Sunflower Corn Burger
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burgers are rarely a health food, but in this case, everything in the patty is healthy, and it’s packed with protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
You will need
- 1 can chickpeas
- ¾ cup frozen corn
- ½ cup chopped fresh parsley
- ⅓ cup sunflower seeds
- ⅓ cup cornichon pickles
- ⅓ cup wholegrain bread crumbs (gluten-free, if desired/required)
- ¼ bulb garlic (or more if you want a stronger flavor)
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil, plus more for frying
- 1 tbsp nutritional yeast (or 1 tsp yeast extract)
- 2 tsp ground cumin
- 2 tsp red pepper flakes
- 2 tsp black pepper, coarse ground
- 1 tsp Dijon mustard
- To serve: 4 burger buns; these are not usually healthy, so making your own is best, but if you don’t have the means/time, then getting similarly shaped wholegrain bread buns works just fine.
- Optional: your preferred burger toppings, e.g. greenery, red onion, tomato slices, avocado, jalapeños, whatever does it for you
Note: there is no need to add salt; there is enough already in the pickles.
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Combine all the ingredients except the buns (and any optional toppings) in a food processor, pulsing a few times for a coarse texture (not a purée).
2) Shape the mixture into 4 burger patties, and let them chill in the fridge for at least 30 minutes.
3) Heat a skillet over a medium-high heat with some olive oil, and fry the burgers on both sides until they develop a nice golden crust; this will probably take about 4 minutes per side.
4) Assemble in the buns with any toppings you want, and serve:
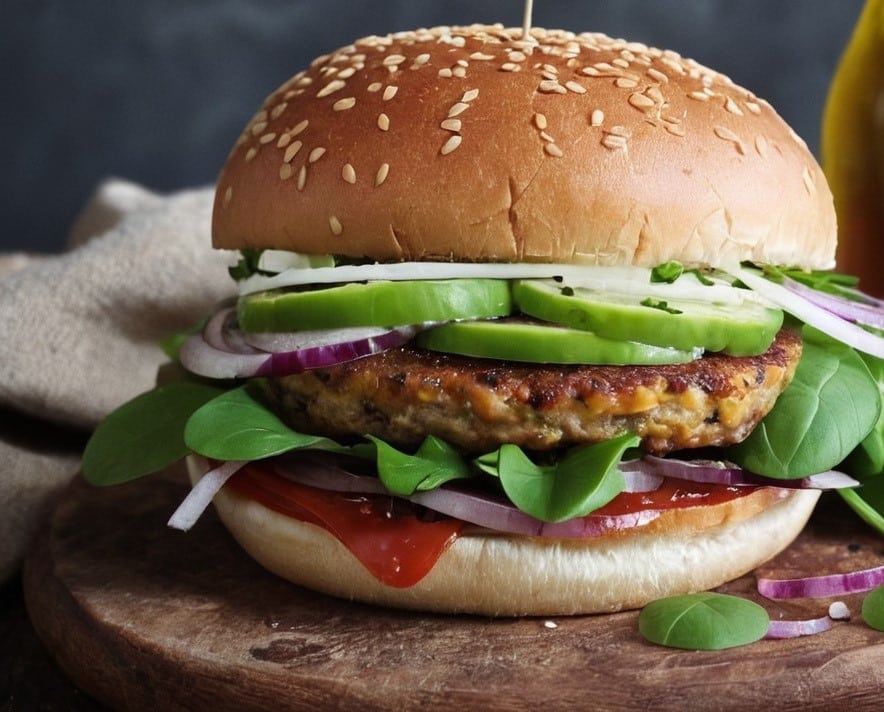

Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Sunflower Seeds vs Pumpkin Seeds – Which is Healthier? ← pumpkin seeds have more micronutrients; sunflower seeds have more healthy fats; feel free to use either or both in this recipe
- What Omega-3 Fatty Acids Really Do For Us
- Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Here’s how to help protect babies and kids from RSV
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What you need to know
- RSV is a respiratory virus that is especially dangerous for babies and young children.
- There are two ways to help protect babies from RSV: vaccination during pregnancy and giving babies nirsevimab, an RSV antibody shot.
- If someone in your household has RSV, watch for signs of severe illness and take steps to help prevent it from spreading.
Respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, is a very contagious seasonal respiratory illness that is especially dangerous for infants and young children. Cases rose dramatically last month, and an increasing number of kids and older adults with RSV are being hospitalized across the United States.
Fortunately, pregnant people can get vaccinated during pregnancy or get their infants and young children an RSV antibody shot to help them stay healthy.
Read on to learn about symptoms of RSV, how to help prevent infants and children from getting very sick, and what families should do if someone in their household is sick with the virus.
What are the symptoms of RSV in babies and young children?
RSV symptoms in young children may include a runny nose, decreased eating and drinking, and coughing, which may lead to wheezing and difficulty breathing.
Infants with RSV may show symptoms like irritability, decreased activity and appetite, and life-threatening pauses in breathing (apnea) that last for more than 10 seconds. Most infants with RSV will not develop a fever, but babies who are born prematurely, have weakened immune systems, or have chronic lung disease are more likely to become very sick.
Who is eligible for an RSV antibody shot?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that babies younger than 8 months whose gestational parent did not receive an RSV vaccine during pregnancy receive nirsevimab between October and March, when RSV typically peaks. This antibody shot delivers proteins that can help protect them against RSV.
Nirsevimab is also recommended for children between 8 and 19 months who are at increased risk of severe RSV, including children who are born prematurely, have chronic lung disease or severe cystic fibrosis, are immunocompromised, or are American Indians or Alaska Natives.
Nirsevimab is typically covered by insurance or costs $495 out of pocket. Children who are eligible for the CDC’s Vaccines for Children Program can receive nirsevimab at no cost.
How can families help prevent RSV from spreading?
It’s recommended that children and adults who are sick with RSV stay home and away from others. If your infant or child has difficulty breathing or develops blue or gray skin, take them to an emergency room right away.
People who are infected with RSV can spread the disease when they cough or sneeze; have close contact with others; or touch, cough, or sneeze on shared surfaces. Help protect your family from catching and spreading RSV at home and in public places by ensuring that everyone covers their mouths during coughing and sneezing, washes their hands often, and wears a high-quality, well-fitting mask.
For more information, talk to your health care provider.
This article first appeared on Public Good News and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.
Share This Post
-
Build Muscle (Healthily!)
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Do You Have To Gain?
We have previously promised a three-part series about changing one’s weight:
- Losing weight (specifically, losing fat)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining muscle)
- Gaining weight (specifically, gaining fat)
And yes, that last one is also something that some people want/need to do (healthily!), and want/need help with that.
There will be, however, no need for a “losing muscle” article, because (even though sometimes a person might have some reason to want to do this), it’s really just a case of “those things we said for gaining muscle? Don’t do those and the muscle will atrophy naturally”.
Here’s the first part: How To Lose Weight (Healthily!)
While some people will want to lose fat, please do be aware that the association between weight loss and good health is not nearly so strong as the weight loss industry would have you believe:
And, while BMI is not a useful measure of health in general, it’s worth noting that over the age of 65, a BMI of 27 (which is in the high end of “overweight”, without being obese) is associated with the lowest all-cause mortality:
BMI and all-cause mortality in older adults: a meta-analysis
Body weight, muscle mass, and protein:
That BMI of 27, or whatever weight you might wish to be, ignores body composition. You’re probably aware that volume-for-volume, muscle weighs more than fat.
You’re also probably aware that if we’re not careful, we tend to lose muscle as we get older. This is known as age-related sarcopenia:
Protein, & Fighting Sarcopenia
Dr. Gabrielle Lyon, our featured expert in the above article, recommends getting at least 1.6g of protein per kg of body weight per day (Americans, divide your weight in pounds by 2.2 to get your weight in kg).
So for example, if you weigh 165lb, that’s 75kg, that’s 1.6×75=120g of protein per day.
There is an upper limit to how much protein per day is healthy, and that limit is probably around 2g of protein per kg of body weight per day:
Protein: How Much Do We Need, Really?
You may be wondering: should we go for animal or plant protein? In which case, the short version is:
- If you only care about muscle growth, any complete sources of protein are fine
- If you care about your general health too, then avoiding red meat is best, but other common protein sources are all fine
- Unprocessed is (unsurprisingly) better than processed in either case
Longer version: Plant vs Animal Protein: Head to Head
What exercises are best for muscle-building?
Of course, different muscles require different exercises, but for all of them, resistance training is what builds muscle the most, and it’s pretty much impossible to build a lot of muscle otherwise.
Check out: Resistance Is Useful! (Especially As We Get Older)
Prepare to fail!
No, really, prepare to fail. Because while resistance training in general is good for maintaining strong muscles and bones, you will only gain muscle if your current muscle is not enough to do the exercise:
- If you do a heavy resistance exercise without undue difficulty, your muscles will say to each other “Good job, team! That was hard, but luckily we were strong enough; no changes necessary”.
- If you do a heavy resistance exercise to the point where you can no longer do it (called: training to failure), then your muscles will say to each other “Oof, what a task! What we’ve got here is clearly not enough, so we’ll have to add more muscle for next time”.
Safety note: training to failure comes with safety risks. If using free weights or weight machines, please do so under well-trained supervision. If doing it with bodyweight (e.g. press-ups until you can press no more) or resistance bands, please check with your doctor first to ensure this is safe for you.
You can also increase the effectiveness of your resistance training by doing it in a way that “confuses” your muscles, making it harder for them to adapt in the moment, and thus forcing them to adapt more in the long term (e.g. get bigger and stronger):
HIIT, But Make It HIRT: High Intensity Resistance Training
Make time for recovery
While many kinds of exercise can be done daily, exercise to build muscle(s) means at the very least resting that muscle (or muscle group) the next day.
For this reason, a lot of bodybuilders have for example a week’s schedule that might look like:
- Monday: Upper body training
- Wednesday: Lower body training
- Friday: Core strength training
…and rest on other days. This gives most muscles a full week of recovery, and every muscle at least 48 hours of recovery.
Note: bodybuilders, like children (who are also doing a lot of body-building, in their own way) need more sleep in order to allow for this recovery and growth to occur. Serious bodybuilders often aim for 12 hours sleep per day. This might be impractical, undesirable, or even impossible for some people, but it’s a factor to be borne in mind and not forgotten.
See also:
Overdone It? How To Speed Up Recovery After Exercise (According To Actual Science)
Anything else that can (safely and healthily) be done to promote muscle growth?
There are a lot of supplements on the market; some are healthy and helpful, other not so much. Here are some we’ve written about:
- What To Eat, Take, And Do Before A Workout
- Creatine: Very Different For Young & Old People
- Ginseng: Exercising With Less Soreness!
- Taurine’s Benefits For Heart Health And More
- Topping Up Testosterone? What To Consider
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Encyclopedia Of Herbal Medicine – by Andrew Chevallier
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
A common problem with a lot of herbal medicine is it’s “based on traditional use only”, while on the other hand, learning about the actual science of it can mean poring through stacks of Randomized Clinical Trials, half of which are paywalled.
This beautifully and clearly-illustrated book bridges that gap. It gives not just the history, but also the science, of the use of many medicinal herbs (spotlight on 100 key ones; details on 450 more).
It gives advice on growing, harvesting, processing, and using the herbs, as well as what not to do (with regard to safety). And in case you don’t fancy yourself a gardener, you’ll also find advice on places one can buy herbs, and what you’ll need to know to choose them well (controlling for quality etc).
You can read it cover-to-cover, or look up what you need by plant in its general index, or by ailment (200 common ailments listed). As for its bibliography, it does list many textbooks, but not individual papers—though it does cite 12 popular scientific journals too.
Bottom line: if you want a good, science-based, one-stop book for herbal medicine, this is a top-tier choice.
Click here to check out the Encyclopedia of Herbal Medicine, and expand your home remedy repertoire!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Food for Life – by Dr. Tim Spector
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book is, as the author puts it, “an eater’s guide to food and nutrition”. Rather than telling us what to eat or not eat, he provides an overview of what the latest science has to say about various foods, and leaves us to make our own informed decisions.
He also stands firmly by the “personalized nutrition” idea that he introduced in his previous book which we reviewed the other day, and gives advice on what tests we might like to perform.
The writing style is accessible, without shying away from reference to hard science. Dr. Spector provides lots of information about key chemicals, genes, gut bacteria, and more—as well as simply providing a very enjoyable read along the way.
Bottom line: if you’d like a much better idea of what food is (and isn’t) doing what, this book is an invaluable resource.
Click here to check out Food for Life, and make the best decisions for you!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Is Air-Fried Food Really Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Air-frying has a reputation for being healthy—and it generally is, provided it’s used carefully:
Just one thing to watch out for
An air-fryer is basically a small convection oven that uses circulating air rather than immersion in oil to cook food. The smallness of an air-fryer is a feature not a bug—if you get an air-fryer over a certain size, then congratulations, you just have a convection oven. The small size it what helps it to cook so efficiently. This is one reason that they’re not really used in industrial settings.
The documentary-makers from this video had their food (chicken, fish, and fries) lab-tested (for fat, cholesterol, and acrylamide), and found:
- Air-frying significantly reduced saturated fat (38–53%) and trans fats (up to 55%) in some foods.
- Cholesterol reduction varied depending on the food type.
- Acrylamide levels in air-fried potatoes were much higher due to cooking time and temperature.
About that acrylamide: acrylamide forms in starchy foods at high temperatures and may pose cancer risks (the research is as yet unclear, with conflicting evidence). Air-frying can cause higher acrylamide levels if cooking is prolonged or temperatures are too high.
Recommendations to reduce acrylamide:
- Soak potatoes before cooking.
- Use lower temperatures (e.g. 180℃/350℉) and shorter cooking times.
- Avoid over-browning food.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Unlock Your Air-Fryer’s Potential!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Ruminating vs Processing
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
When it comes to traumatic experiences, there are two common pieces of advice for being able to move forwards functionally:
- Process whatever thoughts and feelings you need to process
- Do not ruminate
The latter can seem, at first glance, a lot like the former. So, how to tell them apart, and how to do one without the other?
Getting tense
One major difference between the two is the tense in which our mental activity takes place:
- processing starts with the traumatic event (or perhaps even the events leading up to the traumatic event), analyses what happened and if possible why, and then asks the question “ok, what now?” and begins work on laying out a path for the future.
- rumination starts with the traumatic event (or perhaps even the events leading up to the traumatic event), analyses what happened and if why, oh why oh why, “I was such an idiot, if only I had…” and gets trapped in a fairly tight (and destructive*) cycle of blame and shame/anger, never straying far from the events in question.
*this may be directly self-destructive, but it can also sometimes be only indirectly self-destructive, for example if the blame and anger is consciously placed with someone else.
This idea fits in, by the way, with Dr. Elisabeth Kübler-Ross’s “five stages of grief” model; rumination here represents the stages “bargaining”, “despair”, and “anger”, while emotional processing here represents the stage “acceptance”. Thus, it may be that rumination does have a place in the overall process—just don’t get stuck there!
For more on healthily processing grief specifically:
What Grief Does To The Body (And How To Manage It)
Grief, by the way, can be about more than the loss of a loved one; a very similar process can play out with many other kinds of unwanted life changes too.
What are the results?
Another way to tell them apart is to look at the results of each. If you come out of a long rumination session feeling worse than when you started, it’s highly unlikely that you just stopped too soon and were on the verge of some great breakthrough. It’s possible! But not likely.
- Processing may be uncomfortable at first, and if it’s something you’ve ignored for a long time, that could be very uncomfortable at first, but there should quite soon be some “light at the end of the tunnel”. Perhaps not even because a solution seems near, but because your mind and body recognize “aha, we are doing something about it now, and thus may find a better way forward”.
- Rumination tends to intensify and prolong uncomfortable emotions, increases stress and anxiety, and likely disrupts sleep. At best, it may serve as a tipping point to seek therapy or even just recognize “I should figure out a way to deal with this, because this isn’t doing me any good”. At worst, it may serve as a tipping point to depression, and/or substance abuse, and/or suicidality.
See also: How To Stay Alive (When You Really Don’t Want To) ← which also has a link back to our article on managing depression, by the way!
Did you choose it, really?
A third way to tell them apart is the level of conscious decision that went into doing it.
- Processing is almost always something that one decides “ok, let’s figure this out”, and sits down to figure it out.
- Rumination tends to be about as voluntary as social media doomscrolling. Technically we may have decided to begin it (we also might not have made any conscious decision, and just acted on impulse), but let’s face it, our hands weren’t at the wheel for long, at all.
A good way to make sure that it is a conscious process, is to schedule time for it in advance, and then do it only during that time. If thoughts about it come up at other times, tell yourself “no, leave that for later”, and then deal with it when (and only when) the planned timeslot arrives.
It’s up to you and your schedule what time you pick, but if you’re unsure, consider an hour in the early evening. That means that the business of the day is behind you, but it’s also not right before bed, so you should have some decompression time as a buffer. So for example, perhaps after dinner you might set a timer* for an hour, and sit down to journal, brainstorm, or just plain think, about the matter that needs processing.
*electronic timers can be quite jarring, and may distract you while waiting for the beeps. So, consider investing in a relaxing sand timer like this one instead.
Is there any way to make rumination less bad?
As we mentioned up top, there’s a case to be made for “rumination is an early part of the process that gets us where we need to go, and may not be skippable, or may not be advisable to skip”.
So, if you are going to ruminate, then firstly, we recommend again bordering it timewise (with a timer as above) and having a plan to pull yourself out when you’re done rather than getting stuck there (such as: The Off-Button For Your Brain: How To Stop Negative Thought Spirals).
And secondly, you might want to consider the following technique, which allows one to let one’s brain know that the thing we’re thinking about / imagining is now to be filed away safely; not lost or erased, but sent to the same place that nightmares go after we wake up:
A Surprisingly Powerful Tool: Eye Movement Desensitization & Reprocessing (EMDR)
What if I actually do want to forget?
That’s not usually recommendable; consider talking it through with a therapist first. However, for your interest, there is a way:
The Dark Side Of Memory (And How To Forget)
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: