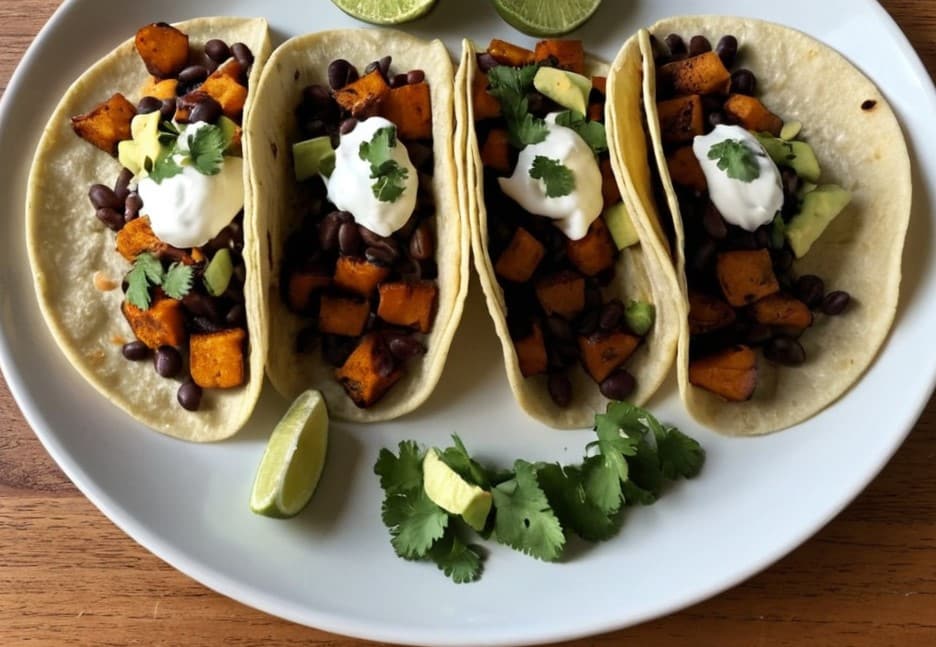Gymnema Sylvestre: The “Sugar Destroyer”
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Leaf That Stops Sugar From “Working”
Gymnema sylvestre, whose botanical name in Greek and Latin means “naked thread of the woods”, and is in various Indian languages referred to be names that translate as “sugar destroyer”, has the most prosaic name in Australia: the Australian cowplant.
In English it’s mostly called by the Greek “gymnema” though, so that’s what we’ll call it here.
You may be wondering: “the sugar destroyer?”
And no, it doesn’t actually destroy sugar. But it does do quite a bit of sugar-related stuff. Here’s the science for it…
Blocks sugar receptors in your tongue
This is what it is most well-known for, and it is a topical effect, so you won’t get this from a pill, but you will get this from the leaves, or from drinking it as a tea made from the leaves.
The effect last several hours, during which time your ability to taste sweetness will be reduced, which not only makes sweet foods less appealing because they’re no longer tasting sweet, but also, once you get used to it, when you actually do taste sweet foods, they will now taste too sweet.
So, it doesn’t just temporarily curb cravings; it offers a long-term escape from such, too.
You may be wondering: “what about artificially sweetened foods and drinks?”
And the answer is: yes, it blocks perception of the sweetness of those too:
Effects of sweetness perception and caloric value of a preload on short term intake ← this study used gymnema as the sweetness-blocker, testing sugary drinks, aspartame-sweetened drinks, and unsweetened drinks
Blocks sugar receptors in the gut, too
Long story short: this slows down the absorption of sugars from the gut, thus resulting in a gentler blood sugar curve, minimizing spikes, and (because of the body’s use of blood sugars as it goes) overall lower blood sugar levels.
Want the long version? Here it is:
Benefits beyond sugar-blocking
It also prevents the accumulation of triglycerides in muscles and the liver, as well as decreasing fatty acid accumulation in the blood. In simpler terms: it lowers LDL (“bad” cholesterol”, including VLDL). As a bonus, it increases HDL (“good” cholesterol) while it’s at it.
The vast majority of the studies for this are on rats and mice though, of which you can see very many listed in the “similar articles” under this systematic review of studies:
A systematic review of Gymnema sylvestre in obesity and diabetes management
We did find one good quality human RCT, testing gymnema along with several other treatments (they found that each worked, and/but using a combination yielded the best results):
(the title says “on weight loss”, but rest assured the study also gives information about its effects on total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, overall triglycerides, and serum leptin levels, as well as excretion of urinary fat metabolites—suffice it to say, they were thorough)
Is it safe?
It has a good safety profile in general, but if you are diabetic, proceed with caution and discuss it with your endocrinologist, since it will be affecting your blood sugar levels and insulin levels. While it’s probably not enough to replace metformin or similar, it is enough that taking it carelessly could result in an unexpected hypo.
Similarly, if you have any heart condition and especially if you are being treated for that with medication, do speak with your cardiologist since its antilipemic action could potentially lower your cholesterol more than expected, and doctors don’t like surprises.
As ever, no list of contraindications will be exhaustive, and we can’t speak for your specific situation, so checking with your pharmacist/doctor is always a good idea.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon ← we’ve linked to a tea version of it so you can enjoy the full effects; if you prefer capsule form, you can click through from there to shop around 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Some women’s breasts can’t make enough milk, and the effects can be devastating
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many new mothers worry about their milk supply. For some, support from a breastfeeding counsellor or lactation consultant helps.
Others cannot make enough milk no matter how hard they try. These are women whose breasts are not physically capable of producing enough milk.
Our recently published research gives us clues about breast features that might make it difficult for some women to produce enough milk. Another of our studies shows the devastating consequences for women who dream of breastfeeding but find they cannot.
Some breasts just don’t develop
Unlike other organs, breasts are not fully developed at birth. There are key developmental stages as an embryo, then again during puberty and pregnancy.
At birth, the breast consists of a simple network of ducts. Usually during puberty, the glandular (milk-making) tissue part of the breast begins to develop and the ductal network expands. Then typically, further growth of the ductal network and glandular tissue during pregnancy prepares the breast for lactation.
But our online survey of women who report low milk supply gives us clues to anomalies in how some women’s breasts develop.
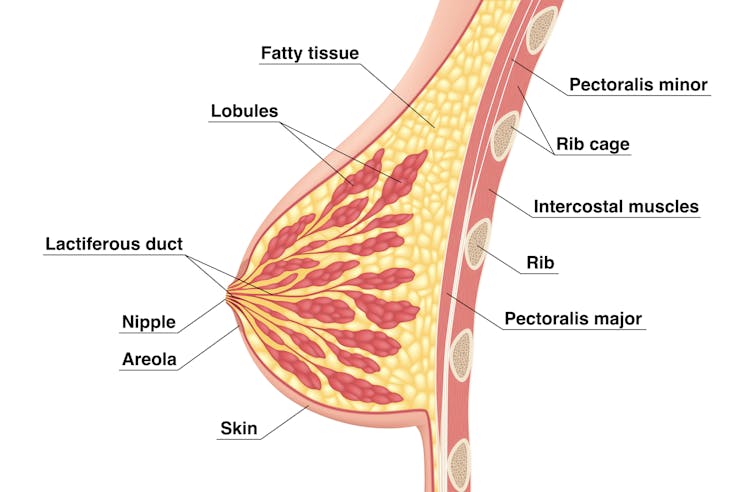
We’re not talking about women with small breasts, but women whose glandular tissue (shown in this diagram as “lobules”) is underdeveloped and have a condition called breast hypoplasia.
Sometimes not enough glandular tissue, shown here as lobules, develop.
Tsuyna/ShutterstockWe don’t know how common this is. But it has been linked with lower rates of exclusive breastfeeding.
We also don’t know what causes it, with much of the research conducted in animals and not humans.
However, certain health conditions have been associated with it, including polycystic ovary syndrome and other endocrine (hormonal) conditions. A high body-mass index around the time of puberty may be another indicator.
Could I have breast hypoplasia?
Our survey and other research give clues about who may have breast hypoplasia.
But it’s important to note these characteristics are indicators and do not mean women exhibiting them will definitely be unable to exclusively breastfeed.
Indicators include:
- a wider than usual gap between the breasts
- tubular-shaped (rather than round) breasts
- asymmetric breasts (where the breasts are different sizes or shapes)
- lack of breast growth in pregnancy
- a delay in or absence of breast fullness in the days after giving birth
In our survey, 72% of women with low milk supply had breasts that did not change appearance during pregnancy, and about 70% reported at least one irregular-shaped breast.
The effects
Mothers with low milk supply – whether or not they have breast hyoplasia or some other condition that limits their ability to produce enough milk – report a range of emotions.
Research, including our own, shows this ranges from frustration, confusion and surprise to intense or profound feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair.
Some mothers describe “breastfeeding grief” – a prolonged sense of loss or failure, due to being unable to connect with and nourish their baby through breastfeeding in the way they had hoped.
These feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair can trigger symptoms of anxiety and depression for some women.
Feelings of failure, guilt, grief and despair were common.
Bricolage/ShutterstockOne woman told us:
[I became] so angry and upset with my body for not being able to produce enough milk.
Many women’s emotions intensified when they discovered that despite all their hard work, they were still unable to breastfeed their babies as planned. A few women described reaching their “breaking point”, and their experience felt “like death”, “the worst day of [my] life” or “hell”.
One participant told us:
I finally learned that ‘all women make enough milk’ was a lie. No amount of education or determination would make my breasts work. I felt deceived and let down by all my medical providers. How dare they have no answers for me when I desperately just wanted to feed my child naturally.
Others told us how they learned to accept their situation. Some women said they were relieved their infant was “finally satisfied” when they began supplementing with formula. One resolved to:
prioritise time with [my] baby over pumping for such little amounts.
Where to go for help
If you are struggling with low milk supply, it can help to see a lactation consultant for support and to determine the possible cause.
This will involve helping you try different strategies, such as optimising positioning and attachment during breastfeeding, or breastfeeding/expressing more frequently. You may need to consider taking a medication, such as domperidone, to see if your supply increases.
If these strategies do not help, there may be an underlying reason why you can’t make enough milk, such as insufficient glandular tissue (a confirmed inability to make a full supply due to breast hypoplasia).
Even if you have breast hypoplasia, you can still breastfeed by giving your baby extra milk (donor milk or formula) via a bottle or using a supplementer (which involves delivering milk at the breast via a tube linked to a bottle).
More resources
The following websites offer further information and support:
- Australian Breastfeeding Association
- Lactation Consultants of Australia and New Zealand
- Royal Women’s Hospital, Melbourne
- Supply Line Breastfeeders Support Group of Australia Facebook support group
- IGT And Low Milk Supply Support Group Facebook support group
- Breastfeeding Medicine Network Australia/New Zealand
- Supporting breastfeeding grief (a collection of resources).
Shannon Bennetts, a research fellow at La Trobe University, contributed to this article.
Renee Kam, PhD candidate and research officer, La Trobe University and Lisa Amir, Professor in Breastfeeding Research, La Trobe University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
How Nature Provides Us With A Surprisingly Powerful Painkiller
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s well-known (at least to regular 10almonds-readers) that seeing nature, ideally green leaves and blue sky, improves our mood by stimulating production of serotonin.
See also: Neurotransmitter Cheatsheet
But it does a lot more.
Reducing the actual signals of pain
Researchers at the University of Vienna have discovered that viewing nature scenes (even if just on video) alleviates physical pain—not just in self-reported subjective assessments, but also by a reduction of the neural activity that signals pain:
❝Pain is like a puzzle, made up of different pieces that are processed differently in the brain. Some pieces of the puzzle relate to our emotional response to pain, such as how unpleasant we find it. Other pieces correspond to the physical signals underlying the painful experience, such as its location in the body and its intensity.
Unlike placebos, which usually change our emotional response to pain, viewing nature changed how the brain processed early, raw sensory signals of pain.
Thus, the effect appears to be less influenced by participants’ expectations, and more by changes in the underlying pain signals❞
This was tested against, varyingly, viewing an urban environment or viewing an indoor environment, neither of which gave the same benefits.
The setup of the experiment is relevant, so…
Matching soundscape accompanied each visual stimulus. The three pain runs had a total duration of 9 min each, during which one environment was accompanied by 16 painful and 16 non-painful shocks. Neuroimaging was used for all parts, and participants were exposed to all environments:
- First, a cue indicating the intensity of the next shock (red = painful, yellow = not painful) was presented for 2000 milliseconds (ms).
- Second, a variable interval of 3500 ± 1500 ms was shown.
- Third, a cue indicating the intensity of the shock was presented for 1000 ms, accompanied by an electrical shock with a duration of 500 ms.
- Fourth, a variable interval of 3500 ± 1500 ms followed.
- Fifth, after each third trial, participants rated the shock’s intensity and unpleasantness at 6000 ms each.
- Sixth, each trial ended with an intertrial interval (ITI) presented for 2000 ms.
They found that as well as the self-assessment reports being as expected (nature scenes reduced subjective experience of pain),
❝In summary, the multivoxel and region of interest analyses converged in showing that pain responses when exposed to nature as compared to urban or indoor stimuli were associated with a decrease in neural processes related to lower-level nociception-related features (NPS, thalamus), as well as in regions of descending modulatory circuitry associated with attentional alterations of pain that also encode sensory-discriminative aspects (S2, pINS).❞
In other words—to the extent that pain can be quantified objectively by neural imaging—the pain was also objectively reduced, much like with a chemical painkiller.
You can read the paper in full, here:
Nature exposure induces analgesic effects by acting on nociception-related neural processing
How to benefit from this
Well, first there is the obvious, “view nature“.
However, note the timescales involved in the testing periods: 2000 milliseconds is two seconds, and that was the intertrial interval used—the equivalent of a washout phase in an interventional trial (but a drug/supplement/diet washout is usually a number of weeks).
The fact that the test periods were a matter of seconds, and the intertrial period was also literally two seconds, this means:
It works quickly, and the effect disappears quickly, too.
In other words: if you want pain relief from nature, the good news is you can get it immediately while viewing nature, and the bad news is that you have to keep viewing nature to continue enjoying the painkilling effect.
So that’s a limitation, but it’s still clearly a very worthy option for a little respite from chronic pain now and again, for example.
Want to learn more?
We’ve written quite a bit about pain management, including:
- Before You Reach For That Tylenol…
- How To Stop Pain Spreading
- How To Dial Down Your Pain
- Managing Chronic Pain (Realistically!)
- Get The Right Help For Your Pain
- The 7 Approaches To Pain Management
- Science-Based Alternative Pain Relief (When Painkillers Aren’t Helping, These Things Might)
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Neurologists Debunk 11 Brain Myths
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Neuroscientists Dr. Santoshi Billakota and Dr. Brad Kamitaki debunk 11 myths about the brain. How many did you know?
From the top
Without further ado, the myths are…
- “We only use 10% of our brains”: False! We use most parts of our brain at different times, depending on the activity. PET/MRI scans show widespread usage.
- “The bigger the brain, the smarter the creature”: False! While there’s often a correlation, intelligence depends on brain complexity and development of specific regions, not overall size. For this reason get, for example, some corvids that are more intelligent than some dogs.
- “IQ tests are an accurate measure of intelligence”: False! IQ tests measure limited aspects of intelligence and are influenced by external factors like test conditions and education.
- “Video games rot your brain”: False! Video games can improve problem-solving, strategy, and team-building skills when played in moderation.
- “Memory gets worse as you age”: Partly false. While episodic memory may decline, semantic and procedural memory often improve with age.
- “Left-brained people are logical, and right-brained people are creative”: False! Both hemispheres work together, and personality or skills are influenced by environment and experiences, not brain hemispheres.
- “You can’t prevent a stroke”: False! Strokes can often be prevented by managing risk factors like blood pressure, cholesterol, and lifestyle choices.
- “Eating fish makes you smarter”: False! Eating fish, especially those rich in omega-3s, can support brain health but won’t increase intelligence.
- “You can always trust your senses”: False! Senses can be deceptive and influenced by emotions, memories, or neurological conditions.
- “Different sexes have different brains”: False! Structurally, brains are the same regardless of chromosomal sex; differences arise from environmental (including hormonal) and experiential factors—and even there, there’s more than enough overlap that we are far from categorizable as sexually dimorphic.
- “If you have a seizure, you have epilepsy”: False! A seizure can occur from various causes, but epilepsy is defined by recurrent unprovoked seizures and requires specific diagnosis and treatment.
For more on all of these, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
The Dopamine Myth ← a bonus 12th myth!
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Pistachios vs Pecans – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing pistachios to pecans, we picked the pistachios.
Why?
Firstly, the macronutrients: pistachios have twice as much protein and fiber. Pecans have more fat, though in both of these nuts the fats are healthy.
The category of vitamins is an easy win for pistachios, with a lot more of vitamins A, B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, and E. Especially the 8x vitamin A, 7x vitamin B6, 4x vitamin C, and 2x vitamin E, and as the percentages are good too, these aren’t small differences. Pecans, meanwhile, boast only a little more vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid, the one whose name means “it’s everywhere”, because that’s how easy it is to get it).
In terms of minerals, pistachios have more calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium, while pecans have more manganese and zinc. So, a fair win for pistachios on this one.
Adding up the three different kinds of win for pistachios means that *drumroll* pistachios win overall, and it’s not close.
As ever, do enjoy both though, because diversity is healthy!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sweet Potato & Black Bean Tacos
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber, protein, and polyphenols! What more could one ask for? Well, great taste and warm healthy goodness, which these deliver:
You will need
For the sweet potatoes:
- 2 medium sweet potatoes, cubed (we recommend leaving the skin on, but you can peel them if you really want to)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 2 tsp garlic powder
- 2 tsp smoked paprika
- 1 tsp chili powder
- 1 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
For the black beans:
- 2 cans black beans, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups black beans that you cooked yourself)
- ¼ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 fresh jalapeño finely chopped (or ¼ cup jalapeños from a jar, finely chopped) ← adjust quantities per your preference and per the quality of the pepper(s) you’re using; we can’t judge that from here without tasting them, so we give a good basic starting suggestion.
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp red chili flakes
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
For serving:
- 8 small corn tortillas, or your preference if substituting
- 1 avocado, pitted, peeled, cubed, and tossed in lime juice ← we’re mentioning this here because you want to do this as soon as you cut it, to avoid oxidation
- Any other salad you’d like to include; fresh parsley is also a good option when it comes to greenery, or cilantro if you don’t have the soap gene
- Tomato salsa (quantity and spice level per your preference)
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400°F / 200°C.
2) Toss the sweet potato cubes in a large bowl with the rest of the ingredients from the sweet potato section above, ensuring they are evenly coated.
3) Bake them in the oven, on a baking tray lined with baking paper, for about 30 minutes or until tender inside and crispy at the edges. Turn them over halfway through.
4) While that’s happening, mix the black beans in a bowl with the other ingredients from the black bean section above, and heat them gently. You could do this in a saucepan, but honestly, while it’s not glamorous, the microwave is actually better for this. Note: many people find the microwave cooks food unevenly, but there are two reasons for this and they’re both easily fixable:
- instead of using high power for x minutes, use medium power for 2x minutes; this will produce better results
- instead of putting the food just in a bowl, jug, or similar, use a wide bowl or similar container, and then inside that, place a small empty microwave-safe glass jar or similar upturned in the middle, and then add the food around it, so that the food is arranged in a donut shape rather than a wide cylinder shape. This means there is no “middle bit” to go underheated while the edges are heated excessively; instead, it will heat through evenly.
If you really don’t want to do that though, use a saucepan on a very low heat, add a small amount of liquid (or tomato salsa), and stir constantly.
5) Heat the tortillas in a dry skillet for about 30 seconds each on each side, when ready to serve.
6) Assemble the tacos; you can do this how you like but a good order of operations is: tortilla, leafy salad (if using), potato, beans, non-leafy salad including avocado, salsa or other topping per your preference.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- White Potato vs Sweet Potato – Which is Healthier?
- Kidney Beans or Black Beans – Which is Healthier?
- Coconut vs Avocado – Which is Healthier?
- Glutathione: More Than An Antioxidant
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we hit 4/5 today!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
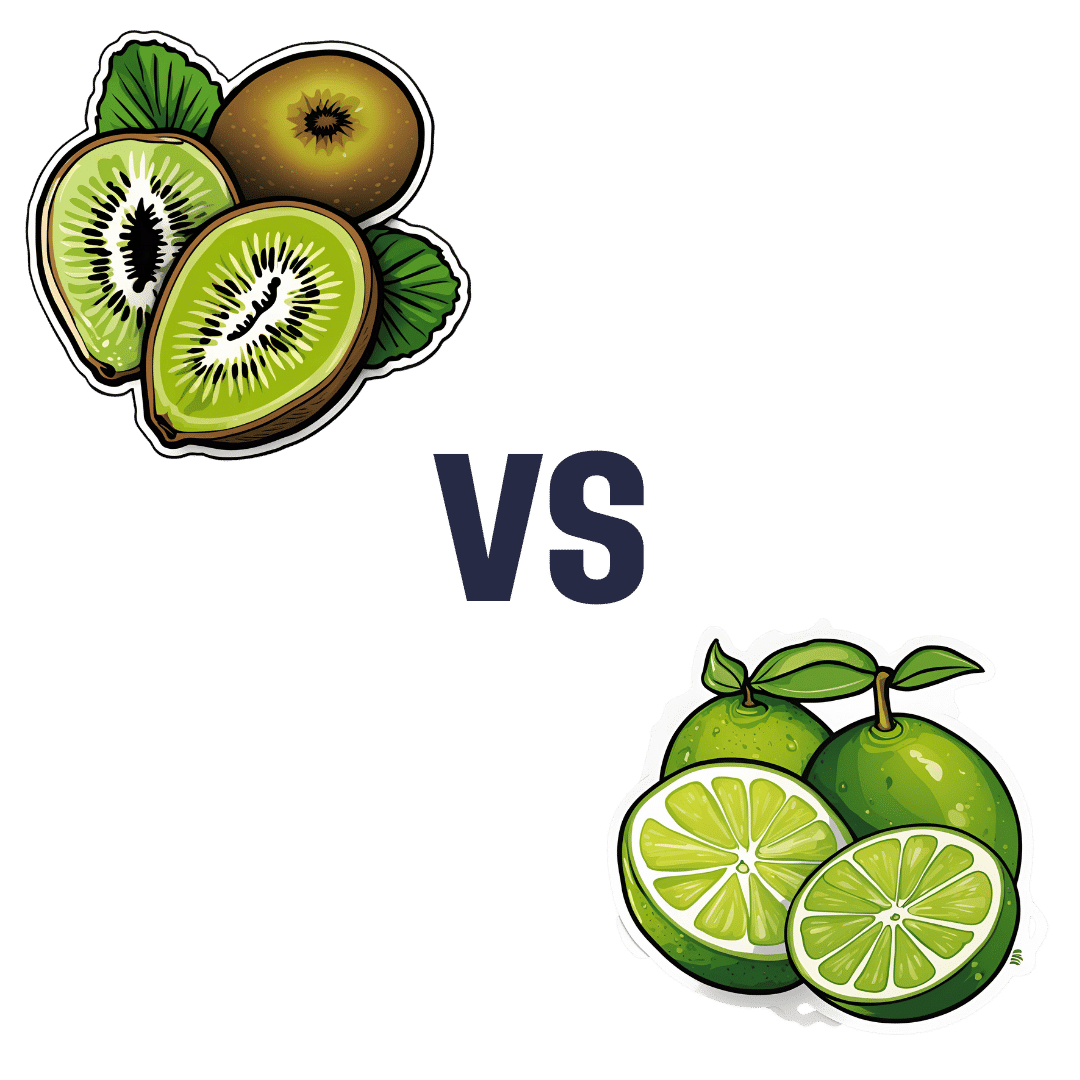
Kiwi vs Lime – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi to lime, we picked the kiwi.
Why?
Looking at the macros first, kiwi has more protein, more carbs, and more fiber. As with most fruits, the fiber is the number we’re most interested in for health purposes; in this case, kiwi is just slightly ahead of lime on all three of those.
In terms of vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while lime has a tiny bit more vitamin B5. As in, the vitamin that’s in pretty much anything and is practically impossible to be deficient in unless you are literally starving to death. You may be thinking: aren’t limes a famously good source of vitamin C? And yes, yes they are. But kiwis have >3x more. In other big differences, kiwis also have >6x more vitamin E and >67 times more vitamin K.
When it comes to minerals, kiwi has more calcium, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, and zinc, while lime has more iron and selenium. Another easy win for kiwis.
In short: enjoy both; both are good. But kiwis are the more nutritionally dense option by almost every way of measuring it.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← kiwi is top of the list; it promotes cancer cell death while sparing healthy cells
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: