No, taking drugs like Ozempic isn’t ‘cheating’ at weight loss or the ‘easy way out’
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
Obesity medication that is effective has been a long time coming. Enter semaglutide (sold as Ozempic and Wegovy), which is helping people improve weight-related health, including lowering the risk of a having a heart attack or stroke, while also silencing “food noise”.
As demand for semaglutide increases, so are claims that taking it is “cheating” at weight loss or the “easy way out”.
We don’t tell people who need statin medication to treat high cholesterol or drugs to manage high blood pressure they’re cheating or taking the easy way out.
Nor should we shame people taking semaglutide. It’s a drug used to treat diabetes and obesity which needs to be taken long term and comes with risks and side effects, as well as benefits. When prescribed for obesity, it’s given alongside advice about diet and exercise.
How does it work?
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA). This means it makes your body’s own glucagon-like peptide-1 hormone, called GLP-1 for short, work better.
GLP-1 gets secreted by cells in your gut when it detects increased nutrient levels after eating. This stimulates insulin production, which lowers blood sugars.
GLP-1 also slows gastric emptying, which makes you feel full, and reduces hunger and feelings of reward after eating.
GLP-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) medications like Ozempic help the body’s own GLP-1 work better by mimicking and extending its action.
Some studies have found less GLP-1 gets released after meals in adults with obesity or type 2 diabetes mellitus compared to adults with normal glucose tolerance. So having less GLP-1 circulating in your blood means you don’t feel as full after eating and get hungry again sooner compared to people who produce more.
GLP-1 has a very short half-life of about two minutes. So GLP-1RA medications were designed to have a very long half-life of about seven days. That’s why semaglutide is given as a weekly injection.
What can users expect? What does the research say?
Higher doses of semaglutide are prescribed to treat obesity compared to type 2 diabetes management (up to 2.4mg versus 2.0mg weekly).
A large group of randomised controlled trials, called STEP trials, all tested weekly 2.4mg semaglutide injections versus different interventions or placebo drugs.
Trials lasting 1.3–2 years consistently found weekly 2.4 mg semaglutide injections led to 6–12% greater weight loss compared to placebo or alternative interventions. The average weight change depended on how long medication treatment lasted and length of follow-up.
Weight reduction due to semaglutide also leads to a reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure of about 4.8 mmHg and 2.5 mmHg respectively, a reduction in triglyceride levels (a type of blood fat) and improved physical function.
Another recent trial in adults with pre-existing heart disease and obesity, but without type 2 diabetes, found adults receiving weekly 2.4mg semaglutide injections had a 20% lower risk of specific cardiovascular events, including having a non-fatal heart attack, a stroke or dying from cardiovascular disease, after three years follow-up.
Who is eligible for semaglutide?
Australia’s regulator, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), has approved semaglutide, sold as Ozempic, for treating type 2 diabetes.
However, due to shortages, the TGA had advised doctors not to start new Ozempic prescriptions for “off-label use” such as obesity treatment and the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme doesn’t currently subsidise off-label use.
The TGA has approved Wegovy to treat obesity but it’s not currently available in Australia.
When it’s available, doctors will be able to prescribe semaglutide to treat obesity in conjunction with lifestyle interventions (including diet, physical activity and psychological support) in adults with obesity (a BMI of 30 or above) or those with a BMI of 27 or above who also have weight-related medical complications.
What else do you need to do during Ozempic treatment?
Checking details of the STEP trial intervention components, it’s clear participants invested a lot of time and effort. In addition to taking medication, people had brief lifestyle counselling sessions with dietitians or other health professionals every four weeks as a minimum in most trials.
Support sessions were designed to help people stick with consuming 2,000 kilojoules (500 calories) less daily compared to their energy needs, and performing 150 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, like brisk walking, dancing and gardening each week.
STEP trials varied in other components, with follow-up time periods varying from 68 to 104 weeks. The aim of these trials was to show the effect of adding the medication on top of other lifestyle counselling.

A review of obesity medication trials found people reported they needed less cognitive behaviour training to help them stick with the reduced energy intake. This is one aspect where drug treatment may make adherence a little easier. Not feeling as hungry and having environmental food cues “switched off” may mean less support is required for goal-setting, self-monitoring food intake and avoiding things that trigger eating.
But what are the side effects?
Semaglutide’s side-effects include nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, constipation, indigestion and abdominal pain.
In one study these led to discontinuation of medication in 6% of people, but interestingly also in 3% of people taking placebos.
More severe side-effects included gallbladder disease, acute pancreatitis, hypoglycaemia, acute kidney disease and injection site reactions.
To reduce risk or severity of side-effects, medication doses are increased very slowly over months. Once the full dose and response are achieved, research indicates you need to take it long term.
Given this long-term commitment, and associated high out-of-pocket cost of medication, when it comes to taking semaglutide to treat obesity, there is no way it can be considered “cheating”.
Read the other articles in The Conversation’s Ozempic series here.
Clare Collins, Laureate Professor in Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Newcastle
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Recommended
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
Sunflower Oil vs Canola Oil – Which is Healthier?
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Our Verdict
When comparing sunflower oil to canola oil, we picked the sunflower oil.
Why?
They’re both terrible! But canola oil is worse. Sunflower oil is marketed as being higher in polyunsaturated fats, which it is, albeit not by much.
Canola oil is very bad for the heart, and sunflower oil is only moderately bad for the heart, to the point that it can be heart-neutral if used sparingly.
As seed oils, they are both sources of vitamin E, but you’d need to drink a cup of oil to get your daily dose, so please just eat some seeds (or nuts, or fruit, or something) instead. It can even be sunflower seeds if you like! Rapeseed* itself (the seed that canola oil is made from) isn’t really sold as a foodstuff, so that one’s less of an option.
*Fun fact: if you’re N. American and wondering what this “rapeseed” is, know that most of the rest of the Anglosphere calls canola oil “rapeseed oil”, as it’s made from rapeseed, which comes from a plant called rape, whose name is unrelated to the crime of the same name, and comes from rāpa, the Latin word for turnip. Anyway, “canola” is a portmanteau of “Canadian” and “Ola” meaning oil, and is a trademark that has made its way into generic use throughout N. America, as a less alarming name.
Back to health matters: while sunflower seeds are healthy in moderation, the ultraprocessed and refined sunflower and canola oils are not.
Canola oil has also been found to be implicated in age-related cognitive decline, whereas sunflower oil has had mixed results in that regard.
In summary
Sunflower oil is relatively, and we stress relatively, healthier than canola oil. Please use a healthier oil than either if you can. Olive oil is good for most things, and if you need something with a higher smoke point (and/or less distinctive flavor), consider avocado oil, which is also very healthy and whose smoke point is even higher than the seed oils we’ve been discussing today.
Want to know more?
Check out:
Avocado Oil vs Olive Oil – Which is Healthier?
Enjoy!
Share This Post
-
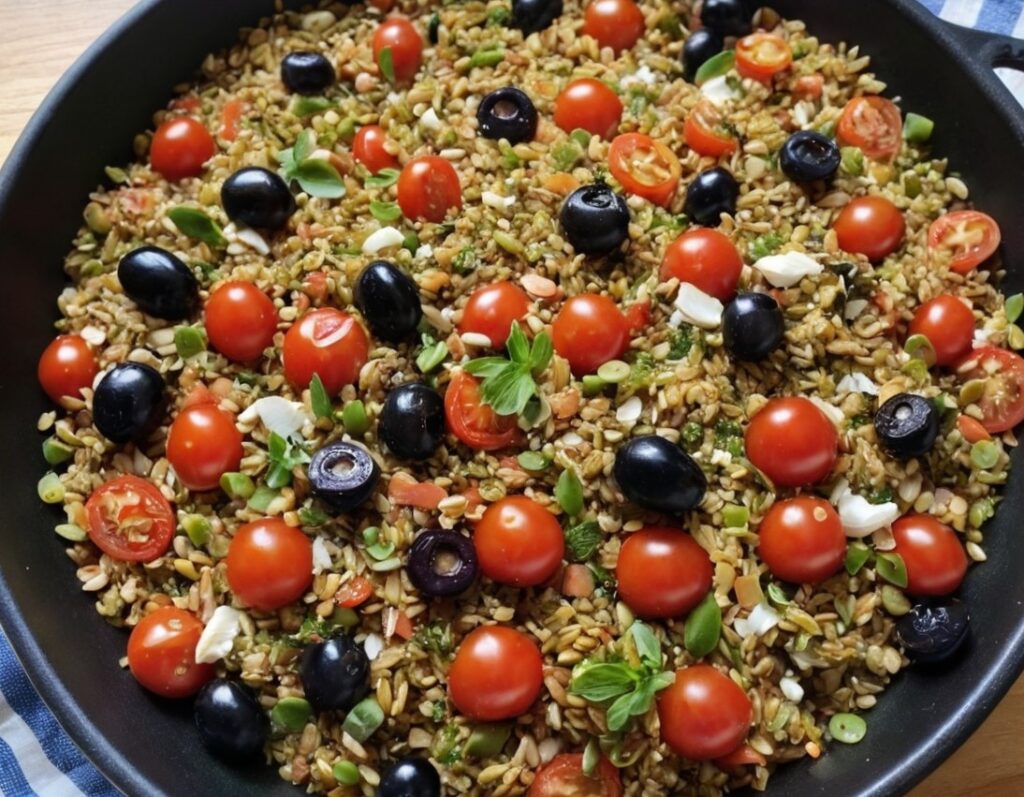
Freekeh Tomato Feast
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Fiber-dense freekeh stars in this traditional Palestinian dish, and the whole recipe is very gut-healthy, not to mention delicious and filling, as well as boasting generous amounts of lycopene and other phytonutrients:
You will need
- 1 cup dried freekeh (if avoiding gluten, substitute a gluten-free grain, or pseudograin such as buckwheat; if making such a substitution, then also add 1 tbsp nutritional yeast—for the flavor as well as the nutrients)
- 1 medium onion, thinly sliced
- 1 2oz can anchovies (if vegan/vegetarian, substitute 1 can kimchi)
- 1 14oz can cherry tomatoes
- 1 cup halved cherry tomatoes, fresh
- ½ cup black olives, pitted
- 1 5oz jar roasted peppers, chopped
- ½ bulb garlic, thinly sliced
- 2 tsp black pepper
- 1 tsp chili flakes
- 1 sprig fresh thyme
- Extra virgin olive oil
Method
(we suggest you read everything at least once before doing anything)
1) Place a heavy-based (cast iron, if you have it) sauté pan over a medium heat. Add some olive oil, then the onion, stirring for about 5 minutes.
2) Add the anchovies, herbs and spices (including the garlic), and stir well to combine. The anchovies will probably soon melt into the onion; that’s fine.
3) Add the canned tomatoes (but not the fresh), followed by the freekeh, stirring well again to combine.
4) Add 2 cups boiling water, and simmer with the lid on for about 40 minutes. Stir occasionally and check the water isn’t getting too low; top it up if it’s getting dry and the freekeh isn’t tender yet.
5) Add the fresh chopped cherry tomatoes and the chopped peppers from the jar, as well as the olives. Stir for just another 2 minutes, enough to let the latest ingredients warm through.
6) Serve, adding a garnish if you wish:
Enjoy!
Want to learn more?
For those interested in some of the science of what we have going on today:
- Why You’re Probably Not Getting Enough Fiber (And How To Fix It)
- Eat More (Of This) For Lower Blood Pressure
- Making Friends With Your Gut (You Can Thank Us Later)
- Lycopene’s Benefits For The Gut, Heart, Brain, & More
- Our Top 5 Spices: How Much Is Enough For Benefits?
Take care!
Share This Post
-
The Herbal Supplement That Rivals Prozac
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Flower Power: St. John’s Wort’s Drug-Level Effectiveness
St. John’s wort is a small yellow flower, extract of which can be bought inexpensively off-the-shelf in pretty much any pharmacy in most places.
It’s sold and used as a herbal mood-brightener.
Does it work?
Yes! It’s actually very effective. This is really uncontroversial, so we’ll keep it brief.
The main findings of studies are that St. John’s wort not only gives significant benefits over placebo, but also works about as well as prescription anti-depressants:
A systematic review of St. John’s wort for major depressive disorder
They also found that fewer people stop taking it, compared to how many stop taking antidepressants. It’s not known how much of this is because of its inexpensive, freely-accessible nature, and how much might be because it gave them fewer adverse side effects:
Clinical use of Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) in depression: A meta-analysis
How does it work?
First and foremost, it’s an SSRI—a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Basically, it doesn’t add serotonin, but it makes whatever serotonin you have, last longer. Same as most prescription antidepressants. It also affects adenosine and GABA pathways, which in lay terms, means it promotes feelings of relaxation, in a similar way to many prescription antianxiety medications.
Mechanism of action of St John’s wort in depression: what is known?
Any problems we should know about?
Yes, definitely. To quote directly from the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health:
St. John’s wort can weaken the effects of many medicines, including crucially important medicines such as:
- Antidepressants
- Birth control pills
- Cyclosporine, which prevents the body from rejecting transplanted organs
- Some heart medications, including digoxin and ivabradine
- Some HIV drugs, including indinavir and nevirapine
- Some cancer medications, including irinotecan and imatinib
- Warfarin, an anticoagulant (blood thinner)
- Certain statins, including simvastatin
I’ve read all that, and want to try it!
As ever, we don’t sell it (or anything else), but here’s an example product on Amazon.
Please be safe and do check with your doctor and/or pharmacist, though!
Share This Post
Related Posts
-
When supplies resume, should governments subsidise drugs like Ozempic for weight loss? We asked 5 experts
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are taking drugs like Ozempic to lose weight. But what do we actually know about them? This month, The Conversation’s experts explore their rise, impact and potential consequences.
You’ve no doubt heard of Ozempic but have you heard of Wegovy? They’re both brand names of the drug semaglutide, which is currently in short supply worldwide.
Ozempic is a lower dose of semaglutide, and is approved and used to treat diabetes in Australia. Wegovovy is approved to treat obesity but is not yet available in Australia. Shortages of both drugs are expected to last throughout 2024.
Both drugs are expensive. But Ozempic is listed on Australia’s Pharmaceutical Benefits Schedule (PBS), so people with diabetes can get a three-week supply for A$31.60 ($7.70 for concession card holders) rather than the full price ($133.80).
Wegovy isn’t listed on the PBS to treat obesity, meaning when it becomes available, users will need to pay the full price. But should the government subsidise it?
Wegovy’s manufacturer will need to make the case for it to be added to the PBS to an independent advisory committee. The company will need to show Wegovy is a safe, clinically effective and cost-effective treatment for obesity compared to existing alternatives.
In the meantime, we asked five experts: when supplies resume, should governments subsidise drugs like Ozempic for weight loss?
Four out of five said yes
This is the last article in The Conversation’s Ozempic series. Read the other articles here.
Disclosure statements: Clare Collins is a National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Leadership Fellow and has received research grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), the Australian Research Council (ARC), the Medical Research Future Fund (MRFF), the Hunter Medical Research Institute, Diabetes Australia, Heart Foundation, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, nib foundation, Rijk Zwaan Australia, the Western Australian Department of Health, Meat and Livestock Australia, and Greater Charitable Foundation. She has consulted to SHINE Australia, Novo Nordisk (for weight management resources and an obesity advisory group), Quality Bakers, the Sax Institute, Dietitians Australia and the ABC. She was a team member conducting systematic reviews to inform the 2013 Australian Dietary Guidelines update, the Heart Foundation evidence reviews on meat and dietary patterns and current co-chair of the Guidelines Development Advisory Committee for Clinical Practice Guidelines for Treatment of Obesity; Emma Beckett has received funding for research or consulting from Mars Foods, Nutrition Research Australia, NHMRC, ARC, AMP Foundation, Kellogg and the University of Newcastle. She works for FOODiQ Global and is a fat woman. She is/has been a member of committees/working groups related to nutrition or food, including for the Australian Academy of Science, the NHMRC and the Nutrition Society of Australia; Jonathan Karnon does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment; Nial Wheate in the past has received funding from the ACT Cancer Council, Tenovus Scotland, Medical Research Scotland, Scottish Crucible, and the Scottish Universities Life Sciences Alliance. He is a fellow of the Royal Australian Chemical Institute, a member of the Australasian Pharmaceutical Science Association and a member of the Australian Institute of Company Directors. Nial is the chief scientific officer of Vaihea Skincare LLC, a director of SetDose Pty Ltd (a medical device company) and a Standards Australia panel member for sunscreen agents. Nial regularly consults to industry on issues to do with medicine risk assessments, manufacturing, design and testing; Priya Sumithran has received grant funding from external organisations, including the NHMRC and MRFF. She is in the leadership group of the Obesity Collective and co-authored manuscripts with a medical writer provided by Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly.
Fron Jackson-Webb, Deputy Editor and Senior Health Editor, The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
To Pee Or Not To Pee
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Is it “strengthening” to hold, or are we doing ourselves harm if we do? Dr. Heba Shaheed explains in this short video:
A flood of reasons not to hold
Humans should urinate 4–6 times daily, but for many people, the demands of modern life often lead to delaying urination, raising questions about its effects on the body.
So first, let’s look at how it all works: the bladder is part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, urethra, and sphincters. Urine is produced by the kidneys and transported via the ureters into the bladder, a hollow organ with a muscular wall. This muscle (called the detrusor) allows the bladder to inflate as it fills with urine (bearing in mind, the main job of any muscle is to be able to stretch and contract).
As the bladder fills, stretch receptors in that muscle signal fullness to the spinal cord. This triggers the micturition reflex, causing the detrusor to contract and the internal urethral sphincter to open involuntarily. Voluntary control over the external urethral sphincter allows a person to delay or release urine as needed.
So, at what point is it best to go forth and pee?
For most people, bladder fullness is first noticeable at around 150-200ml, with discomfort occurring at 400-500ml (that’s about two cups*). Although the bladder can stretch to hold up to a liter, exceeding this capacity can cause it to rupture, a rare but serious condition requiring surgical intervention.
*note, however, that this doesn’t necessarily mean that drinking two cups will result in two cups being in your bladder; that’s not how hydration works. Unless you are already perfectly hydrated, most if not all of the water will be absorbed into the rest of your body where it is needed. Your bladder gets filled when your body has waste products to dispose of that way, and/or is overhydrated (though overhydration is not very common).
Habitually holding urine and/or urinating too quickly (note: not “too soon”, but literally, “too quickly”, we’re talking about the velocity at which it exits the body) can weaken pelvic floor muscles over time. This can lead to bladder pain, urgency, incontinence, and/or a damaged pelvic floor.
In short: while the body’s systems are equipped to handle occasional delays, holding it regularly is not advisable. For the good of your long-term urinary health, it’s best to avoid straining the system and go whenever you feel the urge.
For more on all of this, enjoy:
Click Here If The Embedded Video Doesn’t Load Automatically!
Want to learn more?
You might also like to read:
Keeping your kidneys happy: it’s more than just hydration!
Take care!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails:
-
The Comfort Zone – by Kristen Butler
10almonds is reader-supported. We may, at no cost to you, receive a portion of sales if you purchase a product through a link in this article.
Are you sitting comfortably? Then we’ll begin. Funny, how being comfortable can be a good starting point, then we are advised “You have to get out of your comfort zone”.
And yet, when we think of our personal greatest moments in life, they were rarely uncomfortable moments. Why is that?
Kristen Butler wants us to resolve this paradox, with a reframe:
The comfort zone? That’s actually the “flow” zone.
Just as “slow and steady wins the race”, we can—like the proverbial tortoise—take our comfort with us as we go.
The discomfort zone? That’s the stress zone, the survival zone, the “putting out fires” zone. From the outside, it looks like we’re making a Herculean effort, and perhaps we are, but is it actually so much better than peaceful consistent productivity?
Butler writes in a way that will be relatable for many, and may be a welcome life-ring if you feel like you’ve been playing catch-up for a while.
Is she advocating for complacency, then? No, and she discusses this too. That “complacency zone” is really the “burnout zone” after being in the “survival zone” for too long.
She lays out for us, therefore, a guide for growing in comfort, expanding the comfort zone yes, but by securely pushing it from the inside, not by making a mad dash out and hoping it follows us.
Bottom line: if you’ve been (perhaps quietly) uncomfortable for a little too long for comfort, this book can reframe your approach to get you to a position of sustainable, stress-free growth.
Click here to check out The Comfort Zone, and start building yours!
Don’t Forget…
Did you arrive here from our newsletter? Don’t forget to return to the email to continue learning!
Learn to Age Gracefully
Join the 98k+ American women taking control of their health & aging with our 100% free (and fun!) daily emails: