Aging with Grace – by Dr. David Snowdon
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
First, what this book is not: a book about Christianity. Don’t worry, we didn’t suddenly change the theme of 10almonds.
Rather, what this book is: a book about a famous large (n=678) study into the biology of aging, that took a population sample of women who had many factors already controlled-for, e.g. they ate the same food, had the same schedule, did the same activities, etc—for many years on end. In other words, a convent of nuns.
This allowed for a lot more to be learned about other factors that influence aging, such as:
- Heredity / genetics in general
- Speaking more than one language
- Supplementing with vitamins or not
- Key adverse events (e.g. stroke)
- Key chronic conditions (e.g. depression)
The book does also cover (as one might expect) the role that community and faith can play in healthy longevity, but since the subjects were 678 communally-dwelling people of faith (thus: no control group of faithless loners), this aspect is discussed only in anecdote, or in reference to other studies.
The author of this book, by the way, was the lead researcher of the study, and he is a well-recognised expert in the field of Alzheimer’s in particular (and Alzheimer’s does feature quite a bit throughout).
The writing style is largely narrative, and/but with a lot of clinical detail and specific data; this is by no means a wishy-washy book.
Bottom line: if you’d like to know what nuns were doing in the 1980s to disproportionally live into three-figure ages, then this book will answer those questions.
Click here to check out Aging with Grace, and indeed age with grace!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Are You A Calorie-Burning Machine?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Burn, Calorie, Burn
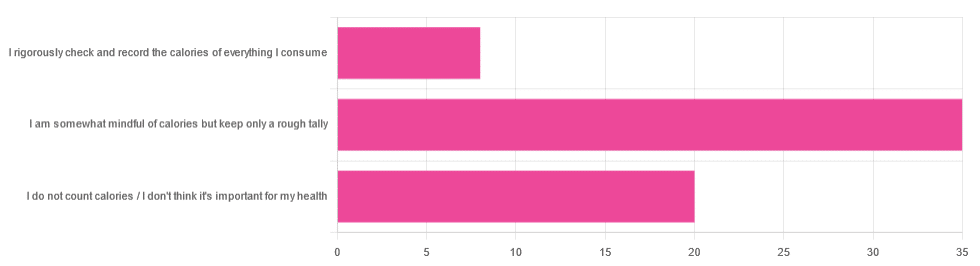
In Tuesday’s newsletter, we asked you whether you count calories, and got the above-depicted, below-described set of answers:
- About 56% said “I am somewhat mindful of calories but keep only a rough tally”
- About 32% said “I do not count calories / I don’t think it’s important for my health”
- About 13% said “I rigorously check and record the calories of everything I consume”
So what does the science say, about the merits of all these positions?
A food’s calorie count is a good measure of how much energy we will, upon consuming the food, have to use or store: True or False?
False, broadly. It can be, at best, a rough guideline. Do you know what a calorie actually is, by the way? Most people don’t.
One thing to know before we get to that: there’s “cal” vs “kcal”. The latter is generally used when it comes to foodstuffs, and it’s what we’ll be meaning whenever we say “calorie” here. 1cal is 1/1000th of a kcal, that’s all.
Now, for what a calorie actually is:
A calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃
Question: so, how to we measure how much food is needed to do that?
Answer: by using a bomb calorimeter! Which is the exciting name for the apparatus used to literally burn food and capture the heat produced to indeed raise the temperature of 1 liter of water by 1℃.
If you’re having trouble imagining such equipment, here it is:
Bomb Calorimeter: Definition, Construction, & Operation (with diagram and FAQs)
The unfortunate implication of the above information
A kilogram of sawdust contains about a 1000 kcal, give or take what wood was used and various other conditions.
However, that does not mean you can usefully eat the sawdust. In other words:
Calorie count tells us only how good something is at raising the temperature of water if physically burned.
Now do you see why oils and sugars have such comparably high calorie counts?
And while we may talk about “burning calories” as a metaphor, we do not, in fact, have a little wood stove inside us burning the food we eat.
A calorie is a calorie: True or False?
Definitely False! Building on from the above… We will get very little energy from sawdust; it’s not just that we can’t use it; we can’t store it either; it’ll mostly pass through as fiber.
(however, please do not use sawdust to get your daily dose of fiber either, as it is not safe for human consumption and may give you diseases, depending on what is lurking in it)
But let’s look at oil and sugar, two very high-calorie categories of food, because they’re really easy to physically burn and they give off a good flame.
A bomb calorimeter may treat them quite equally, but to our body, they are metabolically very different indeed.
For a start, most sugars will get absorbed and processed much more quickly than most oils, and that can overwhelm the liver (responsible for glycogen management), and lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, diabetes, and more. Metabolic syndrome in general, and if you keep it up too much and you may find it’s now a lottery between dying of NAFLD, diabetes, or heart disease (it’ll usually be the heart disease that kills).
See also:
- Which Sugars Are Healthier, And Which Are Just The Same?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
- How To Unfatty A Fatty Liver
Meanwhile, we know all about the different kinds of nutritional profiles that oils can have, and some can promote having high energy without putting on fat, while others can strain the heart. Not even “a fat is a fat”, so “a calorie is a calorie” doesn’t get much mileage outside of a bomb calorimeter!
See also:
A calorie-controlled / calorie-restricted diet is an effective weight loss strategy: True or False?
True, usually! Surprise!
- On the one hand: calories are a wildly imprecise way to reckon the value of food, and using them as a guide to health can be dangerously misleading
- On the other hand: the very activity of calorie-counting itself promotes mindful eating, which is very good for the health
There is a strong difference between the mind of somebody who is carefully logging their pre-bedtime piece of chocolate and reflecting on its nutritional value, vs someone who isn’t sure whether this is their second or third glass of wine, nor how much the glass contained.
So if you want to get most of the benefits of a calorie-controlled diet without counting calories, you may try taking a “mindful eating” approach to diet.
However! If you want to do this for weight loss, be aware, that you will have to practice it all the time, not just for one meal here and there.
You can read more on how to do “mindful eating” here:
Dr. Rupy Aujla: The Kitchen Doctor | Mindful Eating & Interoception
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Seven-Day Sleep Prescription – by Dr. Aric Prather
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You probably already know about sleep hygiene. So, what does this book have to offer?
Dr. Aric Prather offers seven days’ worth of adjustments, practices to take up, from when you get up in the morning to when you lay your head down at night.
Some you’ll surely be familiar with, like avoiding blue light and social media at night.
Others, you might not be familiar with, like scheduling 15 minutes for worrying in the daytime. The rationale for this one is that when you find yourself inclined to worry at a time that will keep you awake, you’ll know that you can put off such thoughts to your scheduled “worrying time”. That they’ll be addressed then, and that you can thus sleep soundly meanwhile.
Where the book really comes into its own is in such things as discussing how to not just manage sleep debt, but how to actually use it in your favour.
Nor does Dr. Prather shy away from the truths of our world… That the world these days is not built for us to sleep well. That there are so many other priorities; to get our work done, to succeed and achieve, to pay bills, to support our kids and partners. That so many of these things make plenty of sense in the moment, but catch up with us eventually.
Bottom line: what this book aims to give is a genuinely sustainable approach to sleeping—controlling what we can, and working with what we can’t. If you’d like to have a better relationship with sleep, this book is an excellent choice.
Click here to check out the Seven-Day Sleep Prescription, and improve yours!
Share This Post
-
Walnuts vs Brazil Nuts – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing walnuts to Brazil nuts, we picked the walnuts.
Why?
Talking macros first, they are about equal in protein, carbs, fats, and fiber; their composition is almost identical in this regard. However, looking a little more closely at the fats, Brazil nuts have more than 2x the saturated fat, while walnuts have nearly 2x the polyunsaturated fat. So, we’ll declare the macros category a moderate win for walnuts.
The category of vitamins is not balanced; walnuts have more of vitamins A, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, C, and choline, while Brazil nuts have more of vitamins B1 and E. A clear and easy win for walnuts.
The category of minerals is interesting, because of one mineral in particular. First let’s mention: walnuts have more iron and manganese, while Brazil nuts have more calcium, copper, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, and selenium. Taken at face value, this is a clear win for Brazil nuts. However…
About that selenium… Specifically, it’s more than 391x higher, and a cup of Brazil nuts would give nearly 10,000x the recommended daily amount of selenium. Now, selenium is an essential mineral (needed for thyroid hormone production, for example), and at the RDA it’s good for good health. Your hair will be luscious and shiny. However, go much above that, and selenium toxicity becomes a thing, you may get sick, and it can cause your (luscious and shiny) hair to fall out. For this reason, it’s recommended to eat no more than 3–4 Brazil nuts per day.
There is one last consideration, and this is oxalates; walnuts are moderately high in oxalates (>50mg/100g) while Brazil nuts are very high in oxalates (>500mg/100g). This won’t affect most people at all, but if you have pre-existing kidney problems (including a history of kidney stones), you might want to go easy on oxalate-containing foods.
For most people, however, walnuts are a very healthy choice, and outshine Brazil nuts in most ways.
Want to learn more?
You might like to read:
Why You Should Diversify Your Nuts
Take care!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Coffee, From A Blood Sugar Management Perspective
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our favorite French biochemist (Jessie Inchauspé) is back, and this time, she’s tackling a topic near and dear to this writer’s heart: coffee ☕💕
What to consider
Depending on how you like your coffee, some or all of these may apply to you:
- Is coffee healthy? Coffee is generally healthy, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes by improving fat burning in the liver and protecting beta cells in the pancreas.
- Does it spike blood sugars? Usually not so long as it’s black and unsweetened. Black coffee can cause small glucose spikes in some people due to stress-induced glucose release, but only if it contains caffeine.
- When is it best to drink it? Drinking coffee after breakfast, especially after a poor night’s sleep, can actually reduce glucose and insulin spikes.
- What about milk? All milks cause some glucose and insulin spikes. While oat milk is generally healthy, for blood sugar purposes unsweetened nut milks or even whole cow’s milk (but not skimmed; it needs the fat) are better options as they cause smaller spikes.
- What about sweetening? Adding sugar to coffee, especially on an empty stomach, obviously leads to large glucose spikes. Alternative sweeteners like stevia or sweet cinnamon are fine substitutes.
For more details on all of those things, plus why Kenyan coffee specifically may be the best for blood sugars, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
- The Bitter Truth About Coffee (or is it?)
- Caffeine: Cognitive Enhancer Or Brain-Wrecker?
- 10 Ways To Balance Blood Sugars
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Brain-Gut Highway: A Two-Way Street
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The Brain-Gut Two-Way Highway
This is Dr. Emeran Mayer. He has the rather niche dual specialty of being a gastroenterologist and a neurologist. He has published over 353 peer reviewed scientific articles, and he’s a professor in the Departments of Medicine, Physiology, and Psychiatry at UCLA. Much of his work has been pioneering medical research into gut-brain interactions.
We know the brain and gut are connected. What else does he want us to know?
First, that it is a two-way interaction. It’s about 90% “gut tells the brain things”, but it’s also 10% “brain tells the gut things”, and that 10% can make more like a 20% difference, if for example we look at the swing between “brain using that 10% communication to tell gut to do things worse” or “brain using that 10% communication to tell gut to do things better”, vs the midpoint null hypothesis of “what the gut would be doing with no direction from the brain”.
For example, if we are experiencing unmanaged chronic stress, that is going to tell our gut to do things that had an evolutionary advantage 20,000–200,000 years ago. Those things will not help us now. We do not need cortisol highs and adrenal dumping because we ate a piece of bread while stressed.
Read more (by Dr. Mayer): The Stress That Evolution Has Not Prepared Us For
With this in mind, if we want to look after our gut, then we can start before we even put anything in our mouths. Dr. Mayer recommends managing stress, anxiety, and depression from the head downwards as well as from the gut upwards.
Here’s what we at 10almonds have written previously on how to manage those things:
- No-Frills, Evidence-Based Mindfulness
- How To Set Anxiety Aside
- The Mental Health First-Aid You’ll Hopefully Never Need
Do eat for gut health! Yes, even if…
Unsurprisingly, Dr. Mayer advocates for a gut-friendly, anti-inflammatory diet. We’ve written about these things before:
…but there’s just one problem:
For some people, such as with IBS, Crohn’s, and colitis, the Mediterranean diet that we (10almonds and Dr. Mayer) generally advocate for, is inaccessible. If you (if you have those conditions) eat as we describe, a combination of the fiber in many vegetables and the FODMAPs* in many fruits, will give you a very bad time indeed.
*Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, Monosaccharides And Polyols
Dr. Mayer has the answer to this riddle, and he’s not just guessing; he and his team did science to it. In a study with hundreds of participants, he measured what happened with adherence (or not) to the Mediterranean diet (or modified Mediterranean diet) (or not), in participants with IBS (or not).
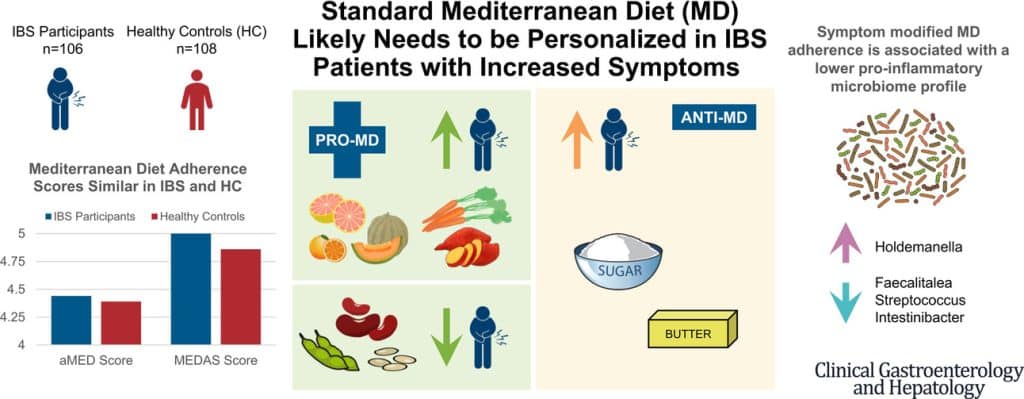
The results and conclusions from that study included:
❝Among IBS participants, a higher consumption of fruits, vegetables, sugar, and butter was associated with a greater severity of IBS symptoms. Multivariate analysis identified several Mediterranean Diet foods to be associated with increased IBS symptoms.
A higher adherence to symptom-modified Mediterranean Diet was associated with a lower abundance of potentially harmful Faecalitalea, Streptococcus, and Intestinibacter, and higher abundance of potentially beneficial Holdemanella from the Firmicutes phylum.
A standard Mediterranean Diet was not associated with IBS symptom severity, although certain Mediterranean Diet foods were associated with increased IBS symptoms. Our study suggests that standard Mediterranean Diet may not be suitable for all patients with IBS and likely needs to be personalized in those with increased symptoms.❞
In graphical form:
And if you’d like to read more about this (along with more details on which specific foods to include or exclude to get these results), you can do so…
- The study itself (full article): The Association Between a Mediterranean Diet and Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Dr. Mayer’s blog (lay explanation): The Benefits of a Modified Mediterranean Diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Want to know more?
Dr. Mayer offers many resources, including a blog, books, recipes, podcasts, and even a YouTube channel:
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy – by Dr. Anne Argur & Dr. Arthur Dalley
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Imagine, if you will, Grey’s Anatomy but beautifully illustrated in color and formatted in a way that’s easy to read—both in terms of layout and searchability, and also in terms of how this book presents anatomy described in a practical, functional context, with summary boxes for each area, so that the primary concepts don’t get lost in the very many details.
(In contrast, if you have a copy of the famous Grey’s Anatomy, you’ll know it’s full of many pages of nothing but tiny dense text, a large amount of which is Latin, with occasional etchings by way of illustration)
Another way in which this does a lot better than the aforementioned seminal work is that it also describes and discusses very many common variations and abnormalities, both congenital and acquired, so that it’s not just a text of “what a theoretical person looks like inside”, but rather also reflects the diverse reality of the human form (we weren’t made identically in a production line, and so we can vary quite a bit).
The book is, of course, intended for students and practitioners of medicine and related fields, so what good is it to the lay person? Well, if you ask the average person where the gallbladder is and why we have one, they will gesture in the general direction of the abdomen, and sort of shrug sheepishly. You don’t have to be that person 🙂
Bottom line: if you’d like to know your acetabulum from your zygomatic arch, this is the best anatomy book this reviewer has yet seen.
Click here to check out Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy, and prepare to be amazed!
PS: this one is expensive, but consider it a fair investment in your personal education, if you’re serious about it!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: