Basic Baked Tofu
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
One of the main criticisms of tofu is that it is tasteless. Well, so is flour, but you’re not supposed to eat it plain, and the same goes for tofu. It’s a blank canvas that you get to decide what to do with—not to mention, it’s a canvas that’s very high in protein, and is a complete protein too, containing all essential amino acids. Anyway, here’s a starter recipe that elevates tofu from “nutrition” to “nutritious tasty snack”!
We were going to do a fancier recipe today, but considered that it might be judicious to cover this basic element first, that can be incorporated into a larger recipe later, a bit like we have done with recipes such as our Tasty Versatile Rice, and Plant-Based Healthy Cream Cheese (amongst others).
You will need
- 1 block of extra-firm tofu; these are quite standardized in size; it should be about 12oz; don’t worry if it’s a little more or less.
- 2 tbsp arrowroot powder (or potato starch if you don’t have arrowroot)
- 1½ tbsp extra virgin olive oil
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp black pepper
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Optional: ½ tsp garlic powder
- Optional: ½ tsp ground turmeric
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 425ºF / 220ºC.
2) Press the tofu for about 15 minutes (to remove excess moisture), using a tofu press if you have one. If you don’t, then here is an example product on Amazon, or alternatively, you can go with the time-honored tradition of cutting the tofu lengthways into slabs, and wrapping it in a lint-free kitchen towel or muslin cloth, and pressing it with heavy books. We don’t recommend pressing for more than about 15 minutes, as you are going to bake the tofu so you don’t want it too dry going in.
3) Cut the tofu into cubes. Size is up to you, but half-inch cubes are very respectable.
4) Combine the tofu cubes in a big bowl with the oil and seasonings, including the nutritional yeast but not the arrowroot powder or potato starch yet. You will need to toss them gently (very gently; they are fragile!) to combine.
5) Add the arrowroot powder or potato starch, and again toss gently to combine. We do this last, because it would stop the other things from sticking properly if we did it earlier.
6) Arrange the tofu on a baking tray lined with baking paper, in a single layer so that the cubes don’t touch. Bake for 15 minutes, turn them over, and bake for a further 15 minutes on the other side. They should now be golden and crisp, but if they’re not, just give them a little more time.
7) Serve as a snack, or set aside for whatever else you’re going to do with them in a larger more complex recipe.
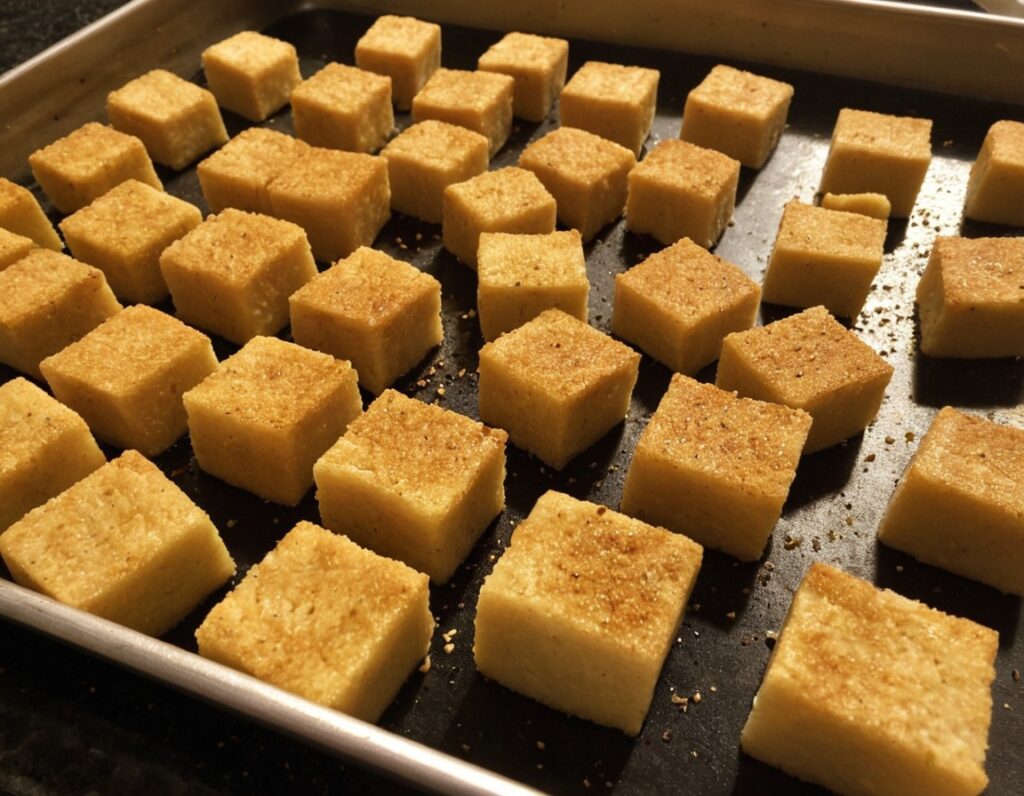

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Tofu vs Seitan – Which is Healthier?
- Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fast Burn – by Dr. Ian K. Smith
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Intermittent fasting seems simple enough: how complicated can “stop eating for a bit” be? Well, there are nuances and tweaks and hacks and “if you do this bit wrong it will sabotage your benefits” things to know about, too.
Dr. Smith takes us through the basic essentials first, and covers each of the main kinds of intermittent fasting, for example:
- Time-restricted eating; 12:12, 16:8, etc, with those being hours fasting vs hours eating
- Caloric restriction models; for example 5:2, where one eats “normally” for 5 days a week, and on two non-consecutive days, eats only 500 calories
- Day off models and more; for example, “no eating on Sundays” that can, depending on your schedule, be anything from a 24-hour fast to 36 hours or more.
…and, most notably, what they each do metabolically.
Then, the real meat of the book is his program. Taking into account the benefits of each form of fasting, he weaves together a 9-week program to first ease us gently into intermittent fasting, and then enjoy the maximum benefits with minimum self-sabotage.
Which is the biggest stumbling-block for many trying intermittent fasting for the first time, so it’s a huge help that he takes care of this here.
He also includes meal plans and recipes; readers can use those or not; the fasting plan stands on its own two feet without them too.
Bottom line: if you’ve been thinking of trying intermittent fasting but have been put off by all the kinds or have had trouble sticking to it, this book may be just what you need.
Click here to check out Fast Burn on Amazon and see what you can achieve!
Share This Post
-
It’s Not Fantastic To Be Plastic
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We Are Such Stuff As Bottles Are Made Of
We’ve written before about PFAS, often found in non-stick coatings and the like:
PFAS Exposure & Cancer: The Numbers Are High
Today we’re going to be talking about microplastics & nanoplastics!
What are microplastics and nanoplastics?
Firstly, they’renot just the now-banned plastic microbeads that have seen some use is toiletries (although those are classified as microplastics too).
Many are much smaller than that, and if they get smaller than a thousandth of a millimeter, then they get the additional classification of “nanoplastic”.
In other words: not something that can be filtered even if you were to use a single-micron filter. The microplastics would still get through, for example:
Scientists find about a quarter million invisible nanoplastic particles in a liter of bottled water
And unfortunately, that’s bad:
❝What’s disturbing is that small particles can appear in different organs and may cross membranes that they aren’t meant to cross, such as the blood-brain barrier❞
Note: they’re crossing the same blood-brain barrier that many of our nutrients and neurochemicals are too big to cross.
These microplastics are also being found in arterial plaque
What makes arterial plaque bad for the health is precisely its plasticity (the arterial walls themselves are elastic), so you most certainly do not want actual plastic being used as part of the cement that shouldn’t even be lining your arteries in the first place:
Microplastics found in artery plaque linked with higher risk of heart attack, stroke and death
❝In this study, patients with carotid artery plaque in which MNPs were detected had a higher risk of a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from any cause at 34 months of follow-up than those in whom MNPs were not detected❞
~ Dr. Raffaele Marfella et al.
(MNP = Micro/Nanoplastics)
Source: Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events
We don’t know how bad this is yet
There are various ways this might not be as bad as it looks (the results may not be repeated, the samples could have been compromised, etc), but also, perhaps cynically but nevertheless honestly, it could also be worse than we know yet—only more experiments being done will tell us which.
In the meantime, here’s a rundown of what we do and don’t know:
Study links microplastics with human health problems—but there’s still a lot we don’t know
Take care!
Share This Post
-
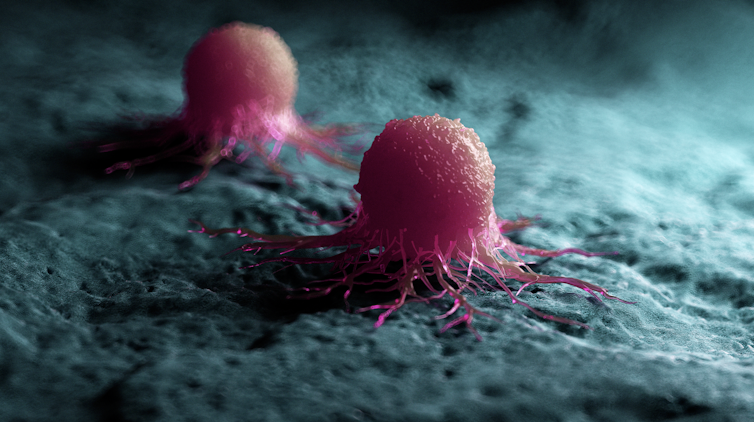
How does cancer spread to other parts of the body?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
All cancers begin in a single organ or tissue, such as the lungs or skin. When these cancers are confined in their original organ or tissue, they are generally more treatable.
But a cancer that spreads is much more dangerous, as the organs it spreads to may be vital organs. A skin cancer, for example, might spread to the brain.
This new growth makes the cancer much more challenging to treat, as it can be difficult to find all the new tumours. If a cancer can invade different organs or tissues, it can quickly become lethal.
When cancer spreads in this way, it’s called metastasis. Metastasis is responsible for the majority (67%) of cancer deaths.
Cells are supposed to stick to surrounding tissue
Our bodies are made up of trillions of tiny cells. To keep us healthy, our bodies are constantly replacing old or damaged cells.
Each cell has a specific job and a set of instructions (DNA) that tells it what to do. However, sometimes DNA can get damaged.
This damage might change the instructions. A cell might now multiply uncontrollably, or lose a property known as adherence. This refers to how sticky a cell is, and how well it can cling to other surrounding cells and stay where it’s supposed to be.
If a cancer cell loses its adherence, it can break off from the original tumour and travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to almost anywhere. This is how metastasis happens.
Many of these travelling cancer cells will die, but some will settle in a new location and begin to form new cancers.
Some cells settle in a new location.
Scipro/ShutterstockParticular cancers are more likely to metastasise to particular organs that help support their growth. Breast cancers commonly metastasise to the bones, liver, and lungs, while skin cancers like melanomas are more likely to end up in the brain and heart.
Unlike cancers which form in solid organs or tissues, blood cancers like leukaemia already move freely through the bloodstream, but can escape to settle in other organs like the liver or brain.
When do cancers metastasise?
The longer a cancer grows, the more likely it is to metastasise. If not caught early, a patient’s cancer may have metastasised even before it’s initially diagnosed.
Metastasis can also occur after cancer treatment. This happens when cancer cells are dormant during treatment – drugs may not “see” those cells. These invisible cells can remain hidden in the body, only to wake up and begin growing into a new cancer months or even years later.
For patients who already have cancer metastases at diagnosis, identifying the location of the original tumour – called the “primary site” – is important. A cancer that began in the breast but has spread to the liver will probably still behave like a breast cancer, and so will respond best to an anti-breast cancer therapy, and not anti-liver cancer therapy.
As metastases can sometimes grow faster than the original tumour, it’s not always easy to tell which tumour came first. These cancers are called “cancers of unknown primary” and are the 11th most commonly diagnosed cancers in Australia.
One way to improve the treatment of metastatic cancer is to improve our ways of detecting and identifying cancers, to ensure patients receive the most effective drugs for their cancer type.
What increases the chances of metastasis and how can it be prevented?
If left untreated, most cancers will eventually acquire the ability to metastasise.
While there are currently no interventions that specifically prevent metastasis, cancer patients who have their tumours surgically removed may also be given chemotherapy (or other drugs) to try and weed out any hidden cancer cells still floating around.
The best way to prevent metastasis is to diagnose and treat cancers early. Cancer screening initiatives such as Australia’s cervical, bowel, and breast cancer screening programs are excellent ways to detect cancers early and reduce the chances of metastasis.
The best way to prevent cancer spreading is to diagnose and treat them early.
Peakstock/ShutterstockNew screening programs to detect cancers early are being researched for many types of cancer. Some of these are simple: CT scans of the body to look for any potential tumours, such as in England’s new lung cancer screening program.
Using artificial intelligence (AI) to help examine patient scans is also possible, which might identify new patterns that suggest a cancer is present, and improve cancer detection from these programs.
More advanced screening methods are also in development. The United States government’s Cancer Moonshot program is currently funding research into blood tests that could detect many types of cancer at early stages.
One day there might even be a RAT-type test for cancer, like there is for COVID.
Will we be able to prevent metastasis in the future?
Understanding how metastasis occurs allows us to figure out new ways to prevent it. One idea is to target dormant cancer cells and prevent them from waking up.
Directly preventing metastasis with drugs is not yet possible. But there is hope that as research efforts continue to improve cancer therapies, they will also be more effective at treating metastatic cancers.
For now, early detection is the best way to ensure a patient can beat their cancer.
Sarah Diepstraten, Senior Research Officer, Blood Cells and Blood Cancer Division, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute and John (Eddie) La Marca, Senior Resarch Officer, Walter and Eliza Hall Institute
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How much time should you spend sitting versus standing? New research reveals the perfect mix for optimal health
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
People have a pretty intuitive sense of what is healthy – standing is better than sitting, exercise is great for overall health and getting good sleep is imperative.
However, if exercise in the evening may disrupt our sleep, or make us feel the need to be more sedentary to recover, a key question emerges – what is the best way to balance our 24 hours to optimise our health?
Our research attempted to answer this for risk factors for heart disease, stroke and diabetes. We found the optimal amount of sleep was 8.3 hours, while for light activity and moderate to vigorous activity, it was best to get 2.2 hours each.
Finding the right balance
Current health guidelines recommend you stick to a sensible regime of moderate-to vigorous-intensity physical activity 2.5–5 hours per week.
However mounting evidence now suggests how you spend your day can have meaningful ramifications for your health. In addition to moderate-to vigorous-intensity physical activity, this means the time you spend sitting, standing, doing light physical activity (such as walking around your house or office) and sleeping.
Our research looked at more than 2,000 adults who wore body sensors that could interpret their physical behaviours, for seven days. This gave us a sense of how they spent their average 24 hours.
At the start of the study participants had their waist circumference, blood sugar and insulin sensitivity measured. The body sensor and assessment data was matched and analysed then tested against health risk markers — such as a heart disease and stroke risk score — to create a model.
Using this model, we fed through thousands of permutations of 24 hours and found the ones with the estimated lowest associations with heart disease risk and blood-glucose levels. This created many optimal mixes of sitting, standing, light and moderate intensity activity.
When we looked at waist circumference, blood sugar, insulin sensitivity and a heart disease and stroke risk score, we noted differing optimal time zones. Where those zones mutually overlapped was ascribed the optimal zone for heart disease and diabetes risk.
You’re doing more physical activity than you think
We found light-intensity physical activity (defined as walking less than 100 steps per minute) – such as walking to the water cooler, the bathroom, or strolling casually with friends – had strong associations with glucose control, and especially in people with type 2 diabetes. This light-intensity physical activity is likely accumulated intermittently throughout the day rather than being a purposeful bout of light exercise.
Our experimental evidence shows that interrupting our sitting regularly with light-physical activity (such as taking a 3–5 minute walk every hour) can improve our metabolism, especially so after lunch.
While the moderate-to-vigorous physical activity time might seem a quite high, at more than 2 hours a day, we defined it as more than 100 steps per minute. This equates to a brisk walk.
It should be noted that these findings are preliminary. This is the first study of heart disease and diabetes risk and the “optimal” 24 hours, and the results will need further confirmation with longer prospective studies.
The data is also cross-sectional. This means that the estimates of time use are correlated with the disease risk factors, meaning it’s unclear whether how participants spent their time influences their risk factors or whether those risk factors influence how someone spends their time.
Australia’s adult physical activity guidelines need updating
Australia’s physical activity guidelines currently only recommend exercise intensity and time. A new set of guidelines are being developed to incorporate 24-hour movement. Soon Australians will be able to use these guidelines to examine their 24 hours and understand where they can make improvements.
While our new research can inform the upcoming guidelines, we should keep in mind that the recommendations are like a north star: something to head towards to improve your health. In principle this means reducing sitting time where possible, increasing standing and light-intensity physical activity, increasing more vigorous intensity physical activity, and aiming for a healthy sleep of 7.5–9 hours per night.
Beneficial changes could come in the form of reducing screen time in the evening or opting for an active commute over driving commute, or prioritising an earlier bed time over watching television in the evening.
It’s also important to acknowledge these are recommendations for an able adult. We all have different considerations, and above all, movement should be fun.
Christian Brakenridge, Postdoctoral research fellow at Swinburne University Centre for Urban Transitions, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Peaches vs Plums – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing peaches to plums, we picked the peaches.
Why?
Both are great! But there is a clear winner out of these two botanically-similar fruits:
In terms of macronutrients they are very similar. Peaches have slightly more protein and plums have slightly more carbs, but the numbers are close enough to make no meaningful difference; they’re both mostly water.
They’re also not too far from each other in the category of vitamins; peaches have more of vitamins B2, B3, B5, E, and choline, while plums have more of vitamins B1, B6, B9, C, and K. They’re equal on vitamin A, by the way, and the vitamins they do differ in, differ by around the same margins, so this category is a clear tie.
When it comes to minerals, however, peaches win easily with more copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc. The two fruits are equal on calcium, and plum is not higher in any minerals.
While they already won easily because of the mineral situation, it should be noted that peaches also have the lower glycemic index. But honestly, plums are fine too; peaches are just even lower.
So: enjoy both, but if you’re going to pick one, peaches boast the most!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer
- Apricots vs Peaches – Which is Healthier?
- Dried Apricots vs Dried Prunes – Which is Healthier? (prunes are dried plums, usually partially rehydrated)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
With all this bird flu around, how safe are eggs, chicken or milk?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Enzo Palombo, Swinburne University of Technology
Recent outbreaks of bird flu – in US dairy herds, poultry farms in Australia and elsewhere, and isolated cases in humans – have raised the issue of food safety.
So can the virus transfer from infected farm animals to contaminate milk, meat or eggs? How likely is this?
And what do we need to think about to minimise our risk when shopping for or preparing food?
AS Foodstudio/Shutterstock How safe is milk?
Bird flu (or avian influenza) is a bird disease caused by specific types of influenza virus. But the virus can also infect cows. In the US, for instance, to date more than 80 dairy herds in at least nine states have been infected with the H5N1 version of the virus.
Investigations are under way to confirm how this happened. But we do know infected birds can shed the virus in their saliva, nasal secretions and faeces. So bird flu can potentially contaminate animal-derived food products during processing and manufacturing.
Indeed, fragments of bird flu genetic material (RNA) were found in cow’s milk from the dairy herds associated with infected US farmers.
However, the spread of bird flu among cattle, and possibly to humans, is likely to have been caused through contact with contaminated milking equipment, not the milk itself.
The test used to detect the virus in milk – which uses similar PCR technology to lab-based COVID tests – is also highly sensitive. This means it can detect very low levels of the bird flu RNA. But the test does not distinguish between live or inactivated virus, just that the RNA is present. So from this test alone, we cannot tell if the virus found in milk is infectious (and capable of infecting humans).
It’s best to stick with pasteurised milk. Amnixia/Shutterstock Does that mean milk is safe to drink and won’t transmit bird flu? Yes and no.
In Australia, where bird flu has not been reported in dairy cattle, the answer is yes. It is safe to drink milk and milk products made from Australian milk.
In the US, the answer depends on whether the milk is pasteurised. We know pasteurisation is a common and reliable method of destroying concerning microbes, including influenza virus. Like most viruses, influenza virus (including bird flu virus) is inactivated by heat.
Although there is little direct research on whether pasteurisation inactivates H5N1 in milk, we can extrapolate from what we know about heat inactivation of H5N1 in chicken and eggs.
So we can be confident there is no risk of bird flu transmission via pasteurised milk or milk products.
However, it’s another matter for unpasteurised or “raw” US milk or milk products. A recent study showed mice fed raw milk contaminated with bird flu developed signs of illness. So to be on the safe side, it would be advisable to avoid raw milk products.
How about chicken?
Bird flu has caused sporadic outbreaks in wild birds and domestic poultry worldwide, including in Australia. In recent weeks, there have been three reported outbreaks in Victorian poultry farms (two with H7N3 bird flu, one with H7N9). There has been one reported outbreak in Western Australia (H9N2).
The strains of bird flu identified in the Victorian and Western Australia outbreaks can cause human infection, although these are rare and typically result from close contact with infected live birds or contaminated environments.
Therefore, the chance of bird flu transmission in chicken meat is remote.
Nonetheless, it is timely to remind people to handle chicken meat with caution as many dangerous pathogens, such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, can be found on chicken carcasses.
Always handle chicken meat carefully when shopping, transporting it home and storing it in the kitchen. For instance, make sure no meat juices cross-contaminate other items, consider using a cool bag when transporting meat, and refrigerate or freeze the meat within two hours.
Avoid washing your chicken before cooking to prevent the spread of disease-causing microbes around the kitchen.
Finally, cook chicken thoroughly as viruses (including bird flu) cannot survive cooking temperatures.
Are eggs safe?
The recent Australian outbreaks have occurred in egg-laying or mixed poultry flocks, so concerns have been raised about bird flu transmission via contaminated chicken eggs.
Can flu viruses contaminate chicken eggs and potentially spread bird flu? It appears so. A report from 2007 said it was feasible for influenza viruses to enter through the eggshell. This is because influenza virus particles are smaller (100 nanometres) than the pores in eggshells (at least 200 nm).
So viruses could enter eggs and be protected from cleaning procedures designed to remove microbes from the egg surface.
Therefore, like the advice about milk and meat, cooking eggs is best.
The US Food and Drug Administration recommends cooking poultry, eggs and other animal products to the proper temperature and preventing cross-contamination between raw and cooked food.
In a nutshell
If you consume pasteurised milk products and thoroughly cook your chicken and eggs, there is nothing to worry about as bird flu is inactivated by heat.
The real fear is that the virus will evolve into highly pathogenic versions that can be transmitted from human to human.
That scenario is much more frightening than any potential spread though food.
Enzo Palombo, Professor of Microbiology, Swinburne University of Technology
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: