Hemp Seeds vs Flax Seeds – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing hemp seeds to flax seeds, we picked the flax.
Why?
Both are great, but quite differently so! In other words, they both have their advantages, but on balance, we prefer the flax’s advantages.
Part of this come from the way in which they are sold/consumed—hemp seeds must be hulled first, which means two things as a result:
- Flax seeds have much more fiber (about 8x more)
- Hemp seeds have more protein (about 2x more), proportionally, at least ← this is partly because they lost a bunch of weight by losing their fiber to the hulling, so the “per 100g” values of everything else go up, even though the amount per seed didn’t change
Since people’s diets are more commonly deficient in fiber than protein, and also since 8x is better than 2x, we consider this a win for flax.
Of course, many people enjoy hemp or flax specifically for the healthy fatty acids, so how do they stack up in that regard?
- Flax seeds have more omega-3s
- Hemp seeds have more omega-6s
This, for us, is a win for flax too, as the omega-3s are generally what we need more likely to be deficient in. Hemp enthusiasts, however, may argue that the internal balance of omega-3s to omega-6s is closer to an ideal ratio in hemp—but nutrition doesn’t exist in a vacuum, so we have to consider things “as part of a balanced diet” (because if one were trying to just live on hemp seeds, one would die), and most people’s diets are skewed far too far in favor or omega-6 compared to omega-3. So for most people, the higher levels of omega-3s are the more useful.
Want to learn more?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Palliative care as a true art form
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How do you ease the pain from an ailment amidst lost words? How can you serve the afflicted when lines start to blur? When the foundation of communication begins to crumble, what will be the pillar health-care professionals can lean on to support patients afflicted with dementia during their final days?
The practice of medicine is both highly analytical and evidence based in nature. However, it is considered a “practice” because at the highest level, it resembles a musician navigating an instrument. It resembles art. Between lab values, imaging techniques and treatment options, the nuances for individualized patient care so often become threatened.
Dementia, a non-malignant terminal illness, involves the progressive cognitive and social decline in those afflicted. Though there is no cure, dementia is commonly met in the setting of end-of-life care. During this final stage of life, the importance of comfort via symptomatic management and communication usually is a priority in patient care. But what about the care of a patient suffering from dementia? While communication serves as the vehicle to deliver care at a high level, medical professionals are suddenly met with a roadblock. And there … behind the pieces of shattered communication and a dampened map of ethical guidelines, health-care providers are at a standstill.
It’s 4:37 a.m. You receive a text message from the overnight nurse at a care facility regarding a current seizure. After lorazepam is ordered and administered, Mr. H, a quick-witted 76-year-old, stabilizes. Phenobarbital 15mg SC qhs was also added to prevent future similar events. You exhale a sigh of relief.
Mr. H. has been admitted to the floor 36 hours earlier after having a seizure while playing poker with colleagues. Since he became your patient, he’s shared many stories from professional and family life with you, along with as many jokes as he could fit in between. However, over the course of the next seven days, Mr. H. would develop aspiration pneumonia, progressing to ventilator dependency and, ultimately, multi-organ failure with rapid cognitive decline.
What strategies and tools would you use to maximize the well-being of your patient during his decline? How would you bridge the gap of understanding between the patient’s family and health-care team to provide the standard of care that all patients are owed?
To give Mr. H. the type of care he would have wanted, upon his hospital admission, he should have been questioned about his understanding of illness along with the goals of care of the medical team. The patient should have been informed that it is imperative to adhere to the medical regimen implemented by his team along with the risks of not doing so. In the event disease-related complications arose, advanced directives should have been documented to avoid any unnecessary measures.
It is important to note, that with each change in status of the patient’s health status, the goal of treatment must be reassessed. The patient or surrogate decision-maker’s understanding of these goals is paramount in maintaining the patient’s autonomy. It is often said that effective communication is the bedrock of a healthy relationship. This is true regardless of type of relationship.
This is why I and Megan Vierhout wrote Integrated End of Life Care in Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide, a book targeted at providing a much-needed road map to navigate the many challenges involved in end-of-life care for individuals with dementia. Ultimately, our aim is to provide a compass for both health-care professionals and the families of those affected by the progressive effects of dementia. We provide practical advice on optimizing communication with individuals with dementia while taking their cognitive limitations, preferences and needs into account.
I invite you to explore the unpredictable terrain of end-of-life care for patients with dementia. Together, we can pave a smoother, sturdier path toward the practice of medicine as a true art form.
This article is republished from healthydebate under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
Ear Candling: Is It Safe & Does It Work?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Does This Practice Really Hold A Candle To Evidence-Based Medicine?
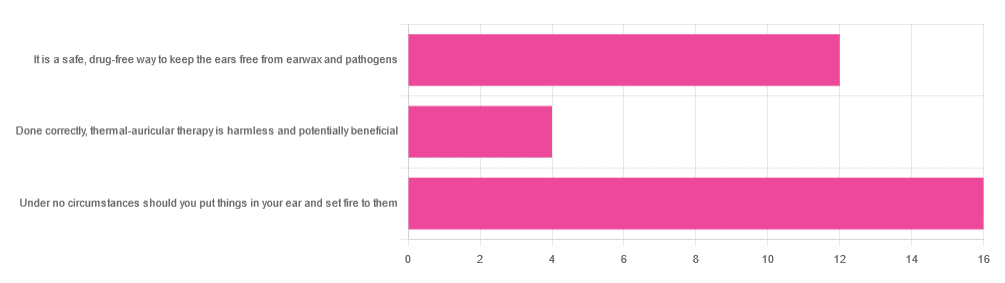
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you your opinion of ear candling, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of responses:
- Exactly 50% said “Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them”
- About 38% said “It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens”
- About 13% said “Done correctly, thermal-auricular therapy is harmless and potentially beneficial”
This means that if we add the two positive-to-candling answers together, it’s a perfect 50:50 split between “do it” and “don’t do it”.
(Yes, 38%+13%=51%, but that’s because we round to the nearest integer in these reports, and more precisely it was 37.5% and 12.5%)
So, with the vote split, what does the science say?
First, a quick bit of background: nobody seems keen to admit to having invented this. One of the major manufacturers of ear candles refers to them as “Hopi” candles, which the actual Hopi tribe has spent a long time asking them not to do, as it is not and never has been used by the Hopi people. Other proposed origins offered by advocates of ear candling include Traditional Chinese Medicine (not used), Ancient Egypt (no evidence of such whatsoever), and Atlantis:
Quackwatch | Why Ear Candling Is Not A Good Idea
It is a safe, drug-free way to keep the ears free from earwax and pathogens: True or False?
False! In a lot of cases of alternative therapy claims, there’s an absence of evidence that doesn’t necessarily disprove the treatment. In this case, however, it’s not even an open matter; its claims have been actively disproven by experimentation:
- It doesn’t remove earwax; on the contrary, experimentation “showed no removal of cerumen from the external auditory canal. Candle wax was actually deposited in some“
- It doesn’t remove pathogens, and the proposed mechanism of action for removing pathogens, that of the “chimney effect”: the idea that the burning candle creates a vacuum that draws wax out of the ear along with debris and bacteria, simply does not work; on the contrary, “Tympanometric measurements in an ear canal model demonstrated that ear candles do not produce negative pressure”.
- It isn’t safe; on the contrary, “Ear candles have no benefit in the management of cerumen and may result in serious injury”
In a medium-sized survey (n=122), the following injuries were reported:
- 13 x burns
- 7 x occlusion of the ear canal
- 6 x temporary hearing loss
- 3 x otitis externa (this also called “swimmer’s ear”, and is an inflammation of the ear, accompanied by pain and swelling)
- 1 x tympanic membrane perforation
Indeed, authors of one paper concluded:
❝Ear candling appears to be popular and is heavily advertised with claims that could seem scientific to lay people. However, its claimed mechanism of action has not been verified, no positive clinical effect has been reliably recorded, and it is associated with considerable risk.
No evidence suggests that ear candling is an effective treatment for any condition. On this basis, we believe it can do more harm than good and we recommend that GPs discourage its use❞
Source: Canadian Family Physician | Ear Candling
Under no circumstances should you put things in your ear and set fire to them: True or False?
True! It’s generally considered good advice to not put objects in general in your ears.
Inserting flaming objects is a definite no-no. Please leave that for the Cirque du Soleil.
You may be thinking, “but I have done this and suffered no ill effects”, which seems reasonable, but is an example of survivorship bias in action—it doesn’t make the thing in question any safer, it just means you were one of the one of the ones who got away unscathed.
If you’re wondering what to do instead… Ear oils can help with the removal of earwax (if you don’t want to go get it sucked out at a clinic—the industry standard is to use a suction device, which actually does what ear candles claim to do). For information on safely getting rid of earwax, see our previous article:
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Grapefruit vs Lemon – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing grapefruit to lemon, we picked the lemon.
Why?
Grapefruit has its merits, but in the battle of the citrus fruits, lemons come out on top nutritionally:
In terms of macros, grapefruit has more carbs while lemons have more fiber. So, while both have a low glycemic index, lemon is still the winner by the numbers.
Looking at the vitamins, here we say grapefruit’s strengths: grapefruit has more of vitamins A, B2, B3, and choline, while lemon has more of vitamins B6 and C. So, a 4:2 win for grapefruit here.
In the category of minerals, lemons retake the lead: grapefruit has more zinc, while lemon has more calcium, copper, iron, manganese, and selenium.
One final consideration that’s not shown in the nutritional values, is that grapefruit contains high levels of furanocoumarin, which can inhibit cytochrome P-450 3A4 isoenzyme and P-glycoptrotein transporters in the intestine and liver—slowing down their drug metabolism capabilities, thus effectively increasing the bioavailability of many drugs manifold.
This may sound superficially like a good thing (improving bioavailability of things we want), but in practice it means that in the case of many drugs, if you take them with (or near in time to) grapefruit or grapefruit juice, then congratulations, you just took an overdose. This happens with a lot of meds for blood pressure, cholesterol (including statins), calcium channel-blockers, anti-depressants, benzo-family drugs, beta-blockers, and more. Oh, and Viagra, too. Which latter might sound funny, but remember, Viagra’s mechanism of action is blood pressure modulation, and that is not something you want to mess around with unduly. So, do check with your pharmacist to know if you’re on any meds that would be affected by grapefruit or grapefruit juice!
PS: the same substance is quite available in pummelos and sour oranges (but not meaningfully in sweet oranges); you can see a chart here showing the relative furanocoumarin contents of many citrus fruits, or lack thereof as the case may be, as it is for lemons and most limes)
Adding up the sections gives us a clear win for lemons, but by all means enjoy either or both; just watch out for that furanocoumarin content of grapefruit if you’re on any meds affected by such (again, do check with your pharmacist, as our list was far from exhaustive—and yes, this question is one that a pharmacist will answer more easily and accurately than a doctor will).
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Top 8 Fruits That Prevent & Kill Cancer ← citrus fruits in general make the list; they inhibit tumor growth and kill cancer cells; regular consumption is also associated with a lower cancer risk 🙂
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
How To Stop Binge-Eating: Flip This Switch!
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
“The Big Eating Therapist” Sarah Dosanjh has insights from both personal and professional experience:
No “Tough Love” Necessary
Eating certain foods is often socially shamed, and it’s easy to internalize that, and feel guilty. While often guilt is considered a pro-social emotion that helps people to avoid erring in a way that will get us excluded from the tribe (bearing in mind that for most of our evolutionary history, exile would mean near-certain death), it is not good at behavior modification when it comes to addictions or anything similar to addictions.
The reason for this is that if we indulge in a pleasure we feel we “shouldn’t” and expect we’d be shamed for, we then feel bad, and we immediately want something to make us feel better. Guess what that something will be. That’s right: the very same thing we literally just felt ashamed about.
So guilt is not helpful when it comes to (for example) avoiding binge-eating.
Instead, Dosanjh points us to a study whereby dieters ate a donut and drank water, before being given candy for taste testing. The control group proceeded without intervention, while the experimental group had a self-compassion intervention between the donut and the candy. This meant that researchers told the participants not to feel bad about eating the donut, emphasizing self-kindness, mindfulness, and common humanity. The study found that those who received the intervention, ate significantly less candy.
What we can learn from this is: we must be kind to ourselves. Allowing ourselves, consciously and mindfully, “a little treat”, secures its status as being “little”, and “a treat”. Then we smile, thinking “yes, that was a nice little thing to do for myself”, and proceed with our day.
This kind of self-compassion helps avoid the “meta-binge” process, where guilt from one thing leads to immediately reaching for another.
For more on this, plus a link to the study she mentioned, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sun-Dried Tomatoes vs Carrots – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sun-dried tomatoes to carrots, we picked the sun-dried tomatoes.
Why?
After tomatoes lost to carrots yesterday, it turns out that sun-drying them is enough to turn the nutritional tables!
This time, it’s the sun-dried tomatoes that have more carbs and fiber, as well as the nominally lower glycemic index (although obviously, carrots are also just fine in this regard; nobody is getting metabolic disease from eating carrots). Still, by the numbers, a win for sun-dried tomatoes.
In terms of vitamins, the fact that they have less water-weight means that proportionally, gram for gram, sun-dried tomatoes have more of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, E, K, and choline, while carrots still have more vitamin A. An easy win for sun-dried tomatoes on the whole, though.
When it comes to minerals, sun-dried tomatoes have more calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, and zinc, while carrots are not higher in any mineral.
Looking at polyphenols, sun-dried tomatoes have more, including a good healthy dose of quercetin; they also have more lycopene, not technically a polyphenol by virtue of its chemical structure (it’s a carotenoid), but a powerful phytochemical nonetheless. And, the lycopene content is higher in sun-dried tomatoes (compared to raw tomatoes) not just because of the loss of water-weight making a proportional difference, but also because the process itself improves the lycopene content, much like cooking does.
All in all, a clear and overwhelming win for sun-dried tomatoes.
Just watch out, as this is about the sun-dried tomatoes themselves; if you get them packed in vegetable oil, as is common, it’ll be a very different nutritional profile!
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Tomatoes vs Carrots – Which is Healthier? ← see the difference!
Enjoy!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Bates Method for Better Eyesight Without Glasses − by Dr. William Bates
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a very popular book and method, albeit not a very new one. It was first published in 1920; self-published by Dr. Bates, as the American Medical Association (AMA) considered it quackery.
Of course, our understanding of eyesight has improved a lot in the past 100 years, so, with the benefit of an extra century of ophthalmological research, who was on the right side of history?
As it turns out, all of Dr. Bates’ ideas have been firmly disproven, and eyes simply do not work the way he thought they do (for example, he believed that rather than adjusting the lens for focus, the muscles around the eye elongate the eyeball; this absolutely is not how focusing works, and while how much those muscles squeeze the eye does vary depending on some physiological factors, there are no known exercises that can change them).
Nevertheless, for the interested, his techniques include such things as:
- putting pressure on one’s eyes with one’s hands (which can increase glaucoma risk)
- visualization, rather than actual viewing, of an eye chart (this is ironic, because the book cover promises that an eye chart is included; it is not; perhaps it was hoped that we would visualize it more vividly and thus see it?)
- sunning, which is not only directly looking at the sun, but also using a burning glass to increase the focus of the sunlight onto one’s eye (please do not do this under any circumstances)
His primary thesis in this work, though, is that eyesight problems of all kinds (from short- and long-sightedness, to more serious things like cataracts and glaucoma) are caused by the tension produced by reading books, so relaxation exercises are his prescription for this.
The style is characteristic of its era and then some; bold claims are made with no evidence, there are no references, and the text is (ironically, given his opinions on tension being produced by reading books) quite dense. It certainly doesn’t lend itself well to skimming, for example, because something critical can easily be buried in a wall of text of what is, honestly, mostly waffle.
Bottom line: if you’d like to improve your eyesight and reduce your dependency on glasses, then we absolutely cannot recommend this book, and would direct you instead to Vision for Life, Revised Edition – by Dr. Meir Schneider, which is much more consistent with actual science.
Click here if you are, nonetheless, curious about Dr. Bates’ book and wish to check it out!
PS: Dr. Bates certainly was an interesting fellow; he disappeared mysteriously, but was found working as a medical assistant a few weeks later by his wife, whom he now claimed to not recognize. Then he disappeared again two days later (his wife never found him, this time, despite trying for many years), only to show up again, 13 years later, shortly after his wife’s death, whereupon he remarried (to his long-time personal assistant). None of this has anything to do with his fascinating opinions on eyesight, but it’s a story worth mentioning.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: