Almonds vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing almonds to cashews, we picked the almonds.
Why?
Both are great! But here’s why we picked the almonds:
In terms of macros, almonds have a little more protein and more than 4x the fiber. Given how critical fiber is to good health, and how most people in industrialized countries in general (and N. America in particular) aren’t getting enough, we consider this a major win for almonds.
Things are closer to even for vitamins, but almonds have a slight edge. Almonds are higher in vitamins A, B2, B3, B9, and especially 27x higher in vitamin E, while cashews are higher in vitamins B1, B5, B6, C & K. So, a moderate win for almonds.
In the category of minerals, cashews do a bit better on average. Cashews have moderately more copper, iron, phosphorus, selenium, and zinc, while almonds boast 6x more calcium, and slightly more manganese and potassium. We say this one’s a slight win for cashews.
Adding the categories up, however, makes it clear that almonds win the day.
However, of course, enjoy both! Diversity is healthy. Just, if you’re going to choose between them, we recommend almonds.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Almonds vs Walnuts – Which is Healthier?
- Pistachios vs Cashews – Which is Healthier?
- Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts!
- What Matters Most For Your Heart?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How (And Why) To Train Your Pre-Frontal Cortex
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Dr. Chapman’s Keys For Mental Focus
This is Dr. Sandra Chapman; she’s a cognitive neuroscientist, on a mission to, in her words, further our understanding of:
- what makes the brain stronger, faster and last longer
- what enhances human cognitive capacity, and
- what enhances the underlying brain systems across the lifespan.
To this end, she’s also the founder and Chief Director of the Center For Brain Health, where she has worked on her mission for the past 25 years (clocking up hundreds of peer-reviewed publications to her name), as well as being a professor of Behavioral and Brain Sciences at UT Dallas.
What does she want us to know?
Get your brain into gear
When it comes to your brainpower, it is “use it or lose it”, but it is also perfectly possible to use it and lose it.
Why?
Very often, what we are using our brains for is high-strain, low-yield stuff, such as multitasking, overthinking, or overthinking while multitasking. And to make it worse, we often do it without sufficient rest.
This is the equivalent of owning a Ferrari but trying to drive it in second and third gear at once by switching between the two as rapidly as possible. And doing that for 18 hours each day.
Suffice it to say, you’ll be going nowhere quickly.
An alternative “use” of brainpower is low-strain, low-yield stuff, such as having to pay close attention to a boring conversation. It’s enough to stop your mind from doing anything else, but not enough to actually stimulate you.
This is the equivalent of owning a Ferrari but keeping it idling. The wear and tear is minimal this time, but you’re not actually going anywhere either.
Better, of course, are the other two quadrants:
- low-strain, high-yield: consistently using our brain in relatively non-taxing ways that encourage its development
- high-strain, high-yield: here the Ferrari metaphor definitely fails, because unlike cars, our bodies (including our brains) are machines that benefit from judicious regular progressive overloading (but just by a bit, and with adequate recovery time between overloads).
See also: 12 Weeks To Measurably Boost Your Brain
How to do the “low-strain, low-yield” part
When it comes to “what’s the most important part of the brain to help in the face of cognitive decline?” the usual answer is either to focus on memory (hippocampi) or language (various parts, but for example Wernicke’s area and Broca’s area), since people most fear losing memory, and language is very important both socially and practically.
Those are indeed critical, and we at 10almonds stand by them, but Dr. Chapman (herself having originally trained as speech and language pathologist!) makes a strong case for adding a third brain part to the list.
Specifically, she advocates for strengthening the pre-frontal cortex, which is responsible for inhibition, task-switching, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. If that seems like a lot, do remember it’s a whole cortex and not one of the assorted important-but-small brain bits we mentioned above.
How? She has developed training programs for this, based on what she calls Strategic Memory Advanced Reasoning Tactics (SMART), to support support attention, planning, judgment and emotional management.
You can read more about those programs here:
Center For Brain Health | Our Programs
Participation in those is mostly not free, however, if you join their…
Center For Brain Health | BrainHealth Project
…then they will periodically invite you to join pilot programs, research programs, and the like, which will either be free or they-pay-you affairs—because this is how science is done, and you can read about yourself (anonymized, of course) later in peer-reviewed papers of the kind we often cite here.
If you’re not interested in any of that though, we will say that according to Dr. Chapman, the keys are:
Inhibition: be conscious of this function of your brain, and develop it. This is the function of your brain that stops you from making mistakes—or put differently: stops you from saying/doing something stupid.
Switching: do this consciously; per “I am now doing this task, now I am switching to this other task”, rather than doing the gear-grinding thing we discussed earlier
Working memory: this is effectively your brain’s RAM. Unlike the RAM of a computer (can be enhanced by adding another chip or replacing with a bigger chip), our brain’s RAM can be increased by frequent use, and especially by judicious use of progressive overloading (with rests between!) which we’ll discuss in the high-strain, high-yield section.
Flexibility: this is about creative problem-solving, openness to new ideas, and curiosity
See also: Curiosity Kills The Neurodegeneration
How to do the “high-strain, high-yield” part
Delighting this chess-playing writer, Dr. Chapman recommends chess. Although, similar games such as go (a Chinese game that looks simpler than chess but actually requires more calculation) work equally well too.
Why?
Games like chess and go cause structural changes that are particularly helpful, in terms of engaging in such foundational tasks as learning, abstract reasoning, problem-solving and self-control:
Chess Practice as a Protective Factor in Dementia
Basically, it checks (so to speak) a lot of boxes, especially for the pre-frontal cortex. Some notes:
- Focusing on the game is required for brain improvement; simply pushing wood casually will not do it. Ideally, calculating several moves ahead will allow for strong working memory use (because to calculate several moves ahead, one will have to hold increasingly many possible positions in the mind while doing so).
- The speed of play must be sufficiently slow as to allow not only for thinking, but also for what in chess is called “blunder-checking”, in other words, having decided on one’s move, pausing to consider whether it is a mistake, and actively trying to find evidence that it is. This is the crucial “inhibition habit”, and when one does it reflexively, one will make fewer mistakes. Tying this to dementia, see for example how one of the common symptoms of dementia is falling for scams that one wouldn’t have previously. How did cognitive decline make someone naïve? It didn’t, per se; it just took away their ability to, having decided what to do, pause to consider whether it was a mistake, and actively trying to find evidence that it is.
- That “conscious switching” that we talked about, rather than multitasking? In chess, there is a difference between strategy and tactics. Don’t worry about what that difference is for now (learn it if you want to take up chess), but know that strong players will only strategize while it is their opponent’s turn, and only calculate (tactics) while it is their own turn. It’s very tempting to flit constantly between one and the other, but chess requires players to have the mental discipline be able to focus on one task or the other and stick with that task until it’s the appointed time to switch.
If you feel like taking up chess, this site (and related app, if you want it) is free (it’s been funded by voluntary donations for a long time now) and good and even comes with free tuition and training tools: LiChess.org
Here’s another site that this writer (hi, it’s me) personally uses—it has great features too, but many are paywalled (I’m mostly there just because I’ve been there nearly since its inception, so I’m baked into the community now): Chess.com
Want to know more?
You might like this book by Dr. Chapman, which we haven’t reviewed yet but it did inform large parts of today’s article:
Make Your Brain Smarter: Increase Your Brain’s Creativity, Energy, and Focus – by Dr. Sandra Chapman
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
How Internal Organs Can Be Affected By Spicy Foods (Doctor Explains)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Capsaicin has an array of health-giving properties in moderation, but consumed in immoderation and/or without building up tolerance first, can cause problems—serious health issues such as heart attacks, brain spasms, torn esophagus, and even death can occur.
Heating up
Capsaicin, the compound that gives peppers their “heat”, is a chemical irritant and neurotoxin that activates pain receptors (TRPV1) tricking the brain into sensing heat, leading to a burning sensation, sweating, and flushing. The pain signal can also trigger the fight-or-flight response, causing a surge of adrenaline. Endorphins are eventually released, creating a pain-relief effect similar to a runner’s high, and ultimately it reduces systemic inflammation, boosts the metabolism, and increases healthy longevity.
However, in cases of extreme consumption and/or lack of preparation, woe can befall, for example:
- A man ruptured his esophagus after vomiting from eating a ghost pepper.
- A participant experienced severe brain blood vessel constriction (reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome) after eating a Carolina reaper.
- A 25-year-old suffered permanent heart damage from cayenne pepper pills due to restricted blood flow.
- A teenager died after the “one chip challenge,” although the cause of death was undetermined.
So, what does moderation and preparation look like?
Moderation can be different to different people, since genetics do play a part—some people have more TRPV1 receptors than other people. However, for all people (unless in case of having an allergy or similar), acclimatization is important, and a much bigger factor than genetics.
Writer’s anecdote: on the other hand, when my son was a toddler I once left the room and came back to find him cheerfully drinking hot sauce straight from the bottle, so it can be suspected that genetics are definitely relevant too, as while I did season his food and he did already enjoy curries and such, he didn’t exactly have a background of entering chili-eating competitions.
Still, regardless of genes (unless you actually have a medical condition that disallows this), a person who regularly eats spicy food will develop an increasing tolerance for spicy food, and will get to enjoy the benefits without the risks, provided they don’t suddenly jump way past their point of tolerance.
On which note, in this video you can also see what happens when Dr. Deshauer goes from biting a jalapeño (relatively low on the Scoville heat scale) to biting a Scotch bonnet pepper (about 10x higher on the Scoville heat scale):
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Capsaicin For Weight Loss And Against Inflammation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
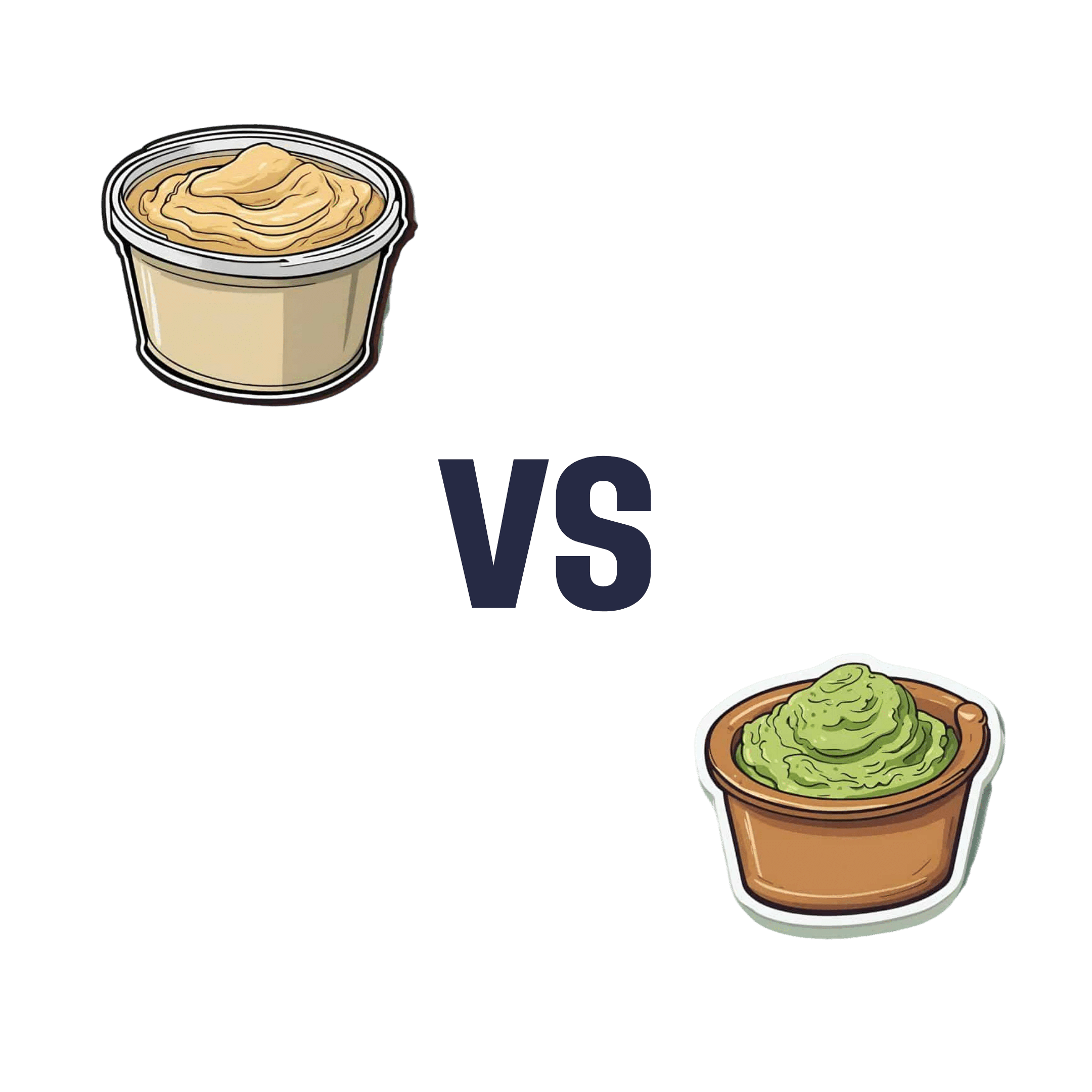
Hummus vs Guacamole – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hummus to guacamole, we picked the guacamole.
Why?
First up, let’s assume that the standards are comparable, for example that both have been made with simple whole foods. The hummus is mostly chickpeas with tahini and a little olive oil and some seasoning; the guacamole is mostly avocado with a little lime juice and some seasoning.
In terms of macronutrients, hummus has slightly more protein and fiber, 2x the carbohydrates (but they are healthy carbs), and usually slightly less fat (but the fats are healthy in both cases).
In terms of micronutrients, the hummus is rich in iron and B vitamins, and the guacamole is rich in potassium, magnesium, vitamins C, E, and K.
So far, it’s pretty much tied. What else is there to consider?
We picked the guacamole because some of its nutrients (especially the potassium, magnesium, and vitamin K) are more common deficiencies in most people’s diets than iron and B vitamins. So, on average, it’s probably the one with the nutrients that you need more of at any given time.
So, it was very very close, and it came down to the above as the deciding factor.
However!
- If you like one and not the other? Eat that one; it’s good.
- If you like both but feel like eating one of them in particular? Eat that one; your body is probably needing those nutrients more right now.
- If you are catering for a group of people? Serve both!
- If you are catering for just yourself and would enjoy both? Serve both! There’s nobody to stop you!
Want to read more?
You might like: Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Metabolical – by Dr. Robert Lustig
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The premise of this book itself is not novel: processed food is bad, food giants lie to us, and eating better makes us less prone to disease (especially metabolic disease).
What this book does offer that’s less commonly found is a comprehensive guide, a walkthrough of each relevant what and why and how, with plenty of good science and practical real-world examples.
In terms of unique selling points, perhaps the greatest strength of this book is its focus on two things in particular that affect many aspects of health: looking after our liver, and looking after our gut.
The style is… A little dramatic perhaps, but that’s just the style; there’s no hyperbole, he is stating well-established scientific facts.
Bottom line: very much of chronic disease would be a lot less diseasey if we all ate with these aspects of our health in mind. This book’s a comprehensive guide to that.
Click here to check out Metabolical, and let food be thy medicine!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Encyclopedia Of Herbal Medicine – by Andrew Chevallier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A common problem with a lot of herbal medicine is it’s “based on traditional use only”, while on the other hand, learning about the actual science of it can mean poring through stacks of Randomized Clinical Trials, half of which are paywalled.
This beautifully and clearly-illustrated book bridges that gap. It gives not just the history, but also the science, of the use of many medicinal herbs (spotlight on 100 key ones; details on 450 more).
It gives advice on growing, harvesting, processing, and using the herbs, as well as what not to do (with regard to safety). And in case you don’t fancy yourself a gardener, you’ll also find advice on places one can buy herbs, and what you’ll need to know to choose them well (controlling for quality etc).
You can read it cover-to-cover, or look up what you need by plant in its general index, or by ailment (200 common ailments listed). As for its bibliography, it does list many textbooks, but not individual papers—though it does cite 12 popular scientific journals too.
Bottom line: if you want a good, science-based, one-stop book for herbal medicine, this is a top-tier choice.
Click here to check out the Encyclopedia of Herbal Medicine, and expand your home remedy repertoire!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Feel Great, Lose Weight – by Dr. Rangan Chatterjee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that losing weight sustainably tends to be harder than simply losing weight. We know that weight loss needs to come with lifestyle change. But how to get there?
One of the biggest problems that we might face while trying to lose weight is that our “metabolic thermostat” has got stuck at the wrong place. Trying to move it just makes our bodies think we are starving, and everything gets even worse. We can’t even “mind over matter” our way through it with willpower, because our bodies will do impressive things on a cellular level in an attempt to save us… Things that are as extraordinary as they are extraordinarily unhelpful.
Dr. Rangan Chatterjee is here to help us cut through that.
In this book, he covers how our metabolic thermostat got stuck in the wrong place, and how to gently tease it back into a better position.
Some advices won’t be big surprises—go for a whole foods diet, avoiding processed food, for example. Probably not a shocker.
Others are counterintuitive, but he explains how they work—exercising less while moving more, for instance. Sounds crazy, but we assure you there’s a metabolic explanation for it that’s beyond the scope of this review. And there’s plenty more where that came from, too.
Bottom line: if your weight has been either slowly rising, or else very stable but at a higher point than you’d like, Dr. Chatterjee can help you move the bar back to where you want it—and keep it there.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: