PlantYou: Scrappy Cooking – by Carleigh Bodrug
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This is a book that took “whole foods plant-based diet” and ran with it.
“Whole foods”, you say? Carleigh Bodrug has you covered in this guide to using pretty much everything.
One of the greatest strengths of the book is its “Got this? Make that” section, for using up those odds and ends that you’d normally toss.
You may be thinking: “ok, but if to use this unusual ingredient I have to buy four other ingredients to make this recipe, generating waste from those other ingredients, then this was a bad idea”, but fear not.
Bodrug covers that too, and in many cases leftover “would get wasted” ingredients can get turned into stuff that can go into longer-term storage one way or another, to use at leisure.
Which also means that on the day “there’s nothing in the house to eat” and you don’t want to go grocery-shopping, or if some global disaster causes the supply lines to fail and the stores become empty (that could never happen though, right?), you will have the mystical ability to conjure a good meal out of assorted odds and ends that you stored because of this book.
Bottom line: if you love food and hate food waste, this is a great book for you.
Click here to check out Scrappy Cooking, and do domestic magic!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
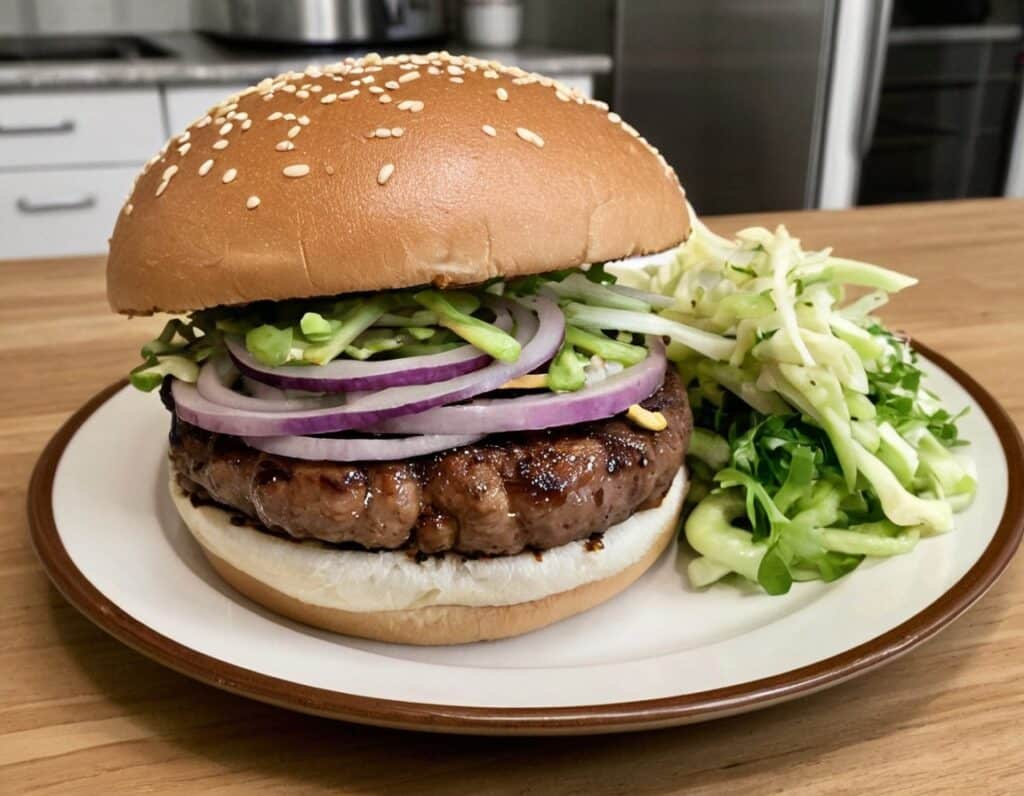
Teriyaki Chickpea Burgers
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burgers are often not considered the healthiest food, but they can be! Ok, so the teriyaki sauce component itself isn’t the healthiest, but the rest of this recipe is, and with all the fiber this contains, it’s a net positive healthwise, even before considering the protein, vitamins, minerals, and assorted phytonutrients.
You will need
- 2 cans chickpeas, drained and rinsed (or 2 cups of chickpeas, cooked drained and rinsed)
- ¼ cup chickpea flour (also called gram flour or garbanzo bean flour)
- ¼ cup teriyaki sauce
- 2 tbsp almond butter (if allergic, substitute with a seed butter if available, or else just omit; do not substitute with actual butter—it will not work)
- ½ bulb garlic, minced
- 1 large chili, minced (your choice what kind, color, or even whether or multiply it)
- 1 large shallot, minced
- 1″ piece of ginger, grated
- 2 tsp teriyaki sauce (we’re listing this separately from the ¼ cup above as that’ll be used differently)
- 1 tsp yeast extract (even if you don’t like it; trust us, it’ll work—this writer doesn’t like it either but uses it regularly in recipes like these)
- 1 tbsp black pepper
- 1 tsp fennel powder
- ½ tsp sweet cinnamon
- ½ tsp MSG or 1 tsp low-sodium salt
- Extra virgin olive oil for frying
For serving:
- Burger buns (you can use our Delicious Quinoa Avocado Bread recipe)
- Whatever else you want in there; we recommend mung bean sprouts, red onion, and a nice coleslaw
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Preheat the oven to 400℉ / 200℃.
2) Roast the chickpeas spaced out on a baking tray (lined with baking paper) for about 15 minutes. Leave the oven on afterwards; we still need it.
3) While that’s happening, heat a little oil in a skillet to a medium heat and fry the shallot, chili, garlic, and ginger, for about 2–3 minutes. You want to release the flavors, but not destroy them.
4) Let them cool, and when the chickpeas are done, let them cool for a few minutes too, before putting them all into a food processor along with the rest of the ingredients from the main section, except the oil and the ¼ cup teriyaki sauce. Process them into a dough.
5) Form the dough into patties; you should have enough dough for 4–6 patties depending on how big you want them.
6) Brush them with the teriyaki sauce; turn them onto a baking tray (lined with baking paper) and brush the other side too. Be generous.
7) Bake them for about 15 minutes, turn them (taking the opportunity to add more teriyaki sauce if it seems to merit it) and bake for another 5–10 minutes.
8) Assemble; we recommend the order: bun, a little coleslaw, burger, red onion, more coleslaw, mung bean sprouts, bun, but follow your heart!
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Three Daily Servings of Beans/Legumes?
- Hoisin Sauce vs Teriyaki Sauce – Which is Healthier?
- Sprout Your Seeds, Grains, Beans, Etc
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits? ← we scored 4/5 today!
- Monosodium Glutamate: Sinless Flavor-Enhancer Or Terrible Health Risk?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
Citicoline: Better Than Dietary Choline?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Citicoline: Better Than Dietary Choline?
Citicoline, also known as cytidine diphosphate-choline (or CDP-Choline, to its friends, or cytidine 5′-diphosphocholine if it wants to get fancy) is a dietary supplement that the stomach can metabolize easily for all the brain’s choline needs. What are those needs?
Choline is an essential nutrient. We technically can synthesize it, but only in minute amounts, far less than we need. Choline is a key part of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, as well as having other functions in other parts of the body.
As for citicoline specifically… it appears to do the job better than dietary sources of choline:
❝Intriguing data, showing that on a molar mass basis citicoline is significantly less toxic than choline, are also analyzed.
It is hypothesized that, compared to choline moiety in other dietary sources such as phosphatidylcholine, choline in citicoline is less prone to conversion to trimethylamine (TMA) and its putative atherogenic N-oxide (TMAO).
Epidemiological studies have suggested that choline supplementation may improve cognitive performance, and for this application citicoline may be safer and more efficacious.❞
Source: Citicoline: A Superior Form of Choline?
Great! What does it do?
What doesn’t it do? When it comes to cognitive function, anyway, citicoline covers a lot of bases.
Short version: it improves just about every way a brain’s healthy functions can be clinically measured. From cognitive improvements in all manner of tests (far beyond just “improves memory” etc; also focus, alertness, verbal fluency, logic, computation, and more), to purely neurological things like curing tinnitus (!), alleviating mobility disorders, and undoing alcohol-related damage.
One of the reasons it’s so wide in its applications, is that it has a knock-on effect to other systems in the brain, including the dopaminergic system.
Long version: Citicoline: pharmacological and clinical review, 2022 update
(if you don’t want to sit down for a long read, we recommend skimming to the charts and figures, which are very elucidating even alone)
Spotlight study in memory
For a quick-reading example of how it helps memory specifically:
Keeping dementia at bay
For many older people looking to improve memory, it’s less a matter of wanting to perform impressive feats of memory, and more a matter of wanting to keep a sharp memory throughout our later years.
Dr. Maria Bonvicini et al. looked into this:
❝We selected seven studies including patients with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease or post-stroke dementia
All the studies showed a positive effect of citicoline on cognitive functions. Six studies could be included in the meta-analysis.
Overall, citicoline improved cognitive status, with pooled standardized mean differences ranging from 0.56 (95% CI: 0.37-0.75) to 1.57 (95% CI: 0.77-2.37) in different sensitivity analyses❞
The researchers concluded “yes”, and yet, called for more studies, and of higher quality. In many such studies, the heterogeneity of the subjects (often, residents of nursing homes) can be as much a problem (unclear whether the results will be applicable to other people in different situations) as it is a strength (fewer confounding variables).
Another team looked at 47 pre-existing reviews, and concluded:
❝The review found that citicoline has been proven to be a useful compound in preventing dementia progression.
Citicoline has a wide range of effects and could be an essential substance in the treatment of many neurological diseases.
Its positive impact on learning and cognitive functions among the healthy population is also worth noting.❞
Source: Application of Citicoline in Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review
The dopamine bonus
Remember how we said that citicoline has a knock-on effect on other systems, including the dopaminergic system? This means that it’s been studied (and found meritorious) for alleviating symptoms of Parkinson’s disease:
❝Patients with Parkinson’s disease who were taking citicoline had significant improvement in rigidity, akinesia, tremor, handwriting, and speech.
Citicoline allowed effective reduction of levodopa by up to 50%.
Significant improvement in cognitive status evaluation was also noted with citicoline adjunctive therapy.❞
Source: Citicoline as Adjuvant Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Where to get it?
We don’t sell it, but here’s an example product on Amazon, for your convenience
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
Coffee, From A Blood Sugar Management Perspective
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our favorite French biochemist (Jessie Inchauspé) is back, and this time, she’s tackling a topic near and dear to this writer’s heart: coffee ☕💕
What to consider
Depending on how you like your coffee, some or all of these may apply to you:
- Is coffee healthy? Coffee is generally healthy, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes by improving fat burning in the liver and protecting beta cells in the pancreas.
- Does it spike blood sugars? Usually not so long as it’s black and unsweetened. Black coffee can cause small glucose spikes in some people due to stress-induced glucose release, but only if it contains caffeine.
- When is it best to drink it? Drinking coffee after breakfast, especially after a poor night’s sleep, can actually reduce glucose and insulin spikes.
- What about milk? All milks cause some glucose and insulin spikes. While oat milk is generally healthy, for blood sugar purposes unsweetened nut milks or even whole cow’s milk (but not skimmed; it needs the fat) are better options as they cause smaller spikes.
- What about sweetening? Adding sugar to coffee, especially on an empty stomach, obviously leads to large glucose spikes. Alternative sweeteners like stevia or sweet cinnamon are fine substitutes.
For more details on all of those things, plus why Kenyan coffee specifically may be the best for blood sugars, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Black Coffee vs Orange Juice – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing black coffee to orange juice, we picked the coffee.
Why?
While this one isn’t a very like-for-like choice, it’s a choice often made, so it bears examining.
In favor of the orange juice, it has vitamins A and C and the mineral potassium, while the coffee contains no vitamins or minerals beyond trace amounts.
However, to offset that: drinking juice is one of the worst ways to consume sugar; the fruit has not only been stripped of its fiber, but also is in its most readily absorbable state (liquid), meaning that this is going to cause a blood sugar spike, which if done often can lead to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and more. Now, the occasional glass of orange juice (and resultant blood sugar spike) isn’t going to cause disease by itself, but everything we consume tips the scales of our health towards wellness or illness (or sometimes both, in different ways), and in this case, juice has a rather major downside that ought not be ignored.
In favor of the coffee, it has a lot of beneficial phytochemicals (mostly antioxidant polyphenols of various kinds), with no drawbacks worth mentioning unless you have a pre-existing condition of some kind.
Coffee can of course be caffeinated or decaffeinated, and we didn’t specify which here. Caffeine has some pros and cons that at worst, balance each other out, and whether or not it’s caffeinated, there’s nothing in coffee to offset the beneficial qualities of the antioxidants we mentioned before.
Obviously, in either case we are assuming consuming in moderation.
In short:
- orange juice has negatives that at least equal, if not outweigh, its positives
- coffee‘s benefits outweigh any drawbacks for most people
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
In This Oklahoma Town, Most Everyone Knows Someone Who’s Been Sued by the Hospital
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
McALESTER, Okla. — It took little more than an hour for Deborah Hackler to dispense with the tall stack of debt collection lawsuits that McAlester Regional Medical Center recently brought to small-claims court in this Oklahoma farm community.
Hackler, a lawyer who sues patients on behalf of the hospital, buzzed through 51 cases, all but a handful uncontested, as is often the case. She bantered with the judge as she secured nearly $40,000 in judgments, plus 10% in fees for herself, according to court records.
It’s a payday the hospital and Hackler have shared frequently over the past three decades, records show. The records indicate McAlester Regional Medical Center and an affiliated clinic have filed close to 5,000 debt collection cases since the early 1990s, most often represented by the father-daughter law firm of Hackler & Hackler.
Some of McAlester’s 18,000 residents have been taken to court multiple times. A deputy at the county jail and her adult son were each sued recently, court records show. New mothers said they compare stories of their legal run-ins with the medical center.
“There’s a lot that’s not right,” Sherry McKee, a dorm monitor at a tribal boarding school outside McAlester, said on the courthouse steps after the hearing. The hospital has sued her three times, most recently over a $3,375 bill for what she said turned out to be vertigo.
In recent years, major health systems in Virginia, North Carolina, and elsewhere have stopped suing patients following news reports about lawsuits. And several states, such as Maryland and New York, have restricted the legal actions hospitals can take against patients.
But with some 100 million people in the U.S. burdened by health care debt, medical collection cases still clog courtrooms across the country, researchers have found. In places like McAlester, a hospital’s debt collection machine can hum away quietly for years, helped along by powerful people in town. An effort to limit hospital lawsuits failed in the Oklahoma Legislature in 2021.
In McAlester, the lawsuits have provided business for some, such as the Adjustment Bureau, a local collection agency run out of a squat concrete building down the street from the courthouse, and for Hackler, a former president of the McAlester Area Chamber of Commerce. But for many patients and their families, the lawsuits can take a devastating toll, sapping wages, emptying retirement accounts, and upending lives.
McKee said she wasn’t sure how long it would take to pay off the recent judgment. Her $3,375 debt exceeds her monthly salary, she said.
“This affects a large number of people in a small community,” said Janet Roloff, an attorney who has spent years assisting low-income clients with legal issues such as evictions in and around McAlester. “The impact is great.”
Settled more than a century ago by fortune seekers who secured land from the Choctaw Nation to mine coal in the nearby hills, McAlester was once a boom town. Vestiges of that era remain, including a mammoth, 140-foot-tall Masonic temple that looms over the city.
Recent times have been tougher for McAlester, now home by one count to 12 marijuana dispensaries and the state’s death row. The downtown is pockmarked by empty storefronts, including the OKLA theater, which has been dark for decades. Nearly 1 in 5 residents in McAlester and the surrounding county live below the federal poverty line.
The hospital, operated by a public trust under the city’s authority, faces its own struggles. Paint is peeling off the front portico, and weeds poke up through the parking lots. The hospital has operated in the red for years, according to independent audit reports available on the state auditor’s website.
“I’m trying to find ways to get the entire community better care and more care,” said Shawn Howard, the hospital’s chief executive. Howard grew up in McAlester and proudly noted he started his career as a receptionist in the hospital’s physical therapy department. “This is my hometown,” he said. “I am not trying to keep people out of getting care.”
The hospital operates a clinic for low-income patients, whose webpage notes it has “limited appointments” at no cost for patients who are approved for aid. But data from the audits shows the hospital offers very little financial assistance, despite its purported mission to serve the community.
In the 2022 fiscal year, it provided just $114,000 in charity care, out of a total operating budget of more than $100 million, hospital records show. Charity care totaling $2 million or $3 million out of a $100 million budget would be more in line with other U.S. hospitals.
While audits show few McAlester patients get financial aid, many get taken to court.
Renee Montgomery, the city treasurer in an adjoining town and mother of a local police officer, said she dipped into savings she’d reserved for her children and grandchildren after the hospital sued her last year for more than $5,500. She’d gone to the emergency room for chest pain.
Dusty Powell, a truck driver, said he lost his pickup and motorcycle when his wages were garnished after the hospital sued him for almost $9,000. He’d gone to the emergency department for what turned out to be gastritis and didn’t have insurance, he said.
“Everyone in this town probably has a story about McAlester Regional,” said another former patient who spoke on the condition she not be named, fearful to publicly criticize the hospital in such a small city. “It’s not even a secret.”
The woman, who works at an Army munitions plant outside town, was sued twice over bills she incurred giving birth. Her sister-in-law has been sued as well.
“It’s a good-old-boy system,” said the woman, who lowered her voice when the mayor walked into the coffee shop where she was meeting with KFF Health News. Now, she said, she avoids the hospital if her children need care.
Nationwide, most people sued in debt collection cases never challenge them, a response experts say reflects widespread misunderstanding of the legal process and anxiety about coming to court.
At the center of the McAlester hospital’s collection efforts for decades has been Hackler & Hackler.
Donald Hackler was city attorney in McAlester for 13 years in the ’70s and ’80s and a longtime member of the local Lions Club and the Scottish Rite Freemasons.
Daughter Deborah Hackler, who joined the family firm 30 years ago, has been a deacon at the First Presbyterian Church of McAlester and served on the board of the local Girl Scouts chapter, according to the McAlester News-Capital newspaper, which named her “Woman of the Year” in 2007. Since 2001, she also has been a municipal judge in McAlester, hearing traffic cases, including some involving people she has sued on behalf of the hospital, municipal and county court records show.
For years, the Hacklers’ debt collection cases were often heard by Judge James Bland, who has retired from the bench and now sits on the hospital board. Bland didn’t respond to an inquiry for interview.
Hackler declined to speak with KFF Health News after her recent court appearance. “I’m not going to visit with you about a current client,” she said before leaving the courthouse.
Howard, the hospital CEO, said he couldn’t discuss the lawsuits either. He said he didn’t know the hospital took its patients to court. “I had to call and ask if we sue people,” he said.
Howard also said he didn’t know Deborah Hackler. “I never heard her name before,” he said.
Despite repeated public records requests from KFF Health News since September, the hospital did not provide detailed information about its financial arrangement with Hackler.
McAlester Mayor John Browne, who appoints the hospital’s board of trustees, said he, too, didn’t know about the lawsuits. “I hadn’t heard anything about them suing,” he said.
At the century-old courthouse in downtown McAlester, it’s not hard to find the lawsuits, though. Every month or two, another batch fills the docket in the small-claims court, now presided over by Judge Brian McLaughlin.
After court recently, McLaughlin, who is not from McAlester, shook his head at the stream of cases and patients who almost never show up to defend themselves, leaving him to issue judgment after judgment in the hospital’s favor.
“All I can do is follow the law,” said McLaughlin. “It doesn’t mean I like it.”
About This Project
“Diagnosis: Debt” is a reporting partnership between KFF Health News and NPR exploring the scale, impact, and causes of medical debt in America.
The series draws on original polling by KFF, court records, federal data on hospital finances, contracts obtained through public records requests, data on international health systems, and a yearlong investigation into the financial assistance and collection policies of more than 500 hospitals across the country.
Additional research was conducted by the Urban Institute, which analyzed credit bureau and other demographic data on poverty, race, and health status for KFF Health News to explore where medical debt is concentrated in the U.S. and what factors are associated with high debt levels.
The JPMorgan Chase Institute analyzed records from a sampling of Chase credit card holders to look at how customers’ balances may be affected by major medical expenses. And the CED Project, a Denver nonprofit, worked with KFF Health News on a survey of its clients to explore links between medical debt and housing instability.
KFF Health News journalists worked with KFF public opinion researchers to design and analyze the “KFF Health Care Debt Survey.” The survey was conducted Feb. 25 through March 20, 2022, online and via telephone, in English and Spanish, among a nationally representative sample of 2,375 U.S. adults, including 1,292 adults with current health care debt and 382 adults who had health care debt in the past five years. The margin of sampling error is plus or minus 3 percentage points for the full sample and 3 percentage points for those with current debt. For results based on subgroups, the margin of sampling error may be higher.
Reporters from KFF Health News and NPR also conducted hundreds of interviews with patients across the country; spoke with physicians, health industry leaders, consumer advocates, debt lawyers, and researchers; and reviewed scores of studies and surveys about medical debt.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF—an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
Subscribe to KFF Health News’ free Morning Briefing.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Why scrapping the term ‘long COVID’ would be harmful for people with the condition
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The assertion from Queensland’s chief health officer John Gerrard that it’s time to stop using the term “long COVID” has made waves in Australian and international media over recent days.
Gerrard’s comments were related to new research from his team finding long-term symptoms of COVID are similar to the ongoing symptoms following other viral infections.
But there are limitations in this research, and problems with Gerrard’s argument we should drop the term “long COVID”. Here’s why.
A bit about the research
The study involved texting a survey to 5,112 Queensland adults who had experienced respiratory symptoms and had sought a PCR test in 2022. Respondents were contacted 12 months after the PCR test. Some had tested positive to COVID, while others had tested positive to influenza or had not tested positive to either disease.
Survey respondents were asked if they had experienced ongoing symptoms or any functional impairment over the previous year.
The study found people with respiratory symptoms can suffer long-term symptoms and impairment, regardless of whether they had COVID, influenza or another respiratory disease. These symptoms are often referred to as “post-viral”, as they linger after a viral infection.
Gerrard’s research will be presented in April at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. It hasn’t been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
After the research was publicised last Friday, some experts highlighted flaws in the study design. For example, Steven Faux, a long COVID clinician interviewed on ABC’s television news, said the study excluded people who were hospitalised with COVID (therefore leaving out people who had the most severe symptoms). He also noted differing levels of vaccination against COVID and influenza may have influenced the findings.
In addition, Faux pointed out the survey would have excluded many older people who may not use smartphones.
The authors of the research have acknowledged some of these and other limitations in their study.
Ditching the term ‘long COVID’
Based on the research findings, Gerrard said in a press release:
We believe it is time to stop using terms like ‘long COVID’. They wrongly imply there is something unique and exceptional about longer term symptoms associated with this virus. This terminology can cause unnecessary fear, and in some cases, hypervigilance to longer symptoms that can impede recovery.
But Gerrard and his team’s findings cannot substantiate these assertions. Their survey only documented symptoms and impairment after respiratory infections. It didn’t ask people how fearful they were, or whether a term such as long COVID made them especially vigilant, for example.
Tens of thousands of Australians, and millions of people worldwide, have long COVID.
New Africa/ShutterstockIn discussing Gerrard’s conclusions about the terminology, Faux noted that even if only 3% of people develop long COVID (the survey found 3% of people had functional limitations after a year), this would equate to some 150,000 Queenslanders with the condition. He said:
To suggest that by not calling it long COVID you would be […] somehow helping those people not to focus on their symptoms is a curious conclusion from that study.
Another clinician and researcher, Philip Britton, criticised Gerrard’s conclusion about the language as “overstated and potentially unhelpful”. He noted the term “long COVID” is recognised by the World Health Organization as a valid description of the condition.
A cruel irony
An ever-growing body of research continues to show how COVID can cause harm to the body across organ systems and cells.
We know from the experiences shared by people with long COVID that the condition can be highly disabling, preventing them from engaging in study or paid work. It can also harm relationships with their friends, family members, and even their partners.
Despite all this, people with long COVID have often felt gaslit and unheard. When seeking treatment from health-care professionals, many people with long COVID report they have been dismissed or turned away.
Last Friday – the day Gerrard’s comments were made public – was actually International Long COVID Awareness Day, organised by activists to draw attention to the condition.
The response from people with long COVID was immediate. They shared their anger on social media about Gerrard’s comments, especially their timing, on a day designed to generate greater recognition for their illness.
Since the start of the COVID pandemic, patient communities have fought for recognition of the long-term symptoms many people faced.
The term “long COVID” was in fact coined by people suffering persistent symptoms after a COVID infection, who were seeking words to describe what they were going through.
The role people with long COVID have played in defining their condition and bringing medical and public attention to it demonstrates the possibilities of patient-led expertise. For decades, people with invisible or “silent” conditions such as ME/CFS (myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome) have had to fight ignorance from health-care professionals and stigma from others in their lives. They have often been told their disabling symptoms are psychosomatic.
Gerrard’s comments, and the media’s amplification of them, repudiates the term “long COVID” that community members have chosen to give their condition an identity and support each other. This is likely to cause distress and exacerbate feelings of abandonment.
Terminology matters
The words we use to describe illnesses and conditions are incredibly powerful. Naming a new condition is a step towards better recognition of people’s suffering, and hopefully, better diagnosis, health care, treatment and acceptance by others.
The term “long COVID” provides an easily understandable label to convey patients’ experiences to others. It is well known to the public. It has been routinely used in news media reporting and and in many reputable medical journal articles.
Most importantly, scrapping the label would further marginalise a large group of people with a chronic illness who have often been left to struggle behind closed doors.
Deborah Lupton, SHARP Professor, Vitalities Lab, Centre for Social Research in Health and Social Policy Centre, and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Automated Decision-Making and Society, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: