Healthiest-Three-Nut Butter
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’re often telling you to “diversify your nuts”, so here’s a great way to get in three at once with no added sugar, palm oil, or preservatives, and only the salt you choose to put in. We’ve picked three of the healthiest nuts around, but if you happen to be allergic, don’t worry, we’ve got you covered too.
You will need
- 1 cup almonds (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. chia, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 cup walnuts (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. pumpkin, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 cup pistachios (if allergic, substitute a seed, e.g. poppy, and make it ½ cup)
- 1 tbsp almond oil (if allergic, substitute extra virgin olive oil) (if you prefer sweet nut butter, substitute 1 tbsp maple syrup; the role here is to emulsify the nuts, and this will do the same job)
- Optional: ¼ tsp MSG or ½ tsp low-sodium salt
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1a) If using nuts, heat your oven to 350℉ / 180℃. Place the nuts on a baking tray lined with baking paper, and bake/roast for about 10 minutes, but keep an eye on it to ensure the nuts don’t burn, and jiggle them if necessary to ensure they toast evenly. Once done, allow to cool.
1b) If using seeds, you can either omit that step, or do the same for 5 minutes if you want to, but really it’s not necessary.
2) Blend all ingredients (nuts/seeds, oil, MSG/salt) in a high-speed blender. Note: this will take about 10 minutes in total, and we recommend you do it in 30-second bursts so as to not overheat the motor. You also may need to periodically scrape the mixture down the side of the blender, to ensure a smooth consistency.
3) Transfer to a clean jar, and enjoy at your leisure:

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- Sesame Seeds vs Poppy Seeds – Which is Healthier?
- If You’re Not Taking Chia, You’re Missing Out
- Sea Salt vs MSG – Which is Healthier?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Managing Jealousy
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Jealousy is often thought of as a young people’s affliction, but it can affect us at any age—whether we are the one being jealous, or perhaps a partner.
And, the “green-eyed monster” can really ruin a lot of things; relationships, friendships, general happiness, physical health even (per stress and anxiety and bad sleep), and more.
The thing is, jealousy looks like one thing, but is actually mostly another.
Jealousy is a Scooby-Doo villain
That is to say: we can unmask it and see what much less threatening thing is underneath. Which is usually nothing more nor less than: insecurities
- Insecurity about losing one’s partner
- Insecurity about not being good enough
- Insecurity about looking bad socially
…etc. The latter, by the way, is usually the case when one’s partner is socially considered to be giving cause for jealousy, but the primary concern is not actually relational loss or any kind of infidelity, but rather, looking like one cannot keep one’s partner’s full attention romantically/sexually. This drives a lot of people to act on jealousy for the sake of appearances, in situations where they might otherwise, if they didn’t feel like they’d be adversely judged for it, be considerably more chill.
Thus, while monogamy certainly has its fine merits, there can also be a kind of “toxic monogamy” at hand, where a relationship becomes unhealthy because one partner is just trying to live up to social expectations of keeping the other partner in check.
This, by the way, is something that people in polyamorous and/or open relationships typically handle quite neatly, even if a lot of the following still applies. But today, we’re making the statistically safe assumption of a monogamous relationship, and talking about that!
How to deal with the social aspect
If you sit down with your partner and work out in advance the acceptable parameters of your relationship, you’ll be ahead of most people already. For example…
- What counts as cheating? Is it all and any sex acts with all and any people? If not, where’s the line?
- What about kissing? What about touching other body parts? If there are boundaries that are important to you, talk about them. Nothing is “too obvious” because it’s astonishing how many times it will happen that later someone says (in good faith or not), “but I thought…”
- What about being seen in various states of undress? Or seeing other people in various states of undress?
- Is meaningless flirting between friends ok, and if so, how do we draw the line with regard to what is meaningless? And how are we defining flirting, for that matter? Talk about it and ensure you are both on the same page.
- If a third party is possibly making moves on one of us under the guise of “just being friendly”, where and how do we draw the line between friendliness and romantic/sexual advances? What’s the difference between a lunch date with a friend and a romantic meal out for two, and how can we define the difference in a way that doesn’t rely on subjective “well I didn’t think it was romantic”?
If all this seems like a lot of work, please bear in mind, it’s a lot more fun to cover this cheerfully as a fun couple exercise in advance, than it is to argue about it after the fact!
See also: Boundary-Setting Beyond “No”
How to deal with the more intrinsic insecurities
For example, when jealousy is a sign of a partner fearing not being good enough, not measuring up, or perhaps even losing their partner.
The key here might not shock you: communication
Specifically, reassurance. But critically, the correct reassurance!
A partner who is jealous will often seek the wrong reassurance, for example wanting to read their partner’s messages on their phone, or things like that. And while a natural desire when experiencing jealousy, it’s not actually helpful. Because while incriminating messages could confirm infidelity, it’s impossible to prove a negative, and if nothing incriminating is found, the jealous partner can just go on fearing the worst regardless. After all, their partner could have a burner phone somewhere, or a hidden app for cheating, or something else like that. So, no reassurance can ever be given/gained by such requests (which can also become unpleasantly controlling, which hopefully nobody wants).
A quick note on “if you have nothing to fear, you have nothing to hide”: rhetorically that works, but practically it doesn’t.
Writer’s example: when my late partner and I formalized our relationship, we discussed boundaries, and I expressed “so far as I am concerned, I have no secrets from you, except secrets that are not mine to share. For example, if someone has confided in me and asked that I not share it, I won’t. Aside from that, you have access-all-areas in my life; me being yours has its privileges” and this policy itself would already pre-empt any desire to read my messages.
Now indeed, I had nothing to hide. I am by character devoted to a fault. But my friends may well sometimes have things they don’t want me to share, which made that a necessary boundary to highlight (which my partner, an absolute angel by the way and not prone to unhealthy manifestations of jealousy in any case, understood completely).
So, it is best if the partner of a jealous person can explain the above principles as necessary, and offer the correct reassurance instead. Which could be any number of things, but for example:
- I am yours, and nobody else has a chance
- I fully intend to stay with you for life
- You are the best partner I have ever had
- Being with you makes my life so much better
…etc. Note that none of these are “you don’t have to worry about so-and-so”, or “I am not cheating on you”, etc, because it’s about yours and your partner’s relationship. If they ask for reassurances with regard to other people or activities, by all means state them as appropriate, but try to keep the focus on you two.
And if your partner (or you, if it’s you who’s jealous) can express the insecurity in the format…
“I’m afraid of _____ because _____”
…then the “because” will allow for much more specific reassurance. We all have insecurities, we all have reasons we might fear not being good enough for our partner, or losing their affection, and the best thing we can do is choose to trust our partners at least enough to discuss those fears openly with each other.
See also: Save Time With Better Communication ← this can avoid a lot of time-consuming arguments
What about if the insecurity is based in something demonstrably correct?
By this we mean, something like a prior history of cheating, or other reasons for trust issues. In such a case, the jealous partner may well have a reason for their jealousy that isn’t based on a personal insecurity.
In our previous article about boundaries, we talked about relationships (romantic or otherwise) having a “price of entry”. In this case, you each have a “price of entry”:
- The “price of entry” to being with the person who has previously cheated (or similar), is being able to accept that.
- And for the person who cheated (or similar), very likely their partner will have the “price of entry” of “don’t do that again, and also meanwhile accept in good grace that I might be jittery about it”.
And, if the betrayal of trust was something that happened between the current partners in the current relationship, most likely that was also traumatic for the person whose trust was betrayed. Many people in that situation find that trust can indeed be rebuilt, but slowly, and the pain itself may also need treatment (such as therapy and/or couples therapy specifically).
See also: Relationships: When To Stick It Out & When To Call It Quits ← this covers both sides
And finally, to finish on a happy note:
Only One Kind Of Relationship Promotes Longevity This Much!
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Doctors Are as Vulnerable to Addiction as Anyone. California Grapples With a Response
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
BEVERLY HILLS, Calif. — Ariella Morrow, an internal medicine doctor, gradually slid from healthy self-esteem and professional success into the depths of depression.
Beginning in 2015, she suffered a string of personal troubles, including a shattering family trauma, marital strife, and a major professional setback. At first, sheer grit and determination kept her going, but eventually she was unable to keep her troubles at bay and took refuge in heavy drinking. By late 2020, Morrow could barely get out of bed and didn’t shower or brush her teeth for weeks on end. She was up to two bottles of wine a day, alternating it with Scotch whisky.
Sitting in her well-appointed home on a recent autumn afternoon, adorned in a bright lavender dress, matching lipstick, and a large pearl necklace, Morrow traced the arc of her surrender to alcohol: “I’m not going to drink before 5 p.m. I’m not going to drink before 2. I’m not going to drink while the kids are home. And then, it was 10 o’clock, 9 o’clock, wake up and drink.”
As addiction and overdose deaths command headlines across the nation, the Medical Board of California, which licenses MDs, is developing a new program to treat and monitor doctors with alcohol and drug problems. But a fault line has appeared over whether those who join the new program without being ordered to by the board should be subject to public disclosure.
Patient advocates note that the medical board’s primary mission is “to protect healthcare consumers and prevent harm,” which they say trumps physician privacy.
The names of those required by the board to undergo treatment and monitoring under a disciplinary order are already made public. But addiction medicine professionals say that if the state wants troubled doctors to come forward without a board order, confidentiality is crucial.
Public disclosure would be “a powerful disincentive for anybody to get help” and would impede early intervention, which is key to avoiding impairment on the job that could harm patients, said Scott Hambleton, president of the Federation of State Physician Health Programs, whose core members help arrange care and monitoring of doctors for substance use disorders and mental health conditions as an alternative to discipline.
But consumer advocates argue that patients have a right to know if their doctor has an addiction. “Doctors are supposed to talk to their patients about all the risks and benefits of any treatment or procedure, yet the risk of an addicted doctor is expected to remain a secret?” Marian Hollingsworth, a volunteer advocate with the Patient Safety Action Network, told the medical board at a Nov. 14 hearing on the new program.
Doctors are as vulnerable to addiction as anyone else. People who work to help rehabilitate physicians say the rate of substance use disorders among them is at least as high as the rate for the general public, which the federal Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration put at 17.3% in a Nov. 13 report.
Alcohol is a very common drug of choice among doctors, but their ready access to pain meds is also a particular risk.
“If you have an opioid use disorder and are working in an operating room with medications like fentanyl staring you down, it’s a challenge and can be a trigger,” said Chwen-Yuen Angie Chen, an addiction medicine doctor who chairs the Well-Being of Physicians and Physicians-in-Training Committee at Stanford Health Care. “It’s like someone with an alcohol use disorder working at a bar.”
From Pioneer to Lagger
California was once at the forefront of physician treatment and monitoring. In 1981, the medical board launched a program for the evaluation, treatment, and monitoring of physicians with mental illness or substance use problems. Participants were often required to take random drug tests, attend multiple group meetings a week, submit to work-site surveillance by colleagues, and stay in the program for at least five years. Doctors who voluntarily entered the program generally enjoyed confidentiality, but those ordered into it by the board as part of a disciplinary action were on the public record.
The program was terminated in 2008 after several audits found serious flaws. One such audit, conducted by Julianne D’Angelo Fellmeth, a consumer interest lawyer who was chosen as an outside monitor for the board, found that doctors in the program were often able to evade the random drug tests, attendance at mandatory group therapy sessions was not accurately tracked, and participants were not properly monitored at work sites.
Today, MDs who want help with addiction can seek private treatment on their own or in many cases are referred by hospitals and other health care employers to third parties that organize treatment and surveillance. The medical board can order a doctor on probation to get treatment.
In contrast, the California licensing boards of eight other health-related professions, including osteopathic physicians, registered nurses, dentists, and pharmacists, have treatment and monitoring programs administered under one master contract by a publicly traded company called Maximus Inc. California paid Maximus about $1.6 million last fiscal year to administer those programs.
When and if the final medical board regulations are adopted, the next step would be for the board to open bidding to find a program administrator.
Fall From Grace
Morrow’s troubles started long after the original California program had been shut down.
The daughter of a prominent cosmetic surgeon, Morrow grew up in Palm Springs in circumstances she describes as “beyond privileged.” Her father, David Morrow, later became her most trusted mentor.
But her charmed life began to fall apart in 2015, when her father and mother, Linda Morrow, were indicted on federal insurance fraud charges in a well-publicized case. In 2017, the couple fled to Israel in an attempt to escape criminal prosecution, but later they were both arrested and returned to the United States to face prison sentences.
The legal woes of Morrow’s parents, later compounded by marital problems related to the failure of her husband’s business, took a heavy toll on Morrow. She was in her early 30s when the trouble with her parents started, and she was working 16-hour days to build a private medical practice, with two small children at home. By the end of 2019, she was severely depressed and turning increasingly to alcohol. Then, the loss of her admitting privileges at a large Los Angeles hospital due to inadequate medical record-keeping shattered what remained of her self-confidence.
Morrow, reflecting on her experience, said the very strengths that propel doctors through medical school and keep them going in their careers can foster a sense of denial. “We are so strong that our strength is our greatest threat. Our power is our powerlessness,” she said. Morrow ignored all the flashing yellow lights and even the red light beyond which serious trouble lay: “I blew through all of it, and I fell off the cliff.”
By late 2020, no longer working, bedridden by depression, and drinking to excess, she realized she could no longer will her way through: “I finally said to my husband, ‘I need help.’ He said, ‘I know you do.’”
Ultimately, she packed herself off to a private residential treatment center in Texas. Now sober for 21 months, Morrow said the privacy of the addiction treatment she chose was invaluable because it shielded her from professional scrutiny.
“I didn’t have to feel naked and judged,” she said.
Morrow said her privacy concerns would make her reluctant to join a state program like the one being considered by the medical board.
Physician Privacy vs. Patient Protection
The proposed regulations would spare doctors in the program who were not under board discipline from public disclosure as long as they stayed sober and complied with all the requirements, generally including random drug tests, attendance at group sessions, and work-site monitoring. If the program put a restriction on a doctor’s medical license, it would be posted on the medical board’s website, but without mentioning the doctor’s participation in the program.
Yet even that might compromise a doctor’s career since “having a restricted license for unspecified reasons could have many enduring personal and professional implications, none positive,” said Tracy Zemansky, a clinical psychologist and president of the Southern California division of Pacific Assistance Group, which provides support and monitoring for physicians.
Zemansky and others say doctors, just like anyone else, are entitled to medical privacy under federal law, as long as they haven’t caused harm.
Many who work in addiction medicine also criticized the proposed new program for not including mental health problems, which often go hand in hand with addiction and are covered by physician health programs in other states.
“To forgo mental health treatment, I think, is a grave mistake,” Morrow said. For her, depression and alcoholism were inseparable, and the residential program she attended treated her for both.
Another point of contention is money. Under the current proposal, doctors would bear all the costs of the program.
The initial clinical evaluation, plus the regular random drug tests, group sessions, and monitoring at their work sites could cost participants over $27,000 a year on average, according to estimates posted by the medical board. And if they were required to go for 30-day inpatient treatment, that would add an additional $40,000 — plus nearly $36,000 in lost wages.
People who work in the field of addiction medicine believe that is an unfair burden. They note that most programs for physicians in other states have outside funding to reduce the cost to participants.
“The cost should not be fully borne by the doctors, because there are many other people that are benefiting from this, including the board, malpractice insurers, hospitals, the medical association,” said Greg Skipper, a semi-retired addiction medicine doctor who ran Alabama’s state physician health program for 12 years. In Alabama, he said, those institutions contribute to the program, significantly cutting the amount doctors have to pay.
The treatment program that Morrow attended in spring of 2021, at The Menninger Clinic in Houston, cost $80,000 for a six-week stay, which was covered by a concerned family member. “It saved my life,” she said.
Though Morrow had difficulty maintaining her sobriety in the first year after treatment, she has now been sober since April 2, 2022. These days, Morrow regularly attends therapy and Alcoholics Anonymous and has pivoted to become an addiction medicine doctor.
“I am a better doctor today because of my experience — no question,” Morrow said. “I am proud to be a doctor who’s an alcoholic in recovery.”
This article was produced by KFF Health News, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Share This Post
-
The Spice Of Life
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Have a question or a request? You can always hit “reply” to any of our emails, or use the feedback widget at the bottom!
In cases where we’ve already covered something, we might link to what we wrote before, but will always be happy to revisit any of our topics again in the future too—there’s always more to say!
As ever: if the question/request can be answered briefly, we’ll do it here in our Q&A Thursday edition. If not, we’ll make a main feature of it shortly afterwards!
So, no question/request too big or small
❝Great newsletter. Am taking turmeric for inflammation of hips and feet. Works like magic. Would like to know how it works, and what tumeric is best combined with – also whether there any risks in longterm use.❞
Glad you’re enjoying! As for turmeric, it sure is great, isn’t it? To answer your questions in a brief fashion:
- How it works: it does a lot of things, but perhaps its most key feature is its autoxidative metabolites that mediate its anti-inflammatory effect. Thus, it slows or inhibits oxidative stress that would otherwise cause inflammation, increase cancer risk, and advance aging.
- Best combined with: black pepper
- Any risks in long-term use: there are no known risks in long-term use ← that’s just one study, but there are lots. Some studies were prompted by reported hepatotoxicity of curcumin supplements, but a) the reports themselves seem to be without evidence b) the reported hepatoxicity was in relation to contaminants in the supplements, not the curcumin itself c) clinical trials were unable to find any hepatotoxicity (or other) risks anyway. Here’s an example of such a study.
You might also like our previous main feature: Why Curcumin (Turmeric) Is Worth Its Weight In Gold
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Astaxanthin: Super-Antioxidant & Neuroprotectant
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Think Pink For Brain Health!
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid that’s found in:
- certain marine microalgae
- tiny crustaceans that eat the algae
- fish (and flamingos!) that eat the crustaceans
Yes, it’s the one that makes things pink.
But it does a lot more than that…
Super-antioxidant
Move over, green tea! Astaxanthin has higher antioxidant activity than most carotenoids. For example, it is 2–5 times more effective than alpha-carotene, lutein, beta-carotene, and lycopene:
Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids
We can’t claim credit for naming it a super-antioxidant though, because:
Astaxanthin: A super antioxidant from microalgae and its therapeutic potential
Grow new brain cells
Axtaxanthin is a neuroprotectant, but that’s to be expected from something with such a powerful antioxidant ability.
What’s more special to astaxanthin is that it assists continued adult neurogenesis (creation of new brain cells):
❝The unique chemical structure of astaxanthin enables it to cross the blood-brain barrier and easily reach the brain, where it may positively influence adult neurogenesis.
Furthermore, astaxanthin appears to modulate neuroinflammation by suppressing the NF-κB pathway, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and limiting neuroinflammation associated with aging and chronic microglial activation.
By modulating these pathways, along with its potent antioxidant properties, astaxanthin may contribute to the restoration of a healthy neurogenic microenvironment, thereby preserving the activity of neurogenic niches during both normal and pathological aging. ❞
That first part is very important, by the way! There are so many things that our brain needs, and we can eat, but the molecules are unable to pass the blood-brain barrier, meaning they either get wasted, or used elsewhere, or dismantled for their constituent parts. In this case, it zips straight into the brain instead.
See also:
How To Grow New Brain Cells (At Any Age)
(Probably) good for the joints, too
First, astaxanthin got a glowing report in a study we knew not to trust blindly:
…and breathe. What a title that was! But, did you catch why it’s not to be trusted blindly? It was down at the bottom…
❝Conflict of interest statement
NOVAREX Co., Ltd. funded the study. Valensa International provided the FlexPro MD® ingredients, and NOVAREX Co., Ltd. encapsulated the test products (e.g., both FlexPro MD® and placebo)❞
Studies where a supplement company funded the study are not necessarily corrupt, but they can certainly sway publication bias, i.e. the company funds a bunch of studies and then pulls funding from the ones that aren’t going the way it wants.
So instead let’s look at:
Astaxanthin attenuates joint inflammation induced by monosodium urate crystals
and
Astaxanthin ameliorates cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis
…which had no such conflicts of interest.
They agree that astaxanthin indeed does the things (attenuates joint inflammation & ameliorates cartilage damage).
However, they are animal studies (rats), so we’d like to see studies with humans to be able to say for sure how much it helps these things.
Summary of benefits
Based on the available research, astaxanthin…
- is indeed a super-antioxidant
- is a neuroprotective agent
- also assists adult neurogenesis
- is probablygood for joints too
How much do I take, and is it safe?
A 2019 safety review concluded:
❝Recommended or approved doses varied in different countries and ranged between 2 and 24 mg.
We reviewed 87 human studies, none of which found safety concerns with natural astaxanthin supplementation, 35 with doses ≥12 mg/day.❞
Source: Astaxanthin: How much is too much? A safety review
In short: for most people, it’s very safe and well-tolerated. If you consume it to an extreme, you will likely turn pink, much as you would turn orange if you did the same thing with carrots. But aside from that, the risks appear to be minimal.
However! If you have a seafood allergy, please take care to get a supplement that’s made from microalgae, not one that’s made from krill or other crustaceans, or from other creatures that eat those.
Where can I get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ketogenic Diet: Burning Fat Or Burning Out?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
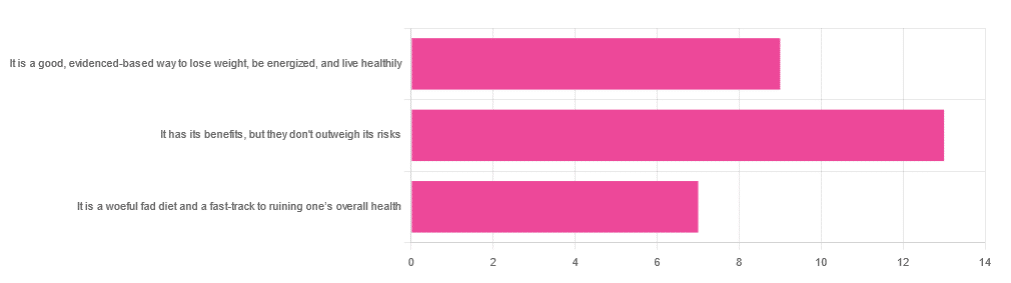
In Wednesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your opinion of the keto diet, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- About 45% said “It has its benefits, but they don’t outweigh the risks”
- About 31% said “It is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily”
- About 24% said “It is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health”
So what does the science say?
First, what is the ketogenic diet?
There are two different stories here:
- Per science, it’s a medical diet designed to help treat refractory epilepsy in children.
- Per popular lore, it’s an energizing weight loss diet for Instagrammers and YouTubers.
Can it be both? The answer is: yes, but with some serious caveats, which we’ll cover over the course of today’s feature.
The ketogenic diet works by forcing the body to burn fat for energy: True or False?
True! This is why it helps for children with refractory epilepsy. By starving the body (including the brain) of glucose, the liver must convert fat into fatty acids and ketones, which latter the brain (and indeed the rest of the body) can now use for energy instead of glucose, thus avoiding one of the the main triggers of refractory epilepsy in children.
See: The Ketogenic Diet: One Decade Later | Pediatrics
Even the pediatric epilepsy studies, however, conclude it does have unwanted side effects, such as kidney stones, constipation, high cholesterol, and acidosis:
Source: Dietary Therapies for Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet is good for weight loss: True or False?
True! Insofar as it does cause weight loss, often rapidly. Of course, so do diarrhea and vomiting, but these are not usually held to be healthy methods of weight loss. As for keto, a team of researchers recently concluded:
❝As obesity rates in the populace keep rising, dietary fads such as the ketogenic diet are gaining traction.
Although they could help with weight loss, this study had a notable observation of severe hypercholesterolemia and increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among the ketogenic diet participants.❞
~ Dr. Shadan Khdher et al.
On which note…
The ketogenic diet is bad for the heart: True or False?
True! As Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz concluded recently:
❝In terms of cardiovascular mortality, the low-carb pattern is more beneficial than very low-carbohydrate (including the ketogenic diet). There is still scarce evidence comparing ketogenic to the Mediterranean diet.
Other safety concerns in cardiovascular patients such as adverse events related to ketosis, fat-free mass loss, or potential pharmacological interactions should be also taken into consideration in future research.❞
~ Dr. Joanna Popiolek-Kalisz
Read in full: Ketogenic diet and cardiovascular risk: state of the art review
The ketogenic diet is good for short-term weight loss, but not long-term maintenance: True or False?
True! Again, insofar as it works in the short term. It’s not the healthiest way to lose weight and we don’t recommend it, but it did does indeed precipitate short-term weight loss. Those benefits are not typically observed for longer than a short time, though, as the above-linked paper mentions:
❝The ketogenic diet does not fulfill the criteria of a healthy diet. It presents the potential for rapid short-term reduction of body mass, triglycerides level, Hb1Ac, and blood pressure.
Its efficacy for weight loss and the above-mentioned metabolic changes is not significant in long-term observations.❞
~ Ibid.
The ketogenic diet is a good, evidence-based way to lose weight, be energized, and live healthily: True or False?
False, simply, as you may have gathered from the above, but we’ve barely scratched the surface in terms of the risks.
That said, as mentioned, it will induce short-term weight loss, and as for being energized, typically there is a slump-spike-slump in energy:
- At first, the body is running out of glucose, and so naturally feels weak and tired.
- Next, the body enters ketosis, and so feels energized and enlivened ← this is the part where the popular enthusiastic reviews come from
- Then, the body starts experiencing all the longer-term problems associated with lacking carbohydrates and having an overabundance of fat, so becomes gradually more sick and tired.
Because of this, the signs of symptoms of being in ketosis (aside from: measurably increased ketones in blood, breath, and urine) are listed as:
- Bad breath
- Weight loss
- Appetite loss
- Increased focus and energy
- Increased fatigue and irritability
- Digestive issues
- Insomnia
The slump-spike-slump we mentioned is the reason for the seemingly contradictory symptoms of increased energy and increased fatigue—you get one and then the other.
Here’s a small but illustrative study, made clearer by its participants being a demographic whose energy levels are most strongly affected by dietary factors:
The ketogenic diet is a woeful fad diet and a fast-track to ruining one’s overall health: True or False?
True, subjectively in the first part, as it’s a little harsher than we usually go for in tone, though it has been called a fad diet in scientific literature. The latter part (ruining one’s overall health) is observably true.
One major problem is incidental-but-serious, which is that a low-carb diet is typically a de facto low-fiber diet, which is naturally bad for the gut and heart.
Other things are more specific to the keto diet, such as the problems with the kidneys:
However, kidney stones aren’t the worst of the problems:
Is Losing Weight Worth Losing Your Kidney: Keto Diet Resulting in Renal Failure
We’re running out of space and the risks associated with the keto diet are many, but for example even in the short term, it already increases osteoporosis risk:
❝Markers of bone modeling/remodeling were impaired after short-term low-carbohydrate high-fat diet, and only one marker of resorption recovered after acute carbohydrate restoration❞
~ Dr. Ida Heikura et al.
A Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Impairs Markers of Bone Health in Response to Exercise
Want a healthier diet?
We recommend the Mediterranean diet.
See also: Four Ways To Upgrade The Mediterranean
(the above is about keeping to the Mediterranean diet, while tweaking one’s choices within it for a specific extra health focus such as an anti-inflammatory upgrade, a heart-healthy upgrade, a gut-healthy upgrade, and a brain-healthy upgrade)
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Truth About Statins – by Barbara H. Roberts, M.D.
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All too often, doctors looking to dispense a “quick fix” will prescribe from their playbook of a dozen or so “this will get you out of my office” drugs. Most commonly, things that treat symptoms rather than the cause. Sometimes, this can be fine! For example, in some cases, painkillers and antidepressants can make a big improvement to people’s lives. What about statins, though?
Prescribed to lower cholesterol, they broadly do exactly that. However…
Dr. Roberts wants us to know that we could be missing the big picture of heart health, and making a potentially fatal mistake.
This is not to say that the book argues that statins are necessarily terrible, or that they don’t have their place. Just, we need to understand what they will and won’t do, and make an informed choice.
To which end, she does advise regards when statins can help the most, and when they may not help at all. She also covers the questions to ask if your doctor wants to prescribe them. And—all so frequently overlooked—the important differences between men’s and women’s heart health, and the implications these have for the efficacy (or not) of statins.
With regard to the “alternatives to cholesterol-lowering drugs” promised in the subtitle… we won’t keep any secrets here:
Dr. Roberts (uncontroversially) recommends the Mediterranean diet. She also provides two weeks’ worth of recipes for such, in the final part of the book.
All in all, an important book to read if you or a loved one are taking, or thinking of taking, statins.
Pick up your copy of The Truth About Statins on Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: