Kiwi Fruit vs Pineapple – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing kiwi fruit to pineapple, we picked the kiwi.
Why?
In terms of macros, they’re mostly quite comparable, being fruits made of mostly water, and a similar carb count (slightly different proportions of sugar types, but nothing that throws out the end result, and the GI is low for both). Technically kiwi has twice the protein, but they are fruits and “twice the protein” means “0.5g difference per 100g”. Aside from that, and more meaningfully, kiwi also has twice the fiber.
When it comes to vitamins, kiwi has more of vitamins A, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while pineapple has more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6. This would be a marginal (6:5) win for kiwi, but kiwi’s margins of difference are greater per vitamin, including 72x more vitamin E (with a cupful giving 29% of the RDA, vs a cupful of pineapple giving 0.4% of the RDA) and 57x more vitamin K (with a cupful giving a day’s RDA, vs a cupful of pineapple giving a little under 2% of the RDA). So, this is a fair win for kiwi.
In the category of minerals, things are clear: kiwi has more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while pineapple has more manganese. An overwhelming win for kiwi.
Looking at their respective anti-inflammatory powers, pineapple has its special bromelain enzymes, which is a point in its favour, but when it comes to actual polyphenols, the two fruits are quite balanced, with kiwi’s flavonoids vs pineapple’s lignans.
Adding up the sections, it’s a clear win for kiwi—but pineapple is a very respectable fruit too (especially because of its bromelain content), so do enjoy both!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Bromelain vs Inflammation & Much More
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Drug & Supplement Combo That Reverses Aging
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
So far, its effects have been dramatic (in a good way) in mice; human trials are now underway.
How does it work?
It builds from previous work, in which a Japanese research team created an “anti-aging vaccine”, that responded to a problem more specific than aging as a whole, namely atherosclerosis.
They found that a certain* protein was upregulated (i.e., it was made at a greater rate resulting in greater quantities) in patients (mouse and human alike) with atherosclerosis. So, they immunized the mice against that protein, and long story short, everything improved for them, from their atherosclerosis to general markers of aging—including growing back fur that had been lost due to age-related balding (just like in humans). They also lived longer, as is to be expected of a mouse who is now biologically younger.
*To avoid being mysterious: it was glycoprotein nonmetastatic melanoma protein B, known to its friends as GPNMB.
You may be wondering: how can one be immunized against a protein? If so, do bear in mind, a virus is also a protein. In this case, they developed an RNA vaccine, that works in a similar way to the COVID vaccines we all know and love (albeit with a different target).
You can read about this in abundant detail here: Senolytic vaccination improves normal and pathological age-related phenotypes and increases lifespan in progeroid mice
Hot on the heels of that, new approaches were found, including…
The combination
We’ll not keep you waiting; the combination is dasatinib plus quercetin, or else fisetin alone.
It’s about killing senescent (aging) “zombie cells” while sparing healthy cells, which that drug (dasatinib) and those supplements (quercetin and fisetin) do.
The researchers noted:
❝Senescent cells are resistant to apoptosis, which is governed through the upregulation of senescent cell anti-apoptotic pathways (SCAPs). Compounds were subsequently identified that disrupted the SCAPs, inducing death of senescent cells while leaving healthy cells unaffected. Forty-six potential senolytic agents were discovered through this process. To advance translational efforts, the majority of research has focused on agents with known safety profiles and limited off-target effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
The best characterized senolytic agents are dasatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for use in humans for cancer treatment, and quercetin, a naturally occurring plant flavonoid. The agents have a synergistic effect, making their combination more potent for senescent cell clearance (Zhu et al., 2015). As senescent cells do not divide and accumulate over a period of weeks, they can be administered using an intermittent approach, which further serves to reduce the risk of side effects (Kirkland and Tchkonia, 2020).
In preclinical trials, the combination of dasatinib and quercetin (D + Q) have been found to alleviate numerous chronic medical conditions including vascular stiffness, osteoporosis, frailty, and hepatic stenosis❞
Source: A geroscience motivated approach to treat Alzheimer’s disease: Senolytics move to clinical trials
As to how they expanded on this research:
❝In our study, oral D + Q were intermittently administered to tau transgenic mice with late-stage pathology (approximated to a 70-year-old human with advanced AD) (Musi et al., 2018). The treatment effectively reduced cellular senescence and associated senescence-associated secretory phenotype incidence. The 35 % reduction in neurofibrillary tangles was accompanied by enhanced neuron density, decreased ventricular enlargement, diminished tau accumulation, and restoration of aberrant cerebral blood flow. A subsequent preclinical study validated the findings, reporting that intermittently administered D + Q cleared senescent cells in the central nervous system, reduced amyloid-β plaques, attenuated neuroinflammation, and enhanced cognition❞
Source: Ibid.
And now taking it to humans:
❝The first clinical trial of D + Q for early-stage Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) has completed enrollment (Gonzales et al., 2021). The primary aim of the open-label pilot study was to examine the central nervous system penetrance of D and Q in a small sample of older adults with early-stage AD (NCT04063124). In addition, two placebo-controlled trials of D + Q for neurodegenerative disease are underway (NCT04685590 and NCT04785300).
One of the trials in development is a multi-site, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of senolytic therapy in older adults with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or early-stage dementia (Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) Global 0.5–1) due to AD (elevated CSF total tau/Aβ42 ratio).
The treatment regimen will consist of 12-weeks of intermittently administered oral D + Q.❞
Source: Ibid.
The study is actually completed now, but its results are not yet published (again, at time of writing). Which means: they have the data, and now they’re writing the paper.
We look forward to providing an update about that, when the paper is published!
In the meantime…
Dasatinib is a drug usually prescribed to people with certain kinds of leukemia, and suffice it to say, it’s prescription-only. And unlike drugs that are often prescribed off-label (such as metformin for weight loss), getting your doctor to prescribe you an anticancer drug is unlikely unless you have the cancer in question.
You may be wondering: how is an anticancer drug helpful against aging? And the answer is that cancer and aging are very interrelated, and both have to do with “these old cells just won’t die, and are using the resources needed for young healthy cells”. So in both cases, killing those “zombie cells” while sparing healthy ones, is what’s needed. However, your doctor will probably not buy that as a reason to prescribe you a drug that is technically chemotherapy.
Quercetin, on the other hand, is a readily-available supplement, as is fisetin, and both have glowing (in a good way) safety profiles.
Want to know more?
You can read more about each of quercetin and fisetin (including how to get them), here:
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Many Faces Of Cosmetic Surgery
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Cosmetic Surgery: What’s The Truth?
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion on elective cosmetic surgeries, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 48% said “Everyone should be able to get what they want, assuming informed consent”
- About 28% said “It can ease discomfort to bring features more in line with normalcy”
- 15% said “They should be available in the case of extreme disfigurement only”
- 10% said “No elective cosmetic surgery should ever be performed; needless danger”
Well, there was a clear gradient of responses there! Not so polarizing as we might have expected, but still enough dissent for discussion
So what does the science say?
The risks of cosmetic surgery outweigh the benefits: True or False?
False, subjectively (but this is important).
You may be wondering: how is science subjective?
And the answer is: the science is not subjective, but people’s cost:worth calculations are. What’s worth it to one person absolutely may not be worth it to another. Which means: for those for whom it wouldn’t be worth it, they are usually the people who will not choose the elective surgery.
Let’s look at some numbers (specifically, regret rates for various surgeries, elective/cosmetic or otherwise):
- Regret rate for elective cosmetic surgery in general: 20%
- Regret rate for knee replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 17.1%
- Regret rate for hip replacement (i.e., not cosmetic): 4.8%
- Regret rate for gender-affirming surgeries (for transgender patients): 1%
So we can see, elective surgeries have an 80–99% satisfaction rate, depending on what they are. In comparison, the two joint replacements we mentioned have a 82.9–95.2% satisfaction rate. Not too dissimilar, taken in aggregate!
In other words: if a person has studied the risks and benefits of a surgery and decides to go ahead, they’re probably going to be happy with the results, and for them, the benefits will have outweighed the risks.
Sources for the above numbers, by the way:
- What is the regret rate for plastic surgery?
- Decision regret after primary hip and knee replacement surgery
- A systematic review of patient regret after surgery—a common phenomenon in many specialties but rare within gender-affirmation surgery
But it’s just a vanity; therapy is what’s needed instead: True or False?
False, generally. True, sometimes. Whatever the reasons for why someone feels the way they do about their appearance—whether their face got burned in a fire or they just have triple-J cups that they’d like reduced, it’s generally something they’ve already done a lot of thinking about. Nevertheless, it does also sometimes happen that it’s a case of someone hoping it’ll be the magical solution, when in reality something else is also needed.
How to know the difference? One factor is whether the surgery is “type change” or “restorative”, and both have their pros and cons.
- In “type change” (e.g. rhinoplasty), more psychological adjustment is needed, but when it’s all over, the person has a new nose and, statistically speaking, is usually happy with it.
- In “restorative” (e.g. facelift), less psychological adjustment is needed (as it’s just a return to a previous state), so a person will usually be happy quickly, but ultimately it is merely “kicking the can down the road” if the underlying problem is “fear of aging”, for example. In such a case, likely talking therapy would be beneficial—whether in place of, or alongside, cosmetic surgery.
Here’s an interesting paper on that; the sample sizes are small, but the discussion about the ideas at hand is a worthwhile read:
Does cosmetic surgery improve psychosocial wellbeing?
Some people will never be happy no matter how many surgeries they get: True or False?
True! We’re going to refer to the above paper again for this one. In particular, here’s what it said about one group for whom surgeries will not usually be helpful:
❝There is a particular subgroup of people who appear to respond poorly to cosmetic procedures. These are people with the psychiatric disorder known as “body dysmorphic disorder” (BDD). BDD is characterised by a preoccupation with an objectively absent or minimal deformity that causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning.
For several reasons, it is important to recognise BDD in cosmetic surgery settings:
Firstly, it appears that cosmetic procedures are rarely beneficial for these people. Most patients with BDD who have had a cosmetic procedure report that it was unsatisfactory and did not diminish concerns about their appearance.
Secondly, BDD is a treatable disorder. Serotonin-reuptake inhibitors and cognitive behaviour therapy have been shown to be effective in about two-thirds of patients with BDD❞
~ Dr. David Castle et al. (lightly edited for brevity)
Which is a big difference compared to, for example, someone having triple-J breasts that need reducing, or the wrong genitals for their gender, or a face whose features are distinct outliers.
Whether that’s a reason people with BDD shouldn’t be able to get it is an ethical question rather than a scientific one, so we’ll not try to address that with science.
After all, many people (in general) will try to fix their woes with a haircut, a tattoo, or even a new sportscar, and those might sometimes be bad decisions, but they are still the person’s decision to make.
And even so, there can be protectionist laws/regulations that may provide a speed-bump, for example:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
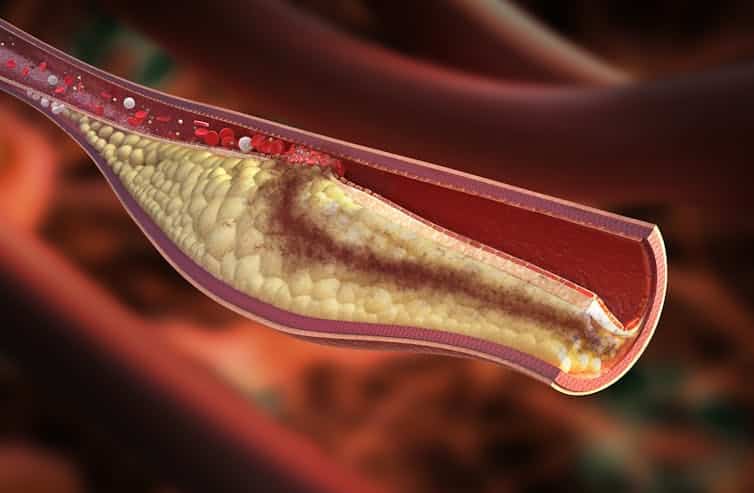
Microplastics found in artery plaque linked with higher risk of heart attack, stroke and death
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Microplastics and nanoplastics are everywhere in our environment – including in our oceans and lakes, farmland, and even Arctic ice algae.
Microplastics have also been found inside of us – with studies detecting them in various tissues including in the lungs, blood, heart and placenta. Understandably, concern is rising about the potential risks of microplastics on our health.
However, while a growing body of research has focused on microplastics and nanoplastics, there’s still a lack of direct evidence that their presence in human tissues is harmful to our health – and it’s uncertain if they are related to particular diseases.
A new study has uncovered a correlation between microplastics and heart health, though. The researchers found that people who had detectable microplastics and nanoplastics in the plaque in their arteries had a higher risk of heart attack, stroke and death.
Heart health
The researchers looked at 257 people altogether. All of the patients were already undergoing preventative surgery to remove plaque from their carotid arteries (the main arteries that supply the brain with blood). This allowed the researchers to collect plaque samples and perform a chemical analysis. They then followed up with participants 34 months later.
Of the 257 participants, 150 were found to have the presence of microplastics and nanoplastics in their arterial plaque – mainly fragments of two of the most commonly used plastics in the world, polyethylene (used in grocery bags, bottles and food packaging) and polyvinyl chloride (used in flooring, cladding and pipes).
A statistical analysis of this data found that patients with microplastics and nanoplastics in their plaque had a higher risk of suffering a heart attack, stroke or death from any cause, compared with those who had no microplastics or nanoplastics in their plaque.
The researchers also analysed the macrophages (a type of immune cell that helps remove pathogens from the body) in the patients’ arteries. They found that participants who’d had microplastics and nanoplastics in their plaque also had evidence of plastic fragments in their macrophages.
They also looked at whether certain genes associated with inflammation (which can be a sign of disease) were switched on in the participants. They found that the participants who’d had microplastics and nanoplastics in their plaque also had signs of inflammation in their genes.
The microplastics were found in samples of plaque extracted from the carotid artery. Rocos/ Shutterstock These results may suggest an accumulation of nanoplastics and microplastics in carotid plaque could partly trigger inflammation. This inflammation may subsequently change the way plaque behaves in the body, making it less stable and triggering it to form a blood clot – which can eventually block blood flow, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Interestingly, the researchers also found the presence of nanoplastics and microplastics was more common in participants who had diabetes and cardiovascular disease. This raises a lot of questions which have yet to be answered – such as why microplastics were more common in these participants, and if there may be a correlation between other diseases and the presence of microplastics in the body.
Other health risks
This study only focused on patients who had carotid artery disease and were already having surgery to remove the build-up of plaque. As such, it’s unclear whether the findings of this study can be applied to a larger population of people.
However, it isn’t the first study to show a link between microplastics and nanoplastics with poor health. Research suggests some of this harm may be due to the way microplastics and nanoplastics interact with proteins in the body.
For example, some human proteins adhere to the surface of polystyrene nanoplastics, forming a layer surrounding the nanoparticle. The formation of this layer may influence the activity and transfer of nanoplastics in human organs.
Another study suggested that nanoplastics can interact with a protein called alpha-synuclein, which in mouse studies has been shown to play a crucial role in facilitating communication between nerve cells. These clumps of nanoplastics and protein may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.
My published PhD research in chicken embryos found that nanoplastics may cause congenital malformations due to the way they interact with a protein called cadherin6B. Based on the interactions myself and fellow researchers saw, these malformations may affect the embryo’s eyes and neural tube, as well as the heart’s development and function.
Given the fact that nanoplastics and microplastics are found in carotid plaque, we now need to investigate how these plastics got into such tissues.
In mice, it has been demonstrated that gut macrophages (a type of white blood cell) can absorb microplastics and nanoplastics into their cell membrane. Perhaps a similar mechanism is taking place in the arteries, since nanoplastics have been identified in samples of carotid plaque macrophages.
The findings from this latest study add to a growing body of evidence showing a link between plastic products and our health. It is important now for researchers to investigate the specific mechanisms by which microplastics and nanoplastics cause harm in the body.
Meiru Wang, Postdoctoral Researcher, Molecular Biology and Nanotoxicology, Leiden University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Green Coffee Bean Extract: Coffee Benefits Without The Coffee?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Coffee is, on balance, very good for the health in moderation. We wrote about it here:
The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
Some quick facts before moving on:
- Coffee is the world’s biggest source of antioxidants
- 65% reduced risk of Alzheimer’s for coffee-drinkers
- 67% reduced risk of type 2 diabetes for coffee-drinkers
- 43% reduced risk of liver cancer for coffee-drinkers
- 53% reduced suicide risk for coffee-drinkers
Those are some compelling statistics!
But what about the caffeine content?
Assuming one doesn’t have a caffeine sensitivity, caffeine is also healthy in moderation—but it is easy to accidentally become dependent on it, so it can be good to take a “tolerance break” once in a while, and then reintroduce it with more modest moderation:
Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
We also, for that matter, have discussed its impact on the gut:
Coffee & Your Gut ← surprise, it’s a positive impact
What if I don’t like coffee?
We suspect that, having seen the title of this article, you know what the answer’s going to be here:
Green coffee bean extract is the extract from green (i.e. unroasted) coffee beans. It has one or two advantages over drinking coffee:
- For those who do not like drinking coffee, this supplement sidesteps that neatly
- Roasting coffee beans destroys a lot (sometimes almost all; it depends on the temperature and duration) of their chlorogenic acid, a highly beneficial polyphenol; using unroasted (i.e. green) coffee beans avoids that
See: Role of roasting conditions in the level of chlorogenic acid content in coffee beans
All about GCE and CGA
That’s “green coffee extract” and “chlorogenic acid”, respectively, bearing in mind that the latter is found generously in the former.
As to what it does:
❝CGA is an important and biologically active dietary polyphenol, playing several important and therapeutic roles such as antioxidant activity, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, neuroprotective, anti-obesity, antiviral, anti-microbial, anti-hypertension, free radicals scavenger and a central nervous system (CNS) stimulator. Furthermore, CGA causes hepatoprotective effects.❞
👆 Those are the things we know for sure that it does. And it may do even more things:
❝In addition, it has been found that CGA could modulate lipid metabolism and glucose in both genetically and healthy metabolic related disorders. It is speculated that CGA can perform crucial roles in lipid and glucose metabolism regulation and thus help to treat many disorders such as hepatic steatosis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity as well.❞
Read in full: Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research
About lipid metabolism…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum total cholesterol levels.
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly reduces serum LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels.
- Increases in HDL (“good” cholesterol) after green coffee bean extract consumption are significant in green coffee bean extract dosages ≥400mg/day.
About blood glucose and insulin…
- Green coffee extract supplementation significantly improved fasting blood sugar levels
- Green coffee extract supplementation at ≥400 mg/day significantly lowered postprandial insulin levels (that’s good)
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, but here for your convenience is an example product on Amazon 😎
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Xylitol vs Erythritol – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing xylitol to erythritol, we picked the xylitol.
Why?
They’re both sugar alcohols, which so far as the body is concerned are neither sugars nor alcohols in the way those words are commonly understood; it’s just a chemical term. The sugars aren’t processed as such by the body and are passed as dietary fiber, and nor is there any intoxicating effect as one might expect from an alcohol.
In terms of macronutrients, while technically they both have carbs, for all functional purposes they don’t and just have a little fiber.
In terms of micronutrients, they don’t have any.
The one thing that sets them apart is their respective safety profiles. Xylitol is prothrombotic and associated with major adverse cardiac events (CI=95, adjusted hazard ratio=1.57, range=1.12-2.21), while erythritol is also prothrombotic and more strongly associated with major adverse cardiac events (CI=95, adjusted hazard ratio=2.21, range=1.20-4.07).
So, xylitol is bad and erythritol is worse, which means the relatively “healthier” is xylitol. We don’t recommend either, though.
Studies for both:
- Xylitol is prothrombotic and associated with cardiovascular risk
- The artificial sweetener erythritol and cardiovascular event risk
Links for the specific products we compared, in case our assessment hasn’t put you off them:
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- The WHO’s New View On Sugar-Free Sweeteners ← the WHO’s advice is “don’t”
- Stevia vs Acesulfame Potassium – Which is Healthier? ← stevia’s pretty much the healthiest artificial sweetener around, though, if you’re going to use one
- The Fascinating Truth About Aspartame, Cancer, & Neurotoxicity ← under the cold light of science, aspartame isn’t actually as bad as it was painted a few decades ago, mostly by a viral hoax letter. Per the WHO’s advice, it’s still good to avoid sweeteners in general, however.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Magnesium Glycinate vs Magnesium Citrate – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing magnesium glycinate to magnesium citrate, we picked the citrate.
Why?
Both are fine sources of magnesium, a nutrient in which it’s very common to be deficient—a lot of people don’t eat many leafy greens, beans, nuts, and so forth that contain it.
A quick word on a third contender we didn’t include here: magnesium oxide is probably the most widely-sold magnesium supplement because it’s cheapest to make. It also has woeful bioavailability, to the point that there seems to be negligible benefit to taking it. So we don’t recommend that.
Magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate are both absorbed well, but magnesium citrate is the most well-absorbed form of magnesium supplement.
In terms of the relative merits of the glycine or the citric acid (the “other part” of magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate, respectively), both are also great nutrients, but the amount delivered with the magnesium is quite small in each case, and so there’s nothing here to swing it one way or the other.
For this reason, we went with the magnesium citrate, as the most readily bioavailable!
Want to try them out?
Here they are on Amazon:
Magnesium glycinate | Magnesium citrate
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: