The Case of the Armadillo: Is It Spreading Leprosy in Florida?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — In an open-air barn at the edge of the University of Florida, veterinarian Juan Campos Krauer examines a dead armadillo’s footpads and ears for signs of infection.
Its claws are curled tight and covered in blood. Campos Krauer thinks it was struck in the head while crossing a nearby road.
He then runs a scalpel down its underside. He removes all the important organs: heart, liver, kidneys. Once the specimens are bottled up, they’re destined for an ultra-cold freezer in his lab at the college.
Campos Krauer plans to test the armadillo for leprosy, an ancient illness also known as Hansen’s disease that can lead to nerve damage and disfigurement in humans. He and other scientists are trying to solve a medical mystery: why Central Florida has become a hot spot for the age-old bacteria that cause it.
Leprosy remains rare in the United States. But Florida, which often reports the most cases of any state, has seen an uptick in patients. The epicenter is east of Orlando. Brevard County reported a staggering 13% of the nation’s 159 leprosy cases in 2020, according to a Tampa Bay Times analysis of state and federal data.
Many questions about the phenomenon remain unanswered. But leprosy experts believe armadillos play a role in spreading the illness to people. To better understand who’s at risk and to prevent infections, about 10 scientists teamed up last year to investigate. The group includes researchers from the University of Florida, Colorado State University, and Emory University in Atlanta.
“How this transmission is happening, we really don’t know,” said Ramanuj Lahiri, chief of the laboratory research branch for the National Hansen’s Disease Program, which studies the bacteria involved and cares for leprosy patients across the country.
‘Nothing Was Adding Up’
Leprosy is believed to be the oldest human infection in history. It probably has been sickening people for at least 100,000 years. The disease is highly stigmatized — in the Bible, it was described as a punishment for sin. In more modern times, patients were isolated in “colonies” around the world, including in Hawaii and Louisiana.
In mild cases, the slow-growing bacteria cause a few lesions. If left untreated, they can paralyze the hands and feet.
But it’s actually difficult to fall ill with leprosy, as the infection isn’t very contagious. Antibiotics can cure the ailment in a year or two. They’re available for free through the federal government and the World Health Organization, which launched a campaign in the 1990s to eliminate leprosy as a public health problem.
In 2000, reported U.S. cases dropped to their lowest point in decades with 77 infections. But they later increased, averaging about 180 per year from 2011 to 2020, according to data from the National Hansen’s Disease Program.
During that time, a curious trend emerged in Florida.
In the first decade of the 21st century, the state logged 67 cases. Miami-Dade County noted 20 infections — the most of any Florida county. The vast majority of its cases were acquired outside the U.S., according to a Times analysis of Florida Department of Health data.
But over the next 10 years, recorded cases in the state more than doubled to 176 as Brevard County took center stage.
The county, whose population is about a fifth the size of Miami-Dade’s, logged 85 infections during that time — by far the most of any county in the state and nearly half of all Florida cases. In the previous decade, Brevard noted just five cases.
Remarkably, at least a quarter of Brevard’s infections were acquired within the state, not while the individuals were abroad. India, Brazil, and Indonesia diagnose more leprosy cases than anywhere, reporting over 135,000 infections combined in 2022 alone. People were getting sick even though they hadn’t traveled to such areas or been in close contact with existing leprosy patients, said Barry Inman, a former epidemiologist at the Brevard health department who investigated the cases and retired in 2021.
“Nothing was adding up,” Inman said.
A few patients recalled touching armadillos, which are known to carry the bacteria. But most didn’t, he said. Many spent a lot of time outdoors, including lawn workers and avid gardeners. The cases were usually mild.
It was difficult to nail down where people got the illness, he added. Because the bacteria grow so slowly, it can take anywhere from nine months to 20 years for symptoms to begin.
Amoeba or Insect Culprits?
Heightened awareness of leprosy could play a role in Brevard’s groundswell of cases.
Doctors must report leprosy to the health department. Yet Inman said many in the county didn’t know that, so he tried to educate them after noticing cases in the late 2000s.
But that’s not the sole factor at play, Inman said.
“I don’t think there’s any doubt in my mind that something new is going on,” he said.
Other parts of Central Florida have also recorded more infections. From 2011 to 2020, Polk County logged 12 cases, tripling its numbers compared with the previous 10 years. Volusia County noted 10 cases. It reported none the prior decade.
Scientists are honing in on armadillos. They suspect the burrowing critters may indirectly cause infections through soil contamination.
Armadillos, which are protected by hard shells, serve as good hosts for the bacteria, which don’t like heat and can thrive in the animals whose body temperatures range from a cool 86-95 degrees.
Colonists probably brought the disease to the New World hundreds of years ago, and somehow armadillos became infected, said Lahiri, the National Hansen’s Disease Program scientist. The nocturnal mammals can develop lesions from the illness just as humans can. More than 1 million armadillos occupy Florida, estimated Campos Krauer, an assistant professor in the University of Florida’s Department of Large Animal Clinical Sciences.
How many carry leprosy is unclear. A study published in 2015 of more than 600 armadillos in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, and Mississippi found that about 16% showed evidence of infection. Public health experts believe leprosy was previously confined to armadillos west of the Mississippi River, then spread east.
Handling the critters is a known hazard. Lab research shows that single-cell amoebas, which live in soil, can also carry the bacteria.
Armadillos love to dig up and eat earthworms, frustrating homeowners whose yards they damage. The animals may shed the bacteria while hunting for food, passing it to amoebas, which could later infect people.
Leprosy experts also wonder if insects help spread the disease. Blood-sucking ticks might be a culprit, lab research shows.
“Some people who are infected have little to no exposure to the armadillo,” said Norman Beatty, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Florida. “There is likely another source of transmission in the environment.”
Campos Krauer, who’s been searching Gainesville streets for armadillo roadkill, wants to gather infected animals and let them decompose in a fenced-off area, allowing the remains to soak into a tray of soil while flies lay eggs. He hopes to test the dirt and larvae to see if they pick up the bacteria.
Adding to the intrigue is a leprosy strain found only in Florida, according to scientists.
In the 2015 study, researchers discovered that seven armadillos from the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which is mostly in Brevard but crosses into Volusia, carried a previously unseen version of the pathogen.
Ten patients in the region were stricken with it, too. At the genetic level, the strain is similar to another type found in U.S. armadillos, said Charlotte Avanzi, a Colorado State University researcher who specializes in leprosy.
It’s unknown if the strain causes more severe disease, Lahiri said.
Reducing Risk
The public should not panic about leprosy, nor should people race to euthanize armadillos, researchers warn.
Scientists estimate that over 95% of the global human population has a natural ability to ward off the disease. They believe months of exposure to respiratory droplets is needed for person-to-person transmission to occur.
But when infections do happen, they can be devastating.
“If we better understand it,” Campos Krauer said, “the better we can learn to live with it and reduce the risk.”
The new research may also provide insight for other Southern states. Armadillos, which don’t hibernate, have been moving north, Campos Krauer said, reaching areas like Indiana and Virginia. They could go farther due to climate change.
People concerned about leprosy can take simple precautions, medical experts say. Those working in dirt should wear gloves and wash their hands afterward. Raising garden beds or surrounding them with a fence may limit the chances of soil contamination. If digging up an armadillo burrow, consider wearing a face mask, Campos Krauer said.
Don’t play with or eat the animals, added John Spencer, a scientist at Colorado State University who studies leprosy transmission in Brazil. They’re legal to hunt year-round in Florida without a license.
Campos Krauer’s team has so far examined 16 dead armadillos found on Gainesville area roads, more than 100 miles from the state’s leprosy epicenter, trying to get a preliminary idea of how many carry the bacteria.
None has tested positive yet.
This article was produced through a partnership between KFF Health News and the Tampa Bay Times.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
What Doesn’t Lycopene Do?
Lycopene is an antioxidant carotenoid famously found in tomatoes; it actually appears in even higher levels in watermelon, though. If you are going to get it from tomato, know that cooking improves the lycopene content rather than removing it (watermelon, on the other hand, can be enjoyed as-is and already has the higher lycopene content).
Antioxidant properties
Let’s reiterate the obvious first, for the sake of being methodical and adding a source. Lycopene is a potent antioxidant with multiple health benefits:
Lycopene: A Potent Antioxidant with Multiple Health Benefits
…and as such, it does all the things you might reasonably expect and antioxidant to do. For example…
Anti-inflammatory properties
In particular, it regulates macrophage activity, reducing inflammation while improving immune response:
Lycopene Regulates Macrophage Immune Response through the Autophagy Pathway Mediated by RIPK1
As can be expected of most antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents, it also has…
Anticancer properties
Scientific papers tend to be “per cancer type”, so we’re just going to give one example, but there’s pretty much evidence for its utility against most if not all types of cancer. We’re picking prostate cancer though, as it’s one that’s been studied the most in the context of lycopene intake—in this study, for example, it was found that men who enjoyed at least two servings of lycopene-rich tomato sauce per week were 30% less likely to develop prostate cancer than those who didn’t:
Dietary lycopene intake and risk of prostate cancer defined by ERG protein expression
If you’d like to see something more general, however, then check out:
Potential Use of Tomato Peel, a Rich Source of Lycopene, for Cancer Treatment
It also fights Candida albicans
Ok, this is not (usually) so life-and-death as cancer, but reducing our C. albicans content (specifically: in our gut) has a lot of knock-on effects for other aspects of our health, so this isn’t one to overlook:
The title does not make this clear, but yes: this does mean it has an antifungal effect. We mention this because often cellular apoptosis is good for an overall organism, but in this case, it simply kills the Candida.
It’s good for the heart
A lot of studies focus just on triglyceride markers (which lycopene improves), but more tellingly, here’s a 10-year observational study in which diets rich in lycopene were associated to a 17–26% lower risk of heart disease:
Relationship of lycopene intake and consumption of tomato products to incident CVD
…and a 39% overall reduced mortality in, well, we’ll let the study title tell it:
…which means also:
It’s good for the brain
As a general rule of thumb, what’s good for the heart is good for the brain (because the brain needs healthy blood flow to stay healthy, and is especially vulnerable when it doesn’t get that), and in this case that rule of thumb is also borne out by the post hoc evidence, specifically yielding a 31% decreased incidence of stroke:
Dietary and circulating lycopene and stroke risk: a meta-analysis of prospective studies
Is it safe?
As a common food product, it is considered very safe.
If you drink nothing but tomato juice all day for a long time, your skin will take on a reddish hue, which will go away if you stop getting all your daily water intake in tomato juice.
In all likelihood, even if you went to extremes, you would get sick from the excess of vitamin A (generally present in the same foods) sooner than you’d get sick from the excess of lycopene.
Want to try some?
We don’t sell it, and also we recommend simply enjoying tomatoes, watermelons, etc, but if you do want a supplement, here’s an example product on Amazon
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
The Fascinating Truth About Aspartame, Cancer, & Neurotoxicity
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is Aspartame’s Reputation Well-Deserved?
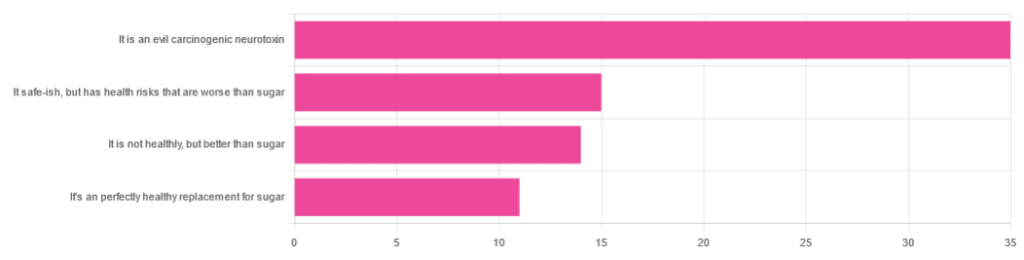
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you for your health-related opinions on aspartame, and got the above-depicted, below-described, set of responses:
- About 47% said “It is an evil carcinogenic neurotoxin”
- 20% said “It is safe-ish, but has health risks that are worse than sugar”
- About 19% said “It is not healthy, but better than sugar”
- About 15% said “It’s a perfectly healthy replacement for sugar”
But what does the science say?
Aspartame is carcinogenic: True or False?
False, assuming consuming it in moderation. In excess, almost anything can cause cancer (oxygen is a fine example). But for all meaningful purposes, aspartame does not appear to be carcinogenic. For example,
❝The results of these studies showed no evidence that these sweeteners cause cancer or other harms in people.❞
~ NIH | National Cancer Institute
Source: Artificial Sweeteners and Cancer
Plenty of studies and reviews have also confirmed this; here are some examples:
- Evaluation of aspartame cancer epidemiology studies based on quality appraisal criteria
- Aspartame, low-calorie sweeteners and disease: Regulatory safety and epidemiological issues
- Aspartame: A review of genotoxicity data
Why then do so many people believe it causes cancer, despite all the evidence against it?
Well, there was a small study involving giving megadoses to rats, which did increase their cancer risk. So of course, the popular press took that and ran with it.
But those results have not been achieved outside of rats, and human studies great and small have all been overwhelmingly conclusive that moderate consumption of aspartame has no effect on cancer risk.
Aspartame is a neurotoxin: True or False?
False, again assuming moderate consumption. If you’re a rat being injected with a megadose, your experience may vary. But a human enjoying a diet soda, the aspartame isn’t the part that’s doing you harm, so far as we know.
For example, the European Food Safety Agency’s scientific review panel concluded:
❝there is still no substantive evidence that aspartame can induce such effects❞
~ Dr. Atkin et al (it was a pan-European team of 21 experts in the field)
Source: Report on the Meeting on Aspartame with National Experts
See also,
❝The data from the extensive investigations into the possibility of neurotoxic effects of aspartame, in general, do not support the hypothesis that aspartame in the human diet will affect nervous system function, learning or behavior.
The weight of existing evidence is that aspartame is safe at current levels of consumption as a nonnutritive sweetener.❞
and
❝The safety testing of aspartame has gone well beyond that required to evaluate the safety of a food additive.
When all the research on aspartame, including evaluations in both the premarketing and postmarketing periods, is examined as a whole, it is clear that aspartame is safe, and there are no unresolved questions regarding its safety under conditions of intended use.❞
Source: Regulatory Toxicology & Pharmacology | Aspartame: Review of Safety
Why then do many people believe it is a neurotoxin? This one can be traced back to a chain letter hoax from about 26 years ago; you can read it here, but please be aware it is an entirely debunked hoax:
Urban Legends | Aspartame Hoax
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Quit Drinking – by Rebecca Dolton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Many “quit drinking” books focus on tips you’ve heard already—cut down like this, rearrange your habits like that, make yourself accountable like so, add a reward element this way, etc.
Dolton takes a different approach.
She focuses instead on the underlying processes of addiction, so as to not merely understand them to fight them, but also to use them against the addiction itself.
This is not just a social or behavioral analysis, by the way, and goes into some detail into the physiological factors of the addiction—including such things as the little-talked about relationship between addiction and gut flora. Candida albans, found in most if not all humans to some extent, gets really out of control when given certain kinds of sugars (including those from alcohol); it grows, eventually puts roots through the intestinal walls (ouch!) and the more it grows, the more it demands the sugars it craves, so the more you feed it.
Quite a motivator to not listen to such cravings! It’s not even you that wants it, it’s the Candida!
Anyway, that’s just one example; there are many. The point here is that this is a well-researched, well-written book that sets itself apart from many of its genre.
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
52 Ways to Walk – by Annabel Streets
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Most of us learned to walk at a very young age and probably haven’t thought much about it since, except perhaps in a case where some injury made it difficult.
Annabel Streets provides a wonderful guide to not just taking up (or perhaps reclaiming) the joy of walking, but also the science of it in more aspects than most of us have considered:
- The physical mechanics of walking—what’s best?
- Boots or shoes? Barefoot?
- Roads, grass, rougher vegetation… Mud?
- Flora & fauna down to the microbiota that affect us
- How much walking is needed, to be healthy?
- Is there such a thing as too much walking?
- What are the health benefits (or risks) of various kinds of weather?
- Is it better to walk quickly or to walk far?
- What about if we’re carrying some injury?
- What’s going on physiologically when we walk?
- And so much more…
Streets writes with a captivating blend of poetic joie-de-vivre coupled with scientific references.
One moment the book is talking about neuroradiology reports of NO-levels in our blood, the impact of Mycobacterium vaccae, and the studied relationship between daily steps taken and production of oligosaccharide 3′-sialyllactose, and the next it’s all:
“As if the newfound lightness in our limbs has crept into our minds, loosening our everyday cares and constraints…”
And all in all, this book helps remind us that sometimes, science and a sense of wonder can and do (and should!) walk hand-in-hand.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Meditation for Fidgety Skeptics – by Dan Harris
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
If you already meditate regularly, this book isn’t aimed at you (though you may learn a thing or two anyway—this reviewer, who has practiced meditation for the past 30 years, learned a thing!).
However, if you’re—as the title suggests—someone who hasn’t so far been inclined towards meditation, you could get the most out of this one. We’ll say more on this (obviously), but first, there’s one other group that may benefit from this book:
If you have already practiced meditation, and/or already understand and want its benefits, but never really made it stick as a habit.
Now, onto what you’ll get:
- A fair scientific overview of meditation as an increasingly evidence-based way to reduce stress and increase both happiness and productivity
- A good grounding in what meditation is and isn’t
- A how-to guide for building up a consistent meditation habit that won’t get kiboshed when you have a particularly hectic day—or a cold.
- An assortment of very common (and some less common) meditative practices to try
- Some great auxiliary tools to build cognitive restructuring into your meditation
We don’t usually cite other people’s reviews, but we love that one Amazon reviewer wrote:
❝I am 3 weeks into daily meditation practice, and I already notice that I am no longer constantly wishing for undercarriage rocket launchers while driving. I will always think your driving sucks, but I no longer wish you a violent death because of it. Yes, I live in Boston❞
Bottom line: if you’re not already meditating daily, this is definitely a book for you. And if you are, you may learn a thing or two anyway!
Click here to get your copy of Meditation For Fidgety Skeptics from Amazon today!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Getting to Neutral – by Trevor Moawad
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We all know that a pessimistic outlook is self-defeating… And yet, toxic positivity can also be a set-up for failure! At some point, reckless faith in the kindly nature of the universe will get crushed, badly. Sometimes that point is a low point in life… sometimes it’s six times a day. But one thing’s for sure: we can’t “just decide everything will go great!” because the world just doesn’t work that way.
That’s where Trevor Moawad comes in. “Getting to neutral” is not a popular selling point. Everyone wants joy, abundance, and high after high. And neutrality itself is often associated with boredom and soullessness. But, Moawad argues, it doesn’t have to be that way.
This book’s goal—which it accomplishes well—is to provide a framework for being a genuine realist. What does that mean?
“I’m not a pessimist; I’m a realist” – every pessimist ever.
^Not that. That’s not what it means. What it means instead is:
- Hope for the best
- Prepare for the worst
- Adapt as you go
…taking care to use past experiences to inform future decisions, but without falling into the trap of thinking that because something happened a certain way before, it always will in the future.
To be rational, in short. Consciously and actively rational.
Feel the highs! Feel the lows! But keep your baseline when actually making decisions.
Bottom line: this book is as much an antidote to pessimism and self-defeat, as it is to reckless optimism and resultant fragility. Highly recommendable.
Click here to check out “Getting to Neutral” and start creating your best, most reason-based life!
PS: in this book, Moawad draws heavily from his own experiences of battling adversity in the form of cancer—of which he died, before this book’s publication. A poignant reminder that he was right: we won’t always get the most positive outcome of any given situation, so what matters the most is making the best use of the time we have.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: