MSG vs. Salt: Sodium Comparison
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
It’s Q&A Day at 10almonds!
Q: Is MSG healthier than salt in terms of sodium content or is it the same or worse?
Great question, and for that matter, MSG itself is a great topic for another day. But your actual question, we can readily answer here and now:
- Firstly, by “salt” we’re assuming from context that you mean sodium chloride.
- Both salt and MSG do contain sodium. However…
- MSG contains only about a third of the sodium that salt does, gram-for-gram.
- It’s still wise to be mindful of it, though. Same with sodium in other ingredients!
- Baking soda contains about twice as much sodium, gram for gram, as MSG.
Wondering why this happens?
Salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is equal parts sodium and chlorine, by atom count, but sodium’s atomic mass is lower than chlorine’s, so 100g of salt contains only 39.34g of sodium.
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO₃) is one part sodium for one part hydrogen, one part carbon, and three parts oxygen. Taking each of their diverse atomic masses into account, we see that 100g of baking soda contains 27.4g sodium.
MSG (monosodium glutamate, C₅H₈NO₄Na) is only one part sodium for 5 parts carbon, 8 parts hydrogen, 1 part nitrogen, and 4 parts oxygen… And all those other atoms put together weigh a lot (comparatively), so 100g of MSG contains only 12.28g sodium.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
What Harm Can One Sleepless Night Do?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ll not bury the lede: a study found that just one night of 24-hour sleep deprivation can alter immune cell profiles in young, lean, healthy people to resemble those of people with obesity and chronic inflammation.
Chronic inflammation, in turn, causes very many other chronic diseases, and worsens most of the ones it doesn’t outright cause.
The reason this happens is because in principle, inflammation is supposed to be good for us—it’s our body’s defenses coming to the rescue. However, if we imagine our immune cells as firefighters, then compare:
- A team of firefighters who are in great shape and ready to deploy at a moment’s notice, are mostly allowed to rest, sometimes get training, and get called out to a fire from time time, just enough to keep them on their toes. Today, something in your house caught fire, and they showed up in 5 minutes and put it out safely.
- A team of firefighters who have been pulling 24-hour shifts every day for the past 20 years, getting called out constantly for lost cats, burned toast, wrong numbers, the neighbor’s music, a broken fridge, and even the occasional fire. Today, your printer got jammed so they broke down your door and also your windows just for good measure, and blasted your general desk area with a fire hose, which did not resolve the problem but now your computer itself is broken.
Which team would you rather have?
The former team is a healthy immune system; the latter is the immune system of someone with chronic inflammation.
But if it’s one night, it’s not chronic, right?
Contingently true. However, the problem is that because the immune profile was made to be like the bad team we described (imagine that chaos in your house, now remember that for this metaphor, it’s your body that that’s happening to), the immediate strong negative health impact will already have knock-on effects, which in turn make it more likely that you’ll struggle to get your sleep back on track quickly.
For example, the next night you may oversleep “to compensate”, but then the following day your sleep schedule is now slid back considerably; one thing leads to another, and a month later you’re thinking “I really must sort my sleep out”.
See also: How Regularity Of Sleep Can Be Even More Important Than Duration ← A recent, large (n=72,269) 8-year prospective* observational study of adults aged 40-79 found a strong association between irregular sleep and major cardiovascular events, to such an extent that it was worse than undersleeping.
*this means they started the study at a given point, and measured what happened for the next eight years—as opposed to a retrospective study, which would look at what had happened during the previous 8 years.
What about sleep fragmentation?
In other words: getting sleep, but heavily disrupted sleep.
The answer is: basically the same deal as with missed sleep.
Specifically, elevated proinflammatory cytokines (in this context, that’s bad) and an increase in nonclassical monocytes—as are typically seen in people with obesity and chronic inflammation.
Remember: these were young, lean, healthy participants going into the study, who signed up for a controlled sleep deprivation experiment.
This is important, because the unhealthy inflammatory profile means that people with such are a lot more likely to develop diabetes, heart disease, Alzheimer’s, and many more things besides. And, famously, most people in the industrialized world are not sleeping that well.
Even amongst 10almonds readers, a health-conscious demographic by nature, 62% of 10almonds readers do not regularly get the prescribed 7–9 hours sleep (i.e. they get under 7 hours).
You can see the data on this one, here: Why You Probably Need More Sleep ← yes, including if you are in the older age range; we bust that myth in the article too!*
*Unless you have a (rare!) mutated ADRB1 gene, which reduces that. But we also cover that in the article, and how to know whether you have it.
With regard to “most people in the industrialized world are not sleeping that well”, this means that most people in the industrialized world are subject to an unseen epidemic of sleep-deprivation-induced inflammation that is creating vulnerability to many other diseases. In short, the lifestyle of the industrialized world (especially: having to work certain hours) is making most of the working population sick.
Dr. Fatema Al-Rashed, lead researcher, concluded:
❝In the long term, we aim for this research to drive policies and strategies that recognize the critical role of sleep in public health.
We envision workplace reforms and educational campaigns promoting better sleep practices, particularly for populations at risk of sleep disruption due to technological and occupational demands.
Ultimately, this could help mitigate the burden of inflammatory diseases like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.❞
You can read the paper in full here: Impact of sleep deprivation on monocyte subclasses and function
What can we do about it?
With regard to sleep, we’ve written so much about this, but here are three key articles that contain a lot of valuable information:
- Get Better Sleep: Beyond The Basics
- Calculate (And Enjoy) The Perfect Night’s Sleep
- Safe Effective Sleep Aids For Seniors
…and with regard to inflammation, a good concise overview of how to dial it down is:
How To Prevent Or Reduce Inflammation
Take care!
Share This Post
-
What is ‘breathwork’? And do I need to do it?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
From “breathwork recipes” to breathing techniques, many social media and health websites are recommending breathwork to reduce stress.
But breathwork is not new. Rather it is the latest in a long history of breathing techniques such as Pranayama from India and qigong from China. Such practices have been used for thousands of years to promote a healthy mind and body.
The benefits can be immediate and obvious. Try taking a deep breath in through your nose and exhaling slowly. Do you feel a little calmer?
So, what’s the difference between the breathing we do to keep us alive and breathwork?
Taras Grebinets/Shutterstock Breathwork is about control
Breathwork is not the same as other mindfulness practices. While the latter focus on observing the breath, breathwork is about controlling inhalation and exhalation.
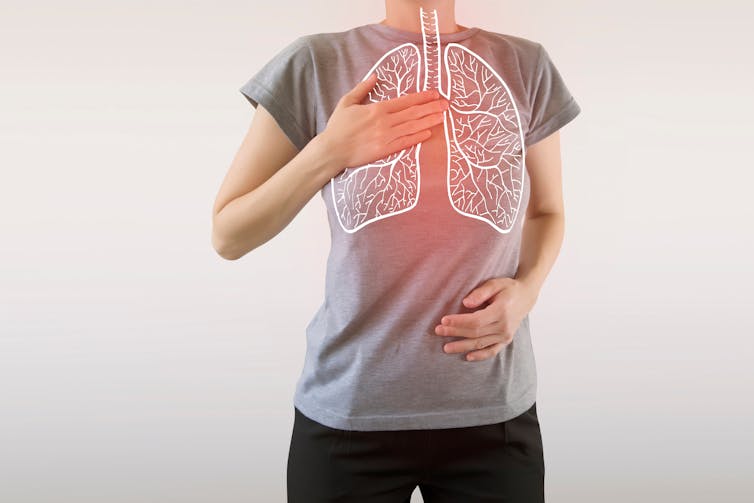
Normally, breathing happens automatically via messages from the brain, outside our conscious control. But we can control our breath, by directing the movement of our diaphragm and mouth.
The diaphragm is a large muscle that separates our thoracic (chest) and abdominal (belly) cavities. When the diaphragm contracts, it expands the thoracic cavity and pulls air into the lungs.
Controlling how deep, how often, how fast and through what (nose or mouth) we inhale is the crux of breathwork, from fire breathing to the humming bee breath.
Breathwork can calm or excite
Even small bits of breathwork can have physical and mental health benefits and complete the stress cycle to avoid burnout.
Calming breathwork includes diaphragmatic (belly) breathing, slow breathing, pausing between breaths, and specifically slowing down the exhale.
In diaphragmatic breathing, you consciously contract your diaphragm down into your abdomen to inhale. This pushes your belly outwards and makes your breathing deeper and slower.
You can also slow the breath by doing:
- box breathing (count to four for each of four steps: breathe in, hold, breathe out, hold), or
- coherent breathing (controlled slow breathing of five or six breaths per minute), or
- alternate nostril breathing (close the left nostril and breathe in slowly through the right nostril, then close the right nostril and breathe out slowly through the left nostril, then repeat the opposite way).
You can slow down the exhalation specifically by counting, humming or pursing your lips as you breathe out.
In contrast to these calming breathing practices, energising fast-paced breathwork increases arousal. For example, fire breathing (breathe in and out quickly, but not deeply, through your nose in a consistent rhythm) and Lion’s breath (breathe out through your mouth, stick your tongue out and make a strong “haa” sound).
What is happening in the body?
Deep and slow breathing, especially with a long exhale, is the best way to stimulate the vagus nerves. The vagus nerves pass through the diaphragm and are the main nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Simulating the vagus nerves calms our sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight) stress response. This improves mood, lowers the stress hormone cortisol and helps to regulate emotions and responses. It also promotes more coordinated brain activity, improves immune function and reduces inflammation.
Taking deep, diaphragmatic breaths also has physical benefits. This improves blood flow, lung function and exercise performance, increases oxygen in the body, and strengthens the diaphragm.
Slow breathing reduces heart rate and blood pressure and increases heart rate variability (normal variation in time between heart beats). These are linked to better heart health.
Taking shallow, quick, rhythmic breaths in and out through your nose stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. Short-term, controlled activation of the stress response is healthy and develops resilience to stress.
Breathing in through the nose
We are designed to inhale through our nose, not our mouth. Inside our nose are lots of blood vessels, mucous glands and tiny hairs called cilia. These warm and humidify the air we breathe and filter out germs and toxins.
We want the air that reaches our airways and lungs to be clean and moist. Cold and dry air is irritating to our nose and throat, and we don’t want germs to get into the body.
Nasal breathing increases parasympathetic activity and releases nitric oxide, which improves airway dilation and lowers blood pressure.
Consistently breathing through our mouth is not healthy. It can lead to pollutants and infections reaching the lungs, snoring, sleep apnoea, and dental issues including cavities and jaw joint problems.
Breathing can be high and shallow when we are stressed. mi_viri/Shutterstock A free workout
Slow breathing – even short sessions at home – can reduce stress, anxiety and depression in the general population and among those with clinical depression or anxiety. Research on breathwork in helping post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is also promising.
Diaphragmatic breathing to improve lung function and strengthen the diaphragm can improve breathing and exercise intolerance in chronic heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. It can also improve exercise performance and reduce oxidative stress (an imbalance of more free radicals and/or less antioxidants, which can damage cells) after exercise.
Waiting at the lights? This could be your signal to do some breathwork. doublelee/Shutterstock A mind-body connection you can access any time
If you feel stressed or anxious, you might subconsciously take shallow, quick breaths, but this can make you feel more anxious. Deep diaphragmatic breaths through your nose and focusing on strong exhalations can help break this cycle and bring calm and mental clarity.
Just a few minutes a day of breathwork can improve your physical and mental health and wellbeing. Daily deep breathing exercises in the workplace reduce blood pressure and stress, which is important since burnout rates are high.
Bottom line: any conscious control of your breath throughout the day is positive.
So, next time you are waiting in a line, at traffic lights or for the kettle to boil, take a moment to focus on your breath. Breathe deeply into your belly through your nose, exhale slowly, and enjoy the benefits.
Theresa Larkin, Associate professor of Medical Sciences, University of Wollongong and Judy Pickard, Senior Lecturer, Clinical Psychology, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Share This Post
-
The Mind-Gut Connection – by Dr. Emeran Mayer
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
We’ve reviewed books about the mind-gut connection before, so what makes this one stand out?
Firstly, it’s a lot more comprehensive than the usual “please, we’re begging you, eat some fiber”.
And yes, of course that’s part of it. Prebiotics, probiotics, reduce fried and processed foods, reduce sugar/alcohol, reduce meat, and again, eat some greenery.
But where this book really comes into its own is looking more thoroughly at the gut microbiota and their function. Dr. Mayer goes well beyond “there are good and bad bacteria” and looks at the relationship each of them have with the body’s many hormones, and especially neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
He also looks at the two-way connection between brain and gut. Yes, our gut gives us “gut feelings”, but 10% of communication between the brain and gut is in the other direction; he explores what that means for us, too.
Finally, he does give a lot of practical advice, not just dietary but also behavioral, to make the most of our mind-gut connection and make it work for our health, rather than against it.
Bottom line: this is the best book on the brain-gut connection that this reviewer has read so far, and certainly the most useful if you already know about gut-healthy nutrition, and are looking to take your understanding to the next level.
Click here to check out The Mind-Gut Connection, and start making yours work for your benefit!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
The Little-Known Truth…
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Myth-Buster, Myth-Buster, Bust Us A Myth (or three!)
Let’s can this myth for good
People think of “canned foods” as meaning “processed foods” and therefore bad. But the reality is it’s all dependent on what’s in the can (check the ingredients!). And as for nutrients?
Many canned fruits and vegetables contain more nutrients than fresh ones! This is because the way they’ve been stored preserves them better. For example:
- Canned tomatoes contain more bioavailable lycopene than fresh
- Canned spinach contains more bioavailable carotene than fresh
- Canned corn contains more bioavailable lutein than fresh
- The list goes on, but you get the idea!
Don’t Want To Take Our Word For It? Read The Scientific Paper Here!
Gaslight, Gymkeep, Girl-loss?
Many women and girls avoid doing weight-training as part of their exercise—or use only the smallest weights—to avoid “bulking up” and “looking like a man”.
Many men, meanwhile, wish it were that easy to bulk up!
The reality is that nobody, unless you have very rare genes, packs on a lot of muscle by accident. Even with the genes for it, it won’t happen unless you’re also eating for it!
Resistance-based strength training (such as lifting weights), is a great way for most people to look after an important part of their long-term health: bone density!
You can’t have strong muscles on weak bones, so strengthening the muscles cues the body to strengthen the bones. In short, your strength-training at age 45 or 55 (or earlier) could be what helps you avoid a broken hip at 65 or 75.
We’re Not Kidding, It Really Is That Important (Read The Study Here)!
Something doesn’t smell right about this
There’s been a big backlash against anti-perspirants and deodorants. The popular argument is that the aluminium in them causes cancer.
This led to many people buying “deodo-rocks”, crystal rocks that can be run under water and then rubbed on the armpits to deodorize “naturally”. But, those crystal rocks are actually alum crystals (guess what they contain…).
The belief that deodorants cause cancer came from studies done by applying deodorant to cells (like the canine kidney cells in this study) in petri dishes. So, assuming you don’t cut out your kidney and then spray it directly with the deodorant, the jury is still out!
A more recent systematic review sorted out quite clearly the ways in which aluminium was, or was not, harmful, and said:
❝Neither is there clear evidence to show use of Al-containing underarm antiperspirants or cosmetics increases the risk of Alzheimer’s Disease or breast cancer. Metallic Al, its oxides, and common Al salts have not been shown to be either genotoxic or carcinogenic.❞
Critical Reviews in Toxicology
…but also says that you should avoid eating aluminium while pregnant or breastfeeding. We hope you can resist the urge.
See The Summary For Yourself Here!
(actually the whole article is there, but we know you value condensed knowledge, so: the abstract at the top will probably tell you all you want to know!)
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Fermenting Everything – by Andy Hamilton
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is not justanother pickling book! This is, instead, what it says on the front cover, “fermenting everything”.
Ok, maybe not literally everything, but every kind of thing that can reasonably be fermented, and it’s probably a lot more things than you might think.
From habanero chutney to lacto-lemonade, aioli to kombucha, Ukrainian fermented tomatoes to kvass. We could go on, but we’d soon run out of space. You get the idea. If it’s a fermented product (food, drink, condiment) and you’ve heard of it, there’s probably a recipe in here.
All in all, this is a great way to get in your gut-healthy daily dose of fermented products!
He does also talk safety, and troubleshooting too. And so long as you have a collection of big jars and a fairly normally-furnished kitchen, you shouldn’t need any more special equipment than that, unless you decide to you your fermentation skills for making beer (which does need some extra equipment, and he offers advice on that—our advice as a health science publication is “don’t drink beer”, though).
Bottom line: with this in hand, you can create a lot of amazing foods/drinks/condiments that are not only delicious, but also great for gut health.
Click here to check out Fermenting Everything, and widen your culinary horizons!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
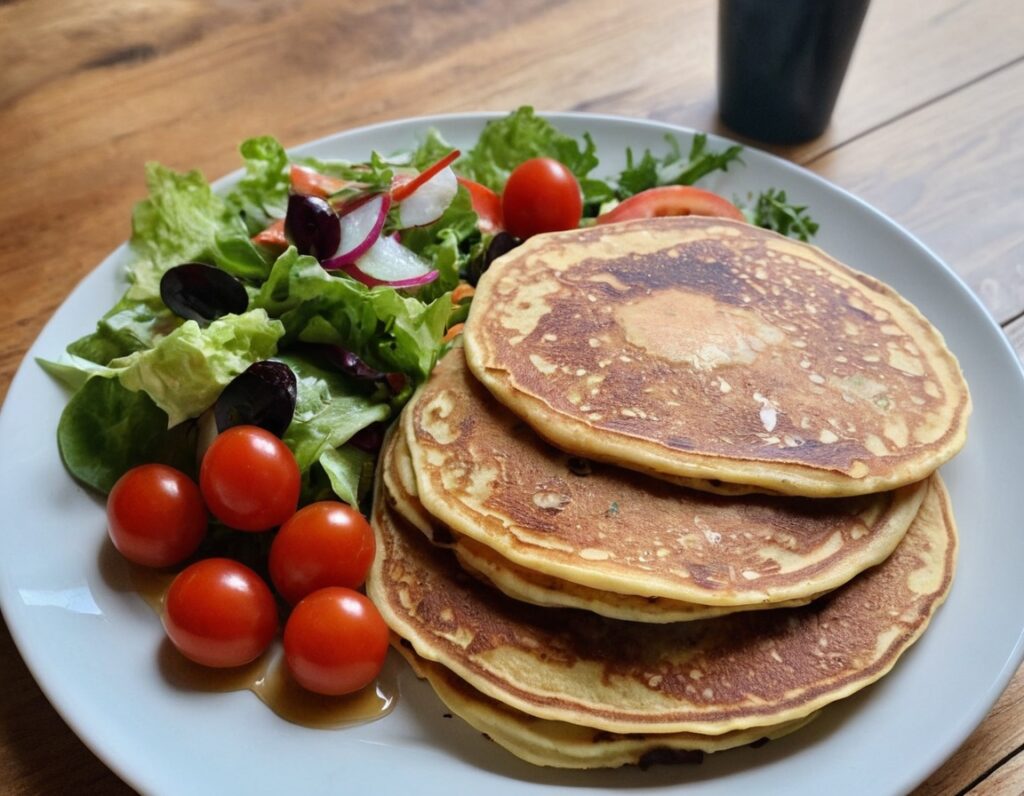
Mineral-Rich Mung Bean Pancakes
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Mung beans are rich in an assortment of minerals, especially iron, copper, phosphorus, and magnesium. They’re also full of protein and fiber! What better way to make pancakes healthy?
You will need
- ½ cup dried green mung beans
- ½ cup chopped fresh parsley
- ½ cup chopped fresh dill
- ¼ cup uncooked wholegrain rice
- ¼ cup nutritional yeast
- 1 tsp MSG, or 2 tsp low-sodium salt
- 2 green onions, finely sliced
- 1 tbsp extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Soak the mung beans and rice together overnight.
2) Drain and rinse, and blend them in a blender with ¼ cup of water, to the consistency of regular pancake batter, adding more water (sparingly) if necessary.
3) Transfer to a bowl and add the rest of the ingredients except for the olive oil, which latter you can now heat in a skillet over a medium-high heat.
4) Add a few spoonfuls of batter to the pan, depending on how big you want the pancakes to be. Cook on both sides until you get a golden-brown crust, and repeat for the rest of the pancakes.
5) Serve! As these are savory pancakes, you might consider serving them with a little salad—tomatoes, olives, and cucumbers go especially well.
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- What’s The Deal With MSG?
- All About Olive Oils: Is “Extra Virgin” Worth It?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: