Plum vs Nectarine – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing plums to nectarines, we picked the nectarines.
Why?
Both are great! But nectarines win at least marginally in each category we look at.
In terms of macros, plums have more carbs while nectarines have more fiber, resulting of course in a lower glycemic index. Plums do have a low GI also; just, nectarines have it better.
When it comes to vitamins, plums have more of vitamins A, B6, C, and K, while nectarines have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, E, and choline.
In the category of minerals, plums are great but not higher in any mineral than nectarines; nectarines meanwhile have more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc.
All in all, enjoy both. And if having dried fruit, then prunes (dried plums) are generally more widely available than dried nectarines. But if you’re choosing one fruit or the other, nectarine is the way to go.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Replacing Sugar: Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Sweet Foods
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sleep Through Insomnia – by Dr. Brandon Peters
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this is not: a guide to get better sleep tonight.
Rather, what it is: a guide to get better sleep in the near future (six weeks).
The way it delivers this is primarily Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I), in 6 weekly lessons, each divided into 3 activities:
- Reflection
- Education
- Setting goals
Now, all parts are important, but we’d say the biggest value here is in the education segment, in part because it helps the reader understand why the reflection is important, and how to usefully set the goals.
“Reflection” may sound quite wishy-washy, but in fact it is very science-based, with questions as prompts, which effectively amount to the “gathering data” part of science.
“Setting goals”, for its part, is intended to be a progressive, step-by-step approach to get you to where you want to be with your sleep.
The style is instructional pop-science, with everything made easy to understand. There are an abundance of scientific references for those who wish to delve further, and sometimes he does go into more neurological detail than a book written by a psychologist might (Dr. Peters being a medical doctor, board-certified in neurology and sleep medicine, and with extensive training in CBT-I).
Bottom line: if you’d like to sleep better and you have the will to commit to a 6-week program (which will not ask anything arduous of you, but you will need to show up for it and do the things), then this book can give you a much better long-term fix than telling you to change your sheets and put your phone away.
Click here to check out Sleep Through Insomnia, and sleep easy!
Share This Post
-
Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Toothpastes and mouthwashes: which kinds help, and which kinds harm?
You almost certainly brush your teeth. You might use mouthwash. A lot of people floss for three weeks at a time, often in January.
There are a lot of options for oral hygiene; variations of the above, and many alternatives too. This is a big topic, so rather than try to squeeze it all in one, this will be a several-part series.
For today, let’s look at toothpastes and mouthwashes, to start!
Toothpaste options
Toothpastes may contain one, some, or all of the following, so here are some notes on those:
Fluoride
Most toothpastes contain fluoride; this is generally recognized as safe though is not without its controversies. The fluoride content is the reason it’s recommended not to swallow toothpaste, though.
The fluoride in toothpaste can cause some small problems if overused; if you see unusually white patches on your teeth (your teeth are supposed to be ivory-colored, not truly white), that is probably a case of localized overcalcification because of the fluoride, and yes, you can have too much of a good thing.
Overall, the benefits are considered to far outweigh the risks, though.
Baking soda
Whether by itself or as part of a toothpaste, baking soda is a safe and effective choice, not just for cosmetic purposes, but for boosting genuine oral hygiene too:
- Enhanced plaque removal to improve gingival health: 3-month randomized clinical study of the effects of baking soda toothpaste on plaque and gingivitis
- The effects of two baking-soda toothpastes in enhancing mechanical plaque removal and improving gingival health: A 6-month randomized clinical study
- The efficacy of baking soda dentifrice in controlling plaque and gingivitis: A systematic review
Activated charcoal
Activated charcoal is great at removing many chemicals from things it touches. That includes the kind you might see on your teeth in the form of stains.
A topical aside on safety: activated charcoal is a common ingredient in a lot of black-colored Halloween-themed foods and drinks around this time of year. Beware, if you ingest these, there’s a good chance of it also cleaning out any meds you are taking. Ask your pharmacist about your own personal meds, but meds that (ingested) activated charcoal will usually remove include:
- Oral HRT / contraceptives
- Antidepressants (many kinds)
- Heart medications (at least several major kinds)
Toothpaste, assuming you are spitting-not-swallowing, won’t remove your medications though. Nor, in case you were worrying, will it strip tooth enamel, even if you have extant tooth enamel erosion:
Source: Activated charcoal toothpastes do not increase erosive tooth wear
However, it’s of no special extra help when it comes to oral hygiene itself, just removing stains.
So, if you’d like to use it for cosmetic reasons, go right ahead. If not, no need.
Hydrogen peroxide
This is generally not a good idea, speaking for the health. For whitening, yes, it works. But for health, not so much:
To be clear, when they say “alter”, they mean “in a bad way”. It increases inflammation and tissue damage.
If buying commercially-available whitening toothpaste made with hydrogen peroxide, the academic answer is that it’s a lottery, because brands’ proprietorial compounding processes vary widely and constantly with little oversight and even less transparency:
Is whitening toothpaste safe for dental health?: RDA-PE method
Mouthwash options
In the case of fluoride and hydrogen peroxide, the same advice (for and against) goes as per toothpaste.
Alcohol
There has been some concern about the potential carcinogenic effect of alcohol-based mouthwashes. According to the best current science, this one’s not an easy yes-or-no, but rather:
- If there are no other cancer risk factors, it does not seem to increase cancer risk
- If there are other cancer risk factors, it does make the risk worse
Read more:
- Does the use of alcohol mouthwash increase the risk of developing oral cancer?
- Alcohol-based mouthwash as a risk factor of oral cancer: A systematic review
Non-Alcohol
Non-alcoholic mouthwashes are not without their concerns either. In this case, the potential problem is changing the oral microbiome (we are supposed to have one!), and specifically, that the spread of what it kills and what it doesn’t may result in an imbalance that causes a lowering of the pH of the mouth.
Put differently: it makes your saliva more acidic.
Needless to say, that can cause its own problems for teeth. The research on this is still emerging, with regard to whether the benefits outweigh the problems, but the fact that it has this effect seems to be a consensus. Here’s an example paper; there are others:
Effects of Chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome
Flossing, scraping, and alternatives
These are important (and varied, and interesting) enough to merit their own main feature, rather than squeezing them in at the end.
So, watch this space for a main feature on these soon!
Share This Post
-
The Vagina Bible – by Dr. Jen Gunter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The vagina is mysterious to most men, and honestly, also to a lot of women. School education on this is minimal, if even extant, and as an adult, everyone’s expected to “just know” stuff. However, here in reality, that isn’t how knowledge works.
To remedy this, gynecologist Dr. Jen Gunter takes 432 pages to give us the low-down and the ins-and-outs of this remarkable organ that affects, and is affected by, a lot of the rest of our health.
(On which note, if you think you already know it, ask yourself: could you write 432 pages about it? If not, you’ll probably still learn some things from this book)
Stylistically, this book is more of a textbook in presentation, but the writing is still very much easy-reading. The focus is mostly on anatomy and physiology, though she does give due attention to relevant healthcare options; what’s good, what’s bad, and what’s just plain unnecessary. In such cases, she always has plenty of science to hand; it’s never just “one woman’s opinion”.
If the book has a downside, it’s that (based on other reviews) it seems to upset some readers with unwelcome truths, but that’s more in the vein of “she’s right, of course, but I didn’t like reading it”.
Bottom line: if you have a vagina, or spend any amount of time in close proximity to one, then this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out The Vagina Bible, and upgrade your knowledge!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The “Love Drug”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Get PEA-Brained!
Today we’ll be looking at phenylethylamine, or PEA, to its friends.
Not to be mistaken for the related amino acid phenylalanine! Both ultimately have effects on the dopaminergic system, but the process and benefits are mostly quite different.
We thought we’d do this one in the week of Valentine’s Day, because of its popular association with love:
❝Phenylethylamine (PEA), an amphetamine-like substance that has been alluringly labeled the “chemical of love,” makes the best case for the love-chocolate connection since it has been shown that people in love may actually have higher levels of PEA in their brain, as surmised from the fact that their urine is richer in a metabolite of this compound. In other words, people thrashing around in the throes of love pee differently from others.❞
Source: Office for Science and Society | The Chemical of Love
What is it?
It’s an amino acid. Because we are mammals, we can synthesize it inside our bodies, so it’s not considered an “essential amino acid”, i.e. one that we need to get from our diet. It is found in some foods, though, including:
- Other animals, especially other mammals
- Various beans, legumes, nuts, seeds. In particular almonds, soybeans, lentils, and chickpeas score highly
- Fermented foods
- Chocolate (popular lore holds this to be a good source of PEA; science finds it to be a fair option, but not in the same ballpark as the other items)
Fun fact: the reason Marvel’s Venom has a penchant for eating humans and chocolate is (according to the comics) because phenylethylamine is an essential amino acid for it.
What does it do for us?
It’s a Central Nervous System (CNS) stimulant, and also helps us synthesize critical neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine (adrenaline) and serotonin:
It works similarly, but not identically, to amphetamines:
Is it safe?
We normally do this after the benefits, but “it works similarly to amphetamines” may raise an eyebrow or two, so let’s do it here:
- It is recommended to take no more than 500mg/day, with 100mg–500mg being typical doses
- It is not recommended to take it at all if you have, or have a predisposition to, any kind of psychotic disorder (especially schizophrenia, or bipolar disorder wherein you sometimes experience mania)
- This isn’t a risk for most people, but if you fall into the above category, the elevated dopamine levels could nudge you into a psychotic/manic episode that you probably don’t want.
See for example: Does phenylethylamine cause schizophrenia?
There are other contraindications too, so speak with your doctor/pharmacist before trying it.
On the other hand, if you are considering ADHD medication, then phenylethylamine could be a safer thing to try first, to see if it helps, before going to the heavy guns of actual amphetamines (as are commonly prescribed for ADHD). Same goes for depression and antidepressants.
What can I expect from PEA?
More dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Mostly the former two. Which means, you can expect stimulation.
For focus and attention, it’s so effective that it has been suggested (as we mentioned above) as a safer alternative to ADHD meds:
β-phenylethylamine, a small molecule with a large impact
…and may give similar benefits to people without ADHD, namely improved focus, attention, and mental stamina:
It also improves mood:
❝Phenylethylamine (PEA), an endogenous neuroamine, increases attention and activity in animals and has been shown to relieve depression in 60% of depressed patients. It has been proposed that PEA deficit may be the cause of a common form of depressive illness.
Effective dosage did not change with time. There were no apparent side effects. PEA produces sustained relief of depression in a significant number of patients, including some unresponsive to the standard treatments. PEA improves mood as rapidly as amphetamine but does not produce tolerance.❞
Source: Sustained antidepressant effect of PEA replacement
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it, but here is an example product on Amazon for your convenience 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Who Screens The Sunscreens?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Screen The Sunscreens!
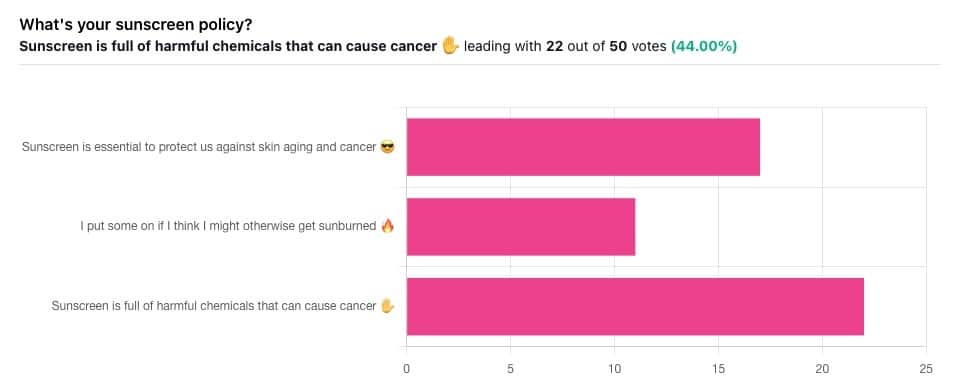
Yesterday, we asked you what your sunscreen policy was, and got a spread of answers. Apparently this one was quite polarizing!
One subscriber who voted for “Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer” wrote:
❝My mom died of complications from melanoma, so we are vigilant about sun and sunscreen. We are a family of campers and hikers and gardeners—outdoors in all seasons—and we never burn❞
Our condolences with regard to your mom! Life is so precious, and when something like that happens, it tends to stick with us. We’re glad you and your family are taking care of yourselves.
Of the subscribers who voted for “I put some on if I think I might otherwise get sunburned”, about half wrote to express uncertainties:
- uncertainty about how safe it is, and
- uncertainty about how helpful it is
…so we’re going to tackle those questions in a moment. But what of those who voted for “Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer”?
Of those, only one wrote a message, which was to say one has to be very careful of what is in the formula.
Let’s take a look, then…
Sunscreen is full of harmful chemicals that can cause cancer: True or False?
False—according to current best science. Research is ongoing!
There are four main chemicals (found in most sunscreens) that people tend to worry about:
- Abobenzone
- Oxybenzone
- Octocrylene
- Ecamsule
Now, these two sound like four brands of rocket fuel, but then, dihydrogen monoxide (DHMO), which is also found in most sunscreens, sounds like a deadly toxin too. That’s water, by the way.
But what of these four chemicals? Well, as we say, research is ongoing, but we found a study that measured all four, to see how much got into the blood, and what adverse effects, if any, this caused.
We’ll skip to their conclusion:
❝In this preliminary study involving healthy volunteers, application of 4 commercially available sunscreens under maximal use conditions resulted in plasma concentrations that exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens. The systemic absorption of sunscreen ingredients supports the need for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings. These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.❞
Now, “exceeded the threshold established by the FDA for potentially waiving some nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens” sounds alarming, so why did they close with the words “These results do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen”?
Let’s skip back up to a line from the results:
❝The most common adverse event was rash, which developed in 1 participant with each sunscreen.❞
This was most probably due to the oxybenzone, which can cause allergic skin reactions in some people.
Let us take a moment to remember the most common adverse event that occurs from not wearing sunscreen: sunburn!
You can read the full study here:
None of those ingredients have been found to be carcinogenic, even at the maximal blood plasma concentrations studied, from applications 4x/day to 75% of the body.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are absolutely very much known to cause cancer, and the effect is cumulative.
Sunscreen is essential to protect us against skin aging and cancer: True or False?
True, unequivocally, unless we live indoors and/or otherwise never go about under sunlight.
“But our ancestors—” lived under the same sun we do, and either used sunscreen or got advanced skin aging and cancer.
Sunscreen of times past ranged from mud to mineral lotions, but it’s pretty much always existed. Even non-human animals that have skin and don’t have fur or feathers, tend to take mud-baths in sunny parts of the world.
If you’d like to avoid oxybenzone and other chemicals, though, you might have your reasons. Maybe you’re allergic, or maybe you read that it’s a potential endocrine disruptor with estrogen-like and anti-androgenic properties that you don’t want.
There are other options, to include physical blockers containing zinc and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective ingredients.
If you’re interested, you can even make your own sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB rays (UVA is what causes skin cancer; UVB is “milder” and is what causes sunburn):
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Truth About Chocolate & Skin Health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? We love to hear from you!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝What’s the science on chocolate and acne? Asking for a family member❞
The science is: these two things are broadly unrelated to each other.
There was a very illustrative study done specifically for this, though!
❝65 subjects with moderate acne ate either a bar containing ten times the amount of chocolate in a typical bar, or an identical-appearing bar which contained no chocolate. Counting of all the lesions on one side of the face before and after each ingestion period indicated no difference between the bars.
Five normal subjects ingested two enriched chocolate bars daily for one month; this represented a daily addition of the diet of 1,200 calories, of which about half was vegetable fat. This excessive intake of chocolate and fat did not alter the composition or output of sebum.
A review of studies purporting to show that diets high in carbohydrate or fat stimulate sebaceous secretion and adversely affect acne vulgaris indicates that these claims are unproved.❞
Source: Effect of Chocolate on Acne Vulgaris
As for what might help against acne more than needlessly abstaining from chocolate:
Why Do We Have Pores, And Could We Not?
…as well as:
Of Brains & Breakouts: The Neuroscience Of Your Skin
And here are some other articles that might interest you about chocolate:
- Chocolate & Health: Fact or Fiction?
- The “Love Drug”: Get PEA-Brained!
- Enjoy Bitter Foods For Your Heart & Brain
Enjoy! And while we have your attention… Would you like this section to be bigger? If so, send us more questions!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: