction. The body loses the ability to turn down the inflammatory response.
Over time, the immune system changes the way it responds by reprogramming to a “low surveillance mode”. The immune system misses early opportunities to destroy threats, and the process of recovery can take longer.
So how can you manage your stress?
We can actively strengthen our immunity and natural defences by managing our stress levels. Rather than letting stress build up, try to address it early and frequently by:
1) Getting enough sleep
Getting enough sleep reduces cortisol levels and inflammation. During sleep, the immune system releases cytokines, which help fight infections and inflammation.
2) Taking regular exercise
Exercising helps the lymphatic system (which balances bodily fluids as part of the immune system) circulate and allows immune cells to monitor for threats, while sweating flushes toxins. Physical activity also lowers stress hormone levels through the release of positive brain signals.
3) Eating a healthy diet
Ensuring your diet contains enough nutrients – such as the B vitamins, and the full breadth of minerals like magnesium, iron and zinc – during times of stress has a positive impact on overall stress levels. Staying hydrated helps the body to flush out toxins.
4) Socialising and practising meditation or mindfulness
These activities increase endorphins and serotonin, which improve mood and have anti-inflammatory effects. Breathing exercises and meditation stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which calms down our stress responses so we can “reset” and reduce cortisol levels.
Sathana Dushyanthen, Academic Specialist & Lecturer in Cancer Sciences & Digital Health| Superstar of STEM| Science Communicator, The University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Radical Remission – by Dr. Kelly Turner
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this is not:an autobiographical account of the “I beat cancer and you can too” pep-talk style.
What it is: a very readable pop-science book based on the author’s own PhD research into radical remission.
She knew that a very small percentage of people experience spontaneous radical remission (or quasi-spontaneous, if the remission is attributed to lifestyle changes, and/or some alternative therapy), but a small percentage of people means a large number worldwide, so she travelled the world studying over 1,000 cases of people with late-stage cancer who had either not gone for conventional anticancer drugs, or had and then stopped, and lived to tell the tale.
While she doesn’t advocate for any particular alternative therapy, she does report on what things came to her attention. She does advocate for some lifestyle changes.
Perhaps the biggest value this book offers is in its promised “9 key factors that can make a real difference”, which are essentially her conclusions from her PhD dissertation.
There isn’t room to talk about them here in a way that wouldn’t be misleading/unhelpful for a paucity of space, so perhaps we’ll do a main feature one of these days.
Bottom line: if you have (or a loved one has) cancer, this is an incredibly sensible book to read. If you don’t, then it’s an interesting and thought-provoking book to read.
Click here to check out Radical Remission, and learn about the factors at hand!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: