Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes – by Dr. Marie Feldman
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
The book doesn’t assume prior knowledge, and does explain the science of diabetes, prediabetes, the terms and the symptoms, what’s going on inside, etc—before getting onto the main meat of the book, the tips.
The promised 100 tips are varied in their application; they range from diet and exercise, to matters of sleep, stress, and even love.
There are bonus tips too! For example, an appendix covers “tips for healthier eating out” (i.e. in restaurants etc) and a grocery list to ensure your pantry is good for defending you against prediabetes.
The writing style is very accessible pop-science; this isn’t like reading some dry academic paper—though it does cite its sources for claims, which we always love to see.
Bottom line: if you’d like to proof yourself against prediabetes, and are looking for “small things that add up” habits to get into to achieve that, this book is an excellent first choice.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
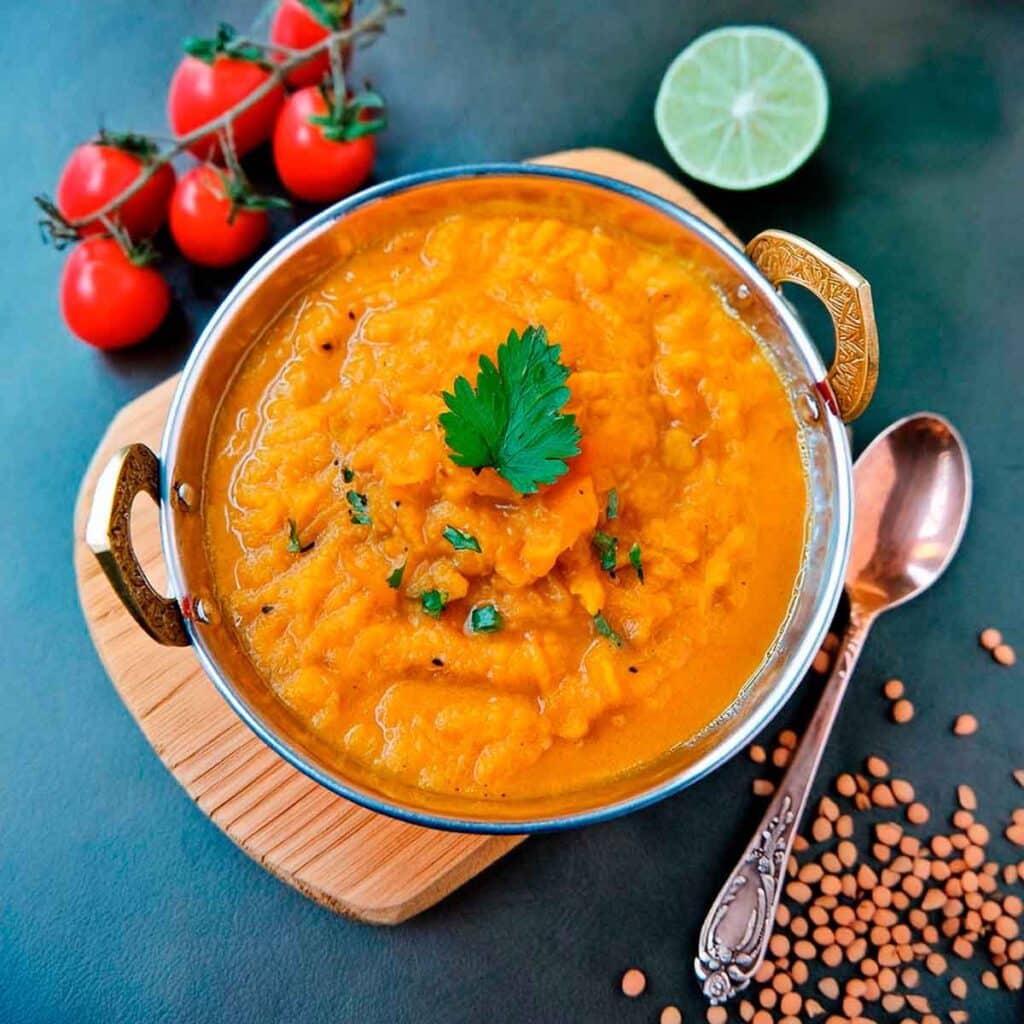
Delicious Daily Daal
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
You’re not obliged to eat this every day, but you might want to. The reason we called this one this, is because it’s a super simple recipe (don’t be put off by the long ingredients list; it’s mostly spices making it look long) which, after you’ve done it a couple of times, you could practically do it in your sleep quickly and easily.
The name “lentil daal” is a bit like “naan bread”—a redundant tautology repeated more than once unnecessarily, but it helps for international clarity. The dish is usually served with naan, by the way, and rice. We don’t have room for those today, maybe we’ll do them another day; for now, you can just cook rice how you normally do, and buy naan if necessary.
Writer’s note: I love strong flavors; many people don’t. For this reason I’m going to give a “basic” version. Please feel free to multiply the spices if you feel so inclined. Where I give “one teaspoon” of a spice below, I’d use a tablespoon at home. Chili peppers can vary in heat a lot even within the same type, so what I do for any given batch is taste one (raw), judge the heat, and use an appropriate number of peppers accordingly. If you don’t want to do that, I suggest just guessing low (as per the instructions below) and if you find at the end you want more heat, you can always stir in a little hot sauce. I know that sounds heretical, but at the end of the day, the primary goal of cooking is to have the meal you want at the end of it.
You will need
- 1 1/2 cups red lentils
- 1 large onion, chopped
- 1 large bulb garlic, minced
- 1 oz ginger, grated
- 2 hot peppers (e.g. serrano), chopped
- 1 tsp ground cumin
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1 tsp ground turmeric
- 1 tsp garam masala (this is also ground, but it doesn’t come any other way)
- 1 tsp chili flakes (omit if you’re not a fan of heat)
- 2 tsp cracked black pepper
- 1 tsp salt ← I wouldn’t recommend multiplying this one unless later, to taste. In fact, instead of 1 tsp salt I use 2 tsp MSG, which has less sodium than 1 tsp salt. But “1 tsp salt” is the “easy to find in the store” version.
- 2 large or 3 small tomatoes, chopped (or 1 can chopped tomatoes)
- 2 shallots, thinly sliced
- 1 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp mustard seeds
- 1 tsp coriander seeds
- 1 tsp black peppercorns
- 1 lime
- 1/2 cup fresh cilantro, or if you have the “that tastes like soap” gene, parsley, chopped
- Coconut oil for cooking (if you don’t like coconut, consider springing for avocado oil—if you use olive oil, it’ll add an olivey taste which changes the dish a lot; not inherently bad, but it feels a lot less like traditional daal; seed oils are less healthy and we don’t recommend them; ghee is a traditional option and not bad in moderation, but not as healthy as the oils we mentioned first)
- Water for cooking the lentils
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) In a saucepan, boil water and add the lentils; let them simmer while doing the next things.
2) Sauté the onions until translucent. This should only take a few minutes.
3) Add the garlic, ginger, and hot peppers, and keep stirring for another couple of minutes.
4) Add the ground spices (cumin, coriander, turmeric, garam masala) chili flakes, and cracked black pepper, as well as the salt or MSG if using (not both), and stir them in quickly but thoroughly.
For the next step, you may need to transfer to larger pan if your sauté pan isn’t big enough to take the volume; if so, that’s fine, the sauté has done its job and can have a rest now. If your sauté pan is big enough, just carry on in the same pan; this is perfect.
5) Add the lentils with the water you cooked them in (there might not be much water left now, as the lentils will have absorbed a lot of it; this is fine) as well as the chopped tomatoes.
6) Simmer until it has the consistency of a very thick sauce (you can add a splash more water here and there if it seems to need more). In the West it’s common to serve lentils “al dente”, but in the East it’s usual to (for dishes like this) cook them until they start to
7) Add the juice of at least 1/2 of your lime, or the whole lime if you feel so inclined.
8) In a pre-heated skillet, flash-fry the sliced shallots and the seeds (cumin, coriander, mustard, black peppercorns) at the hottest temperature you can muster. Don’t worry if the oil smokes; we’re only going to be at this tadka-making stage for a moment and nothing will stick provided you keep it moving. When the seeds start popping, it’s ready. Add it all to the big pan and stir in.
9) Add the cilantro-or-parsley garnish once you’re ready to serve.
Enjoy!
Learn more
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- How Much Spice Is Right?
- Tasty Polyphenols
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Foot Book – by Dr. Todd Brennan & Dr. Leslie Johnston
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
This book really is what the subtitle claims it to be: “everything you need to know to take care of your feet”.
Arthritis, bunions, corns, diabetes, eczema, fungus, gout, heel pain, ingrown toenails, joint issues, and that’s just one item for each of the first 10 letters of the alphabet.
There’s a lot in here; the point is that it covers everything from the “serious” to the “cosmetic”, so whether you want to be a foot model for an expensive perfume company or just want to walk without pain, the answer is probably in here.
The goal of this book is to be comprehensive like that, and also with an open agenda to educate the world as to what it actually is that podiatrists do (hint: their years of medical school and further training in residency are not just so that they can trim toenails nicely).
The style is very light and readable, as one might expect from a pair of doctors with many years of experience of explaining exactly these things to patients every day.
Bottom line: if you have feet and would like them to be/remain in good condition, this book is an invaluable resource!
Click here to check out The Foot Book, and take good care of yours!
Share This Post
-
The Food Additive You Do Want
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Q: When Is A Fiber Not A Fiber?
A: when it’s a resistant starch. What’s it resistant to? Digestion. So, it functions as though a fiber, and by some systems, may get classified as such.
It’s a little like how sucralose is technically a sugar, but the body processes it like a fiber (but beware, because the sweetness of this disaccharide alone can trigger an insulin response anyway—dose dependent)
There may be other problems too:
But today’s not about sucralose, it’s about…
Guar gum’s surprising dietary role
You may have noticed “guar gum” on the list of ingredients of all kinds of things from baked goods to dairy products to condiments to confectionary and more.
It’s also used in cosmetics and explosives, but let’s not focus on that.
It’s used in food products as…
- a bulking agent
- a thickener
- a stabilizer
Our attention was caught by a new study, that found:
Resistant starch intake facilitates weight loss in humans by reshaping the gut microbiota
Often people think of “fiber helps weight loss” as “well yes, if you are bulking out your food with sawdust, you will eat less”, but it’s not that.
There’s an actual physiological process going on here!
We can’t digest it, but our gut microbiota can and will ferment it. See also:
Fiber against pounds: Resistant starch found to support weight loss
Beyond weight loss
Not everyone wants to lose weight, and even where weight loss is a goal, it’s usually not the only goal. As it turns out, adding guar gum into our diet does more things too:
Resistant starch supplement found to reduce liver triglycerides in people with fatty liver disease
(specifically, this was about NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease)
Digging a little, it seems the benefits don’t stop there either:
Diet high in guar gum fiber limits inflammation and delays multiple sclerosis symptoms
(this one was a rodent study, but still, it’s promising and it’s consistent with what one would expect based on what else we know about its function in diet)
Should we just eat foods with guar gum in as an additive?
That depends on what they are, but watch out for the other additives if you do!
You can just buy guar gum by itself, by the way (here’s an example product on Amazon).
It’s doubtlessly no fun to take as a supplement (we haven’t tried this one), but it can be baked into bread, if baking’s your thing, or just used as a thickener in recipes where ordinarily you might use cornstarch or something else.
Can I get similar benefits from other foods?
The relevant quality is also present in resistant starches in general, so you might want to check out these foods, for example:
9 Foods That Are High in Resistant Starch
You can also check out ways to increase your fiber intake in general:
Level-Up Your Fiber Intake! (Without Difficulty Or Discomfort)
Enjoy!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
Exhausted To Energized – by Dr. Libby Weaver
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
There are very many possible causes of low energy; some are obvious; some are not.
Dr. Weaver goes through a comprehensive list that goes beyond the common, to encompass also the “not rare” options—how to test for them where appropriate, and how to improve/fix them where appropriate.
Thus, she talks us through the marvels of mitochondria (including how to keep them happy and healthy and how to promote the generation of new ones), antioxidant defense mechanisms, coenzyme Q10 and friends, B vitamins of various kinds, macronutrients, the autonomic nervous system, sleep and its many factors, blood oxygenation, digestive issues, what’s going on in the spleen, the gallbladder, the liver, the kidneys, the adrenal glands, our thyroid goings-on in all its multifarious wonders, minerals like iodine, iron, magnesium, zinc, our epigenetic factors, and even psychological considerations ranging from stress to grief. In short—and we have shortened the list to pick out particularly salient points—quite a comprehensive rundown of the human body to make your human body less run-down.
The style is on the very readable pop-science, and/but she does bring her professional knowledge to bear on topic (her doctorate is a PhD in biochemistry, and it shows; a lot of explanations come from that angle).
Bottom line: if you are often exhausted and would rather be energized, this this book almost certainly address at least a couple of things you probably haven’t considered—and even just one would make it worthwhile.
Click here to check out Exhausted To Energized, go from exhausted to energized!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
How to keep your teeth young
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
How to keep your teeth young
The association between aging and teeth is so well-established that it’s entered popular idiom, “too long in the tooth”, and when it comes to visual representations, false teeth are well-associated with old age.
And yet, avoiding such outcomes does not get anywhere near so much attention as, say, avoiding wrinkles or hair loss.
At 10almonds, we’ve covered general dental health before, in a three-part series:
- Toothpastes & Mouthwashes: Which Help And Which Harm?
- Flossing, Better (And Easier!)
- Less Common Oral Hygiene Options
Today, we’re going to be looking specifically at keeping our teeth young. What if you have lost your teeth already? Well, gum health remains important, and it’s foundational for everyone, so…
Look after your gums first and last
Hollywood’s most “perfect” whites would be nothing without the gums holding them in place. So, set aside the cosmetic whitening products that often harm gums (anything containing bleach / hydrogen peroxide, is generally a bad idea), andinstead focus on your gums.
As for avoiding gum disease (periodontitis)?
❝In conclusion, periodontitis might enhance the association of biological aging with all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older adults.
Hence, maintaining and enhancing periodontal health is expected to become an intervention to slow aging and extend life span.❞
Source: Does Periodontitis Affect the Association of Biological Aging with Mortality?
Ways to look after gum health include the obvious “floss” and “brush often” and “use fluoride toothpaste”, along with other options we covered in our “Less Common Oral Hygiene Options” article above.
Also important: don’t smoke. It is bad for everything, and this is no exception.
We expect we probably don’t have many subscribers who smoke, but if you do, please consider making quitting a priority.
See also: Smoking, Gum Disease, and Tooth Loss
Consider supplementing with collagen
Everyone’s all about the calcium and vitamin D for bones (and teeth), but a large part of the mass of both is actually collagen. And unlike calcium, which most people not living in a food desert get plenty of, or vitamin D, which is one of the most popular supplements around, collagen is something that gets depleted as we get older. We’ve written about its importance for bones:
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of—Collagen’s benefits are more than skin deep
And as for its role in combatting gum disease and tooth loss:
Nanoscale Dynamics of Streptococcal Adhesion to AGE-Modified Collagen
By the way, that “AGE” there isn’t about chronological age; it’s about advanced glycation end-products. Those are also something you can and should avoid:
A different kind of “spit and polish”
We imagine you have the “polishing” part in hand; that’s tooth-brushing, of course. But spit?
Saliva is hugely important for our oral health, but it’s not something most of us think about a lot. For example, you might not have known (or might have known but not thought much about) that many common medications affect our saliva, including many blood pressure medications and antidepressants:
Impact of ageing and drug consumption on oral health
Because there are so many possibilities, this is the kind of thing to check with your pharmacist or doctor about. But as a rule, if you take a medication whose side-effects include “dry mouth”, this might be you.
Here’s a really useful (academic) article that covers what drugs cause this, how to diagnose it, and what can be done about it:
Hyposalivation in Elderly Patients
If something’s difficult, find a way to make it easier
Sometimes, as we get older, some things that used to be easy, aren’t. We can lose strength, coordination, manual dexterity, memory, attention, and more. Obviously, we try not to, and do what we can to keep ourselves in good health.
But, if you do have some disability that makes for example brushing and/or flossing difficult to do consistently and/or well, consider talking to your doctor to see if there are assistive devices that can help, or some other kind of support that could allow you to do what you need to.
There’s never any shame in getting help if we need it.
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
We Are Such Stuff As Fish Are Made Of
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Research Review: Collagen
For something that’s a very popular supplement, not many people understand what collagen is, where it comes from, or what it does.
In a nutshell:
Collagen is a kind of protein. Our bodies make it naturally, and we can also get more in our diet and/or take extra as a supplement.
Our bodies use collagen in connective tissue, skin, tendon, bone, and cartilage. It has many functions, but a broad description would be “holding things together”.
As we get older, our bodies produce less collagen. Signs of this include wrinkles, loss of skin hydration, and joint pain.
Quick test: pinch the skin on the middle of the back of one of your hands, and then watch what happens when you get low. How quickly and easily did your skin returns to its original shape?
If it was pretty much instantanous and flawless, congratulations, you have plenty of collagen (and also elastin). If you didn’t, you are probably low on both!
(they are quite similar proteins and are made from the same base “stuff”, so if you’re low on one, you’ll usually be low on both)
Quick note: A lot of research out there has been funded by beauty companies, so we had our work cut out for us today, and have highlighted where any research may be biased.
More than skin deep
While marketing for collagen is almost exclusively aimed at “reduce wrinkles and other signs of aging”, it does a lot more than that.
You remember we mentioned that many things from the bones outward are held together by collagen? We weren’t kidding…
Read: Osteoporosis, like skin ageing, is caused by collagen loss which is reversible
Taking extra collagen isn’t the only way
We can’t (yet!) completely halt the age-related loss of collagen, but we can slow it, with our lifestyle choices:
- Don’t smoke tobacco
- Drink only in moderation (or not at all)
- Avoid foods with added sugar, and high-processed foods in general
- Wear sunscreen when appropriate
Can I get collagen from food?
Yep! Just as collagen holds our bodies together, it holds the bodies of other animals together. And, just like collagen is found in most parts of our body but most plentifully in our skin and bones, that’s what to eat to get collagen from other animals, e.g:
- Chicken skin
- Fish skin
- Bone broth ← health benefits and recipes at this link!
What about vegans?
Yes, vegans are also held together by collagen! We do not, however, recommend eating their skin or boiling their bones into broth. Ethical considerations aside, cannibalism can give you CJD!
More seriously, if you’re vegan, you can’t get collagen from a plant-based diet, but you can get the stuff your body uses to make collagen. Basically, you want to make sure you get plenty of:
- Protein (beans, pulses, nuts, etc are all fine; it’s hard to go wrong with this)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- and Zinc
Just be sure to continue to remember to avoid highly-processed foods. So:
- Soy mince/chunks whose ingredients list reads: “soya”? Yes!
- The Incredible Burger or Linda McCartney’s Sausages? Sadly less healthy
Read: Advanced Glycation End Products in Foods and a Practical Guide to Their Reduction in the Diet
Meat-eaters might want to read that one too. By far the worst offenders for AGEs (Advanced Glycation End Products, which can not only cause collagen to stiffen, but also inactivate proteins responsible for collagen repair, along with doing much more serious damage to your body’s natural functions) include:
- Hot dogs
- Bacon
- Fried/roasted/grilled meats
Is it worth it as a supplement?
That depends on you, your age, and your lifestyle, but it’s generally considered safe*
*if you have a seafood allergy, be careful though, as many supplements are from fish or shellfish—you will need to find one that’s free from your allergen
Also, all collagen is animal-derived. So if you’re a vegan, decide for yourself whether this constitutes medicine and if so, whether that makes it ethically permissible to you.
With that out of the way:
What the science says on collagen supplementation
Collagen for skin
Read: Effects of collagen supplementation on skin aging (systematic review and meta-analysis)
The short version is that they selected 19 studies with over a thousand participants in total, and they found:
In the meta-analysis, a grouped analysis of studies showed favorable results of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation compared with placebo in terms of skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkles.
The findings of improved hydration and elasticity were also confirmed in the subgroup meta-analysis.
Based on results, ingestion of hydrolyzed collagen for 90 days is effective in reducing skin aging, as it reduces wrinkles and improves skin elasticity and hydration.
Caveat: while that systematic review had no conflicts of interests, at least some of the 19 studies will have been funded by beauty companies. Here are two, so that you know what that looks like:
Funded by Quiris to investigate their own supplement, Elasten®:
A Collagen Supplement Improves Skin Hydration, Elasticity, Roughness, and Density
Funded by BioCell to investigate their own supplement, BioCell Collagen:
The Effects of Skin Aging Associated with the Use of BioCell Collagen
A note on funding bias: to be clear, the issue is not that the researchers might be corrupt (though that could happen).
The issue is more that sometimes companies will hire ten labs to do ten research studies… and then pull funding from ones whose results aren’t going the way they’d like.
So the “best” (for them) study is the one that gets published.
Here’s another systematic review—like the one at the top of this section—that found the same, with doses ranging from 2.5g–15g per day for 8 weeks or longer:
Read: Oral Collagen Supplementation: A Systematic Review of Dermatological Applications
Again, some of those studies will have been funded by beauty companies. The general weight of evidence does seem clear and favorable, though.
Collagen for bones
Here, we encountered a lot less in the way of potential bias, because this is simply marketed a lot less. Despite being arguably far more important!
We found a high quality multi-vector randomized controlled study with a sample size of 131 postmenopausal women. They had these women take 5g collagen supplement (or placebo), and studied the results over the course of a year.
They found:
- The intake of the supplement increased bone mineral density (BMD)
- Supplementation was also associated with a favorable shift in bone markers, indicating:
- increased bone formation
- reduced bone degradation
Read: Specific Collagen Peptides Improve Bone Mineral Density and Bone Markers in Postmenopausal Wome
A follow-up study with 31 of these women found that taking 5 grams of collagen daily for a total of 4 years was associated with a progressive increase in BMD.
You might be wondering if collagen also helps against osteoarthritis.
The answer is: yes, it does (at least, it significantly reduces the symptoms)
Read: Effect of collagen supplementation on osteoarthritis symptoms
In summary:
- You need collagen for health skin, bones, joints, and more
- Your body makes collagen from your food
- You can help it by getting plenty of protein, vitamins, and minerals
- You can also help it by not doing the usual Bad Things™ (smoking, drinking, eating processed foods, especially processed meats)
- You can also eat collagen directly in the form of other animals’ skin and bones
- You can also buy collagen supplements (but watch out for allergens)
Want to try collagen supplementation?
We don’t sell it (or anything else), but for your convenience…
Check it out: Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (the same as in most of the above studies), 90 days supply at 5g/day
We selected this one because it’s the same kind used in many of the studies, and it doesn’t contain any known allergens.
It’s bovine collagen, meaning it’s from cows, so it’s not vegan, and also some subscribers may want to abstain for religious reasons. We respect that, and/but make our recommendations based solely on the science of health and productivity.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: